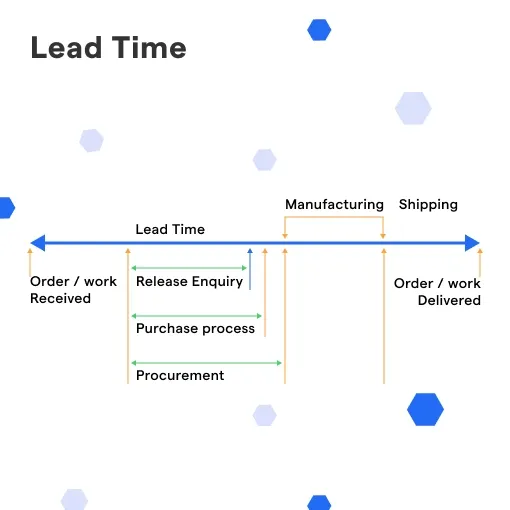
What is Lead Time?
Lead time is the duration between the initiation of a process and its completion. In manufacturing, this is the time between the placement of an order and its delivery. In the software domain, this is the time between the request for a feature and its implementation.
Lead Time in Manufacturing
In a manufacturing setting, lead time can be broken down into three components: material lead time, production or manufacturing lead time, and customer lead time. Material lead time is the time it takes for raw materials to arrive at a factory, manufacturing lead time is the time it takes to create a product, and customer lead time is the time it takes for a product to reach the customer.
Lead Time in the Software Domain
In software development, lead time is the time it takes to complete a change from code commit to code release in production. This includes the time it takes to write code, test it, compile it, and deploy it to customers.
What is Lead Time vs Cycle Time? How are They Different?
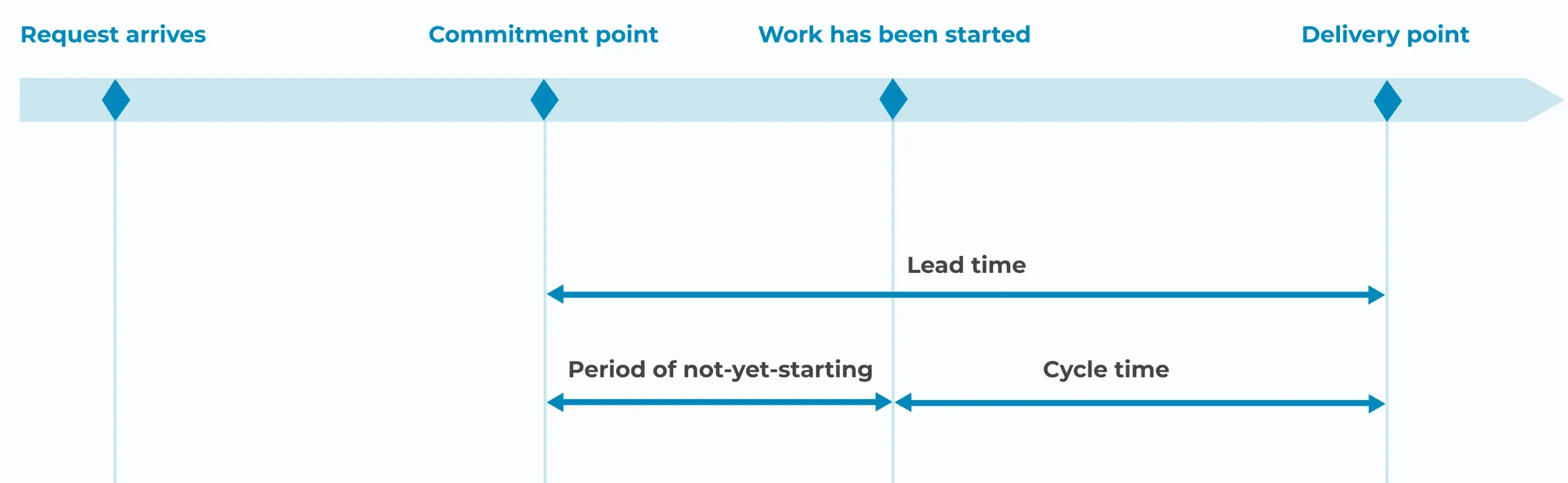
Lead time and cycle time are two important metrics in the world of lean management.
Cycle time is the duration between the start and end of a specific process. Unlike lead time, cycle time only measures the processing time and does not include waiting time.
Lead time tracks the duration between initiation and completion of an entire process. In contrast, cycle time focuses on a specific step in a process.
While lead time includes all the activities involved in order fulfillment, cycle time only considers the time spent on producing the goods or services.
What are the Types of Lead Time?
Lead time can be classified into different types based on the specific process being measured.
- Customer Lead Time
Customer lead time is the time between the placement of an order and the delivery of goods or services to the customer.
- Material Lead Time
Material lead time refers to the duration between the placing of an order and receiving the raw materials needed for production.
- Manufacturing Lead Time
Manufacturing lead time is the time it takes to produce and deliver a product. This includes the time it takes to assemble the product, from its raw materials or component parts to the time it's finished and ready for shipment.
- Cumulative Lead Time
Cumulative lead time is the total time required to perform all the tasks linked to a particular process. This includes the time spent on preparation, production, packaging, labeling and transportation.
Which are the Largest Components of Lead Time?
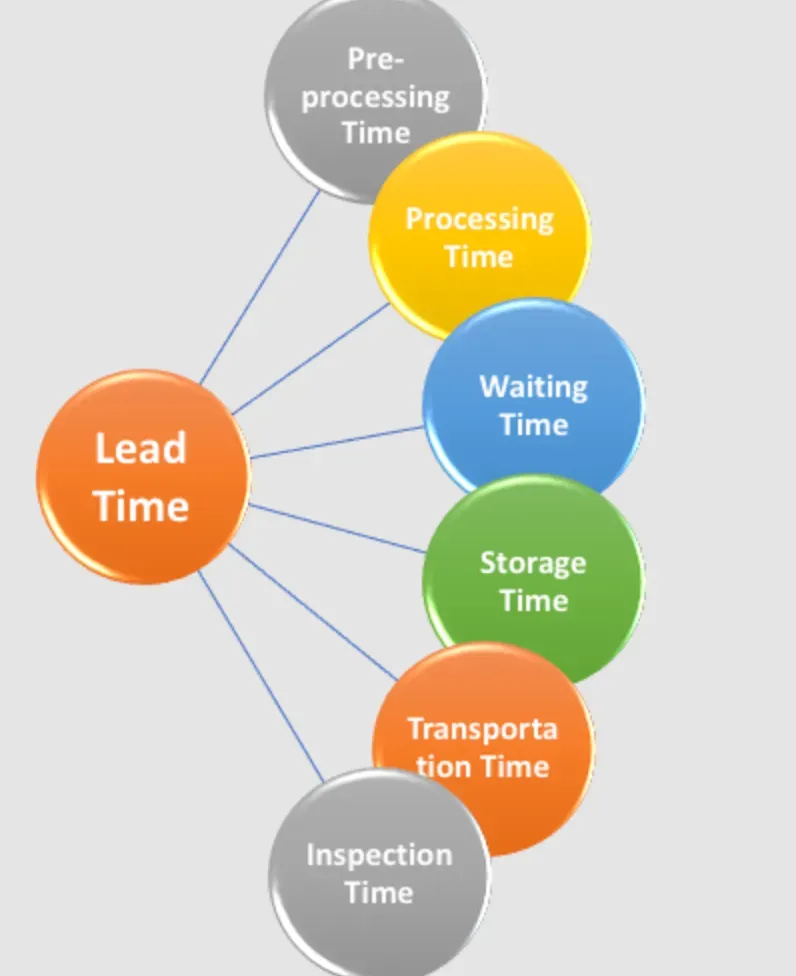
Lead time consists of different components, and it's important to understand them to identify areas that need improvement.
Preprocessing Time
Preprocessing time includes all activities related to planning, administration, and order processing. It's the time that elapses between the arrival of an order and the moment the production process begins.
Processing Time
Processing time is the amount of time required to produce or work on an item. This is the time spent on everything from assembling components, programming code, and any other processes required to make the product.
Waiting Time
Waiting time refers to the time spent waiting for equipment or resources. It includes the time spent waiting for raw materials and machinery to become available and waiting in queue for quality control checks, among other things.
Transportation Time
Transportation time is the time required to move the finished product from one location to another. This includes the time spent packing the goods and transporting them to a retailer or other customers.
Storage Time
Storage time includes all the time products spend in stock or replenishment. When there is too much inventory in stock, storage time increases, which can be costly for the organization.
Inspection Time
Inspection time is the duration it takes to carry out quality checks and ensure that products meet strict quality standards.
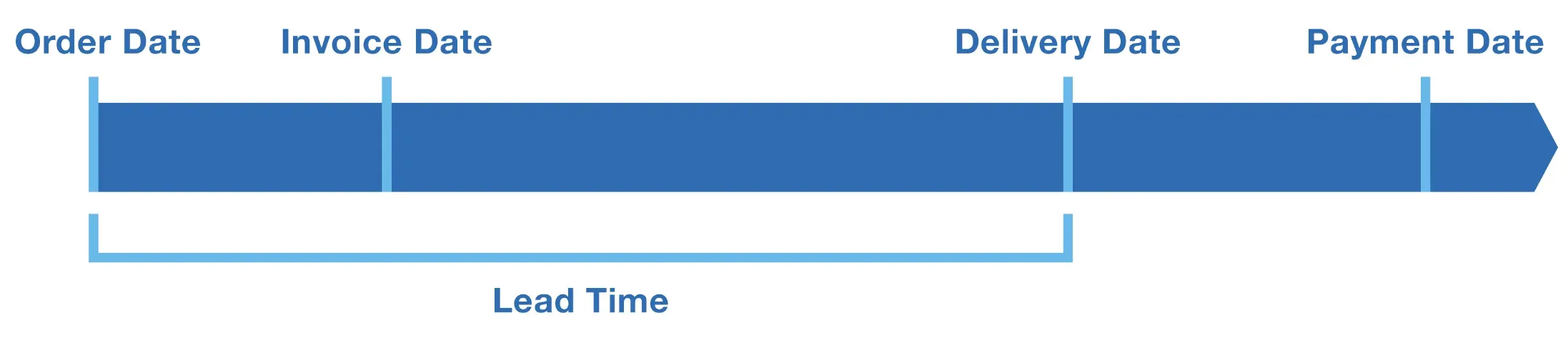
How to Calculate Lead Time?
To calculate lead time, you need to determine the duration between initiation and completion of a process.
Formula for Calculating Lead Time
To calculate lead time, subtract the start time from the end time of the process.
For example, if the manufacturing process starts on January 1st and ends on January 10th, the lead time is 9 days.
Examples of Lead Time Calculation
Suppose an organization receives an order on January 1st and delivers it to the customer on January 20th. The lead time will be 20-1=19 days.
How to Reduce Lead Time?
Strategies for reducing lead time include forecasting demand, streamlining the production process, and improving logistics.
Forecasting Demand
Accurate demand forecasting can help organizations plan their production processes more efficiently, ensuring that the right amount of resources and materials are available when needed.
Streamlining Production Processes
Identify and eliminate bottlenecks and delays in the production process. Implement lean manufacturing principles, reduce setup times, and optimize supply chain operations to improve efficiency.
Improving Logistics
Streamline transportation and delivery processes to minimize transit times. Optimize routes, coordinate shipments, and collaborate with logistics partners to ensure timely and efficient delivery.
Implementing Just-in-Time (JIT) Manufacturing
Adopting a just-in-time manufacturing approach helps minimize inventory holding costs and directly addresses lead time issues by producing goods only when there is demand.
Building Strong Relationships with Suppliers
Collaborate closely with suppliers to establish strong relationships and improve the visibility of the supply chain. This can lead to better coordination, timely deliveries, and reduced lead times.
Steps to Streamline Production Processes
Streamlining production processes involves identifying and eliminating bottlenecks and delays.
This can be achieved by implementing lean manufacturing principles, reducing setup times, and optimizing supply chain operations.
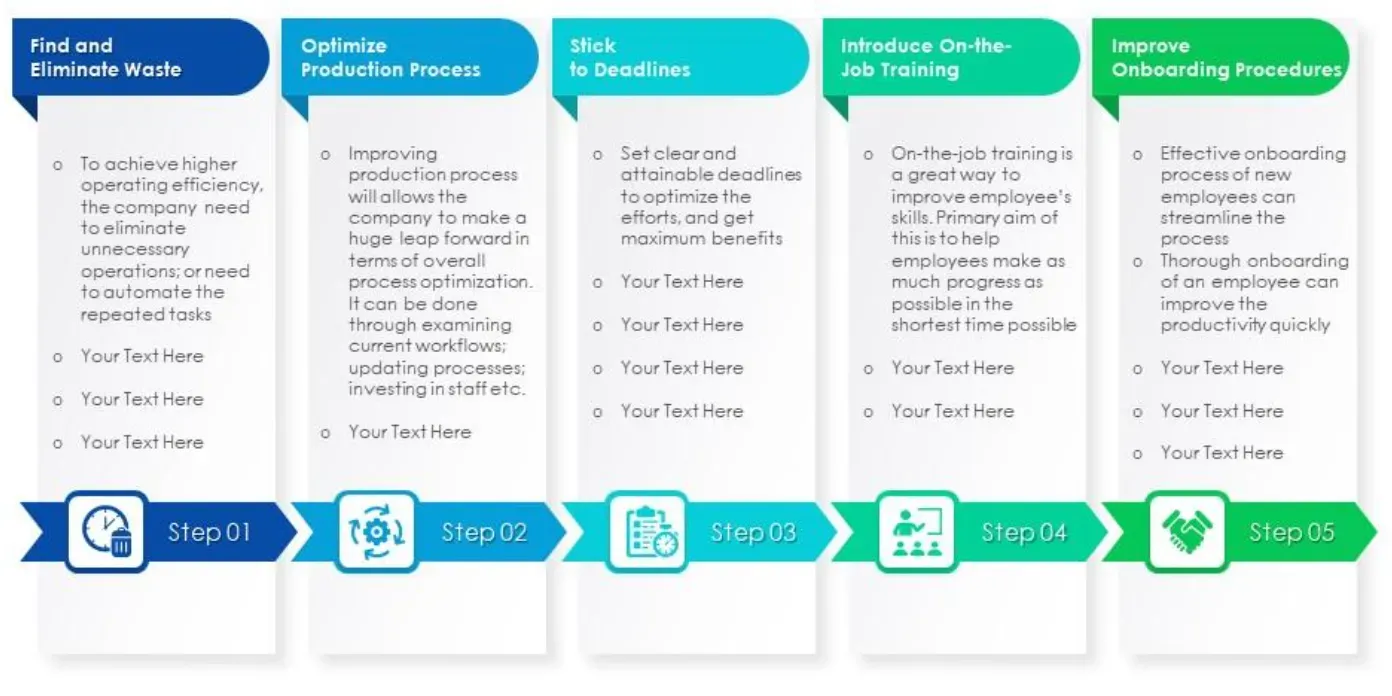
Map the Current Process
Start by mapping out the current production process to identify all the steps involved, from raw material acquisition to finished product delivery. This step helps you understand the existing workflow and identify areas of improvement.
Identify Bottlenecks and Inefficiencies
Analyze the mapped process to identify bottlenecks, delays, and areas of inefficiency. Look for tasks or steps that take longer than necessary, have excessive waiting times, or experience frequent errors or rework.
Implement Lean Principles
Apply lean manufacturing principles to streamline the production process. This includes reducing waste, optimizing flow, and improving overall efficiency.
Use techniques like 5S (Sort, Set in Order, Shine, Standardize, Sustain), value stream mapping, and Just-in-Time (JIT) production to eliminate waste, improve productivity, and reduce lead time.
Improve Collaboration and Communication
Enhance collaboration and communication among different departments and teams involved in the production process.
Encourage cross-functional teamwork, improve information sharing, and establish clear communication channels to ensure smooth coordination and reduce errors or delays caused by miscommunication.
Continuous Improvement
Create a culture of continuous improvement by regularly reviewing and analyzing the streamlined production process.
Use performance metrics, such as Key Performance Indicators (KPIs), to monitor progress and identify further areas for improvement.
Encourage employee feedback and involvement in suggesting and implementing process enhancements.
Remember that streamlining production processes is an ongoing effort, and it may require periodic reevaluation and adjustment to maintain efficiency over time.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What factors can affect lead time?
Lead time can be influenced by factors such as supplier availability, production capacity, transportation delays, and unexpected disruptions in the supply chain.
How can you manage customer expectations regarding lead time?
To manage customer expectations, it's important to provide accurate and transparent information about lead times during the ordering process, as well as alternative solutions when possible.
What strategies can help expedite lead time?
By implementing efficient production processes, optimizing inventory management, leveraging technology, and building strong supplier relationships, you can expedite lead time.
How can you reduce lead time without compromising quality?
Focusing on process improvements, eliminating waste, and enhancing collaboration with suppliers can help streamline operations, enhance productivity, and reduce lead time without compromising quality.
How can you effectively communicate lead times with internal teams?
Effective communication involving project management tools, regular meetings, and timely updates is crucial to ensure internal teams are aware of any changes to lead times and can plan accordingly.