What is Image Processing?
Image processing involves changing an image in some way. This could be simply changing the entire image to grayscale or adjusting the color balance of an image.
More complex tasks might involve complex transformations, such as face recognition or object detection.
Significance
The importance of image processing lies in its versatile applications. From medicine to space exploration, robotics to social media platforms, image processing is pushing barriers and unraveling novel perspectives.
Difference from Computer Vision
While both involve the analysis and manipulation of images, image processing focuses on modifying images to produce a new one.
Computer vision, on the other hand, aims to understand or extract information from the images.
Categories
Image processing falls into two categories: analog and digital.
Analog processes involve the physical alteration of an image, while digital processes use computer algorithms to change an image digitally.
Why is Image Processing Used?
Let's now delve into the reasons behind the widespread use of image processing today. You'll find it to be a truly indispensable tool in various domains.
Medical Imaging
In healthcare, image processing is often used in medical imaging techniques like MRIs and CAT scans to improve image clarity and uncover hidden details.
Satellite Imagery
Satellite images, fraught with noise and distortions, are processed to provide clearer images and more accurate information about our world.
Image Restoration
It's used in restoring old or damaged photos, using various techniques to remove noise, scratches, and other blemishes.
Machine Learning
ML and AI heavily rely on image processing in tasks such as facial recognition, object detection, and other complex tasks.
Autonomous Vehicles
Self-driving cars leverage image processing to recognize traffic signs, detect obstacles, and understand the driving environment.
When is Image Processing Applied?
The application of image processing is a broad territory, covering an incredible array of industries and research areas, let's dive into a few crucial ones.
Biomedical Imaging
Biomedical imaging relies on image processing to enhance images for better diagnosis and study of diseases, helping medical professionals make informed decisions.
Self-Driving Technology
When an autonomous vehicle needs to interpret its environment, image processing comes to the rescue, recognizing traffic signs, obstacles, and more.
Remote Sensing
In remote sensing or satellite imaging, image processing is applied to enhance image quality, correct distortions, and extract useful information.
Video Surveillance
Video surveillance systems use image processing to highlight events, detect motion, identify objects, and provide high-quality surveillance footage.
Augmented and Virtual Reality
Image processing becomes indispensable to provide realistic experiences in VR/AR, simulating lighting conditions, depth perception, and object visualizations.
Who uses Image Processing?
As we'll see now, image processing is the unseen hero, working under layers in industries we might not have thought of.
Healthcare Professionals
Doctors, researchers, and healthcare professionals use image processing when diagnosing diseases, researching medical conditions, or planning surgeries.
Geographers and Environmental Scientists
These scientists use image processing in studying physical landscapes, tracking environmental changes, and monitoring natural disasters.
Photographers and Designers
Professional photographers and designers often use image processing in editing and enhancing photographs, ensuring they get the best possible end result.
Autonomous Vehicle Engineers
Engineers of self-driving vehicles leverage image processing algorithms to design autonomous systems that can safely navigate and interpret complex environments.
Security Personnel
Security and surveillance devices employ image processing for face recognition, object tracking, and detecting suspicious activities.
How does Image Processing work?
Time to roll up our sleeves and delve into the workings of image processing. At this stage, it's like lifting the hood and understanding the mechanics beneath it.
Image Acquisition
This is the first stage where you capture or obtain the digital image to be processed.
Image Enhancement
Image enhancement techniques improve the appearance or emphasize certain features of an image.
Image Restoration
Image restoration is a process of recovering an original image that has been degraded by noise or other factors.
Color Image Processing
This involves the manipulation of colored images to enhance visual perception, object recognition, or other visual tasks.
Image Compression
Image compression reduces the storage necessary for an image or the bandwidth needed to transmit it.
Understanding Key Image Processing Concepts
Getting familiar with essential concepts gives you a strong footing in image processing. Let’s dive into them now.
Pixels
Pixels are the smallest element of an image, each with their own set of color values.
Resolution
Resolution refers to the amount of detail an image can hold. The higher the resolution, the more detail in the image.
Histogram
A histogram represents the distribution of colors (intensity levels) in an image and is often used for contrast adjustment or equalization.
Image Filters
Filters are used to enhance the image or remove unwanted details or noise. These can range from simple blur filters to complex edge detection filters.
Image Transformations
Image transformations change an image in a non-linear or geometric way, such as rotating, scaling, or translating the image.
Best Practices in Image Processing
Understanding best practices in image processing can enable efficient and optimal image analysis. Let's uncover a few of them.
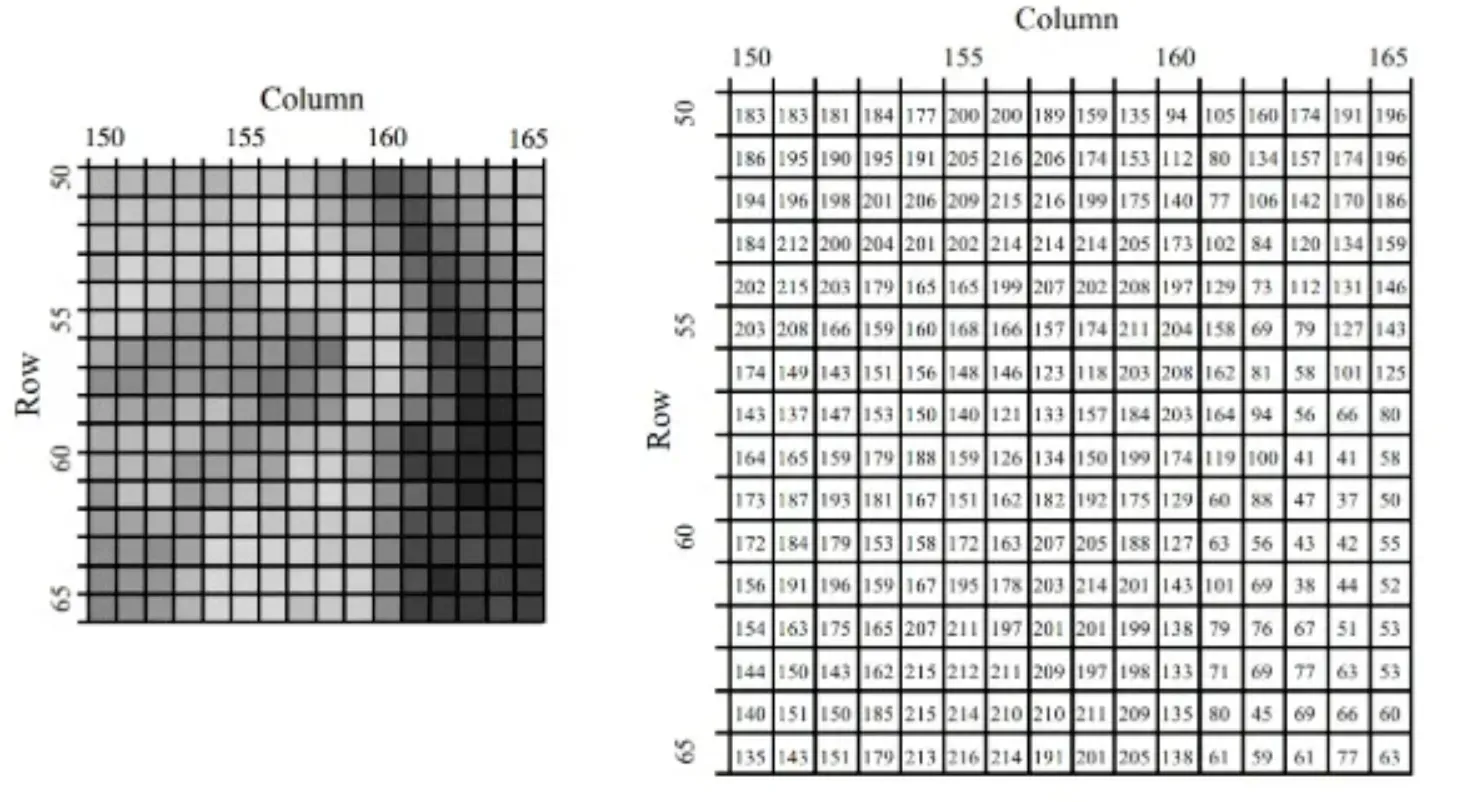
Noise Reduction
Noise reduction should be a preliminary step in many cases, as noise can interfere with the analysis.
Appropriate Filtering
Choosing the right filter can dramatically affect results. It's essential to understand the effect of each type of filter.
Histogram Equalization
Using histogram equalization can improve the contrast of an image, which can aid in analysis.
Proper Image Compression
Understanding the trade-off between quality and size when compressing an image, and choosing the right level of compression is important.
Continuous Learning
The field of image processing is rapidly evolving. It's important to stay informed about the latest techniques, algorithms, and applications.
Challenges in Image Processing
Despite its promise, image processing isn't without its share of hurdles. Let's treat them as catalysts for evolution and betterment.
High Computational Cost
Complex image processing algorithms often come with high computational costs, making real-time applications challenging.
Quality and Resolution Constraints
Due to hardware limitations or transmission constraints, sometimes images are available at a low resolution, which can hinder detailed analysis.
Dependence on Lighting Conditions
Images are captured under varying lighting conditions, and this can significantly impact the outcome of image processing activities.
Handling of Colored Images
Processing colored images is more complex than grayscale ones, as they have multiple color channels and richer information.
Coping with Noise
Image noise can interfere with processing algorithms, and removing or reducing it without impacting important image details can be a significant challenge.
Trends and Future Directions in Image Processing
As we wind up, let’s look at emerging trends that are steering image processing into the future.
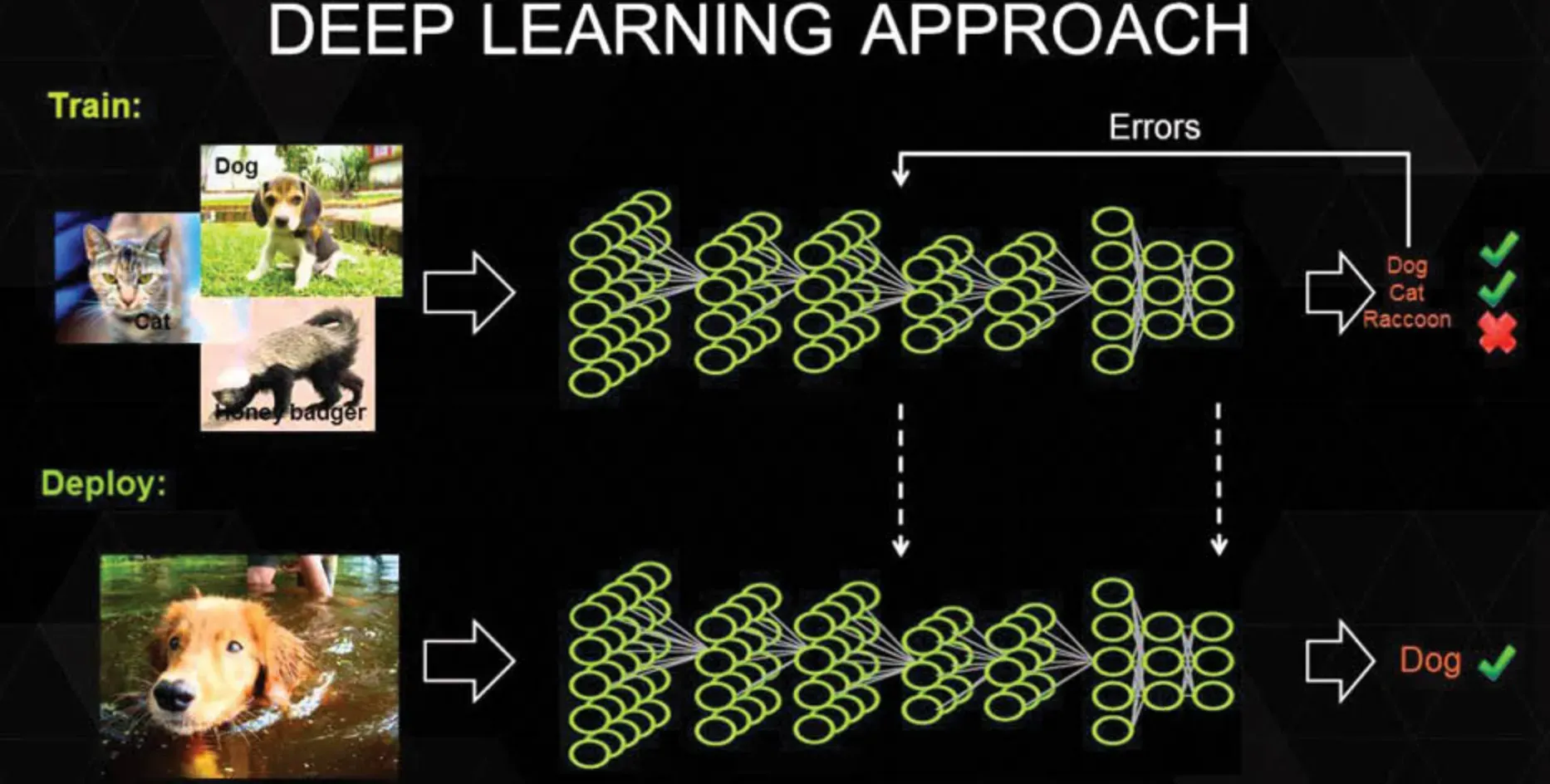
Deep Learning
Deep learning methods, which have achieved significant success in image processing tasks, are becoming more prominent and widespread.
Real-Time Processing
With the increased processing power of modern computers, real-time image processing, even for complex tasks, is becoming feasible and commonplace.
Multi-Image Processing
Processing and interpreting multiple images together, such as sequences of images from videos, are growing in popularity.
Quantum Image Processing
Quantum computers are expected to revolutionize image processing, offering a new frontier for research and applications.
Privacy-Preserving Image Processing
As privacy concerns mount in today’s digital world, the development of privacy-preserving image processing techniques is a vital and emerging field.
Closing up, our journey through the Image Processing glossary illuminates that it's not just a field of modern technology. It's an amalgamation of creativity, logic, science, and information.
Image processing is seeing more innovative applications and deeper impact areas; watch out, this fascinating technology is painting the future manifold with its vibrant palette!
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
How Can Histograms Benefit Image Processing?
Histograms provide valuable insights into an image's overall brightness distribution and contrast, influencing tasks such as histogram equalization for improved image contrast.
How Does Image Segmentation Enhance Image Processing?
Segmentation partitions an image into multiple segments, allowing for detailed analysis and object recognition within these individual segments.
Can Image Processing Be Applied to Real-Time Applications?
Yes, real-time image processing, such as in autonomous vehicles and video surveillance, involves analyzing and processing images as they are captured.
What Is the Role of Filtering in Image Processing?
Filters help in noise reduction, edge detection, and sharpening, crucial for enhancing or modifying an image's characteristics.
Does Image Compression Affect Image Processing?
Image compression can reduce storage requirements and transmission time. However, excessive compression may lead to information loss, affecting subsequent image processing tasks.


