Introduction
Machine vision is watching you. Yes, that’s right. Everywhere you go, there are eyes—robotic eyes—tracking your every move. From the cameras on street corners to the ones in your smartphone, machine vision technology is omnipresent. Why is this happening? How do these systems work? This guide will demystify the world of machine vision.
What is Machine Vision?
Machine vision is a technology that enables machines to interpret and process visual information from the surrounding environment. It involves the use of cameras, image processing software, and hardware to capture, analyze, and understand images or videos. Machine vision is widely used in industrial automation for quality control, inspection, and robot guidance. By mimicking human visual capabilities, it allows for precise and efficient monitoring and decision-making.
Applications of Machine Vision
Machine vision is revolutionizing various industries. Its ability to analyze and interpret visual data is unparalleled. From ensuring product quality to enhancing safety, machine vision lighting is becoming indispensable. Below, we explore some key applications.
Manufacturing and Quality Control
Machine vision AI systems ensure that products meet exact specifications. In electronics, these systems check circuit boards for defects, ensuring reliability. They can detect flaws invisible to the human eye, increasing production efficiency and reducing waste.
Agriculture and Food Inspection
In agriculture, machine vision lighting helps monitor crop health. It identifies diseased plants early, preventing widespread damage. In food inspection, it sorts fruits and vegetables, ensuring only quality produce reaches consumers. This reduces waste and enhances food safety.
Healthcare and Medical Imaging
Machine vision AI aids in medical imaging by providing detailed scans of internal organs. In radiology, it helps doctors detect tumors and other anomalies. It also assists in surgeries by guiding robotic arms, increasing precision and reducing human error.
Automotive and Transportation

In automotive manufacturing, machine vision lighting systems inspect parts for defects, ensuring vehicle safety. They also assist in driverless cars by interpreting road signs and detecting obstacles, enhancing the safety and efficiency of transportation.
Retail and Consumer Goods
Machine vision AI enhances the retail experience. In stores, it monitors inventory levels and provides data for better stock management. It also improves security by recognizing suspicious activities, ensuring a safer shopping environment.
Suggested Reading: Retail Marketing
How Machine Vision Works
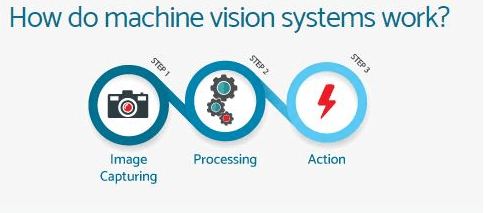
Understanding how machine vision works can seem complex, but it boils down to a few key processes. These systems rely on a combination of image acquisition, processing, and analysis to function. Let’s break down these steps.
Image Acquisition and Processing
Machine vision AI starts with image acquisition. Cameras capture images of the object or scene. In a factory, this could mean snapping photos of products on a conveyor belt. These images are then processed to enhance clarity, adjust contrast, and filter out noise. This preparation ensures the system can accurately analyze the images.
Role of Cameras and Sensors
Cameras and sensors are the eyes of machine vision lighting systems. High-resolution cameras capture detailed images, while sensors detect specific features. In agriculture, sensors can measure the color and texture of crops to assess ripeness. These tools provide the raw data needed for accurate image analysis.
Image Analysis and Interpretation
The final step is image analysis and interpretation. Algorithms analyze the processed images to identify patterns and features. In healthcare, this might involve detecting irregularities in medical scans. The system interprets these findings, providing actionable insights. This allows industries to make informed decisions based on visual data.
Key Technologies in Machine Vision
Machine vision relies on several key technologies to function effectively. These technologies include different types of cameras, lighting techniques, image processing algorithms, and the integration of machine learning and AI. Here’s a closer look at each.
Types of Cameras

CCD (Charge-Coupled Device) cameras are known for high-quality images. They are used in environments where image clarity is critical, such as inspecting semiconductor wafers. CMOS (Complementary Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor) cameras, on the other hand, are faster and more energy-efficient. Thus it makes them ideal for real-time applications like quality control in manufacturing.
Lighting Techniques
Proper machine vision lighting is crucial. Techniques like backlighting and structured lighting help reveal details that are not visible under normal conditions. In automotive inspection, backlighting can highlight scratches on a surface, ensuring only flawless parts are used.
Image Processing Algorithms
Image processing algorithms are the brains behind machine vision. These algorithms enhance images, detect edges, and identify patterns. In retail, these algorithms can analyze shelf images to ensure products are correctly placed and stocked, improving inventory management.
Machine Learning and AI in Machine Vision
Machine learning and AI are transforming machine vision. They enable systems to learn from data and improve over time. In healthcare, AI-powered machine vision can analyze thousands of X-rays to detect early signs of diseases, providing faster and more accurate diagnoses.
Benefits of Machine Vision
Machine vision offers numerous advantages across various industries. These benefits include increased efficiency, improved accuracy, enhanced quality control, and significant cost savings. Let’s explore these in detail.
Increased Efficiency and Productivity

Machine vision systems operate tirelessly and rapidly, unlike human inspectors. In manufacturing, these systems can inspect thousands of parts per minute, identifying defects instantly. This speed boosts overall productivity and keeps production lines running smoothly.
Improved Accuracy and Precision
The precision of machine vision AI systems far exceeds that of human inspection. In the pharmaceutical industry, these systems ensure that each pill is correctly shaped and sized, reducing the risk of defective products reaching consumers. This high level of accuracy minimizes errors.
Enhanced Quality Control
Quality control is a primary benefit of machine vision. In the food industry, these systems can sort and grade fruits, ensuring only the best quality products are packaged. This not only enhances product quality but also increases customer satisfaction.
Cost Savings and ROI
While the initial investment in machine vision may seem high, the long-term savings are substantial. By reducing waste and rework, these systems lower production costs. In electronics manufacturing, detecting and correcting defects early can save millions. The return on investment (ROI) is quickly realized through these ongoing savings.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
How does machine vision work?
Machine vision uses cameras, sensors, and algorithms to capture, analyze, and interpret visual information, enabling automated decision-making and process control.
What are the applications of machine vision?
Applications include quality inspection, object recognition, robotics guidance, barcode reading, and facial recognition.
What are the benefits of machine vision in manufacturing?
Benefits include improved quality control, increased production efficiency, reduced human error, and enhanced product consistency.
How is machine vision different from computer vision?
Machine vision is typically used for industrial applications with a focus on automation, while computer vision encompasses a broader range of image processing and analysis tasks.
What industries commonly use machine vision?
Industries such as manufacturing, automotive, electronics, pharmaceuticals, and food and beverage frequently use machine vision for various automation and inspection processes.
