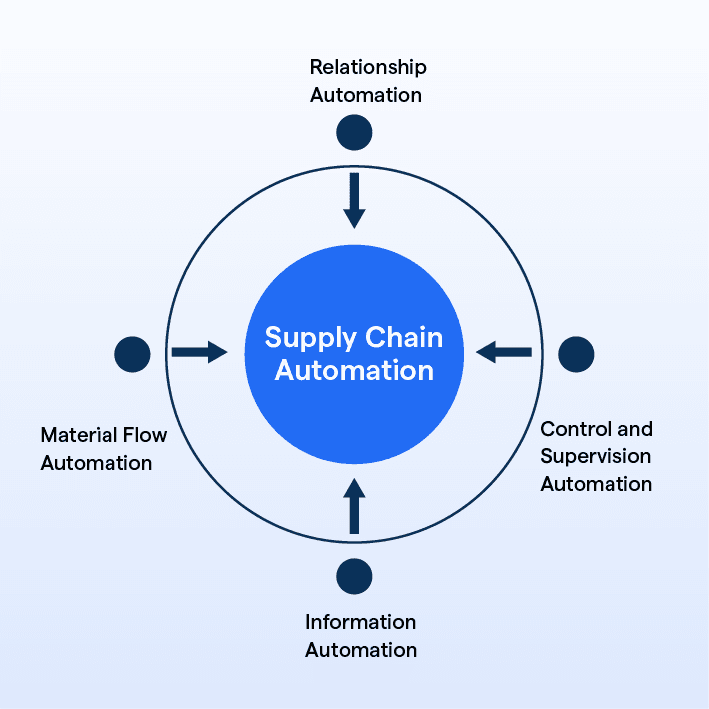
What is Supply Chain Automation?
Supply chain automation involves leveraging digital technologies such as artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning (ML), robotic process automation (RPA), and robotics to streamline and optimize the processes involved in delivering a product or service.
It focuses on automating workflows and using technology to centrally manage the complex web of working parts in a supply chain.
Why is Supply Chain Automation important?
Supply Chain Automation is a game-changer for businesses, offering a plethora of benefits.
By automating processes, companies can decrease operating costs, increase productivity, improve inventory accuracy, enhance time savings and efficiency, integrate with large suppliers, improve compliance and risk management, increase responsiveness and adaptability, enhance customer service, and meet the demands of ever-changing shipping requirements.
What Supply Chain activities can be Automated?
Supply chain automation can be utilized across various activities, including:
Back-Office Automation

By using supply chain automation, back-office tasks such as document procurement and sorting can be enhanced in terms of speed and efficiency.
Automation technology eliminates the risk of human error and reduces the scope for misplacing or incorrectly processing important documents.
Transportation Automation
Artificial intelligence and multi-dimensional monitoring can be used to automate transportation processes.
Real-time tracking of shipments allows for better visibility and the ability to optimize the transportation of materials and products, reducing costs and delivery times.
Some organizations are even exploring the use of autonomous vehicles like drones to further optimize transport within networks.
Warehousing Automation
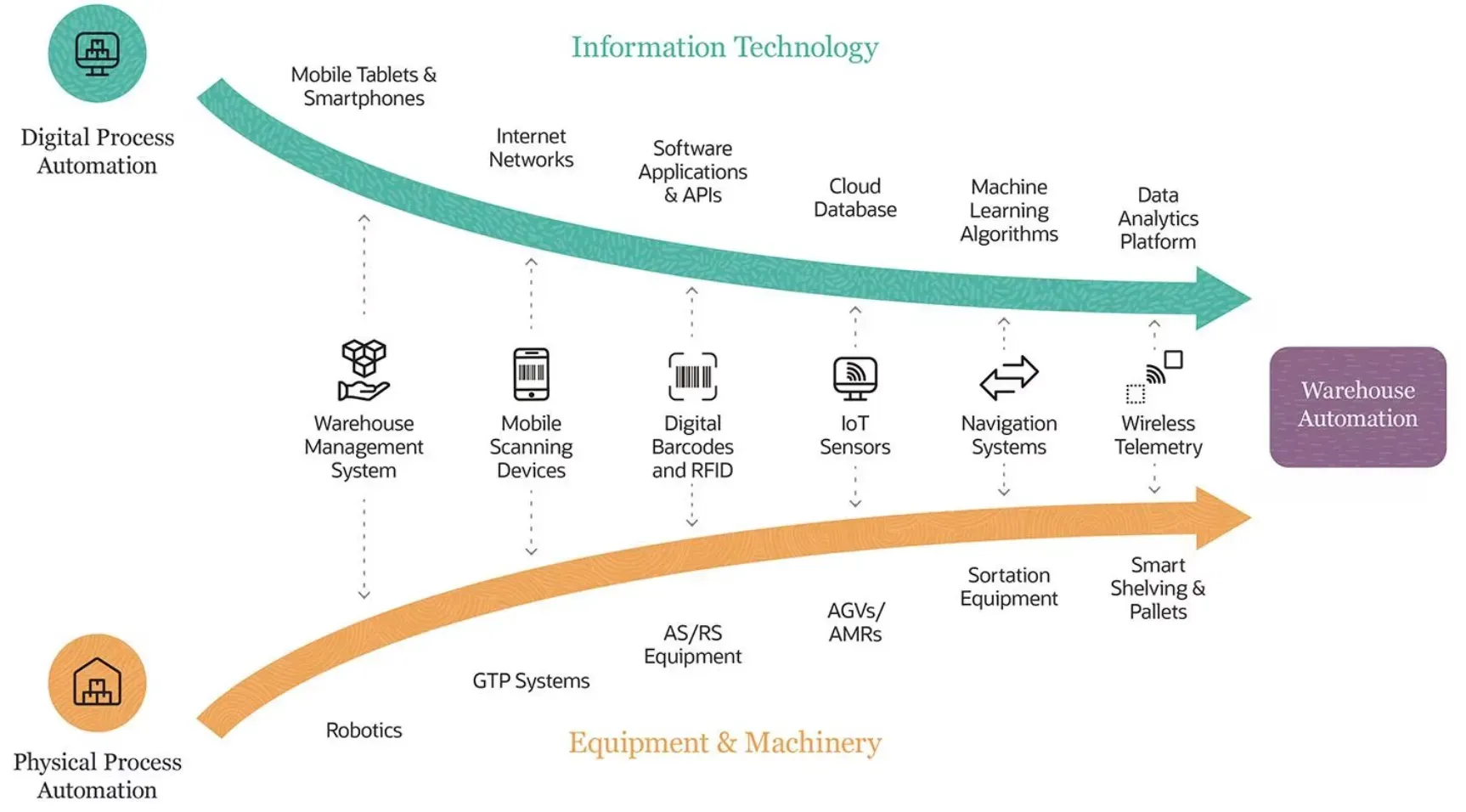
Supply and demand automation can be used to identify out-of-stock or stock-at-hand items in real-time, ensuring accurate inventory management.
Forecasting using historical data and market trends enables businesses to prepare inventory in advance and meet customer demand effectively.
Additionally, automated vehicles like warehouse robots can streamline pick and pack tasks, improving overall warehouse efficiency.
Inventory Management Automation
Inventory Management Automation involves real-time tracking, demand forecasting, automated replenishment, and optimized stock control to maintain accurate inventory levels and avoid stockouts or overstock situations.
Order Processing Automation
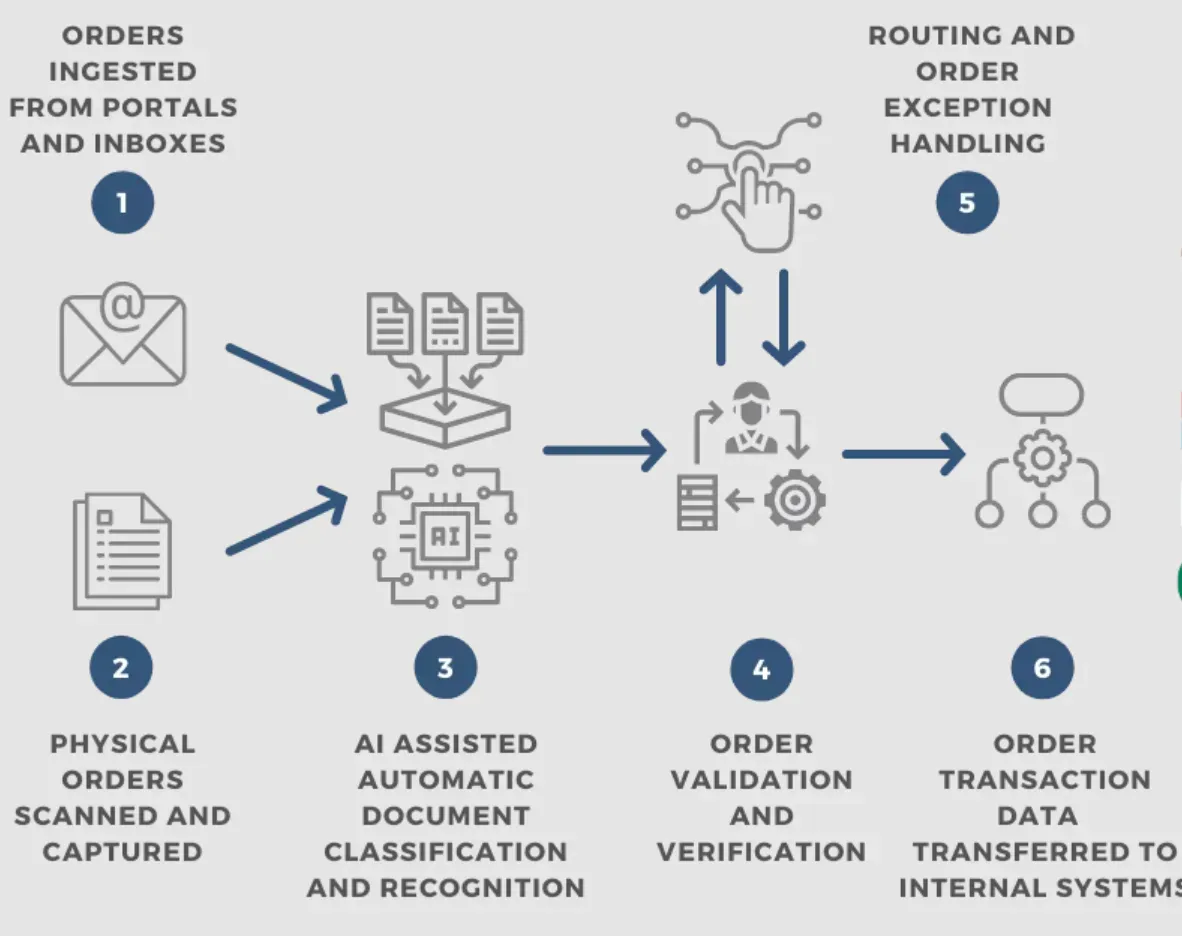
Automating order processing eliminates manual data entry, improves order accuracy, enables faster order fulfillment, and provides real-time order status updates to customers.
Supplier Relationship Automation
Automating supplier management activities, such as vendor onboarding, communication, and performance monitoring, enhances supplier collaboration, reduces lead times, and improves overall supplier relationships.
What are the benefits of Automated Supply Chain Management?

Decreasing Operating Costs
Supply Chain Automation can significantly reduce operating costs by eliminating manual processes, minimizing errors, and optimizing resource allocation.
You'll save on labor costs, reduce inventory holding costs, and improve overall cost efficiency.
Increasing Productivity
Automation streamlines processes, allowing employees to focus on higher-value tasks.
With mundane and repetitive tasks automated, your workforce can dedicate their time and expertise to more crucial activities, ultimately increasing productivity.
Improving Inventory Management Accuracy
Accurate inventory management is crucial for any business.
By automating inventory tracking using technologies like barcode scanning and Radio-frequency Identification (RFID), you can ensure real-time visibility and minimize stock inaccuracies, reducing waste and improving order fulfillment.
Enhancing Time Savings and Efficiency
Supply Chain Automation saves precious time by automating time-consuming tasks like data entry, order processing, and paperwork.
This not only frees up valuable resources but also reduces turnaround time and improves overall efficiency.
Integrating with Large Suppliers
Integrating with larger suppliers can be challenging without automation.
By automating communication, data exchange, and order management, you can seamlessly collaborate with suppliers, improving transparency, efficiency, and overall supply chain performance.
Improving Compliance and Risk Management
Supply Chain Automation enhances compliance with regulatory requirements and simplifies risk management.
With automated processes and strict monitoring, you can reduce errors, ensure compliance, and mitigate risks such as lost shipments, counterfeit products, or unauthorized access to sensitive data.
Increasing Responsiveness and Adaptability

In today's fast-paced business environment, agility is crucial. Supply Chain Automation enables quick response times to market changes, demand fluctuations, and operational disruptions.
With real-time data, predictive analytics, and automated decision-making, you can adjust and adapt your supply chain rapidly.
Enhancing Customer Service
Automation improves customer service by providing accurate and real-time information.
With automated order processing, shipment tracking, and notifications, you can keep your customers informed and deliver a seamless experience.
Meeting Shipping Demands
Supply Chain Automation helps you meet the demands of various shipping requirements.
By utilizing automated transportation and logistics processes, you can handle diverse shipping methods, optimize routes, and ensure on-time deliveries.
Technologies and Tools Used in Supply Chain Automation

Artificial Intelligence (AI)
AI enables machines to perform tasks that typically require human intelligence. It plays a significant role in supply chain planning, demand forecasting, data analysis, and decision-making.
Machine Learning (ML)
ML is a subset of AI that enables algorithms to learn from data and make predictions or decisions without explicit programming. ML algorithms improve over time as they are exposed to more data.
Robotic Process Automation (RPA)
RPA uses software "robots" to automate repetitive and rule-based tasks, mimicking human actions. It optimizes processes and improves accuracy by reducing human errors.
Optical Character Recognition (OCR)
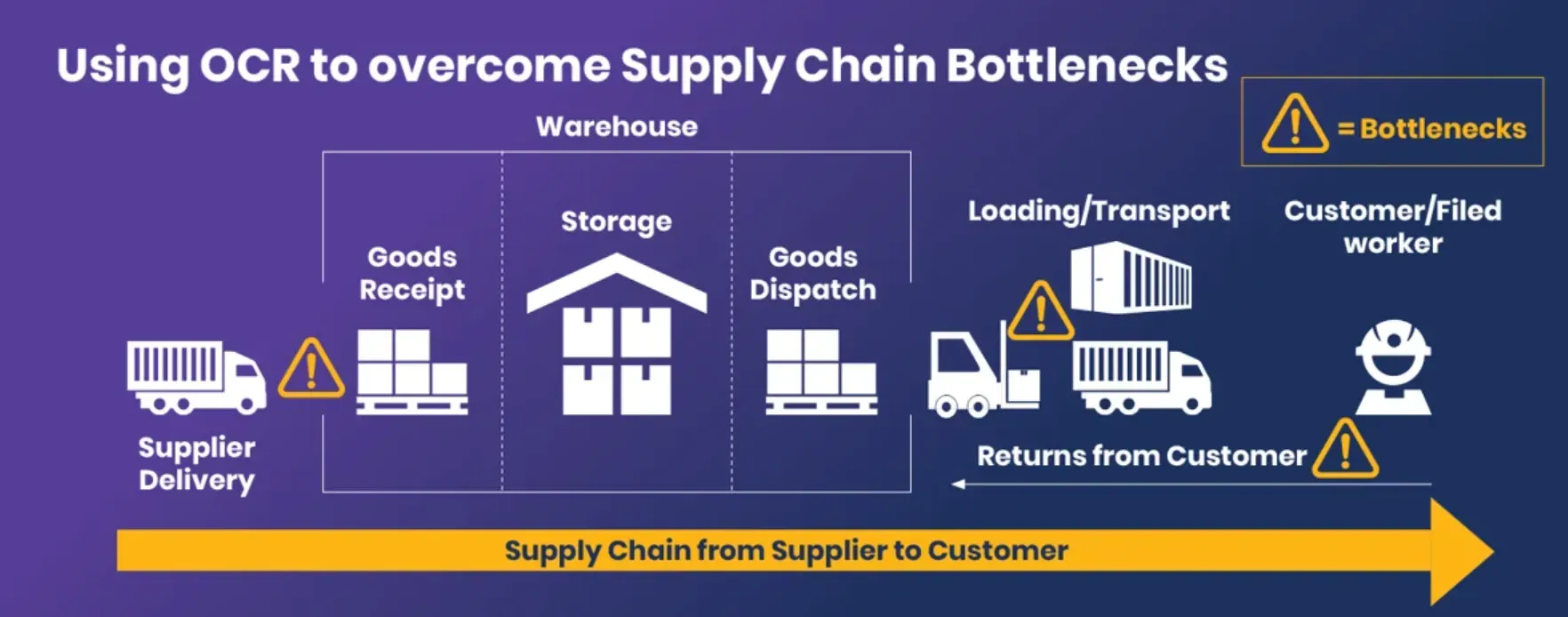
OCR technology converts printed or handwritten text into machine-readable data. It is used for digitizing documents, extracting data, and improving data accuracy.
Robotics
Robotics involves the use of physical robots to perform various tasks within the supply chain, such as picking and packing, inventory management, and materials handling.
Autonomous Vehicles
Autonomous vehicles, including drones and self-driving trucks, are revolutionizing transportation and last-mile delivery by reducing human intervention and increasing efficiency.
Data Analytics and Forecasting
Data analytics and forecasting tools enable businesses to analyze large volumes of data, identify patterns, make predictions, and optimize supply chain decisions.
Barcode and RFID Technology
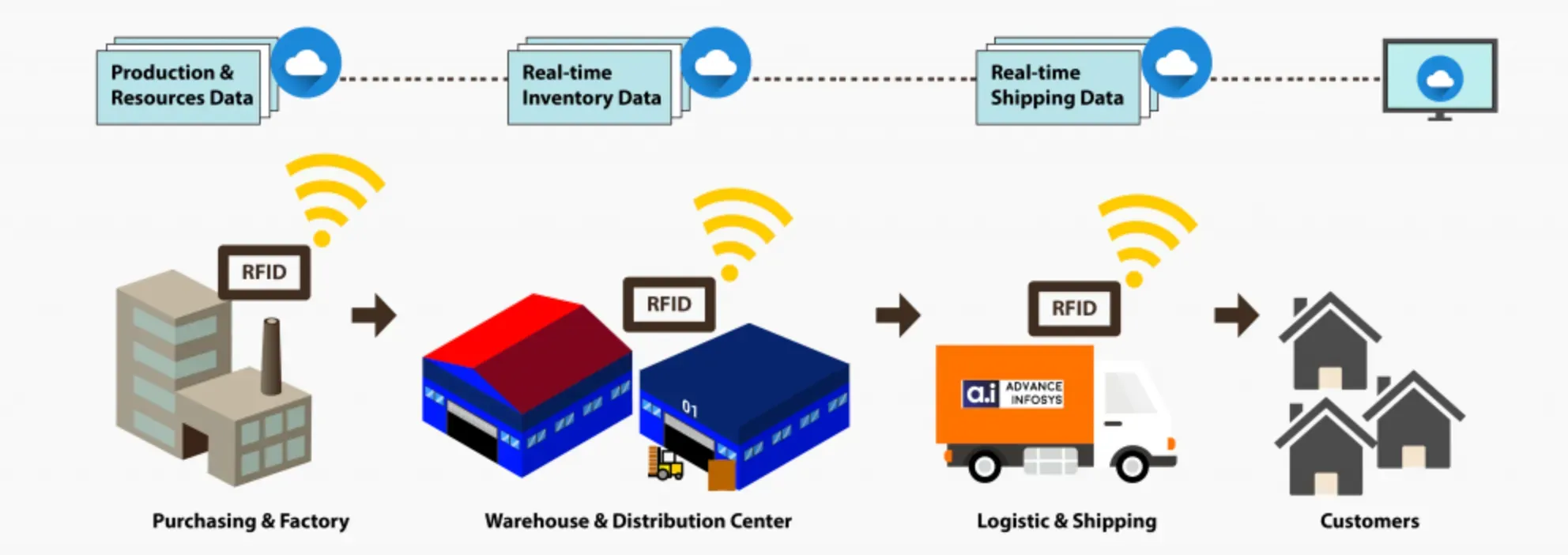
Barcode and RFID technology facilitate automated identification, tracking, and data capture of products and assets throughout the supply chain, ensuring real-time visibility and accurate inventory management.
Warehouse Management Systems (WMS)
WMS software is designed to manage and optimize warehouse operations, including receiving, storage, picking, packing, and shipping. It provides real-time inventory visibility and efficient task management.
Suggested Reading: What is Warehouse Management System?
Supply Chain Management Software (SCM)
SCM software integrates and streamlines supply chain processes, enabling collaboration, visibility, and control across all supply chain partners.
Key Considerations for Implementing Supply Chain Automation
In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the aspect of supply chain automation and lay out the key elements you need to consider while implementing it.
Identifying Processes Suitable for Automation
One of the initial and essential steps in automating your supply chain is identifying which processes are suited for automation.
Not all operations will lend themselves to be automated, and forcing automation can lead to poor results. Evaluating your current processes and selecting the right ones for automation is a crucial determinant of success.
Choosing the Right Technology
The decision to automate is just the start. Choosing the right technology to meet your automation needs is the real challenge.
Available technology options can range from comprehensive ERP systems to specific tools designed for niche tasks. Understanding the nuances of these technologies, assessing their alignment with your needs, and ensuring they integrate well with your existing systems is vital.
Overcoming Implementation Challenges
Even with the right processes and technology, you may face various obstacles during the actual implementation phase.
Common integration issues might crop up, or user resistance might hinder the seamless integration of automated processes. Having a plan on how to overcome these challenges will make your automation journey smoother.
Measuring Success and Pursuing Continuous Improvement
After automation, it's crucial to have a grasp on how well it's working. This involves setting key performance indicators (KPIs) that align directly with your supply chain goals.
Identifying the metrics to measure the effectiveness of automated processes, continuously monitoring these indicators, and making necessary improvements, ensures that your supply chain doesn't just become automated but also stays efficient and lean.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Is implementing Supply Chain Automation expensive?
The cost of implementing Supply Chain Automation varies depending on the scale and complexity of the project. However, the long-term benefits usually outweigh the initial investment, making it a worthwhile investment for many businesses.
What challenges can arise when implementing Supply Chain Automation?
Challenges may include resistance from employees, integration issues with existing systems, data security concerns, and the need for employee training. However, with proper planning and support, these challenges can be overcome.
How does Supply Chain Automation impact the workforce?
Supply Chain Automation can change job roles and responsibilities within the workforce. While certain tasks may become automated, new roles may emerge that require skills in managing and optimizing automated systems.
Can Supply Chain Automation improve sustainability practices?
Yes, Supply Chain Automation can help improve sustainability practices by optimizing energy usage, reducing waste and emissions, and facilitating better tracking and monitoring to ensure compliance with environmental regulations.
What role does technology play in Supply Chain Automation?
Technology is the backbone of Supply Chain Automation. Technologies like IoT, cloud computing, blockchain, and predictive analytics enable real-time tracking, efficient communication, data analysis, and process optimization, driving automation in the supply chain.