What is Behavior Informatics?
Behavior Informatics (BI), at its core, is an interdisciplinary area of research. It blends computer science with psychology to study, model, and understand behaviors, along with developing methods to leverage behavioral data.
The scope of Behavior Informatics is vast and complex. It involves the collection, modeling, analysis, and interpretation of behavior data, which are used in diverse applications, from healthcare and marketing to cybersecurity and social studies.
Driving Factors of Behavior Informatics
Having a basic idea about Behavior Informatics, let's assess the forces driving this field.
Technological Advancements
One of the primary drivers of Behavior Informatics is technology.
With the evolution of data recording and storage capabilities, research uses sophisticated machine learning and AI applications to analyze large-scale behavioral datasets.
Ubiquity of Digital Interactions
The constant surge in digital solutions in our daily lives has made behavior data ubiquitous.
This explosion of data has given rise to opportunities for new insights, driving the growth of Behavior Informatics.
Key Components of Behavior Informatics
Behavior Informatics thrives on several key components. Let's better understand these pillars.
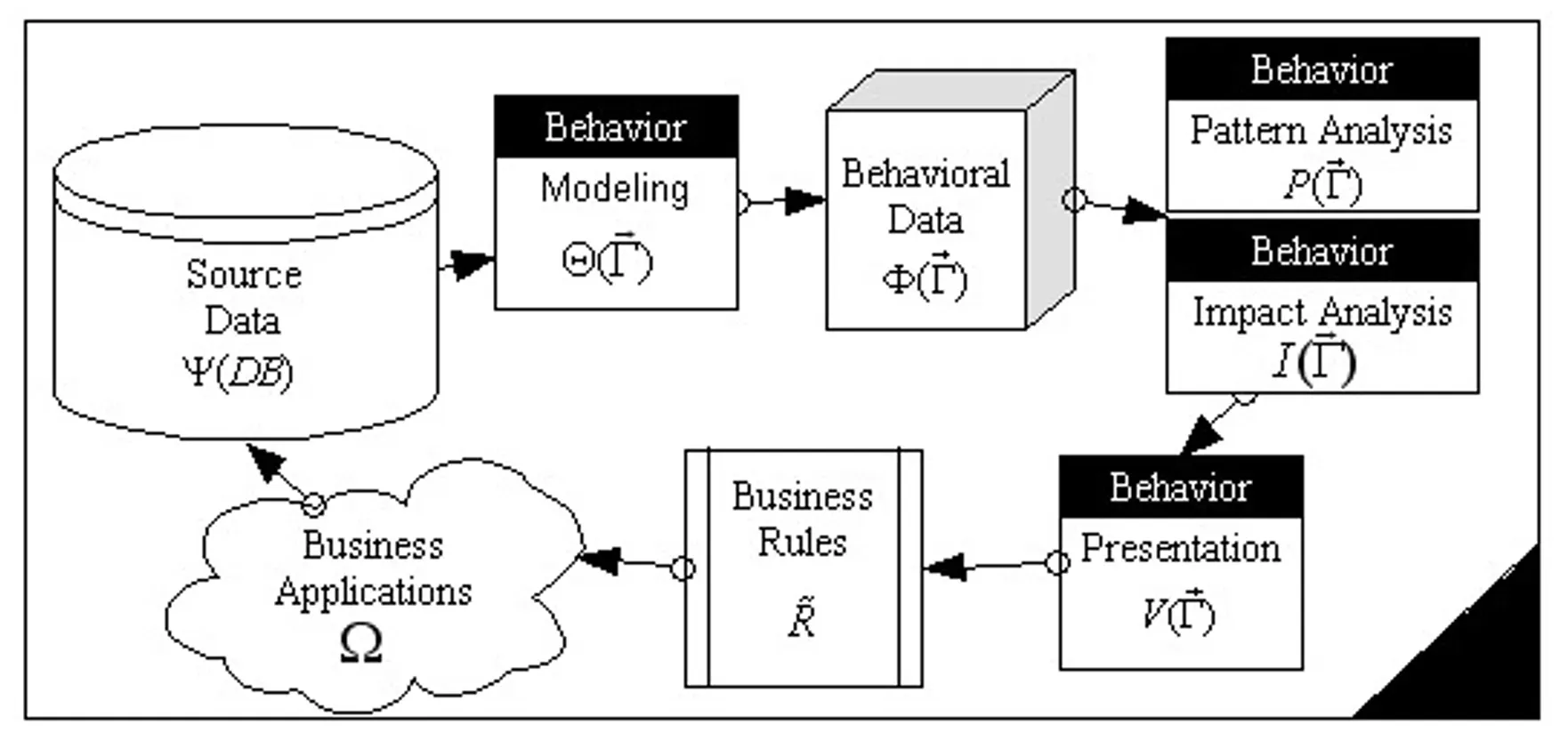
Behavior Data Collection
Behavior data collection refers to the gathering of data relating to human interactions or behaviors.
This could involve digital footprints, direct observations, or self-reports.
Behavior Modeling
In behavior modeling, behavior data are structured into actionable models that attempt to predict or interpret behaviors or trends.
This could involve statistical models, machine learning algorithms, and more.
Methods and Techniques in Behavior Informatics
Behavior Informatics involves various data processing and analysis techniques. Following are a few commonly used methods.
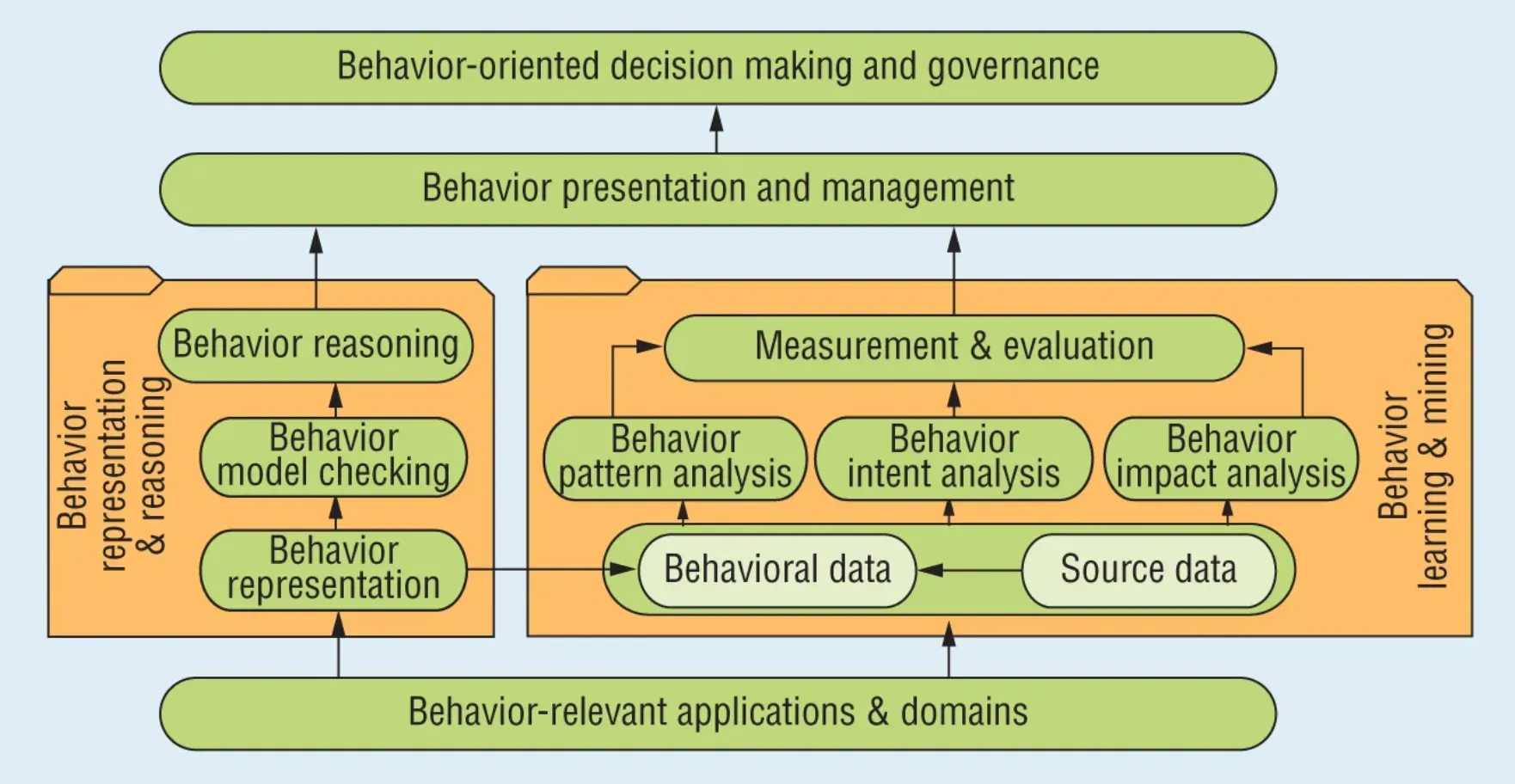
Quantitative Analysis
Quantitative data analysis uses numerical data and employs statistical techniques to investigate behaviors and derive conclusions.
Examples are regression analysis, cluster analysis, or principal component analysis.
Qualitative Analysis
Qualitative data analysis attempts to capture the nuances of human behavior that numeric data often misses.
This analysis may involve content or thematic analysis, interpretative phenomenological analysis, or discourse analysis.
Applications of Behavior Informatics
Proving the value of Behavior Informatics in its diverse applications. Some of the most commonly observed are highlighted below.
Healthcare
In healthcare, Behavior Informatics can provide valuable insights into patient habits, lifestyle, and mental health, enabling personalized treatment plans and preventive measures.
Marketing and Business Strategy
Behavior Informatics plays a vital role in consumer behavior analysis, helping businesses understand their customers better.
Such insights can drive improved marketing strategies and business decisions.
Limitations and Challenges in Behavior Informatics
As with any field of study, Behavior Informatics is not without its challenges. Some of the well-known drawbacks are examined below.
Privacy Concerns
Given the nature of data used in Behavior Informatics, privacy concerns are significant.
Ensuring data anonymization without compromising the quality of analysis is a key challenge.
Interpretation Errors
Erroneous interpretations can arise from misreading the data or applying mistaken assumptions to the models.
These can lead to unproductive or even harmful decisions.
Behavior Informatics: Present and Future
A look at the current state and future outlook of Behavior Informatics rounds off our understanding.
Present View of Behavior Informatics
Right now, Behavior Informatics is a vibrant, growing field, thanks to advancements in technology and data collection.
It's crossing boundaries and merging with multiple disciplines to broaden its scope.
Future Landscape of Behavior Informatics
With the continuous proliferation of digital platforms, the future of behavior informatics shows a clear trend toward more substantial, detailed, and comprehensive behavior data analysis.
Researchers hope to unlock further insights into human behavior, which can have wide-ranging implications across various fields.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
How is Behavior Informatics different from traditional behavioral analysis?
Traditional behavioral analysis often relies on manual observations and surveys. Behavior Informatics leverages data-driven approaches, machine learning, and advanced analytics to gain insights from large-scale data sources.
What are some real-world applications of Behavior Informatics?
Behavior Informatics has applications in various fields, including personalized marketing, healthcare, social network analysis, fraud detection, and public policy. For example, it can be used to predict disease outbreaks or analyze online customer behavior.
How does Behavior Informatics address data privacy and ethics?
Behavior Informatics adheres to ethical standards, ensuring that data is collected with informed consent and that privacy and fairness concerns are addressed through rigorous analysis and transparency.
What are the challenges of working with big data in Behavior Informatics?
Managing and processing large volumes of data can be resource-intensive. Researchers need robust infrastructure and data management practices to harness the potential of big data.
How can one pursue a career in Behavior Informatics?
A career in Behavior Informatics typically requires a strong foundation in data analysis, machine learning, and social sciences. Many universities offer programs and courses in data science and analytics, making it a viable career path for those interested in understanding human behavior through data.