What is an Attribute?
In general terms, an attribute is a quality or characteristic given to a person, object, or concept. In technical areas like computing, an attribute assigns a specific property or value to a variable, object, file, or element.
Attributes are distinct from categories or classifications. While categories or classes group similar items together, attributes define the characteristics or properties of those items.
Uses of Attributes
We use attributes all the time in day-to-day life, often unconsciously. You might refer to someone's attributes when describing their personality or physical features or mention the attributes of a product when shopping.
Attributes in Computer Science
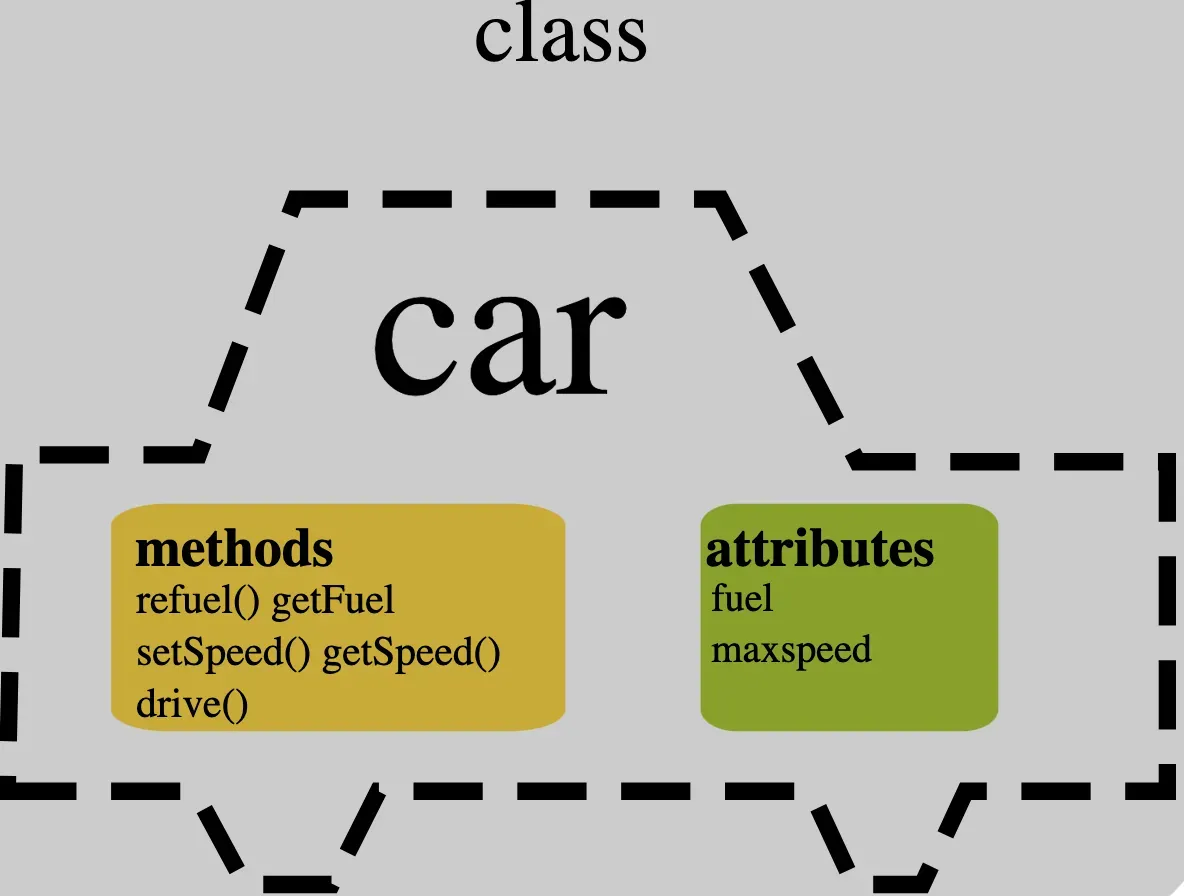
In computer science, attributes refer to additional information about a data object's properties. For example, in a database, an attribute might be the color and model of a car in a "Car" entity.
Attributes in HTML
In HTML, attributes are used within tags to alter their behavior or appearance. For example, the 'src' attribute in an img tag instructs the browser on where to find the image file.
Attributes in Programming
In programming, attributes attach metadata to a code to change its runtime behavior. They can specify properties of types, method parameters, return types, and assemblies in .Net languages like C# or F#.
Impact of Correct Use of Attributes
Using attributes correctly allows for efficient and well-organized data management. It enables sorting and filtering, speeding record-search times in databases.
Accurate and Descriptive Metadata
In the worlds of HTML or other markup languages, using attributes correctly ensures your elements behave as intended and carry the correct metadata.
Proper Program Behavior
In programming, attributes provide additional information for compiler behavior or runtime behavior alterations, thereby ensuring the correct functioning of code.
Improved Usability
In product development, defining useful attributes helps differentiate products, making it easier for customers to identify the items that suit their needs.
Common Errors and Misuse of Attributes
Incorrect assignment of an attribute's value would result in errors in coding, and it could generate incorrect metadata leading to malfunction in applications relying on those attributes.
Absence of Required Attributes
Forgetting to specify required attributes can create issues as well. For example, in HTML, forgetting to put the 'src' attribute in an 'img' tag would result in an image not being displayed.
Incorrect Attribute Use
Using an attribute where it's not intended can lead to coding errors and misinterpretation of the code.
Unclear or Incomplete Attributes
Unclear attribute naming or incomplete attribute listings can lead to confusion and make it harder to understand the characteristics of a given entity.
Embedding of Attributes
In file systems, attributes are metadata details about a file or folder. In Windows, for example, we have attributes such as 'Read-Only,' 'Hidden,' 'System,' and 'Archive.'
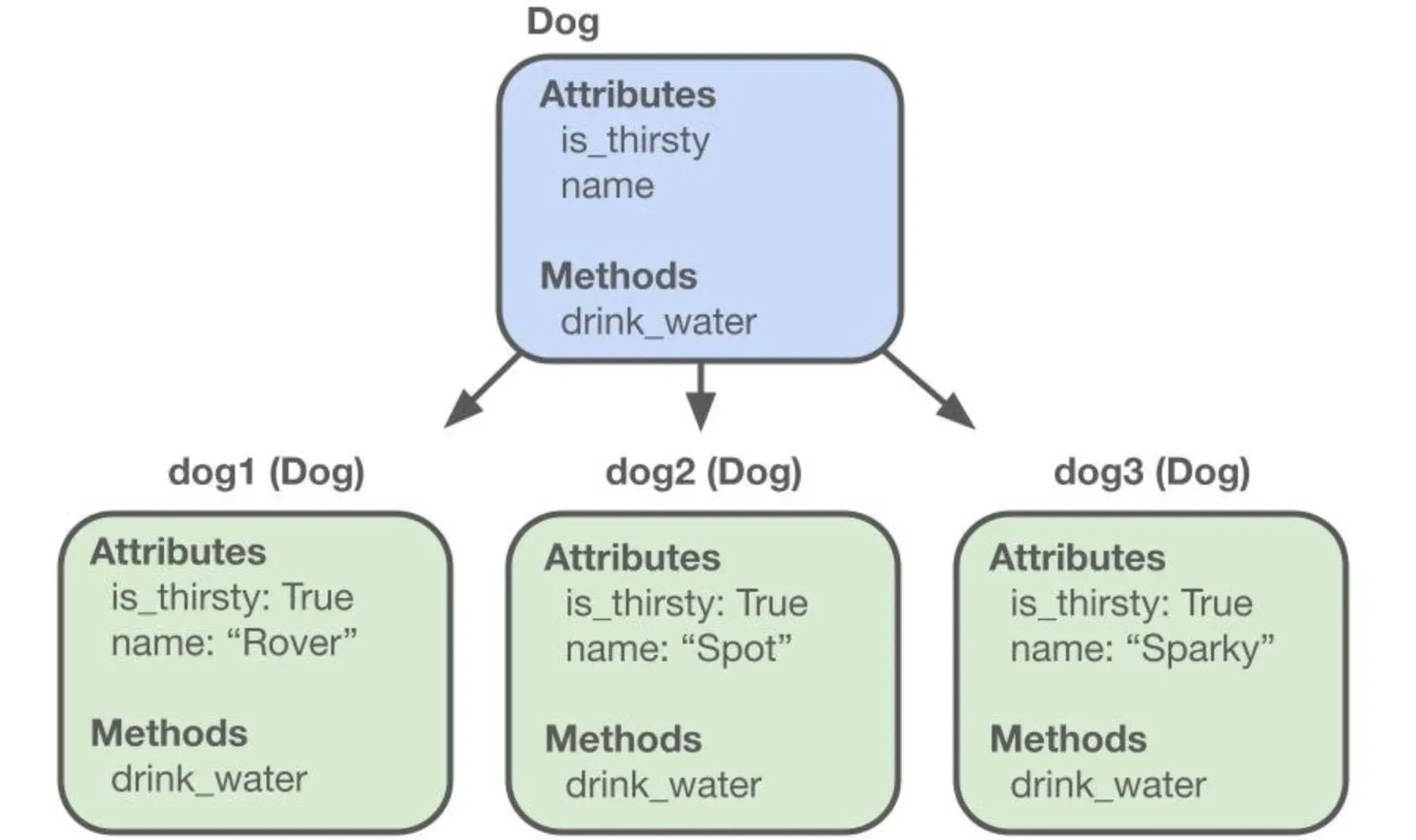
Attributes in Objects
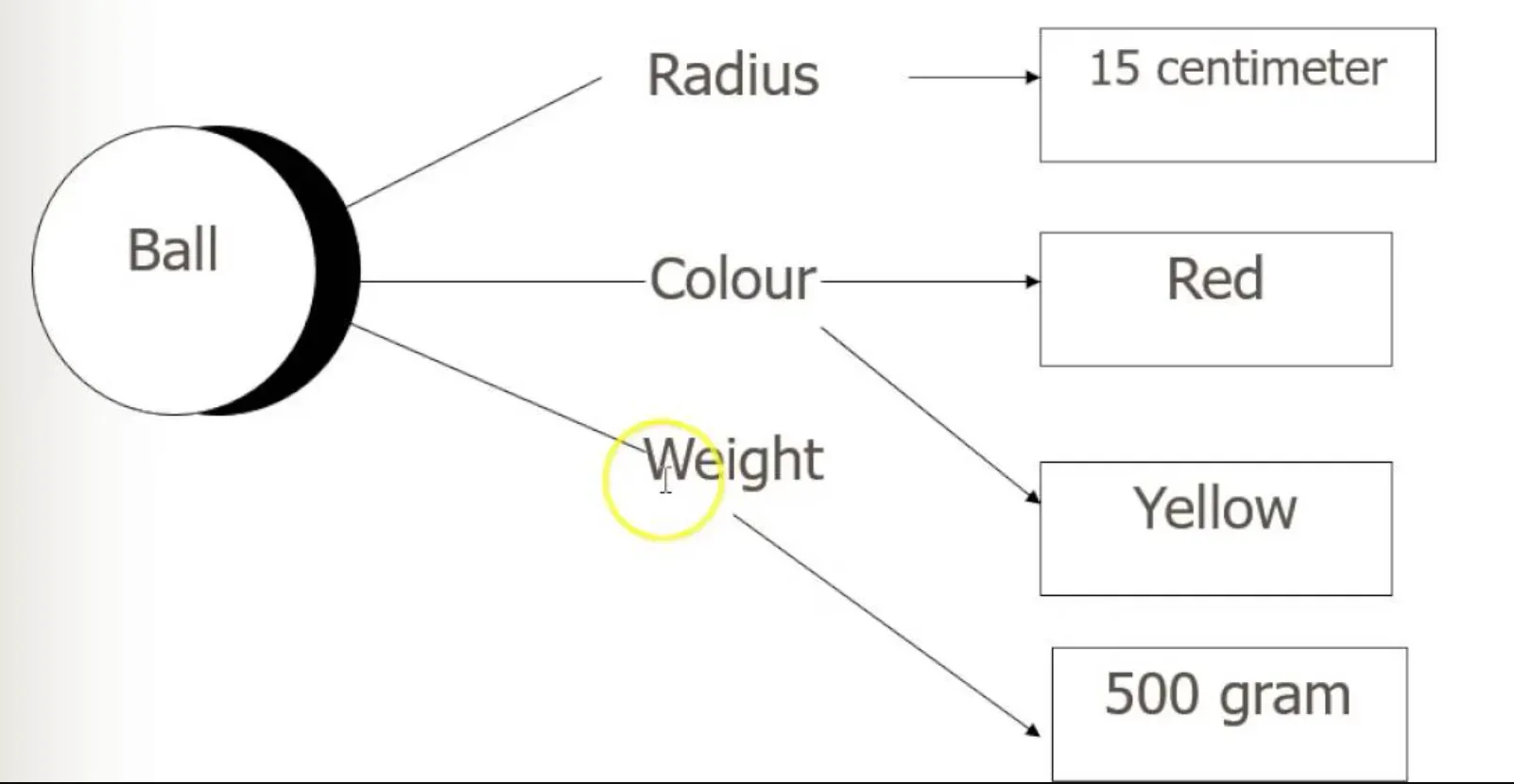
In object-oriented programming, attributes (also known as properties or fields) are the data stored inside an object. For instance, a "Person" object might have attributes like 'name,' 'age,' and 'address.'
Attributes in Markup Languages
In markup languages, like HTML or XML, attributes are added to tags (elements) to provide additional information. For instance, in <img src="image.jpg">, src is an attribute that specifies the image source.
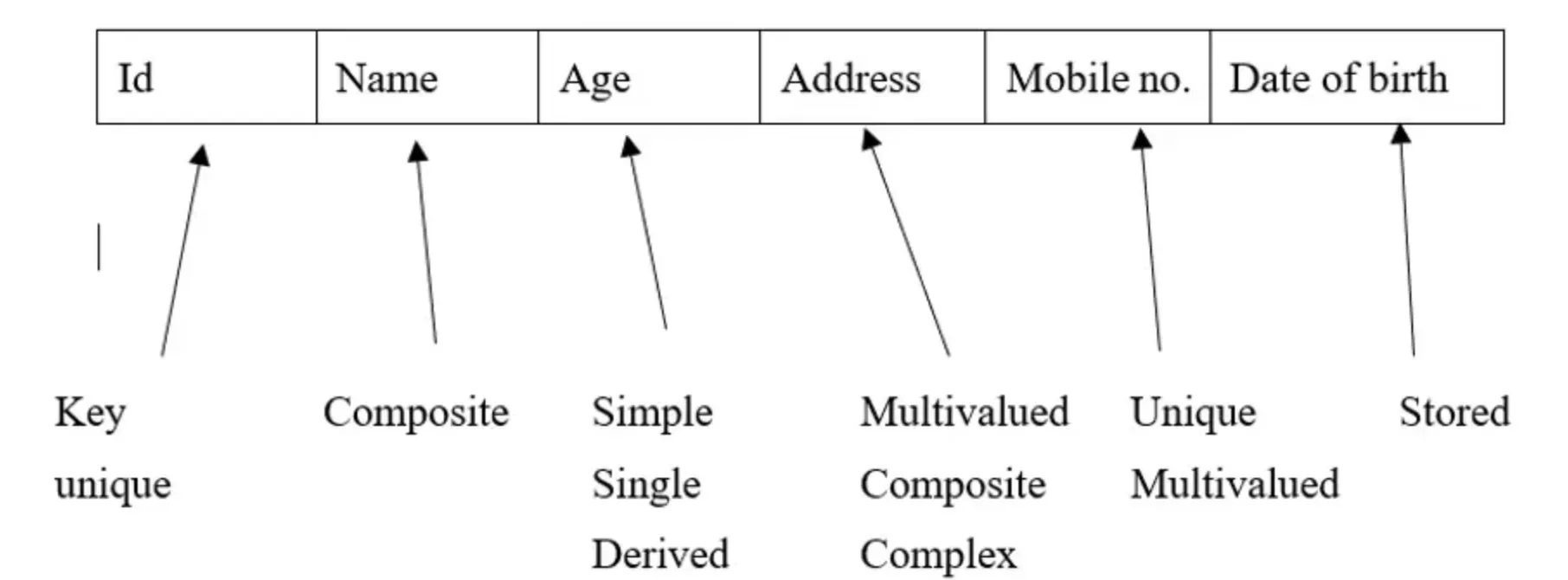
Attributes in Data Models
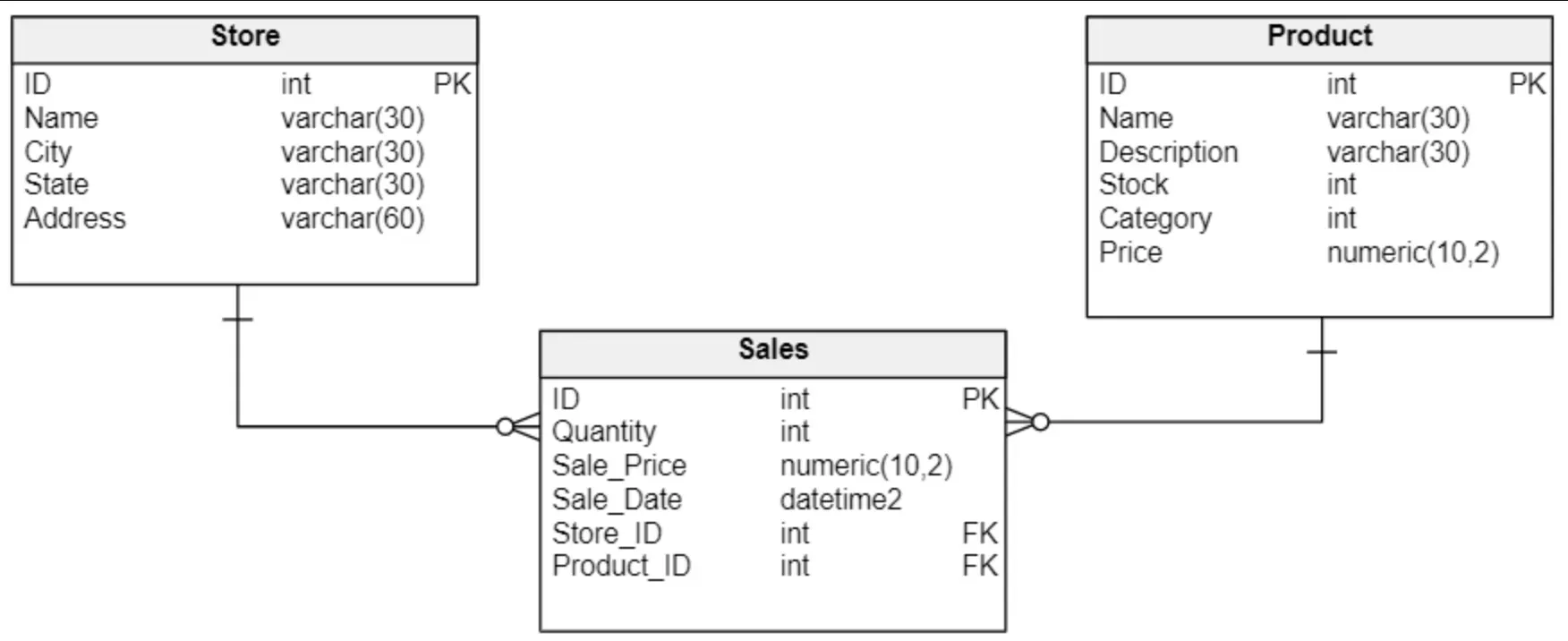
In data modeling, attributes describe the features or characteristics of an entity. For instance, in an employee database, an “Employee” entity might have attributes such as 'Employee ID,' 'Name,' 'Department,' 'Position,' etc.
Enhancement of Attributes
Attributes can be restructured to better meet the requirements of the application or database, making it more efficient and user-friendly.
Attribute Reduction
In some cases, too many attributes can lead to redundancy and complexity. Attribute reduction techniques can be used to eliminate unnecessary attributes, reducing storage needs and processing time.
Normalization
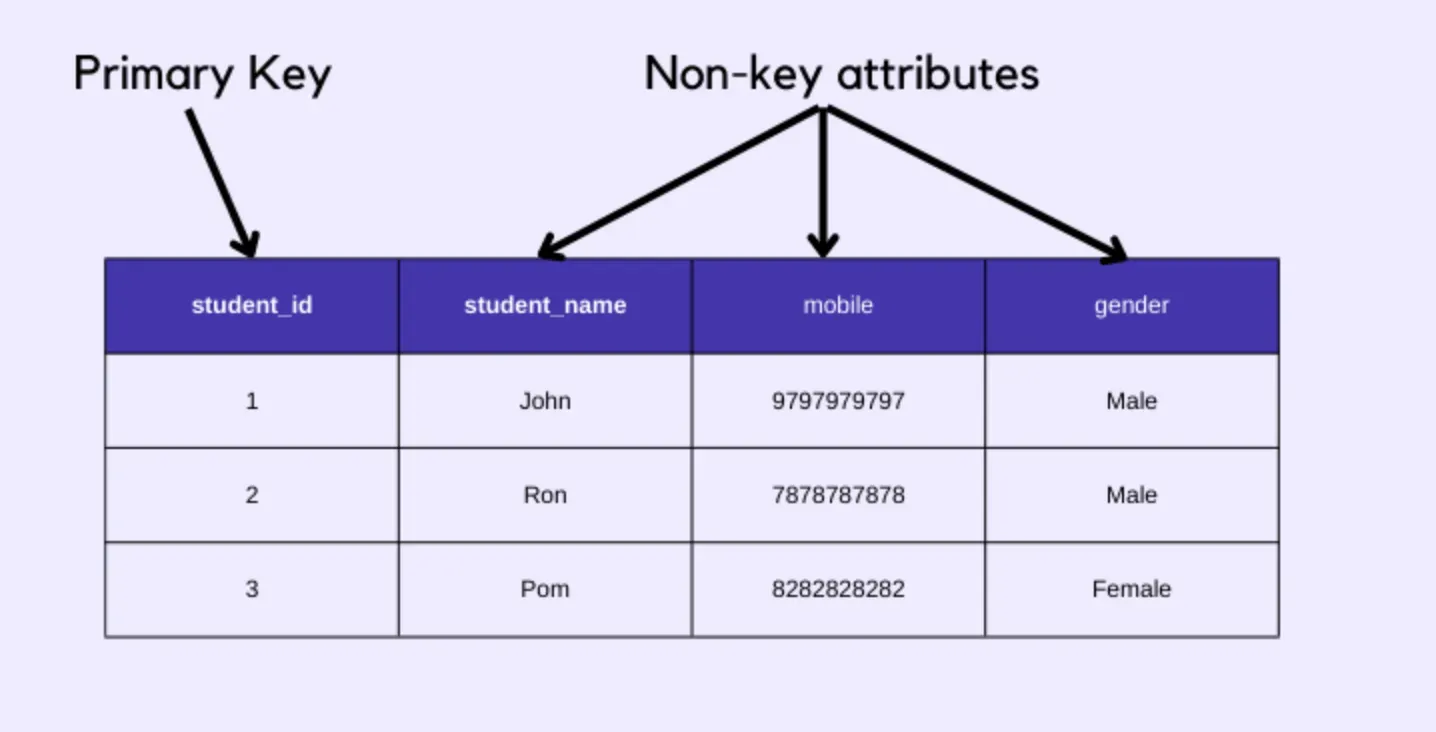
Normalization is a database design technique used to minimize data redundancy and avoid data anomalies. It involves arranging attributes in tables based on their dependencies.
Attribute Encoding
Attribute encoding is the process of transforming the attributes of raw data into a more usable format, especially when dealing with categorical data. Common techniques include one-hot encoding and label encoding.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Is an attribute the same as a property?
In many contexts, 'attribute' and 'property' can be used interchangeably. However, in certain areas like JavaScript, a distinction is made where properties change the object they belong to while attributes do not.
Can an entity or object have multiple attributes?
Yes, an entity or object can have multiple attributes, as long as each attribute represents a different characteristic of that entity or object.
Are all attributes required in HTML?
No, not all attributes are required in HTML. Some like 'src' in an 'img' tag are necessary, while others are optional.
How are attributes used in databases?
In databases, attributes are used to define the characteristics or properties of an entity in a table. They become the columns in the table where specific pieces of data are stored.
Can I add my own attributes to HTML tags?
HTML5 introduced custom 'data' attributes, starting with 'data-' which you can use to embed custom data attributes in all HTML elements.