What is Speech-to-text translation?
Speech-to-text translation, also known as speech recognition, is the process of converting spoken words into written words.
It involves extracting meaning from speech and transcribing it into text.
Who Uses Speech-to-Text Translation?
Speech-to-text translation is used by a wide range of individuals and industries.
This includes professionals needing transcriptions, individuals with hearing impairments, researchers conducting interviews, and companies offering customer support services, among others.
When is Speech-to-Text Translation Used?

Speech-to-text translation can be used whenever there's a need to convert spoken language into text.
This could be during a live presentation, a recorded meeting or interview, a customer service call, or even just to dictate notes and messages.
Where is Speech-to-Text Translation Applied?
From academia to business to personal use, speech-to-text translation is applied in many contexts.
It's found in classroom transcription services, business meeting transcriptions, voice assistants like Siri or Google Assistant, and even in captioning services for TV shows and movies.
Why is Speech-to-Text Translation Important?
Speech-to-text translation bears importance as it facilitates accessibility, aids in data documentation, and enhances efficiency.
It makes information accessible to those with hearing impairments, assists in recording critical details from discussions or presentations, and saves time by reducing manual transcription efforts.
How does Speech-to-Text Translation Work?
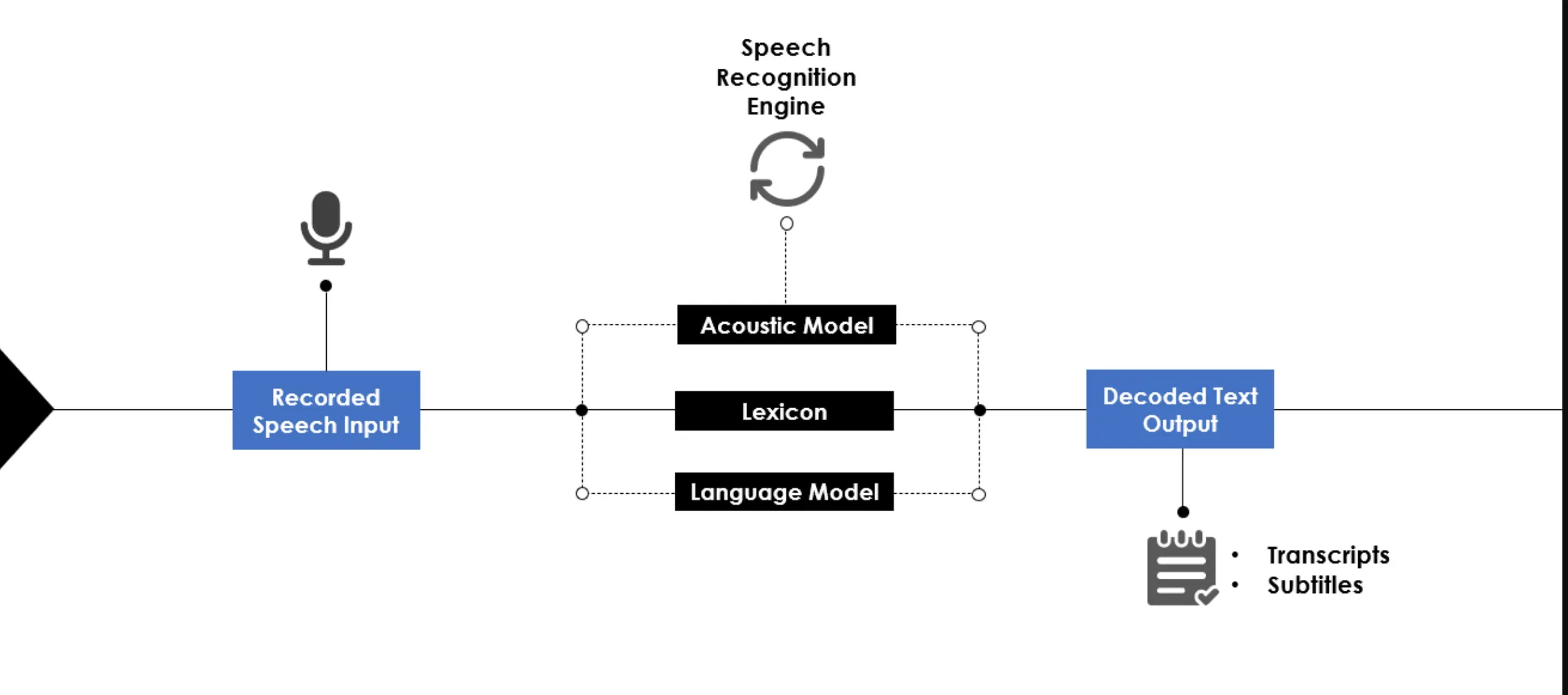
In this section, we'll unravel the inner workings of speech-to-text translation technology, delineating how it converts spoken language into written text with striking accuracy.
Audio Preprocessing
The initial step in speech-to-text translation involves audio preprocessing, where the system filters and normalizes the input audio.
This process helps identify the relevant speech segments and eliminates any background noise or disturbances that may interrupt the translation.
Feature Extraction
Once the audio is preprocessed, feature extraction comes into play.
It focuses on detecting unique speech patterns and phonetic features, such as pitch and frequency, in the audio data.
This simplifies the input, making it recognizable for the system to process further.
Language Modeling
Language modeling is the crux of speech-to-text technology.
At this stage, the system leverages deep learning algorithms, such as recurrent neural networks (RNNs) or transformer models, to analyze the extracted features and predict probable word sequences based on the context.
Decoding
The decoding stage involves employing a process called CTC decoding, which translates the predicted word sequences into continuous, legible text.
This step removes any redundant predictions and reconstructs the text to adhere to proper grammatical and syntactical rules.
Post-Processing
Lastly, post-processing refines the initial translated text further, rectifying errors and taking into account language-specific rules. This final touch ensures the translated text reads smoothly and accurately conveys the original spoken message.
Types of Speech-to-Text Technology
In this section, we'll cover the distinct forms of Speech-to-Text Technology that are shaping how we interact with our devices and platforms.
Automatic speech recognition
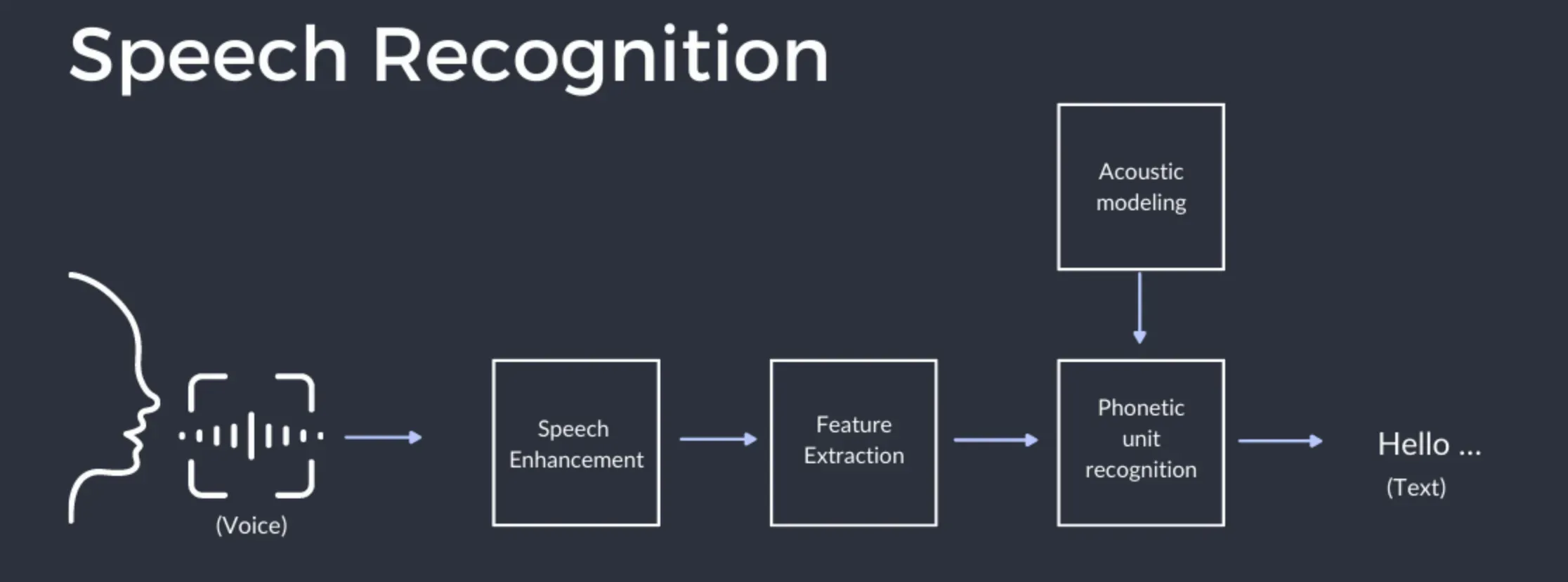
Automatic speech recognition, also known as ASR, is a technology that converts spoken language into written text.
It's used widely, from transcription services to voice assistants like Siri and Alexa. It allows for quick note creation, faster communication, and accessibility for those with certain disabilities.
Suggested Reading: Automated Speech Recognition: Types & Challenges
Digital Assistants
With our phones or smart home devices, we often use Digital Assistants like Siri, Alexa, or Google Assistant, which leverage speech-to-text technology.
These AI-powered assistants understand human speech, making our interactions with machines much more effortless and natural.
Suggested Reading: Digital Assistants: Features & Types
Text-to-speech software

Text-to-speech (TTS) software, while the inverse of speech-to-text technology, is often used into conjunction with it to facilitate complete communication.
This technology operates by converting written text into spoken word, helping those with reading disorders, visual impairment, or those who just want a hands-free digital experience.
Suggested Reading: Text-to-speech: Uses & Privacy
Transcription Services
Specialized transcription services use speech-to-text technology to transcribe live conversations or recorded audio files into text.
These services are of great value in several sectors, including legal, medical, and journalism fields, where accurate transcripts are prerequisites.
Suggested Reading: Speech-to-text Transcription: Types & Applications
Accessibility Features
Speech-to-text technology is embedded in accessibility features in many devices and apps, serving an essential role in supporting those with specific needs.
By converting speech into text, it can assist individuals with hearing impairments and also facilitate communication for those with motor or speech disabilities.
As you can see, the reach of speech-to-text technology is vast. Every day, this tech is bridging gaps, facilitating communication, and breaking down barriers for individuals around the globe.
Advantages of Speech-to-Text Translation

Increase Profits
Speech-to-text translation technology can improve workforce efficiency, allowing employees to spend their time on revenue-generating activities.
Work on the Go
With speech-to-text translator software, you and your team can work efficiently on the go, such as during commuting. Voice typing enables easy note-taking and summarization of meetings.
Improved Accuracy
The best speech-to-text software provides accuracy rates of over 99%, surpassing human transcription. It allows for accurate transcriptions of calls, meetings, and discussions.
Improve Employee Experience
Voice typing promotes employee well-being by enabling flexibility and a healthier work-life balance. It encourages employees to take breaks and work in preferred environments.
Enhance Accessibility
Incorporating speech-to-text translation technology improves accessibility for individuals with disabilities. It provides alternative input methods for those who struggle with conventional typing.
Immediate Digitization
Speech-to-text software enables real-time transcription during meetings, with the ability to distinguish between different speakers. This immediate digitization facilitates easy review and annotation of meeting transcriptions.
Suggested Reading: 5 Ways Woord's Text-to-Speech Tool can save you Time & Money
Applications Of Speech-to-Text Technology

In this section, we'll delve into the various applications of speech-to-text technology, revolutionizing our everyday interactions and professional tasks.
Accessibility and Assistive Tech
One of the pivotal applications of speech-to-text technology lies in the realm of accessibility.
For individuals with hearing impairments or other disabilities, it transforms spoken language into text, thus providing a crucial communication bridge.
Equally, it empowers those with mobility issues to interact with devices more conveniently.
Transcription Services
Transcription services greatly benefit from speech-to-text technology, offering precise and timely results.
Be it for medical, legal, or journalistic purposes, having a reliable technology to convert spoken word into written text can be a real game-changer.
Voice Commands
Responding to a changing landscape of digital user behavior, many companies integrate voice commands into their devices and software.
TVs, mobile phones, and even cars now come equipped with voice recognition capabilities, thanks to speech-to-text technology.
Language Learning and Real-Time Translation
Language learning apps use speech-to-text technology to help learners improve their pronunciation.
Additionally, the technology is pivotal in facilitating real-time translation services, eliminating communication barriers and fostering global connection.
Data Analysis
In the world of big data, text is far easier to analyze than speech.
Speech-to-text technology enables qualitative data collection and sentiment analysis, powering in-depth customer insights and better decision-making.
Suggested Reading: Listnr Tech vs Other Text-to-Speech Tools: The Ultimate Battle
The Limitations of Speech-to-Text Technology
In this section, we'll examine the notable constraints of speech-to-text systems, providing insights into the challenges they face in catering to diverse languages, dialects, and audio environments.
Handling Accents and Dialects
A key limitation of speech-to-text technology lies in decoding accents and dialects.
Speech recognition systems often struggle to accurately process audio from speakers with strong or uncommon accents, which may result in transcription errors and inaccuracies.
Tackling Background Noise
Speech-to-text systems work optimally in noise-free environments.
However, real-world situations often involve background noises that can interfere with speech recognition algorithms, reducing the accuracy and efficiency of transcriptions.
Interpreting Unclear Speech
People often speak with varying speeds, tones, and clarity.
Speech-to-text technology can struggle to transcribe speech that is mumbled, slurred, or delivered at an extremely fast pace, leading to inaccuracies in the converted text.
Grasping Contextual Understanding
Unlike human transcribers, speech-to-text systems may falter in deciphering context and conveying the speaker's intent accurately.
Without an inherent understanding of emotions, sarcasm, or cultural nuances, the technology may misinterpret certain phrases or expressions.
Handling Punctuation and Formatting
Capturing punctuation and formatting elements like capitalization is another challenge faced by speech-to-text technology.
Since these aspects are not explicitly spoken, the system must rely on contextual cues, often resulting in inconsistent and error-prone transcriptions.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What devices can be used for Speech-to-Text?
Speech-to-text software can be used on any device with a microphone, such as smartphones, tablets, laptops, desktops, and smart home devices.
Can Speech-to-Text technology recognize multiple languages?
Yes, advanced speech-to-text technology can recognize and transcribe speech in multiple languages, including regional dialects with high accuracy rates.
What factors can affect the accuracy of Speech-to-Text technology?
Background noise, varying accents, and speaking too fast can negatively impact the accuracy of speech-to-text technology. However, advanced algorithms and machine learning are constantly being developed to improve accuracy.
Is Speech-to-Text technology reliable for transcribing lengthy conversations?
Yes, Speech-to-Text technology offers reliable and accurate transcriptions for lengthy conversations, especially when using advanced cloud-based speech recognition technology.
How secure is Speech-to-Text technology for sensitive information?
Cloud-based Speech-to-Text technology is highly secure through the use of encryption and secure access controls. It is vital to select a reputable service provider with robust privacy policies and data security.