What is Semantic Analysis?
Semantic analysis is a technique used to analyze and understand the meaning of words and phrases in a given context. Unlike traditional keyword analysis, which focuses on identifying specific keywords and phrases that are relevant to a particular topic, semantic analysis takes a more holistic approach, considering the broader meaning and context of the words and phrases being analyzed.
Why is Semantic Analysis Important?

Enhancing Natural Language Understanding
Semantic analysis plays a crucial role in improving natural language understanding (NLU) for AI systems, helping them better comprehend human language. It's like giving AI a deeper insight into the world of words and meanings.
Enabling Sentiment Analysis
By understanding the meaning behind text, semantic analysis allows AI systems to perform sentiment analysis, gauging the emotions and opinions expressed. It's like being a detective, uncovering hidden feelings and attitudes.
Improving Information Retrieval
Semantic analysis helps improve search engines and information retrieval systems by considering the meaning and context of search queries. It's like having a knowledgeable librarian who knows exactly where to find the information you need.
Supporting Text Summarization
With semantic analysis, AI systems can generate accurate and meaningful summaries of lengthy text, saving users time and effort. It's like having a personal assistant who can distill complex information into simple, digestible nuggets.
Facilitating Language Translation
Semantic analysis aids in language translation by ensuring that the meaning of the source text is accurately conveyed in the target language. It's like being a skilled interpreter, bridging the gap between languages and cultures.
How Does Semantic Analysis Work?
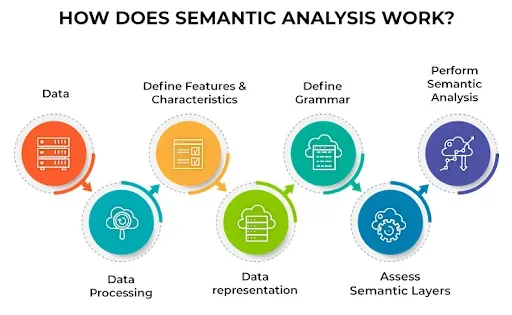
Tokenization and Parsing
Semantic analysis starts with tokenization and parsing, breaking down text into individual words or phrases and analyzing their grammatical structure. It's like dissecting a sentence to reveal its inner workings.
Identifying Entities and Relationships
By recognizing entities (e.g., people, places, objects) and their relationships, semantic analysis helps uncover the meaning behind text. It's like being a matchmaker, connecting the dots between words and concepts.
Resolving Ambiguity
Semantic analysis tackles ambiguity by using context, word sense disambiguation, and other techniques to determine the intended meaning of words or phrases. It's like solving a riddle by considering all the clues.
Analyzing Sentiment and Emotion
By examining word choice, tone, and context, semantic analysis can gauge the sentiment and emotions expressed in text. It's like being an empath, sensing the feelings hidden in words.
Leveraging Knowledge Bases and Ontologies
Semantic analysis often relies on knowledge bases and ontologies, which provide structured information about concepts, categories, and relationships. It's like consulting an encyclopedia to better understand the world and its intricacies.
Types of Semantic Analysis
There are several types of semantic analysis that can be used to optimize your website's content for search engines. These include:
Named Entity Recognition
Named entity recognition is a technique used to identify and classify named entities in a given text. Named entities can include people, places, organizations, and more. By using named entity recognition, you can ensure that your content is optimized for the specific entities that are most relevant to your target audience.
Sentiment Analysis
Sentiment analysis is a technique used to analyze the emotional tone of a given text. By using sentiment analysis, you can better understand how your target audience feels about your brand, products, or services, and adjust your content accordingly.
Topic Modeling
Topic modeling is a technique used to identify the topics and themes that are most relevant to a given text. By using topic modeling, you can ensure that your content is optimized for the specific topics and themes that are most relevant to your target audience.
Use Cases Of Semantic Analysis

Sentiment Analysis
Semantic analysis helps in determining the sentiment behind text data, such as customer reviews or social media posts, enabling businesses to gauge public opinion and improve customer experience.
Information Extraction
Semantic analysis aids in extracting relevant information, such as names, dates, or locations, from unstructured text data, allowing for better organization and understanding of the content.
Text Summarization
By understanding the meaning and context of text data, semantic analysis can generate concise summaries of lengthy articles or documents, saving time and effort for users.
Chatbots and Virtual Assistants
Semantic analysis enables chatbots and virtual assistants to understand user queries, provide accurate responses, and engage in more natural and context-aware conversations.
Content Recommendation
By analyzing the semantic relationships between various pieces of content, semantic analysis can power content recommendation systems that suggest relevant articles, videos, or products based on user preferences and interests.
Tools for Semantic Analysis
There are several tools available for conducting semantic analysis, including Google's Natural Language API, IBM Watson, and more. These tools can help you analyze the meaning of words and phrases in your content, identify named entities, analyze sentiment, and more.
Best Practices for Semantic Analysis

Choose the Right Tools and Techniques
Select the appropriate tools, libraries, and techniques for your specific semantic analysis task. Consider factors such as language support, scalability, and accuracy.
Clean and Preprocess Data
Ensure the data you're working with is clean and well-preprocessed. This may involve removing irrelevant information, correcting spelling errors, and converting text to lowercase.
Handle Ambiguity and Context
Develop strategies to handle ambiguity and understand context, such as using word sense disambiguation techniques or incorporating external knowledge sources.
Use Domain-Specific Resources
Leverage domain-specific resources, such as domain-specific ontologies or lexicons, to improve the accuracy and relevance of your semantic analysis.
Evaluate and Iterate
Continuously evaluate your semantic analysis model's performance and iterate to improve its accuracy. Consider using a combination of quantitative metrics and qualitative feedback from domain experts.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is Semantic Analysis?
Semantic analysis is the process of understanding the meaning of text or speech by examining its structure, context, and relationships between words or phrases.
How is Semantic Analysis used in NLP?
In natural language processing (NLP), semantic analysis helps systems understand human language, enabling tasks like sentiment analysis, information extraction, and text summarization.
What are the challenges in Semantic Analysis?
Challenges in semantic analysis include handling ambiguity, understanding context, and dealing with idiomatic expressions, sarcasm, or cultural references.
How does Semantic Analysis differ from Syntactic Analysis?
While syntactic analysis focuses on the structure and grammar of the language, semantic analysis delves into the meaning behind words, phrases, and sentences.
Can Semantic Analysis be applied to multiple languages?
Yes, semantic analysis can be applied to multiple languages, but it requires language-specific resources and models to understand linguistic nuances and cultural context.