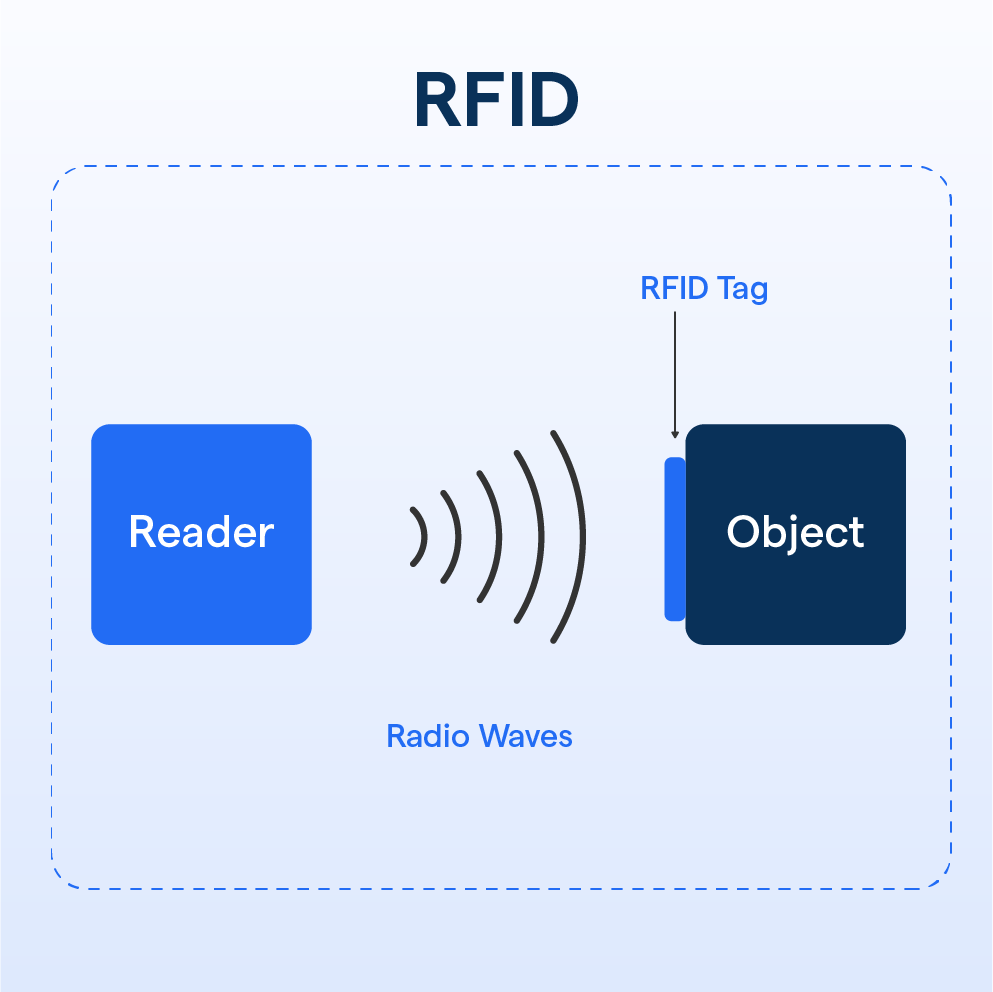
What is RFID?
Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) is a wireless technology that uses electromagnetic fields to identify and track objects. Devices called RFID tags or transponders carry data about the items to which they are attached.
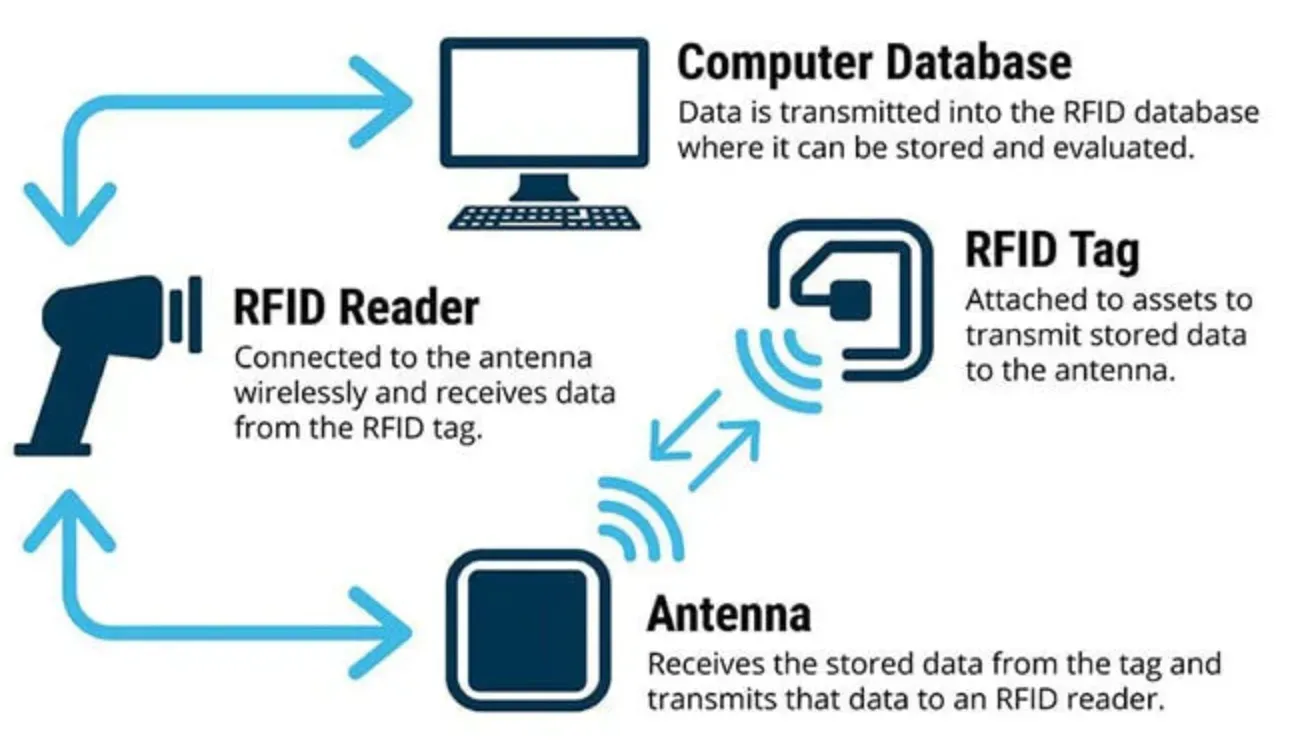
Components of an RFID System
An RFID system comprises three integral parts: RFID tags, RFID Readers, and an Antenna. The tags hold crucial information while the readers retrieve this data. The antenna facilitates communication between the two.
Advantages of Using RFID
RFID brings an array of benefits to the table. Let's explore some of them.
Inventory Management
RFID streamlines inventory management by providing quick, precise, and real-time tracking of items. It mitigates the risk of human errors, improving the overall efficiency of inventory tracking.
Time Saving and Cost Reduction
RFID saves significant time and money by automating the scanning process. Unlike barcodes, RFID tags can be read from a distance and do not need to be in the line of sight of the reader, enabling mass scanning and reducing labour costs.
Types of RFID Systems
RFID systems come in several forms, each ideally suited to different applications.
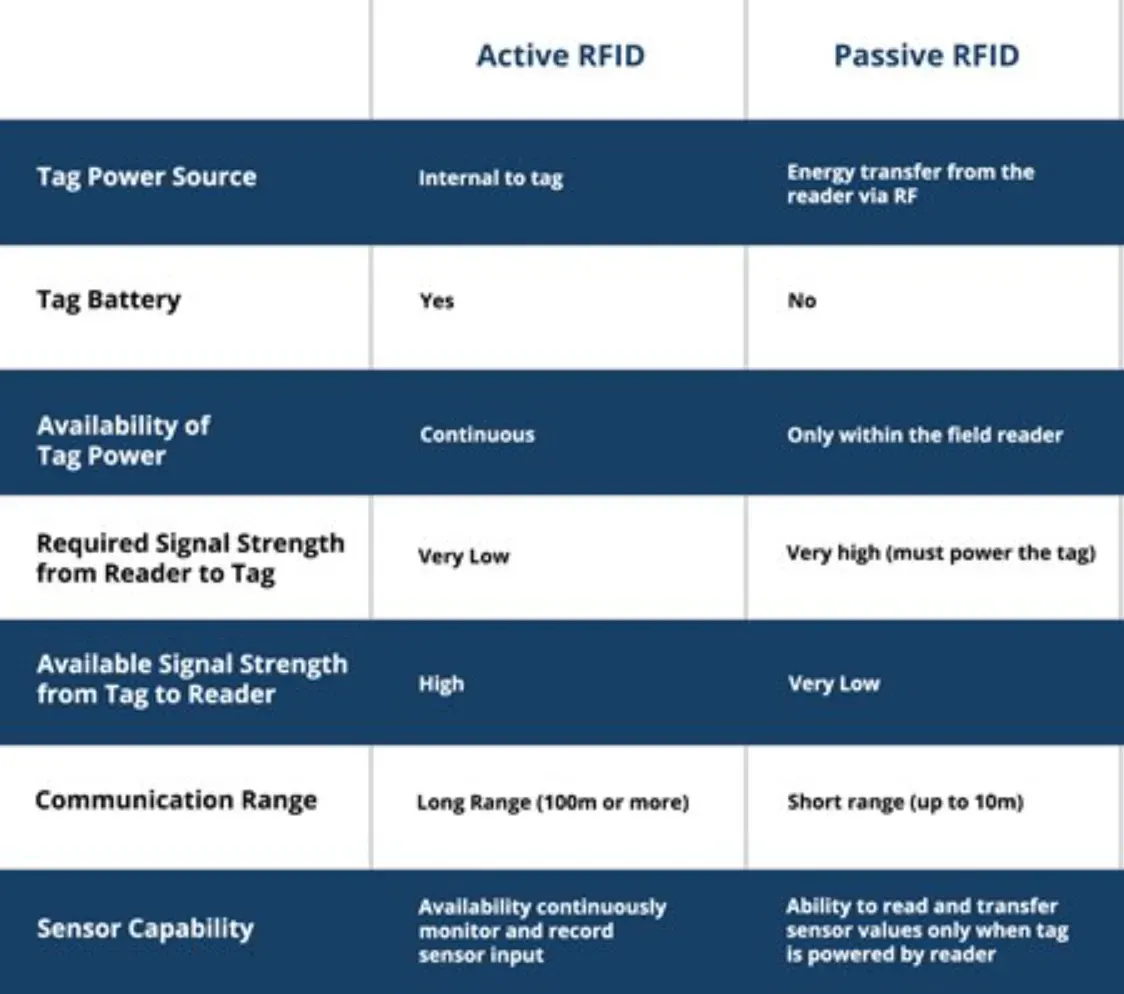
Active RFID Systems
Active RFID tags use a power source to emit signals, enabling them to communicate over larger distances. These systems suit applications requiring a wide scanning range, such as tracking vehicles or shipping containers.
Passive RFID Systems
Passive RFID tags draw power from the reader's radio waves to respond with their stored information. They are smaller, cheaper, and longer-lasting than active tags, making them ideal for tracking smaller items over short distances.
Applications of RFID
RFID's versatile technology offers a broad spectrum of applications. Here are a few notable ones.
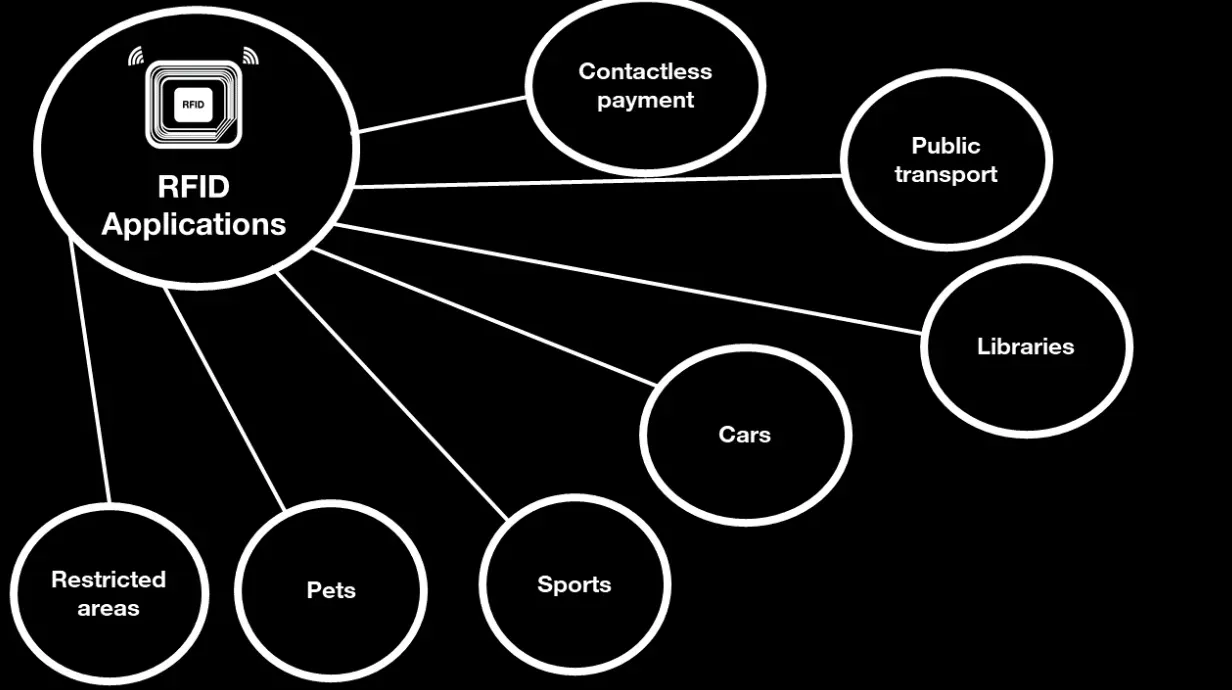
RFID in Retail
The retail industry makes extensive use of RFID for efficient inventory management and theft prevention. It enhances supply chain visibility, enabling retailers to make informed decisions and reduce out-of-stock scenarios.
RFID in Healthcare
In healthcare, RFID tags help track medication, medical equipment, and even patients, reducing errors and increasing safety. They greatly improve asset management, patient care, and staff productivity.
Limitations and Concerns around RFID
Despite RFID’s many boons, there are limitations and concerns that need addressing.
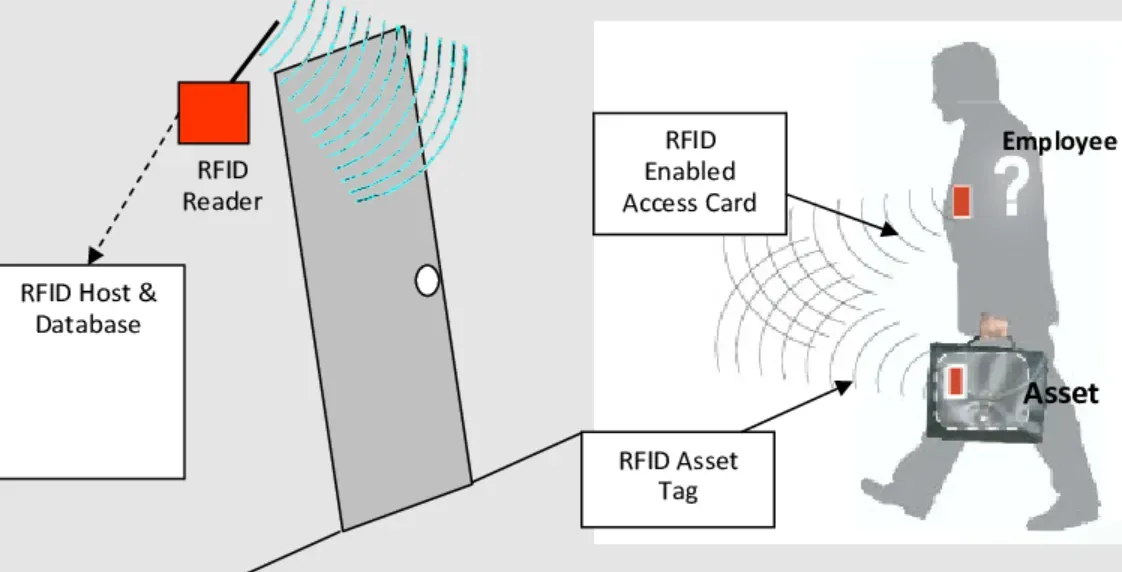
Reading Errors and Interference
RFID systems can experience reading errors if tags are put too close together or near certain materials like metal or liquids. RFID signals can also interfere with some electronic devices, causing erroneous readings.
Privacy Concerns
Privacy concerns arise as RFID tags potentially allow for tracking individuals' behaviour without their consent. For example, RFID-tagged clothes or other personal items could be used to monitor a person's movements.
The RFID Industry
The RFID industry is packed with prominent providers, significant developments, and expanding frontiers.
Major Players in RFID
Renowned companies such as Zebra Technologies, Alien Technology, and Honeywell are key players in the RFID arena. They offer a wide range of RFID solutions tailored to various sectors, from retail to logistics.
Market Growth and Future Prospects
The RFID market is projected to grow substantially in the coming years. Boosted by advancements in IoT and AI, RFID is set to play a crucial role in shaping future industry trends across sectors.
RFID vs Other Technologies
RFDI often draws comparisons with related technologies. Let’s delve into a few of these parallels.
RFID vs Barcodes
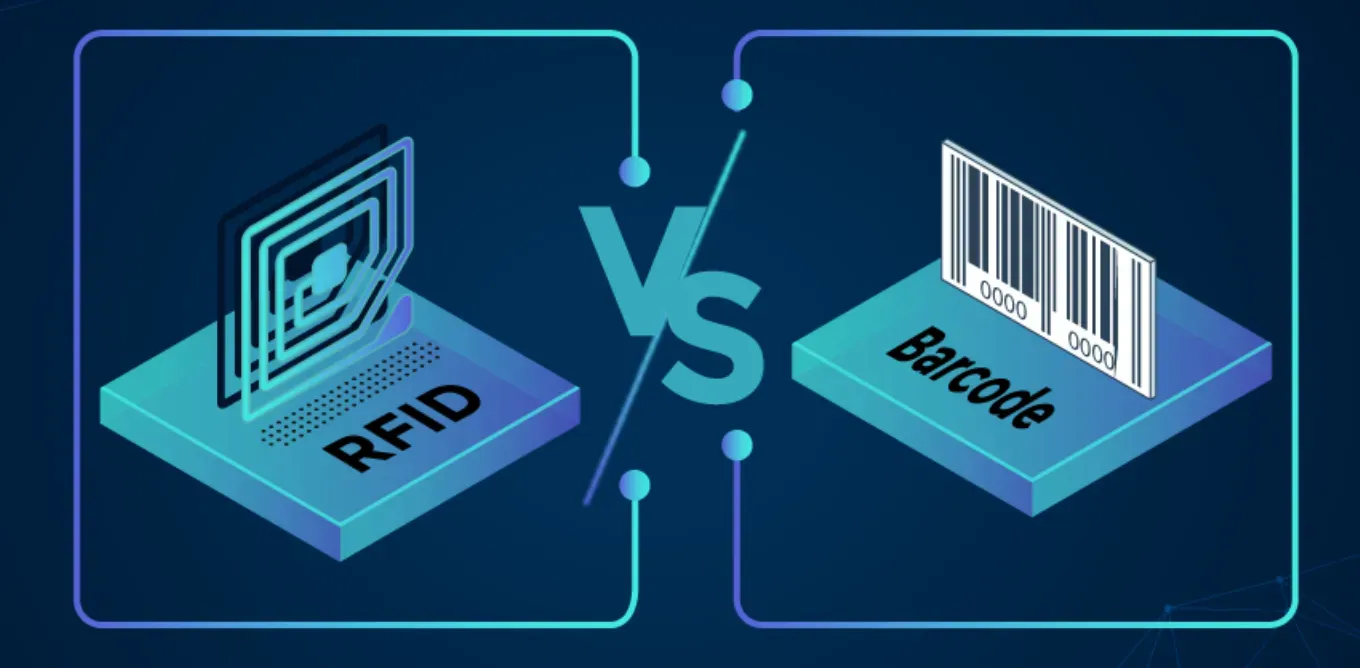
RFID and barcodes both serve to track items. But unlike barcodes, RFID tags can handle a vast amount of data, read multiple tags simultaneously, and operate without line-of-sight requirements, rendering RFID more sophisticated and versatile.
RFID vs NFC
Although Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) and Near Field Communication (NFC) both provide wireless communication and exchange data, NFC operates at a much closer range, making it ideal for secure, more intimate interactions like contactless payments.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Can RFID tags be reused?
Yes, RFID tags can be reused in certain cases. Some tags are designed for multiple uses and can be reprogrammed or reset to be used with new items.
What is the difference between passive and active RFID tags?
Passive RFID tags do not have their own power source and rely on the reader's signal to power them. Active RFID tags have their own power source and can transmit signals over longer distances.
Can RFID tags be read through materials?
RFID tags can be read through certain materials like plastic and cardboard. However, metals and liquids can interfere with the radio waves, making it difficult for the reader to communicate with the tag.
Is RFID technology used in other industries besides inventory management?
Yes, RFID technology is used in various industries like healthcare, logistics, retail, and transportation. It helps in asset tracking, supply chain management, authentication, and improving overall operational efficiency.
How long does an RFID tag typically last?
The lifespan of an RFID tag depends on various factors, such as the type of tag, environmental conditions, and usage. Generally, passive RFID tags can last for several years, while active RFID tags can last for several months to a few years.