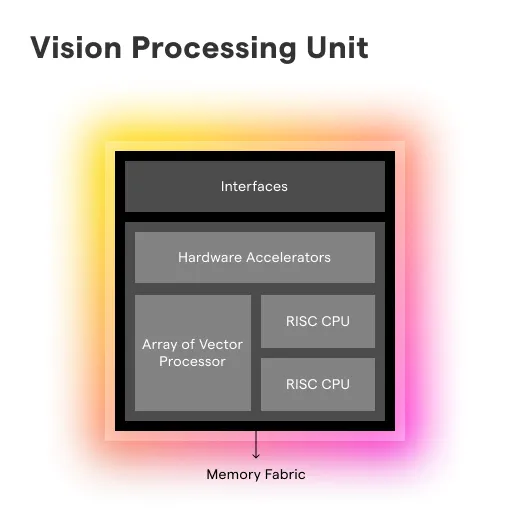
What is a Vision Processing Unit (VPU)?

A Vision Processing Unit, or VPU for short, is a specialized hardware component designed to accelerate the processing of computer vision and artificial intelligence tasks.
It's like a super-smart sidekick to the main processor, specifically engineered to handle the heavy lifting of image and video data analysis.
The purpose of a VPU is to enable devices to quickly process, analyze, and make decisions based on visual inputs, making our gadgets smarter and more efficient.
An Example of a VPU in Use
A VPU shines when deployed in real-time vision applications. For instance, self-driving vehicles employ VPUs to detect objects, navigate routes, and ensure the vehicle's overall safety.
How Does a Vision Processing Unit Work?
Specialized Hardware Architecture
A Vision Processing Unit (VPU) features a specialized hardware architecture optimized for computer vision tasks. This architecture includes dedicated processing elements, memory, and data paths designed to accelerate image processing, object detection, and machine learning algorithms.
Parallel Processing Capabilities
VPUs are designed to handle multiple tasks simultaneously, leveraging parallel processing capabilities to efficiently execute computer vision algorithms. This parallelism allows VPUs to process large amounts of visual data quickly, reducing latency and improving overall performance.
Integration with AI Frameworks
VPUs are compatible with popular AI frameworks like TensorFlow and OpenCV, enabling developers to use existing tools and libraries for computer vision applications. This compatibility simplifies the development process and supports seamless integration of VPU-powered solutions into existing systems.
On-Device Processing
VPUs enable on-device processing of visual data, reducing the need for data transmission to external servers. This approach offers several benefits, including lower latency, improved privacy, and reduced reliance on network connectivity, making it suitable for real-time applications and edge computing.
Adaptable Performance
VPUs are designed to adapt their performance to the specific requirements of the application, balancing processing power, energy consumption, and heat generation. This adaptability allows VPUs to deliver optimal performance in various scenarios, from low-power IoT devices to high-performance robotics and autonomous systems.
VPU vs. GPU vs. CPU: Comparing Processing Units
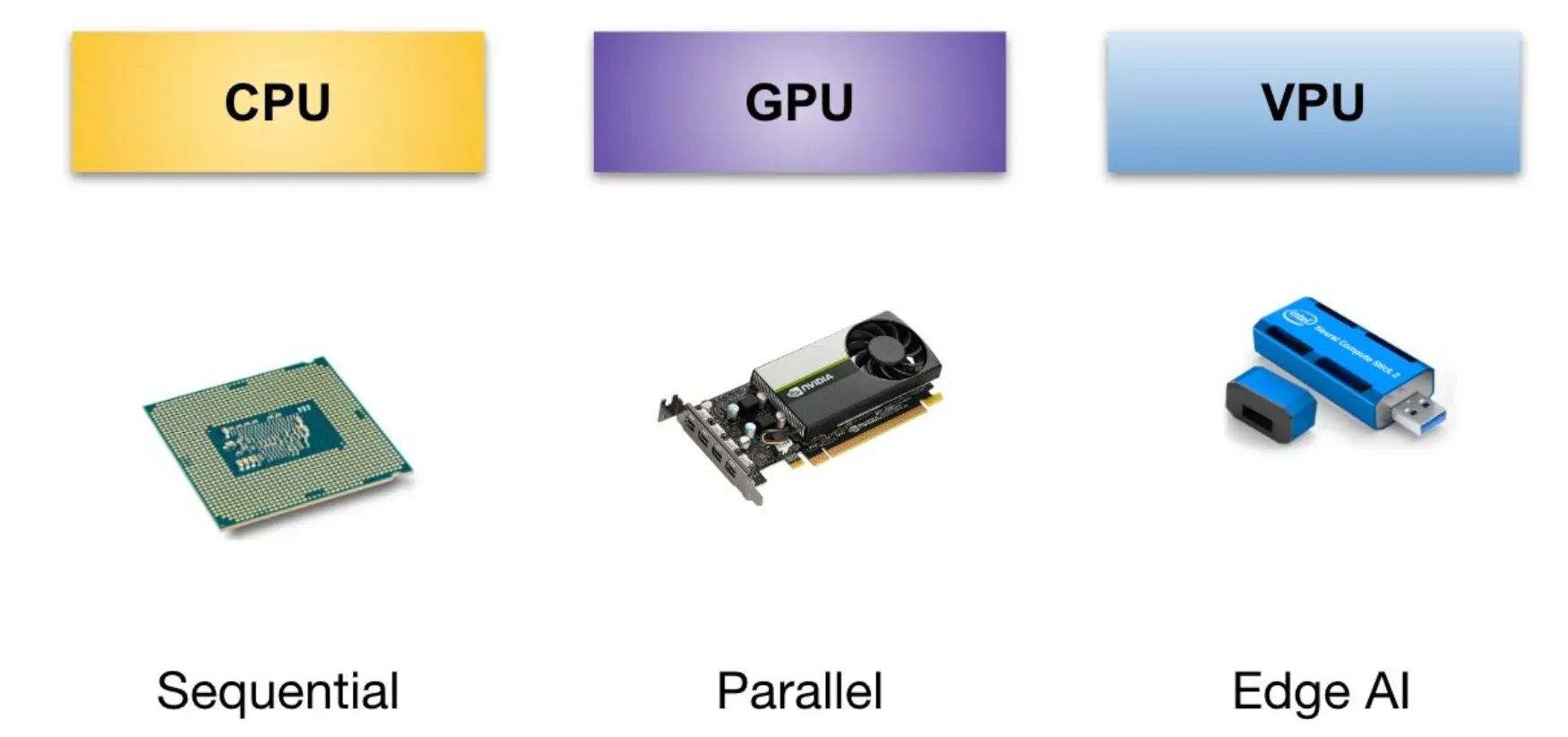
VPUs are custom-built for computer vision and AI tasks. They excel at analyzing visual data and are optimized for energy efficiency and low-latency processing.
GPUs (Graphics Processing Units) are designed for rendering graphics, making them great at parallel processing. While they can handle some AI and computer vision tasks, they're not as specialized as VPUs.
CPUs (Central Processing Units) are the generals of the processing world, capable of executing a wide range of tasks. However, they're not as adept at handling specialized AI and computer vision workloads as VPUs or GPUs.
In short, VPUs are the best choice for vision-centric applications, while GPUs and CPUs have their own strengths in other areas.
When to Use a Vision Processing Unit?
Applications in Robotics and Drones
With their ability to quickly process and analyze visual data, these high-flying devices can navigate their surroundings, recognize objects, and even avoid obstacles with ease. By equipping them with VPUs, we're essentially giving them a set of super-smart eyes to help them see and understand the world around them.
Use Cases in the Automotive Industry
From advanced driver assistance systems (ADAS) to fully autonomous vehicles, VPUs play a crucial role in enabling cars to "see" and make decisions based on visual inputs. They help power features like lane departure warnings, pedestrian detection, and traffic sign recognition, making our rides safer and smarter.
Integration in Smart Cameras and IoT Devices
VPUs are making their mark in the world of smart cameras and Internet of Things (IoT) devices. By integrating VPUs into these gadgets, we're giving them the power of computer vision, enabling features like facial recognition, motion detection, and even smart home automation. It's like upgrading your everyday devices with a pair of intelligent glasses that let them see and understand the world just like we do.
Autonomous Vehicles
VPUs help in the proper functioning of Advanced Driver Assistance Systems (ADAS) by processing road, traffic, and environment data in real-time.
Surveillance Systems
VPUs are used in smart security cameras for facial recognition, activity detection, and threat analysis. They deliver exceptional performance where real-time processing is a must.
Medical and Healthcare Settings
VPUs are in demand in the healthcare sector for applications such as image-based diagnosis, patient monitoring, and even in robotic surgeries.
Retail
VPUs aid in customer recognition, optimizing inventory management, and enhancing customer experience in AI-driven stores. Imagine a store where you can grab what you want and just walk out, with the billing taken care of automatically – that's made possible by VPUs.
Who Benefits from Vision Processing Units?
Robotics and Automation Industry
VPUs enable real-time computer vision capabilities in robotics and automation systems, allowing them to perceive and interact with their environment more efficiently. This improves the performance of tasks like object recognition, navigation, and manipulation.
Automotive and Autonomous Vehicles
The automotive industry benefits from VPUs in the development of advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS) and autonomous vehicles. VPUs provide real-time processing of visual data, enabling features like lane detection, pedestrian recognition, and traffic sign recognition.
Consumer Electronics
VPUs enhance the capabilities of consumer electronics by enabling advanced computer vision features in smartphones, cameras, and wearable devices. This includes applications like facial recognition, augmented reality, and gesture control, improving the overall user experience.
Surveillance and Security
VPUs are used in surveillance and security systems to enable real-time video analytics, such as object tracking, motion detection, and behavior analysis. This improves the effectiveness of security measures and allows for more efficient monitoring and response to incidents.
Healthcare and Medical Imaging
The healthcare industry benefits from VPUs in medical imaging and diagnostic applications, where real-time processing of visual data is crucial. VPUs enable faster and more accurate analysis of medical images, assisting in early detection and diagnosis of diseases and conditions.
Advantages of Vision Processing Units
Enhanced Computer Vision Performance
Vision Processing Units (VPUs) are specifically designed to handle computer vision tasks, resulting in significantly improved performance compared to traditional CPUs and GPUs. This enables faster and more accurate image recognition, object detection, and video processing.
Power Efficiency
VPUs are highly optimized for computer vision tasks, consuming less power than general-purpose processors. This makes them ideal for battery-powered devices and applications where energy efficiency is crucial, such as drones, wearable devices, and IoT systems.
Real-Time Processing Capabilities
The specialized architecture of VPUs allows for real-time processing of visual data, enabling applications to react instantly to changes in the environment. This is particularly important for autonomous systems, robotics, and augmented reality applications, where low-latency processing is essential.
Scalability and Flexibility
VPUs are available in various form factors and performance levels, making them suitable for a wide range of applications. This allows developers and manufacturers to choose the most appropriate VPU for their specific requirements, balancing performance, power consumption, and cost.
Compatibility with AI Frameworks
VPUs typically support popular AI frameworks like TensorFlow and OpenCV, allowing developers to leverage existing tools and libraries for computer vision applications. This simplifies the development process and enables faster deployment of AI-powered solutions.
Challenges and Limitations of Vision Processing Units
Power Consumption
A major challenge for Vision Processing Units (VPUs) is power consumption. Since they process large amounts of visual data, they need considerable energy, which can be a limitation for battery-powered devices like smartphones and drones. Balancing performance and energy efficiency is crucial.
Latency
Latency is another significant challenge for VPUs. In real-time applications, such as autonomous vehicles or robotics, quick and efficient visual data processing is essential. Minimizing latency and enhancing real-time performance requires ongoing improvements to algorithms and hardware architectures.
Cost and Scalability
Developing and producing VPUs can be expensive, making it difficult for smaller companies to compete with established players. As demand for more sophisticated vision processing capabilities grows, scalable solutions become essential. VPU designers must find ways to reduce costs and create modular systems that can be easily upgraded or adapted.
Handling Complex Environments
VPUs often process visual data in complex environments like crowded city streets or busy factory floors. Accurately identifying and tracking multiple objects, even when partially obscured or moving quickly, is challenging. VPU developers must refine algorithms and train systems on diverse datasets to improve handling of real-world scenarios.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is the main role of a Vision Processing Unit (VPU)?
A VPU's core function is to process and analyze visual data rapidly and efficiently. It plays a paramount role in applications requiring real-time image or video analysis.
Why is a VPU important in artificial intelligence?
VPUs are vital to AI because they accelerate the processing of visual data, crucial for applications such as image recognition, object detection, and real-time video analysis.
Can VPUs be used in edge computing devices?
Yes, owing to their compact size and power-efficient design, VPUs are ideal for edge computing devices like drones, security cameras, and autonomous vehicles.
How does a VPU improve the performance of a device?
Through accelerated processing and efficient energy use, a VPU can dramatically improve a device's ability to handle complex visual data algorithms, leading to better overall device performance.
What's the difference between a VPU and a GPU?
While both can process image and video data, a VPU is specifically designed for machine vision tasks and is typically more efficient and power-conservative than a GPU.