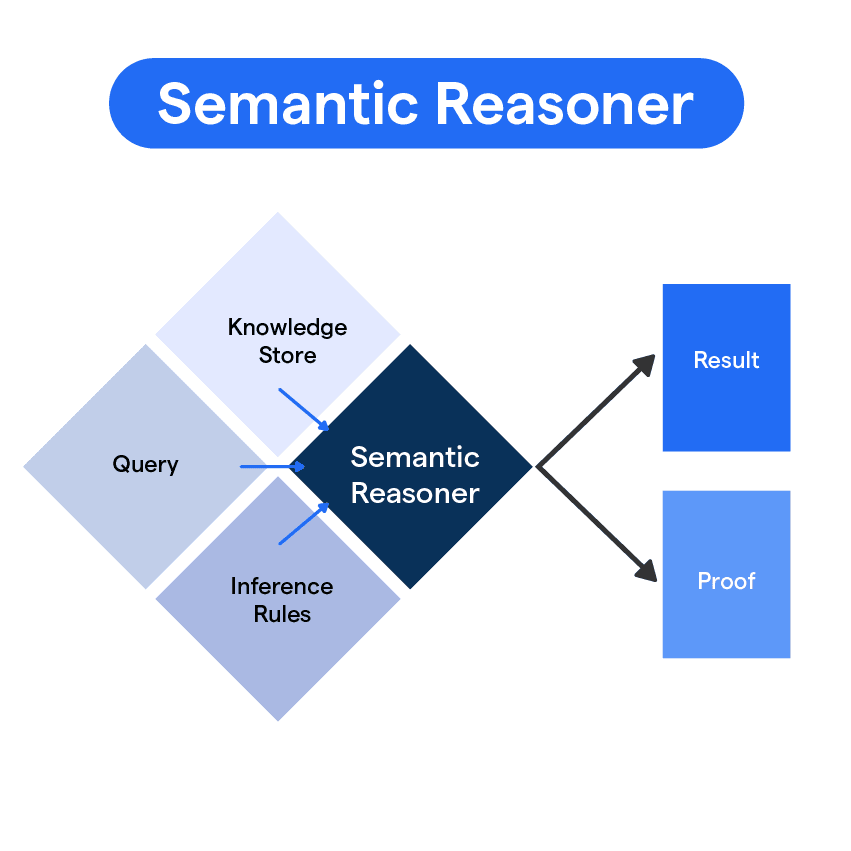
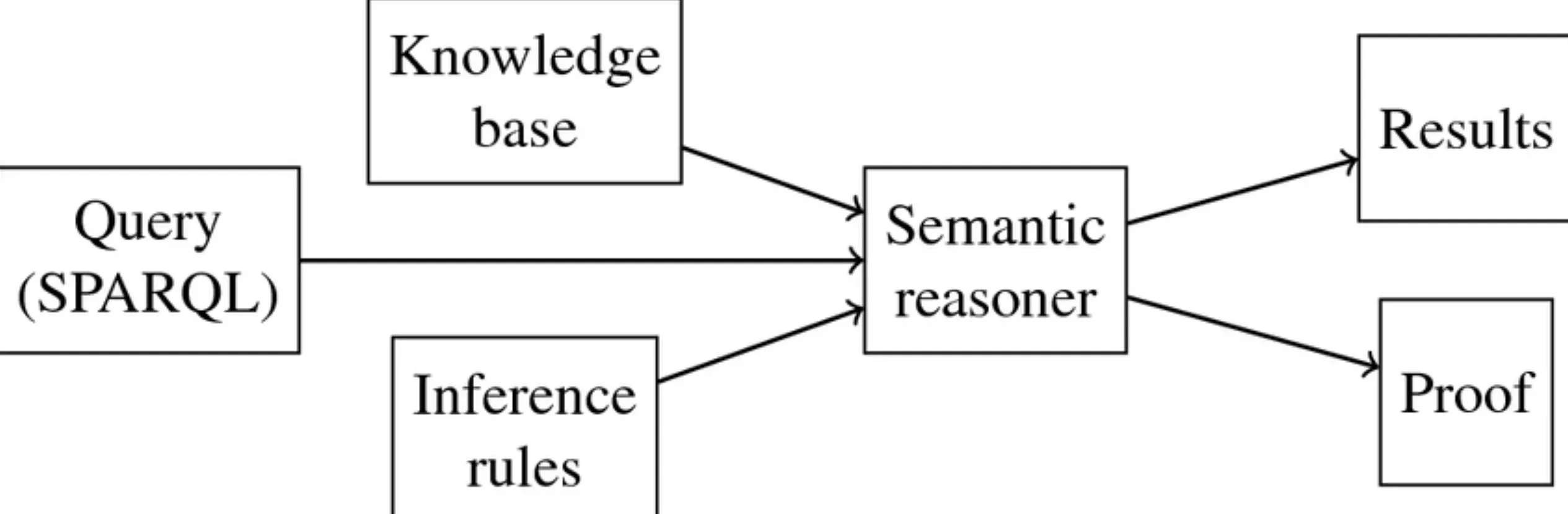
What is a Semantic Reasoner?
A semantic reasoner, also known as a rules engine, reasoning engine, or reasoner, is a software that can infer logical consequences from a given set of axioms or asserted facts. It goes beyond simple inference engines by offering a richer set of mechanisms to perform operations.
Semantic reasoners often use ontology languages and description logic languages to specify the inference rules they employ. Many semantic reasoners utilize first-order predicate logic for performing inference, using techniques like forward chaining and backward chaining.
There are also probabilistic reasoners that employ probabilistic logic networks and non-axiomatic reasoning systems.
What are Ontologies?
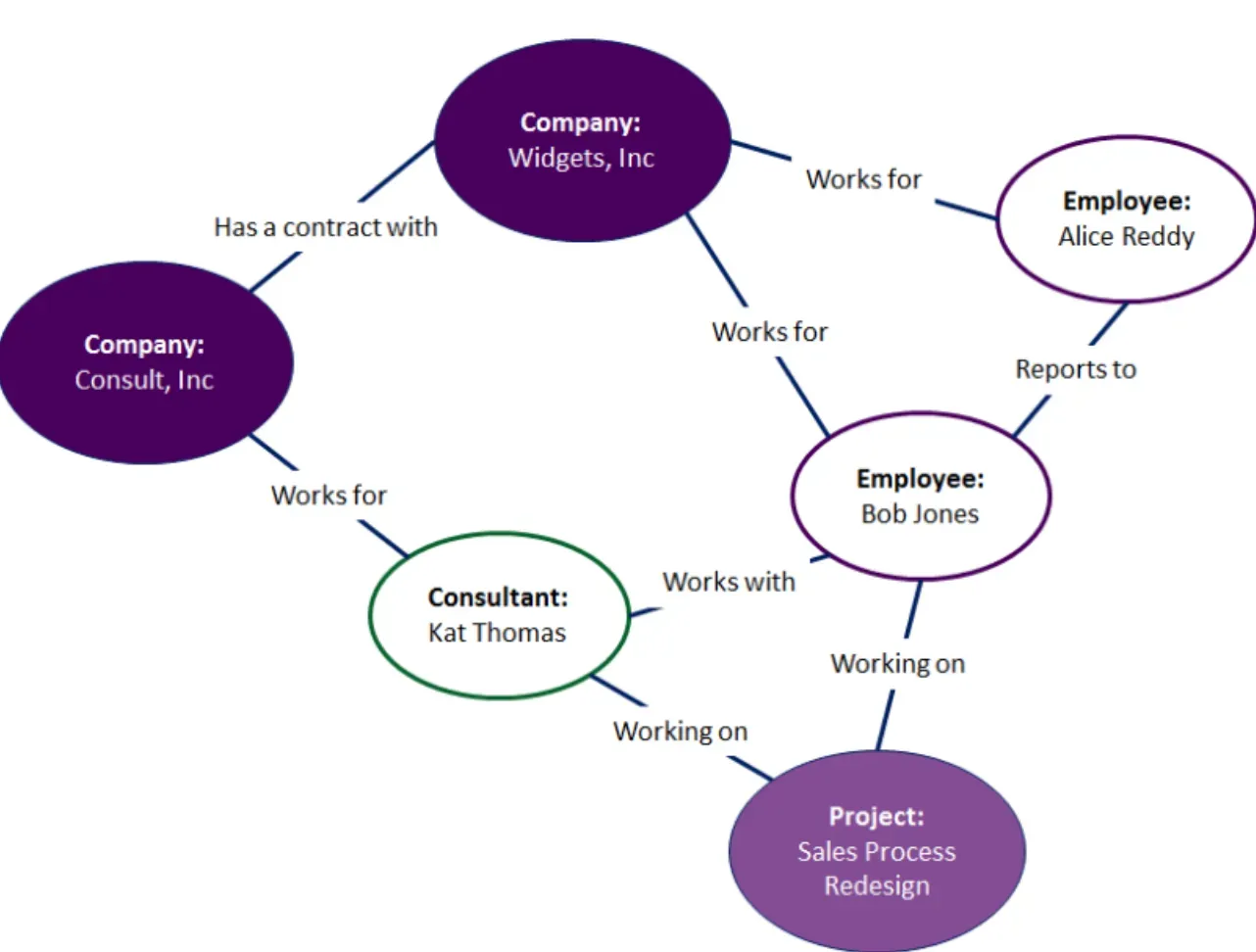
Ontologies are sets of concepts within a specific domain and the relationships between them. They involve formally specifying components such as individuals (instances of objects), classes, attributes, relations, rules, axioms, and restrictions.
Ontologies provide a shareable and reusable knowledge representation that can expand the understanding of a domain.
One example of an ontology language is OWL, which is a semantic web computational logic-based language. OWL is designed to represent rich and complex knowledge about things and their relationships.
When used with an OWL reasoner in RDF triplestores (semantic graph databases), it can detect logical inconsistencies and check for classes that cannot have instances.
Why is a Semantic Reasoner important?
Semantic reasoners play a crucial role in knowledge representation, processing, and the broader field of artificial intelligence. They offer several benefits, including:
Efficient Knowledge Processing: Semantic reasoners can process and analyze large volumes of semantic data quickly, enabling efficient knowledge representation and retrieval.
Enhanced Decision Making: By uncovering hidden relationships and making inferences, semantic reasoners help in better decision making, both in simple and complex scenarios.
Improved Data Integration: Semantic reasoners facilitate the integration of diverse datasets by harmonizing and aligning different representations through semantic annotations and mappings.
When to use a Semantic Reasoner?
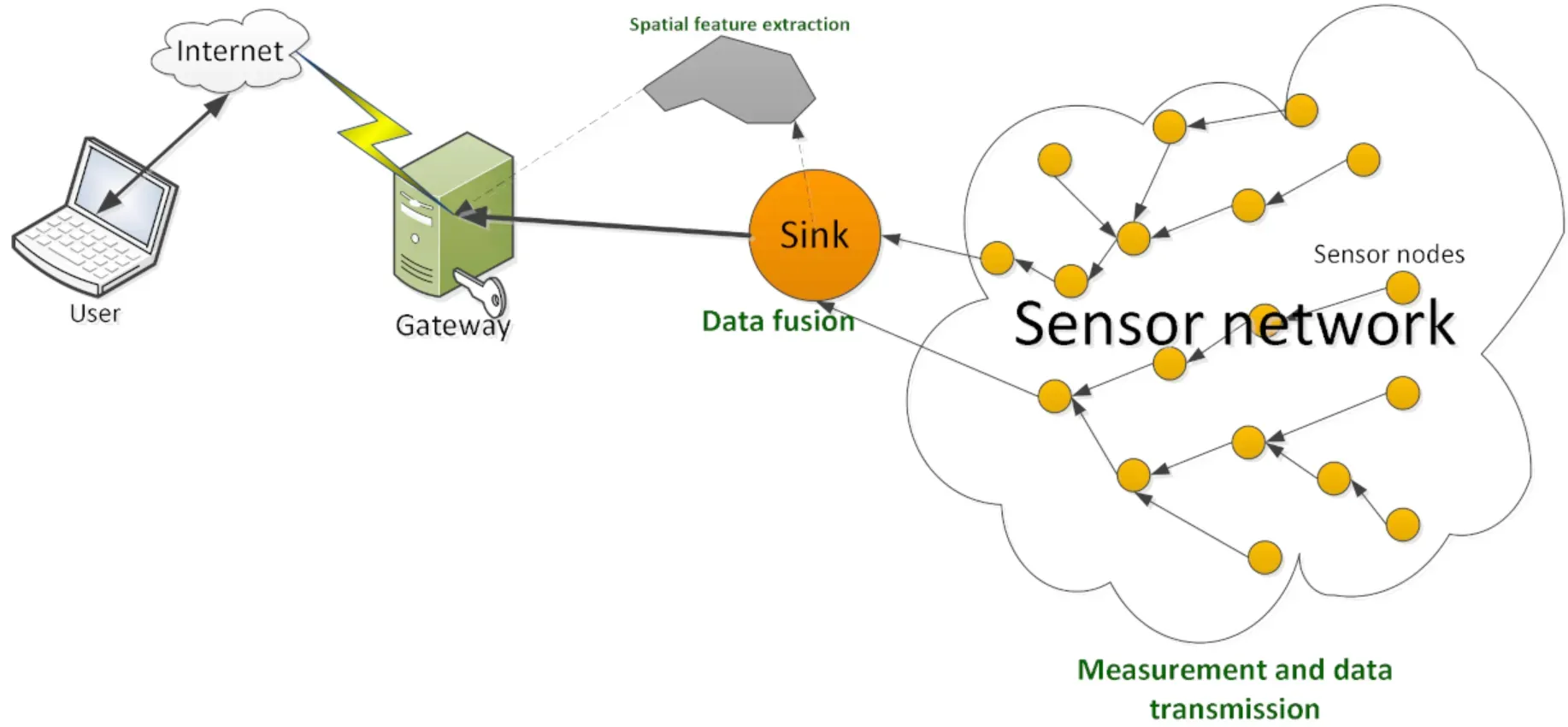
Semantic reasoners can be applied effectively in various scenarios and industries, including healthcare, finance, manufacturing, and more. Here are some cases where a semantic reasoner can prove valuable:
Semantic Search: When you need to enhance search capabilities, enabling users to find relevant information based on context and relationships rather than just keyword matching.
Data Integration: When you have multiple datasets with different schemas and need to integrate them into a unified knowledge graph.
Intelligent Chatbots: When building conversational AI agents that can understand and reason about user queries to provide accurate and relevant responses.
How to implement a Semantic Reasoner?
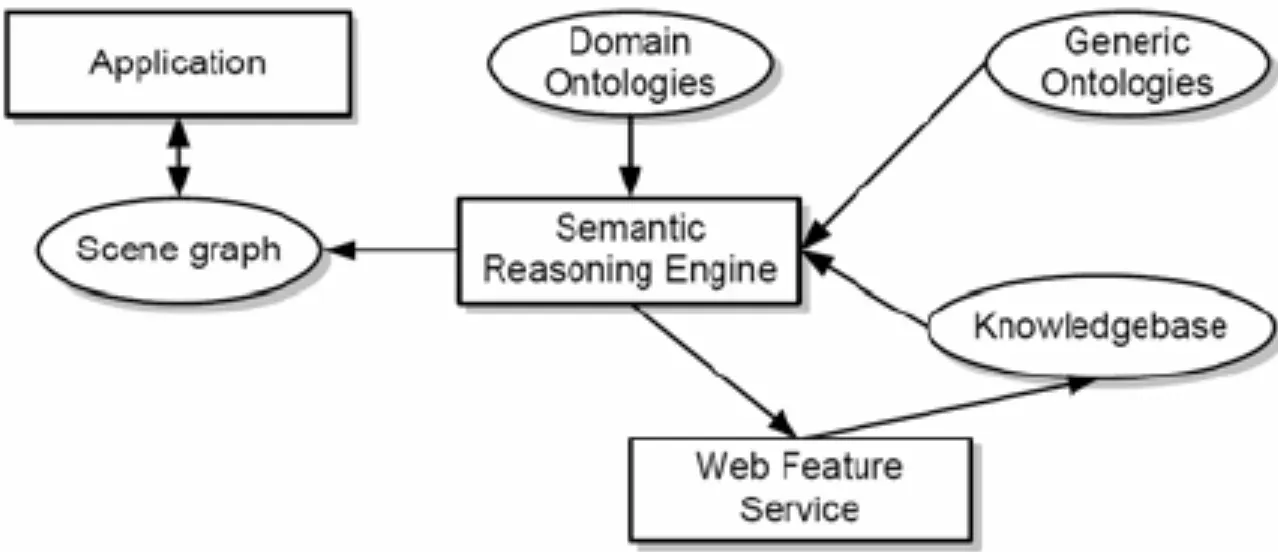
Implementing a semantic reasoner involves the following steps:
- Define Objectives: Clearly define the goals and objectives of using a semantic reasoner in your project or application.
- Choose a Reasoner: Select a semantic reasoner that aligns with your requirements and preferences.
- Prepare Data: Prepare your data by structuring it using semantic standards and formats such as RDF or OWL.
- Integrate Reasoner: Integrate the chosen reasoner into your system or application, ensuring proper data ingestion and processing.
- Test and Optimize: Thoroughly test the reasoner's performance, accuracy, and efficiency, and optimize as needed.
Semantic Reasoners in Action: Real-Life Applications
Semantic reasoners have found applications in various industries, transforming them by enabling intelligent decision-making and automation. Let's explore some industries where semantic reasoners have made a significant impact:
E-Commerce & Retail
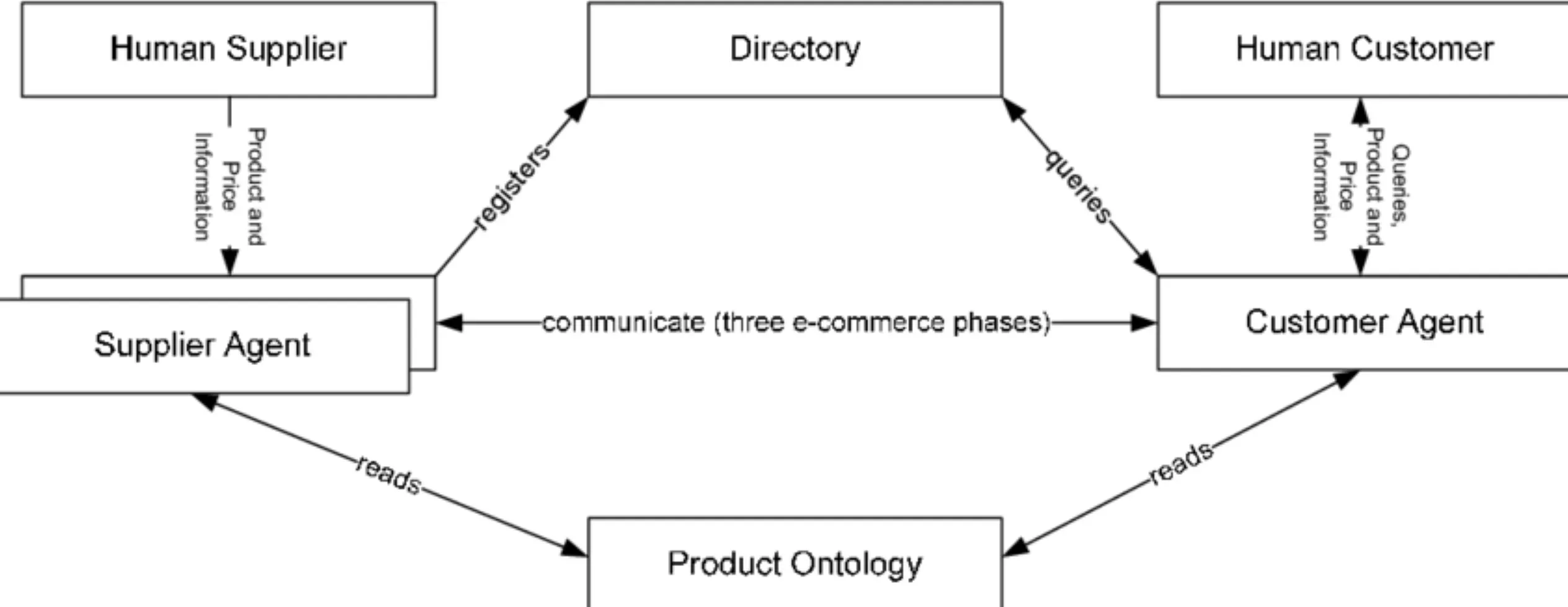
Semantic reasoners help e-commerce platforms and retailers provide personalized product recommendations based on user preferences, behavior analysis, and semantic understanding of their catalog.
This improves customer engagement, conversion rates, and overall customer satisfaction.
Logistics
In the logistics industry, semantic reasoners optimize route planning, resource allocation, and inventory management by efficiently analyzing vast amounts of data.
This helps reduce costs, minimize delays and errors, and improve supply chain efficiency.
Travel & Hospitality
Semantic reasoners are employed to enhance travel and hospitality experiences by personalizing recommendations for flights, accommodations, and tourist attractions.
By considering user preferences, location data, and contextual information, semantic reasoners offer tailored suggestions that meet individual needs.
Suggested Reading:
What is Semantic Relatedness & its techniques
Government
Semantic reasoners play a vital role in government operations and decision-making processes.
They aid in analyzing and interpreting large volumes of data, making it easier to identify trends, patterns, and insights. This enables governments to make informed policy decisions and plan more effectively.
Insurance & Banking
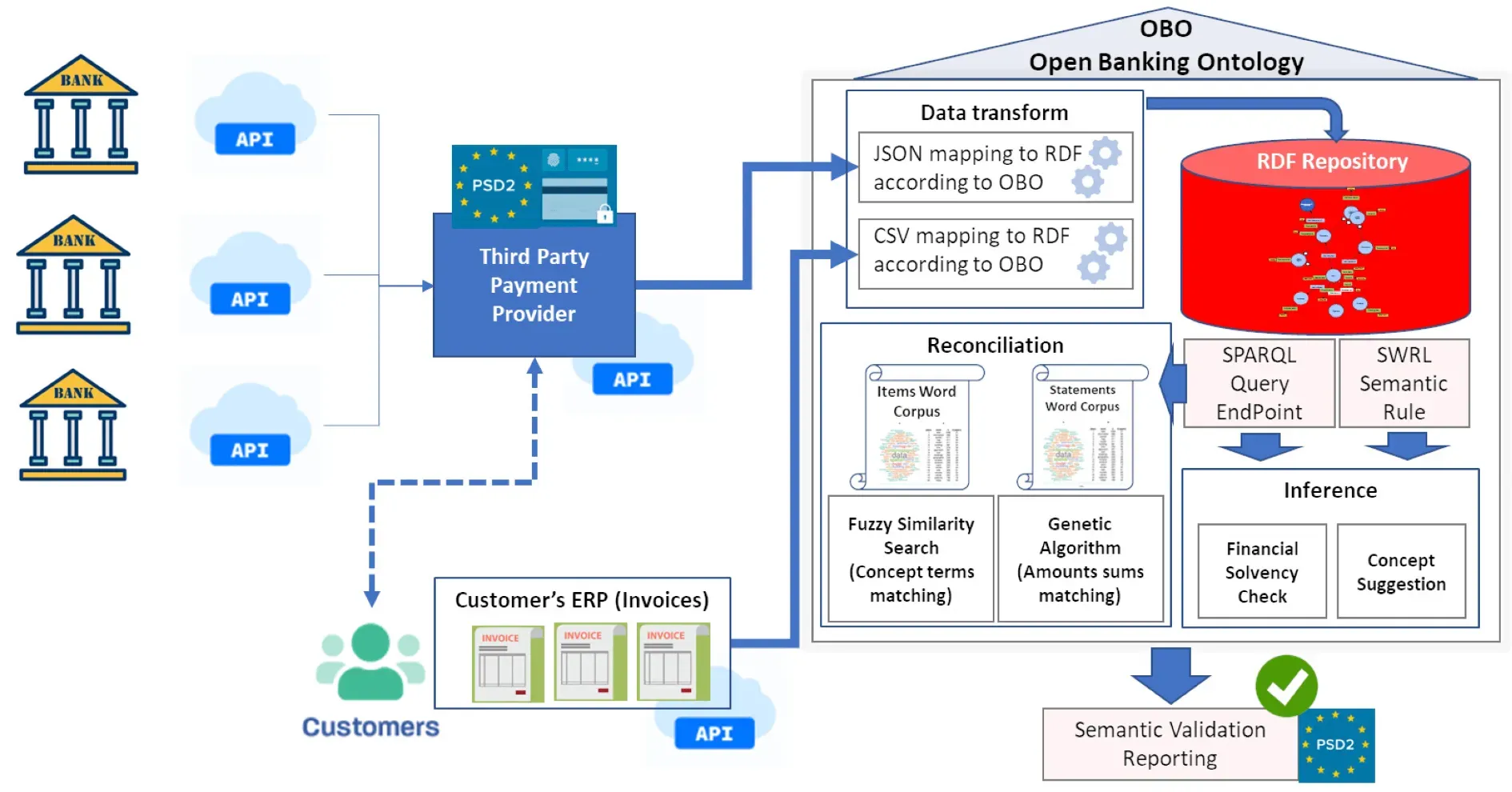
In the insurance and banking sectors, semantic reasoners assist in fraud detection, risk assessment, and compliance monitoring.
By analyzing patterns and anomalies, these reasoners help identify potential fraudulent activities, assess risks accurately, and ensure regulatory compliance.
Real Estate
In the real estate industry, semantic reasoners enable smarter property searches and recommendations.
By considering factors such as location, price, amenities, and user preferences, these reasoners help individuals and businesses find properties that align with their specific requirements.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is the purpose of a semantic reasoner?
A semantic reasoner is designed to perform reasoning and inference on semantic data, helping to uncover hidden connections, resolve inconsistencies, and make logical deductions.
How does a semantic reasoner work?
Semantic reasoners operate on principles of formal logic, using inference mechanisms to process data. They apply rules, axioms, and relationships encoded in knowledge representations to draw conclusions and make inferences.
Who can benefit from using a semantic reasoner?
Professionals such as data scientists, knowledge engineers, and system architects benefit from utilizing semantic reasoners. They aid in analyzing complex datasets, building ontologies, and designing information systems that can reason with complex data structures.
How to choose a semantic reasoner?
Consider factors such as performance, compatibility, and usability when choosing a semantic reasoner. Evaluate scalability, language support, and user interface to ensure it aligns with your project's requirements.