What is Computer Vision?
Computer Vision is a branch of artificial intelligence (AI) aiming to give machines the ability to visually perceive the external world in the same way humans do.
Objective
The objective of Computer Vision is to understand, interpret, and manipulate visual data coming from the real world and transfer that understanding into usable formats such as numbers, categories, or dimensions.
Components
The primary components of Computer Vision include image acquisition, image processing, feature extraction, detection/recognition, and interpretation.
Applications
Computer Vision finds its applications in various fields such as autonomous vehicles, facial recognition systems, image restoration, object tracking, etc.
Principles
The principles of Computer Vision revolve around extracting useful information from the visual data and taking action or making decisions based on that.
Why is Computer Vision Important?
Once we get what computer vision is, the next vital point to understand is its relevance and importance in contemporary tech.
Accurate Data Interpretation
Computer Vision, with its ability to understand and interpret visual data, can provide accurate and precise data interpretation compared to human intervention.
Automated Processes
It helps in automating manual processes by extracting key information from visual data, thus enhancing productivity and efficiency.
Rapid Decision Making
Computer Vision-powered systems can make faster decisions based on real-time visual data interpretation.
Advanced Surveillance
It aids in advanced surveillance by recognizing faces, objects, and patterns, thereby increasing security.
Conquering Challenges
Computer Vision conquers several human-related challenges such as visual impairment, unstructured data, manual errors, etc.
When to Use Computer Vision?
Now that we understand the importance, it's also crucial to determine when the use of Computer Vision could be ideal.
Autonomous Vehicles
In autonomous vehicles, Computer Vision is used for recognizing traffic signs, identifying pedestrians, and avoiding obstacles.
Industrial Inspection
For quality control and defect detection, industries often employ Computer Vision technologies which enhances accuracy and reduces manual effort.
Retail Sector
In the retail sector, Computer Vision can be used for inventory management, customer behavior analysis, and enhancing shopping experiences.
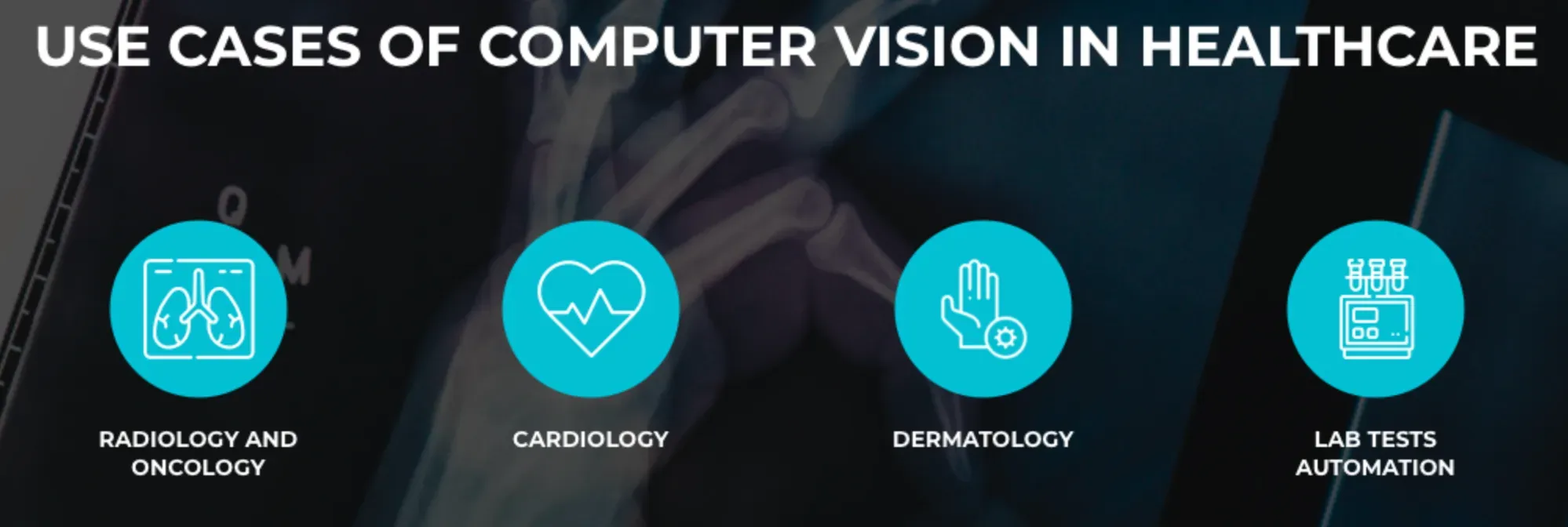
Healthcare
In the healthcare sector, it’s used for disease diagnosis, medical imaging, and monitoring patient’s health conditions closely.
Security and Surveillance
Whether it's facial recognition, intrusion detection, or crowd monitoring, Computer Vision is highly useful in security and surveillance applications.
Where is Computer Vision Used?
Let's dive into some examples of where Computer Vision is currently being utilized.
E-commerce
In E-commerce, it's used for product recommendation, image tagging, and providing personalized shopping experiences.
Autonomous Vehicles
In Autonomous Vehicles, it's utilized for real-time object detection, path planning, and navigation.
Surveillance Systems
In Surveillance Systems, it's applied for crowd management, security checks, and tracking suspicious activities.
Robotics
In Robotics, it's useful in object manipulation, obstacle avoidance, and robot navigation.
Smartphones
In Smartphones, it's deployed for applications like face unlock, augmented reality, and photo editing.
How Does Computer Vision Work?
Understanding the working of Computer Vision can be fascinating. Let’s break it down.
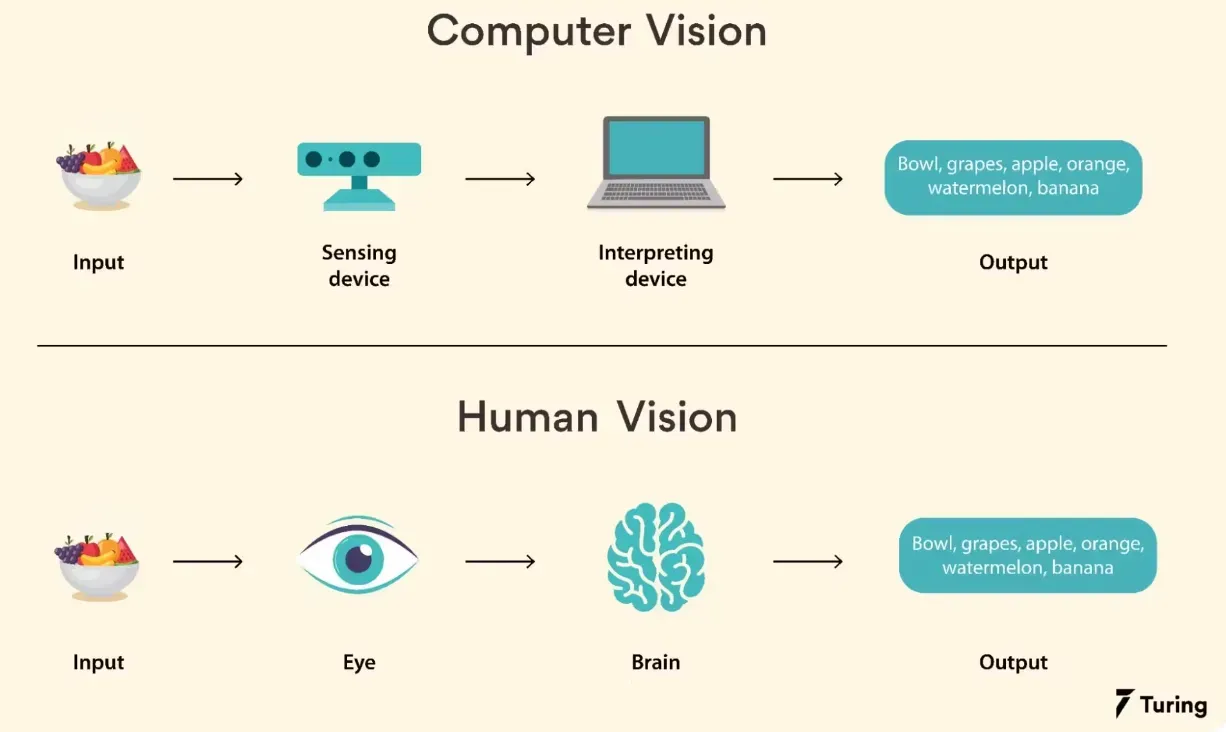
Image Acquisition
The first step is acquiring the image from a camera or other imaging devices.
Preprocessing
The acquired image goes through various preprocessing techniques like filtering, scaling, and color conversion to make it suitable for further processing.
Feature Extraction
Computer Vision algorithms extract relevant features from the preprocessed image, like edges, textures, colors, etc.
Pattern Recognition
The extracted features are classified into various categories using machine learning or deep learning techniques.
Image Interpretation and Understanding
The final step is interpreting and understanding the classified data and using it for decision-making processes.
Suggested Reading:
Boltzmann machine
Challenges in Computer Vision
While Computer Vision has immense potential, there are also many challenges associated with it.
Dealing with Real-World Variations
Handling real-world variations in light, size, orientation, and occlusion is one of the biggest challenges.
High Computational Processing
Computer Vision processes often require high computational power and real-time processing.
Lack of Standardized Datasets
There is a lack of large-scale, standardized datasets for training Computer Vision algorithms.
Suggested Reading:
Machine Vision: Applications and Key Technologies
Ethical and Privacy Concerns
Issues related to data privacy and ethics also pose significant challenges.
Applicability and Generalization
Another challenge is developing Computer Vision systems that are applicable and can generalize well to a variety of scenes and environments.
Trends in Computer Vision
Let's explore some of the key trends in the field of Computer Vision.
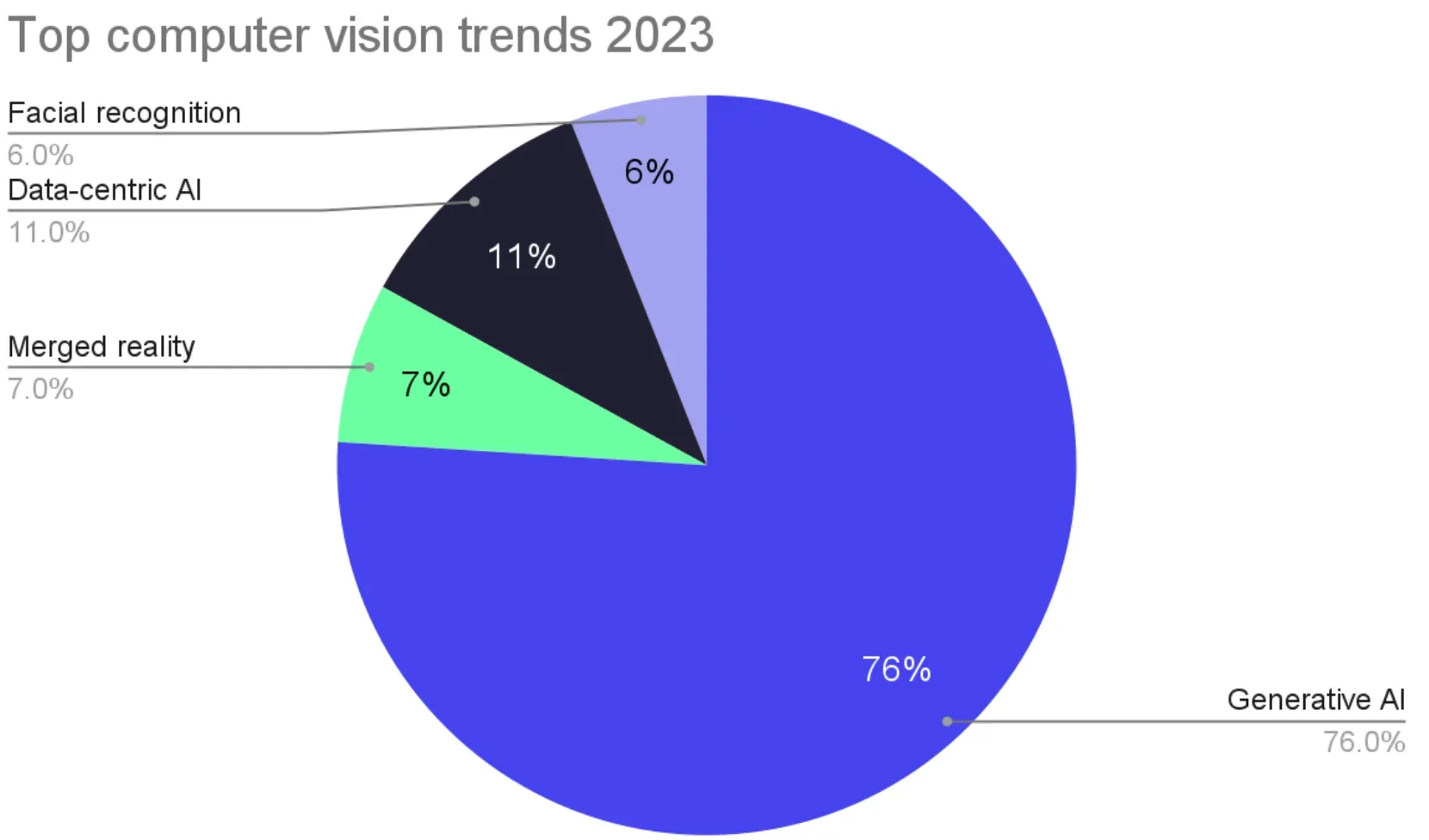
Integration with AI and ML
AI and ML algorithms are increasingly being integrated with Computer Vision for enhancing capabilities.
Rise of 3D Computer Vision
3D Computer Vision techniques, which can understand depth and perspective, are on the rise.
Use in Biometrics
Computer Vision is becoming a key component in biometric technologies like facial recognition and fingerprint scanning.
Edge AI
The trend of moving AI computations to edge devices, enabling real-time decision-making, is gaining momentum in Computer Vision.
Computer Vision as a Service (CVaaS)
More organizations are offering Computer Vision as a Service (CVaaS) platforms, making the technology more accessible.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
How does computer vision interpret images?
Computer vision algorithms process and interpret visual data from the world, translating images and videos into descriptions, identifications, or categorizations, much like how human vision works.
What role does ai play in computer vision?
AI enables computer vision systems to learn from vast amounts of visual data, improving their ability to recognize patterns and make decisions based on what they "see."
Can computer vision systems surpass human vision?
In some tasks, like analyzing vast quantities of images quickly or identifying subtle patterns not easily visible to the human eye, computer vision systems can outperform human vision.
How is computer vision applied in healthcare?
It's employed in diagnosing diseases from medical imagery, like X-rays or MRIs, enhancing accuracy and speed in spotting abnormalities or changes over time.
What challenges does computer vision face?
Key challenges include understanding context, dealing with varied light conditions or occlusions, and requiring substantial computational power for processing and analysis.

