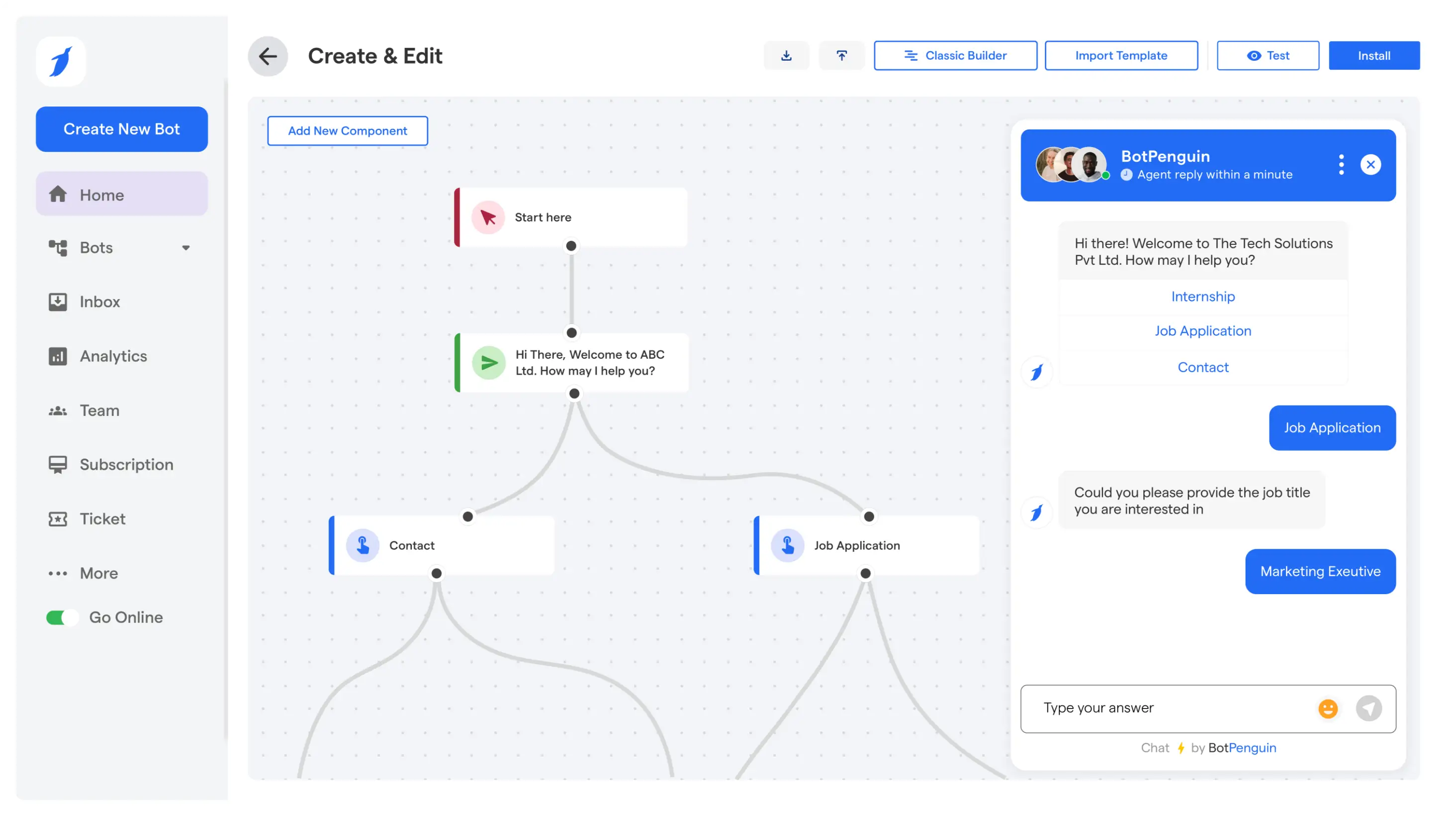
Most businesses believe they are communicating well, but customers often feel ignored or unheard. Messages go out on time, yet replies come late, lack context, or lead nowhere.
Poor tools do not cause this gap, but outdated communication models that treat every message as a one-time event.
That is where conversational messaging changes the game. It replaces isolated messages with continuous, two-way conversations that carry context forward.
This guide explains what conversational messaging really means, how it works in real business scenarios, and why modern teams are moving away from emails, tickets, and one-way notifications.
What is Conversational Messaging
Traditional communication fails when every message is treated as a fresh request.
Customers repeat details. Teams lose context. Response quality drops over time. To fix this, businesses need a model that supports continuity, not isolated replies. That model is conversational messaging.
Conversational messaging is a communication approach in which businesses and customers engage in ongoing, two-way exchanges, with conversation history and context preserved, enabling real-time or near-real-time interactions rather than isolated, one-time messages.
This means every message builds on the previous one. Context carries forward automatically. When a customer follows up, the business sees the full interaction history. Responses stay accurate and relevant.
For example, a customer asks about pricing, returns later with a setup question, and then requests support. All messages stay in one conversation. Nothing resets. The interaction feels informed, not fragmented.
Conversational messaging keeps all customer interactions connected so communication remains continuous, contextual, and responsive.
By preserving context across messages, this approach sets the foundation for faster responses and better experiences.
How Conversational Messaging Works
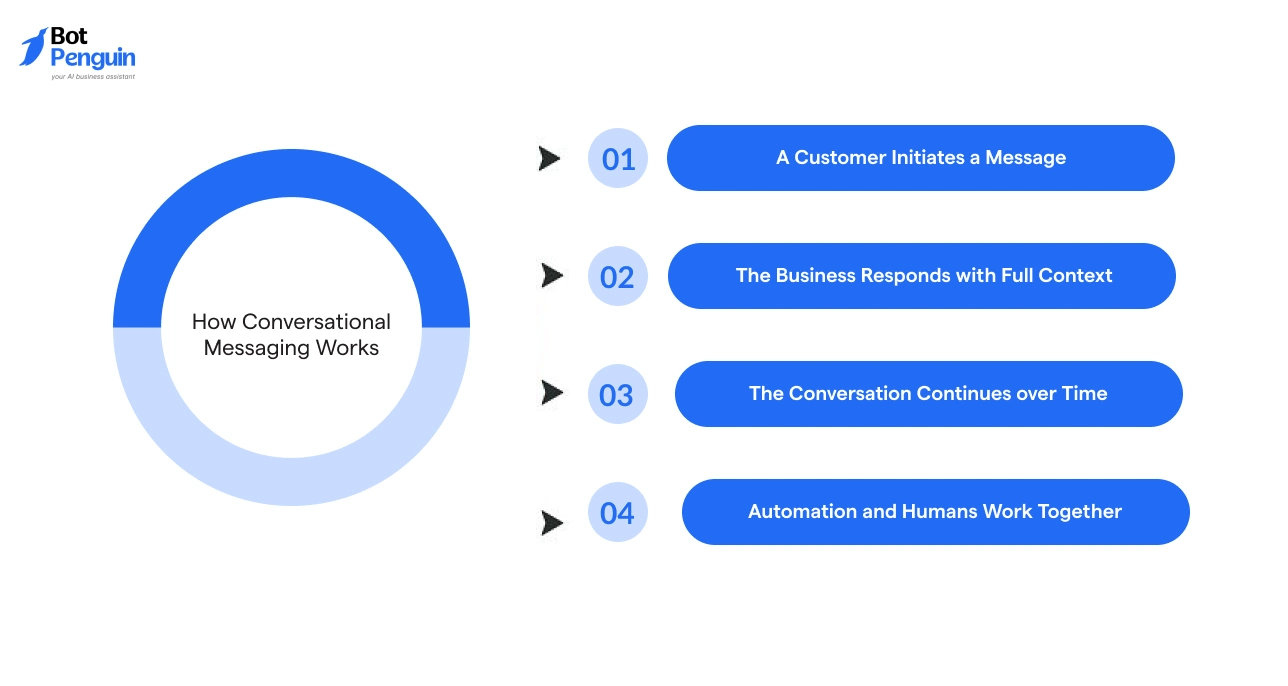
Once the concept is clear, the next question is operational. Businesses want to know how conversational messaging functions in day-to-day communication.
The process is structured, predictable, and designed to maintain context at every stage. Each step builds on the previous interaction instead of resetting the exchange.
Step 1: A Customer Initiates a Message
A conversation begins when a customer reaches out through chat, messaging apps, or social platforms. The intent may be a question, a request, or a follow-up. This message opens a conversation thread that remains active over time.
For example, a customer asks about product availability. That question is logged as the starting point of the interaction.
Step 2: The Business Responds with Full Context
The response is informed by all previous messages in the same thread. Teams can see what the customer asked earlier, what was shared, and what actions were taken. There is no need for the customer to repeat information.
If the customer returns later with a related query, the business already has the full background. This is a core advantage of conversational messaging in practice.
Step 3: The Conversation Continues over Time
Follow-ups remain within the same conversation. The thread stays open across days or weeks. Each new message adds clarity instead of creating a new request.
For example, after resolving an issue, the same conversation can handle a feedback request or a service update without starting over.
Step 4: Automation and Humans Work Together
Routine queries, such as order status or basic questions, can be handled through automation. More complex or sensitive cases are passed to human teams with full context intact.
This balance ensures speed without losing accuracy or accountability.
Together, these steps explain how conversational messaging supports continuity and efficiency.
Conversational Messaging vs Traditional Communication Models
Decision makers need clarity on how this model differs from existing communication methods.
The table below highlights how conversational messaging compares with email, ticket based systems, and one way notifications across real operational factors.
Comparison Table
Conversational Messaging vs Email
Email communication relies on isolated threads and delayed responses. Context is often lost when conversations span days or involve multiple team members. Customers wait for replies, and follow-ups slow the interaction.
With conversational messaging, replies happen in real time or near real time. Messages stay connected within one ongoing conversation. When a customer asks a follow-up question, the full history is visible, which keeps responses accurate and timely.
Conversational Messaging vs Ticket-Based Support
Ticket-based support treats each issue as a case that must be opened and closed. Once a ticket is closed, the context is no longer active. When the customer returns, the process starts again.
In conversational messaging, conversations continue beyond a single issue. The same thread supports follow-ups, clarifications, and future requests. This helps teams understand customer intent over time and respond with better continuity.
Conversational Messaging vs One-Way Notifications
One way notifications deliver updates without allowing interaction. Customers receive information, but cannot respond within the same message.
Conversational messaging allows immediate replies. A delivery update can turn into a reschedule request. A payment reminder can become a support question. Communication remains active instead of static.
Overall, this comparison explains why businesses move toward conversation-based models. The following section focuses on why this shift directly improves customer experience and operational efficiency.
Why Conversational Messaging Matters for Businesses
After comparing communication models, the impact becomes clear. The difference is not only technical. It affects response speed, workload distribution, and revenue outcomes.
This is why businesses adopt conversational messaging as an operating model rather than a channel choice.
Customers Expect Instant, Human-Like Responses
Customers expect replies that acknowledge what was already shared. When a buyer asks about pricing and returns later with a setup question, they expect continuity.
With conversational messaging, the response reflects prior context and timing. This reduces frustration and increases trust.
Teams Reduce Repetition and Manual Effort
Support and sales teams repeatedly ask the same questions. Order details, issue history, and preferences are repeated.
Ongoing conversations remove this waste. Teams see past interactions and act faster. This is a direct result of applying conversational messaging correctly.
Ongoing Conversations Improve Engagement and Conversions
When communication stays active, customers respond more. A product question can turn into a demo request. A service update may prompt an upgrade discussion.
Engagement increases when interactions do not end after a single reply.
Overall the value is practical and measurable. Faster responses, lower effort, and better engagement improve outcomes.
Examples of Conversational Messaging in Real Business Scenarios
Once the operational model is clear, real-world implementations demonstrate how conversational messaging works in production.
These scenarios highlight how businesses use conversational messaging to manage context, reduce response delays, and handle high interaction volumes across core functions.
Customer Support Conversations
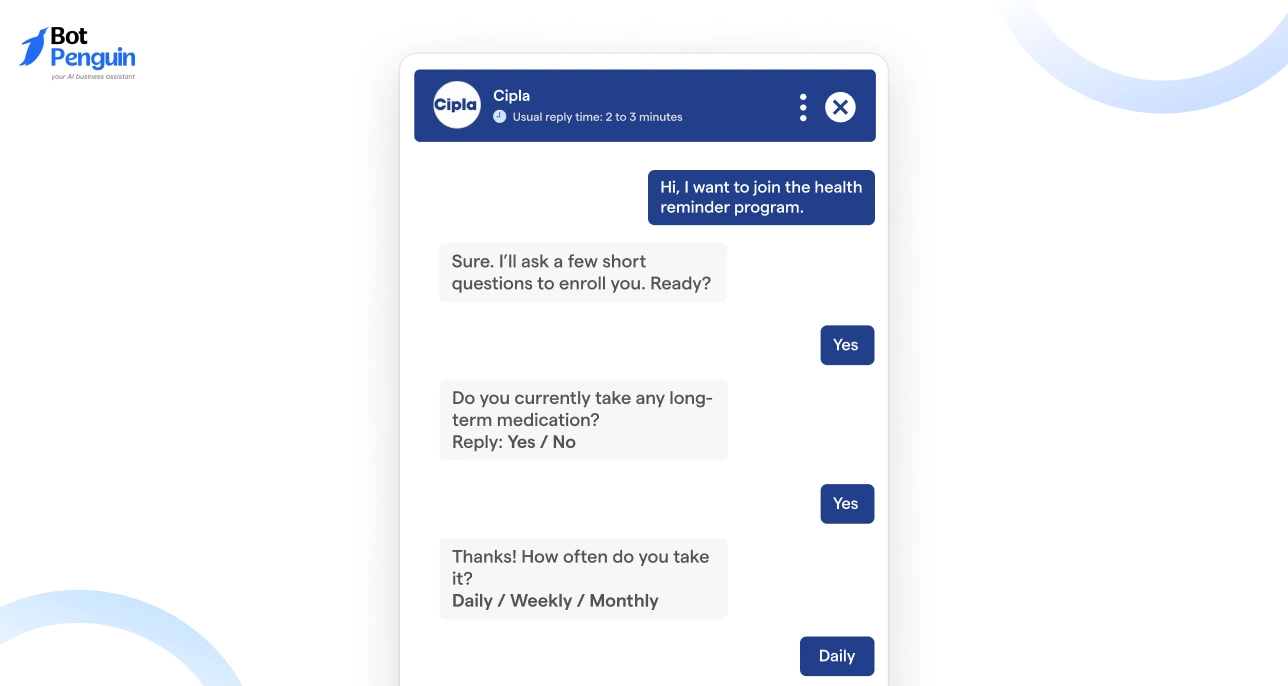
Large-scale support environments require continuity. Conversational messaging helped DVET Maharashtra manage student queries by keeping questions and follow-ups within the same interaction thread. This avoided repeated explanations and reduced manual handling.
In a similar support context, Cipla used conversational messaging to send reminders and respond to follow-up queries with full interaction history available. This improved response accuracy and reduced resolution time.
Sales and Lead Qualification
Lead qualification often breaks when conversations reset. Home Loan Whiz used conversational messaging to manage eligibility checks, document requests, and clarifications within a single, continuous interaction. Leads progressed step by step without losing context.
Galaxy Toyota implemented conversational messaging for enquiry handling and service bookings. Prospects moved from initial questions to confirmed actions without restarting the conversation, improving response speed.
Onboarding and Product Guidance
Onboarding requires continuity across sessions. OckyPocky used conversational messaging to support setup and feature guidance.
Returning users continued from the previous steps rather than restarting, reducing onboarding time.
Order Updates and Follow Ups
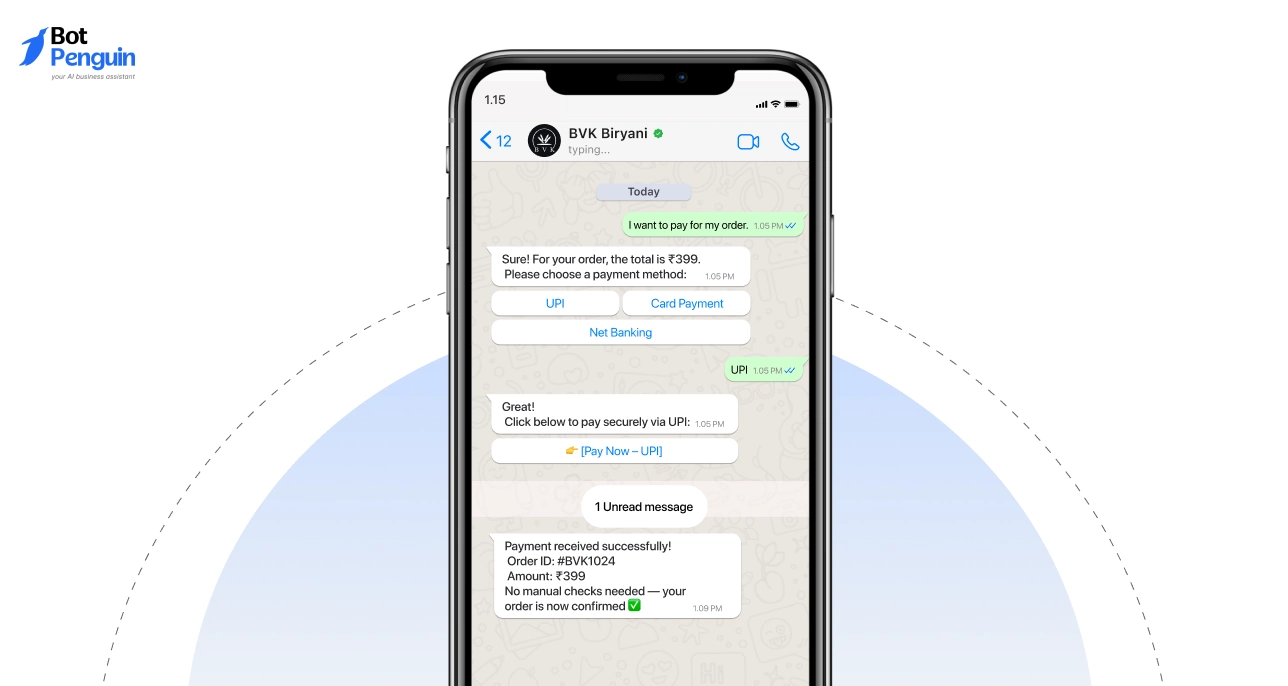
Order communication benefits when updates remain interactive. BVK Biryani used conversational messaging to handle order confirmations and delivery follow-ups in a single thread. This reduced inbound calls and improved response consistency.
TTRacing used conversational messaging to manage customer enquiries and post-purchase communication at scale. Conversations remained active from first contact through follow-ups, reducing response time across teams.
These scenarios demonstrate how conversational messaging functions across support, sales, onboarding, and operations.
The following section explains which channels businesses use to support these conversations and why channel selection matters.
Channels Commonly Used for Conversational Messaging
Once businesses understand how conversations flow, the next decision is where to hold these conversations. Channel choice affects response speed, visibility, and continuity.
Conversational messaging works best when it meets customers where they already communicate. These channels support ongoing interactions without breaking context.
Website Chat
Website chat is often the first touchpoint. A visitor asks a question about pricing or features. The conversation continues even if the user navigates to another page.
When the visitor returns, the earlier discussion remains visible. This keeps responses consistent and relevant.
Messaging Apps Like WhatsApp
Messaging apps are used for direct and frequent communication. Customers ask questions, follow up on orders, or request support.
With conversational messaging applied here, the same thread carries updates, confirmations, and clarifications. The interaction feels continuous instead of transactional.
Social Messaging Platforms
Social platforms support conversations that start publicly and move to private messages. A customer comments on a post and continues the discussion in messages.
Context from earlier interactions helps teams respond accurately and maintain continuity.
In App Messaging
In-app messaging supports users during active product usage. Questions about setup errors or features are answered within the application.
When users return, their history remains available, reducing friction and improving resolution speed.
These channels show where conversational messaging operates today.
The next section explains how automation supports these conversations without removing human involvement.
Conversational Messaging and Automation
After choosing the proper channels, the next challenge is scale. As conversation volume grows, teams cannot respond manually to every request without delays.
This is where automation supports conversational messaging without breaking continuity. Automation adds speed and structure while keeping conversations active and contextual.
How Automation Supports Conversations
Automation handles common questions such as order status, pricing details, or appointment availability. These responses are triggered inside the same conversation thread.
Context from earlier messages remains visible. This ensures replies stay relevant and consistent.
For example, a customer a the delivery status. Automation sharsks aboutes the update. If the customer follows up with a change request, the conversation continues without reset.
This is a practical use of conversational messaging supported by automation.
When Human Escalation Happens
Automation does not replace human involvement. Complex, sensitive, or high-value conversations require human judgment.
When escalation happens, the team receives the full conversation history. There is no need to ask the customer to repeat information.
For example, a billing dispute or contract discussion moves to a human agent with all prior context available. This improves resolution speed and accuracy.
Automation and human support work together to maintain continuity at scale.
The next section explains how businesses implement this model across teams using unified platforms.
How Businesses Implement Conversational Messaging at Scale
Once automation and human collaboration are in place, the next challenge is scale. As message volume increases, businesses need structure without losing continuity.
Scaling conversational messaging requires clear visibility, faster responses, and reliable handoffs across teams. This section explains how organizations operationalize conversations across growing channels and customer bases.
Centralizing Conversations Across Channels
Customers reach out through websites, messaging apps, social platforms and products. Without centralization, conversations get fragmented. Businesses scale by bringing all conversations into one view.
For example, a customer starts on website chat and follows up on a messaging app. When conversations are centralized, the team sees the full history in one place.
This prevents missed context and duplicated work. It is a core requirement when applying conversational messaging at scale.
Adding AI for Faster First Responses
As volume grows, first response time becomes critical. AI helps by responding instantly to common questions while keeping the conversation active.
For example, AI can confirm an order status or share pricing details the moment a message arrives. When the customer replies with a follow-up, the context is already present. Speed improves without sacrificing accuracy.
Ensuring Smooth Human Handoffs
Not every conversation should stay automated. High-value or complex cases require human involvement. At scale, handoffs must be clean and informed.
Agents receive the full conversation history, including previous responses and customer intent. There is no reset and no repeated questioning. This maintains trust and resolution quality.
This is where platforms like BotPenguin come in. They help businesses manage conversational messaging across channels, add AI-driven automation, and route conversations to human teams without losing context.
With the right structure in place, businesses can scale conversations confidently. The next section addresses common questions and concerns that decision makers still have before adopting this model fully.
How to Know if Your Business Needs Conversational Messaging
After understanding platforms and implementation, the next step is self-assessment.
Many businesses already experience the warning signs, but do not link them to their communication model. The indicators below help determine when conversational messaging becomes necessary.
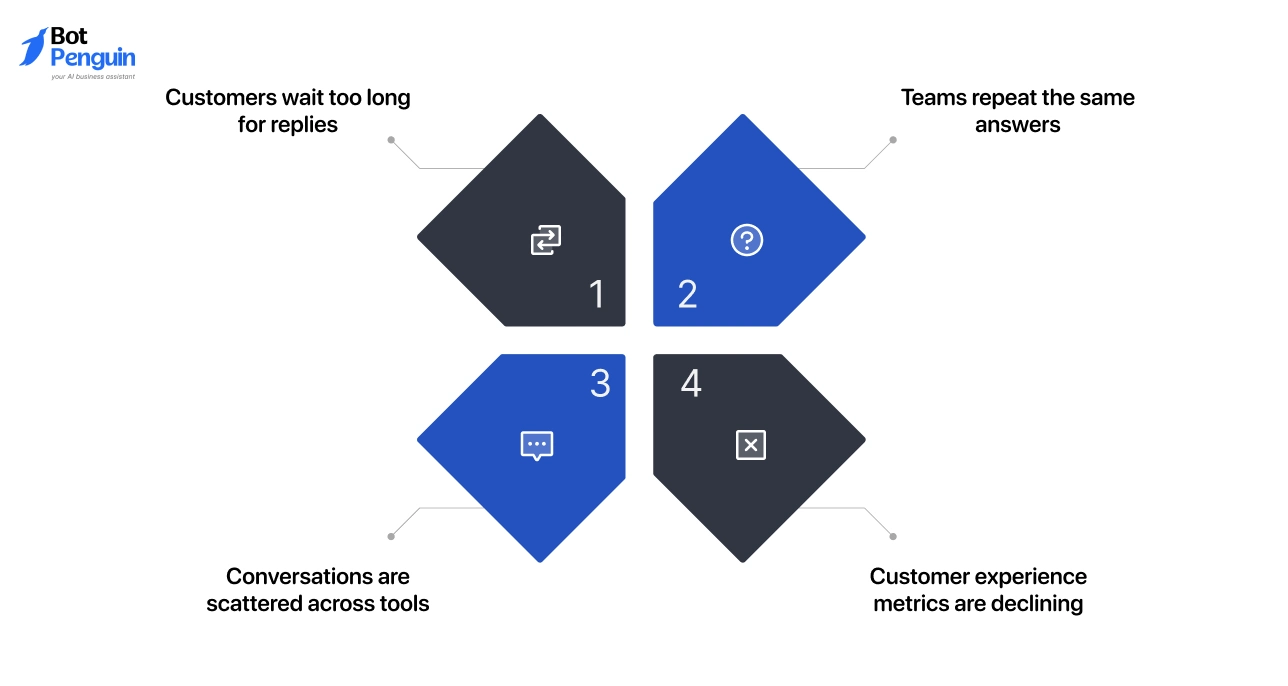
- Customers wait too long for replies: Messages arrive, but responses are delayed. Follow-ups happen before the first reply. Customers lose trust and drop off because the conversation feels inactive.
- Teams repeat the same answers: Agents ask for order details or issue history again. Time is wasted gathering information that already exists. This happens when context is not preserved, which what is conversational messaging is designed to solve.
- Conversations are scattered across tools: A customer starts on website chat, moves to messaging apps, and later emails support. Each interaction lives separately. Teams lack visibility and continuity.
- Customer experience metrics are declining.: First response time increases. Resolution time slows down. Satisfaction scores fall. These trends often point to broken conversation flows.
When these patterns appear, communication needs to shift from isolated messages to connected conversations. The next section explains how businesses can start this transition in a practical and controlled way.
Getting Started with Conversational Messaging
Starting conversational messaging requires structure before scale. Teams that succeed focus on conversation flow, ownership, and visibility rather than jumping straight into automation.
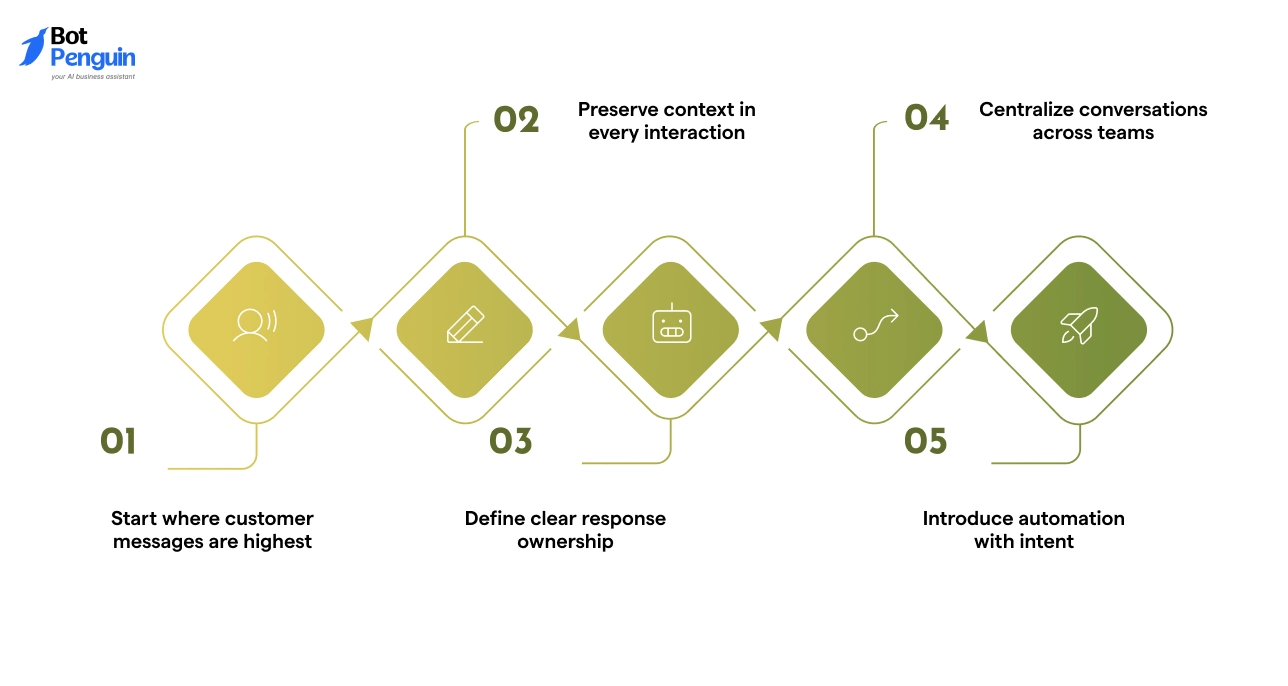
- Start where customer messages are highest: Select the channel with the highest inbound volume. This creates immediate value and avoids spreading efforts too thin.
- Preserve context in every interaction: All replies should stay within the same conversation thread. Follow-ups must never restart the interaction. This is the foundation of conversational messaging.
- Define clear response ownership: Assign responsibility for first responses and escalation. Without this, response time suffers even with the right tools.
- Centralize conversations across teams: Support, sales, and operations should work from the same conversation view. This reduces repetition and improves consistency.
- Introduce automation with intent: Automate predictable questions only after the conversation flow is stable. Automation should assist, not interrupt, the exchange.
At this stage, many businesses turn to platforms like BotPenguin to operationalize these principles. BotPenguin helps centralize conversations across channels, apply automation without breaking context, and route conversations cleanly to human teams as volume grows.
Final Thoughts
After reviewing how conversations work, channels scale, and platforms support execution, the direction is clear. Customer communication has changed permanently.
Static replies and closed tickets no longer meet expectations. Businesses now compete on response quality, speed, and continuity.
Conversational messaging is no longer optional. Customers expect real conversations that carry context across time and channels.
When a buyer follows up on pricing or a user revisits a support issue, the response must reflect prior interactions. This is how trust and efficiency are built.
Platforms like BotPenguin make this transition practical. By combining automation AI and human support in one workflow, businesses can implement conversational messaging without increasing operational complexity.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
How is conversational messaging measured for business performance?
Conversational messaging is measured using response time, conversation completion rate resolution speed, and customer satisfaction trends across channels rather than isolated ticket metrics.
Does conversational messaging require changes to existing CRM systems?
Conversational messaging can work alongside existing CRM systems by syncing conversation history, customer data, and actions without replacing current sales or support tools.
Is conversational messaging suitable for regulated industries?
Conversational messaging can be used in regulated industries when platforms support data control, access management, and audit visibility across conversations.
How does conversational messaging impact internal team collaboration?
Conversational messaging improves collaboration by providing all teams with access to the same conversation history, reducing internal handoffs, miscommunication, and duplicate work.
What risks should businesses consider before adopting conversational messaging?
Conversational messaging requires clear ownership, automation limits, and escalation rules to avoid delayed response, inconsistent tone, or over-automation in sensitive situations.
How does BotPenguin support conversational messaging at scale?
BotPenguin supports conversational messaging by centralizing conversations, adding AI responses, and enabling smooth escalation so teams can handle high message volumes without losing context.