What is Human-Computer Interaction (HCI)?
Human-Computer Interaction (HCI) is a multidisciplinary field of study focusing on the design of computer technology and, in particular, the interaction between humans (the users) and computers.
While initially concerned with computers, HCI has since expanded to cover almost all forms of information technology.
Who is Involved in Human-Computer Interaction (HCI)?
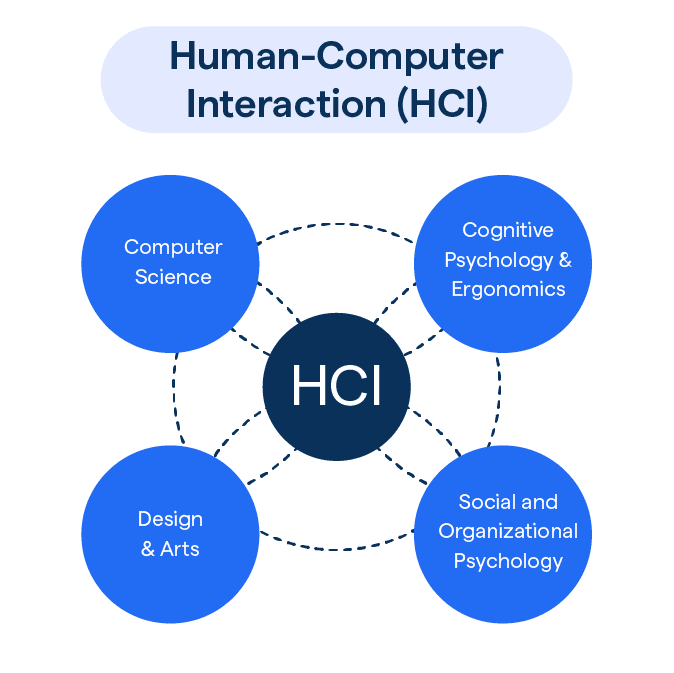
HCI is a broad field that integrates several disciplines, such as computer science, psychology, human factors, information science, and several social science disciplines.
The professionals involved can include user interface (UI) and user experience (UX) designers, software developers, ergonomists, cognitive psychologists, and many more specialist roles.
When did Human-Computer Interaction (HCI) Begin?
The term 'Human-Computer Interaction' was first coined in the 1980s with the mass adoption of graphical user interfaces. However, its roots stretch back to the early days of computing.

The advent of personal computing brought computers into the mainstream, making user-friendly interfaces crucial.
Since then, HCI has been a key component in designing and developing applications that are focused on usability and meet user needs.
Where is Human-Computer Interaction (HCI) Applied?
HCI principles have broad application areas. It's implemented anywhere user interactions with a computing device take place, including handheld devices, desktop applications, websites, and more.
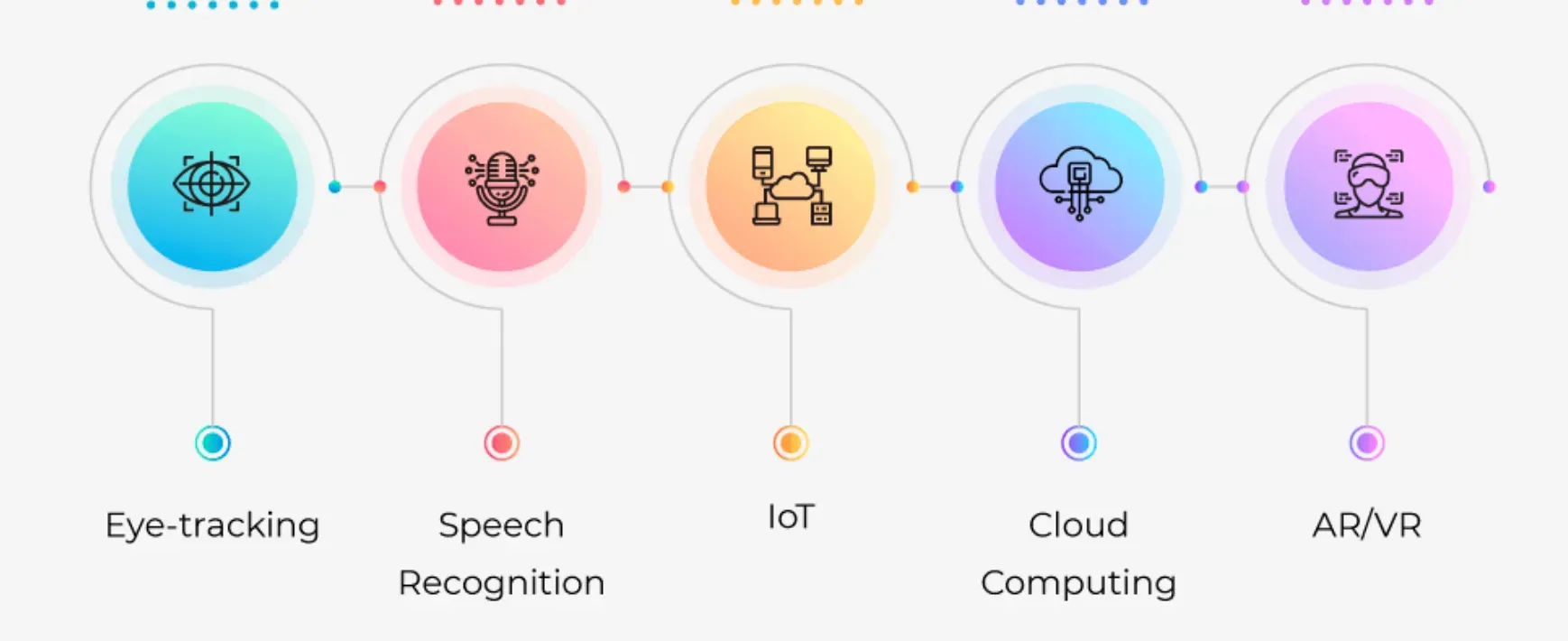
In recent times, HCI's principles also shaped emerging technologies like virtual reality and artificial intelligence interfaces.
Why is Human-Computer Interaction (HCI) Important?
HCI is vital as it places the user and their experiences and needs at the forefront during the development of interactive computing technologies.
It focuses on the practical aspects of technological design and use, working towards making systems that are both useful and usable.
HCI optimizes the interaction between humans and computers, making them efficient, effective, and satisfying for the intended users.
A successful HCI design can result in improved productivity, better user experience, and increased acceptance and satisfaction with technology.
The Goals and Principles of Human-Computer Interaction

In this section, we will understand the in-depth goals and Human Computer Interaction Principles (HCI).
Crafting User-Friendly Systems
A major thrust of Human Computer Interaction Principles are designing systems that balance functionality and user convenience.
These systems aim to streamline tasks by automation, creating interfaces that users find comfortable and efficient to navigate while maintaining a robust security profile to ensure user safety.
Empathizing with Users
Creating empathetic design is central to Human Computer Interaction Principles.
By walking a mile in the end users' shoes, designers cultivate a better understanding of their needs, leading to the development of systems and interfaces that resonate best with their requirements.
Developing Efficient Interactions
HCI's primary aim revolves around creating interactions that are efficient, effective, and safe.
What this implies is that user interactions should achieve the intended outcome swiftly and safely. This increased effectiveness and efficiency can skyrocket productivity levels and user satisfaction, fostering a sense of well-being.
The Seven Pillars of HCI
Proposed by Donald Norman in 1988, the seven guiding Human Computer Interaction Principles include:
- Harnessing both experiential and innate knowledge
- Streamlining task structures
- Maximizing visibility
- Establishing the right mapping (linking user mental models with conceptual and design models)
- Transforming constraints into advantages
- Designing for error
- Standardizing when met by obstacles
The Triad of HCI Components
HCI rests on three fundamental components:
- The User: This represents the individual or group interacting with the system. Understanding their demographics, technical proficiency levels, and physical or cognitive abilities paves the way for an intuitive user interface.
- The Interface: The interface includes the graphical, auditory, or visual elements that the user interacts with.
An excellent interface is not just aesthetically appealing but also user-friendly and rich in feedback mechanisms.
- Counting on Collaborations: The synergistic interaction between the user and interface forms the third pillar of Human Computer Interaction Principles.
The goal is to design an interface the user finds easy to interact with and can leverage optimally to meet their requirements.
Distinguishing HCI from UX
The HCI and User Experience (UX) disciplines share common goals.
However, UX's prime focus lies in adding value to the product by enhancing user experience, while HCI extends its focus to studying psychological impacts, visual communication, and the like.
HCI-Driven Trends in the User Experience Industry
Conversely, HCI has been the driving force behind several emerging trends in the User Experience industry:
- Voice-guided User Interface: These interfaces, powered by voice commands and natural language processing, make the user experience hands-free and convenient.
- Gesture-guided User Interface: These interfaces let users navigate using hand movements and body motions, facilitating an intuitive interaction.
- Virtual and Augmented Reality: While Virtual Reality creates computer-generated environments, Augmented Reality overlays digital information onto the real world, delivering highly interactive experiences.
- Wearable Technology: Wearable devices like fitness trackers and smartwatches use integrated sensors for real-time information access and seamless interaction with digital services.
Human-Computer Interaction Examples
In this section, we will cover some real-life examples of Human-Computer Interaction (HCI).
Voice-Activated Assistants and Smart Speakers

Devices like Amazon Echo, Google Home, and Apple HomePod represent HCI in action as they provide voice-activated assistants capable of understanding spoken language.
Natural language processing, speech recognition, and AI advancements have improved the interaction between users and these devices, making them indispensable modern home appliances.
Touchscreen Devices and Smartphones
One of the most ubiquitous examples of Human-Computer Interaction is the touchscreen interface found in smartphones, tablets, and other devices.
HCI has been integral to the development of these interfaces, ensuring responsive, intuitive touch gestures that allow users to navigate and interact effortlessly with the digital world.
Gesture-Based Interfaces
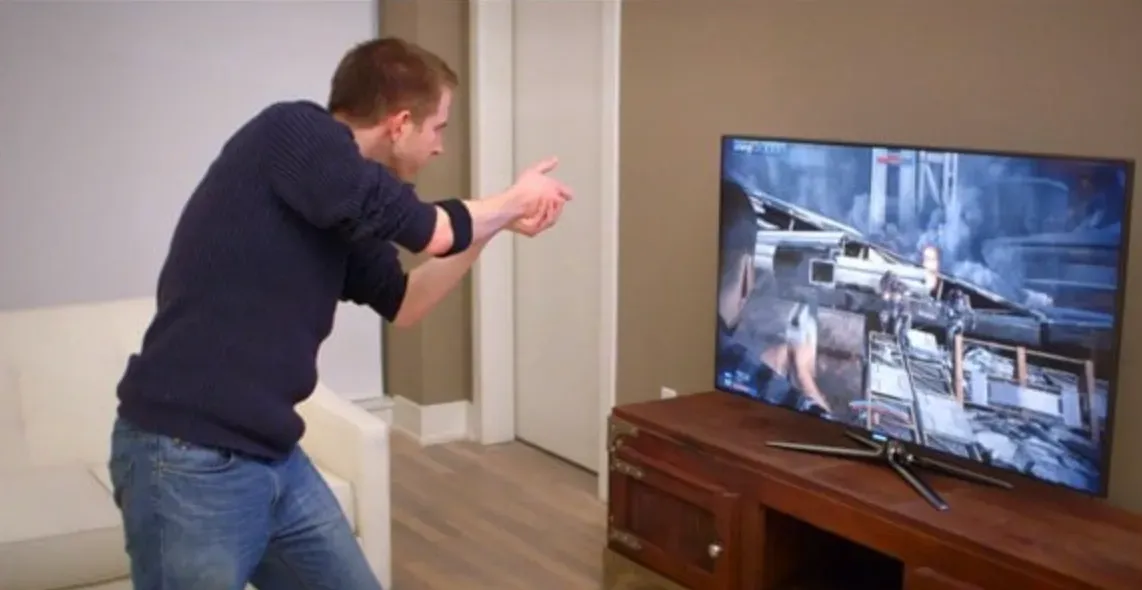

Gesture-based interfaces, such as those featured in Microsoft's Kinect or VR gaming systems, grant users the ability to interact with computing devices through simple bodily movements—this eliminates the need for traditional input devices like controllers, keyboards, or mice.
Accessibility Features
HCI principles have significantly contributed to the development of accessible computing technologies, ensuring that differently-abled users can interact with digital devices effectively.
Examples include screen readers and speech recognition software for visually impaired users or alternative input devices like sip-and-puff systems for people with limited mobility.
Website Navigation and User Experience
HCI's design guidelines and principles have been crucial in shaping modern website design and navigation.
Designers focus on aspects like information architecture, layout consistency, typography, and color schemes to ensure that users can effortlessly find their way around websites and easily access the information they seek.
Smart Home Automation
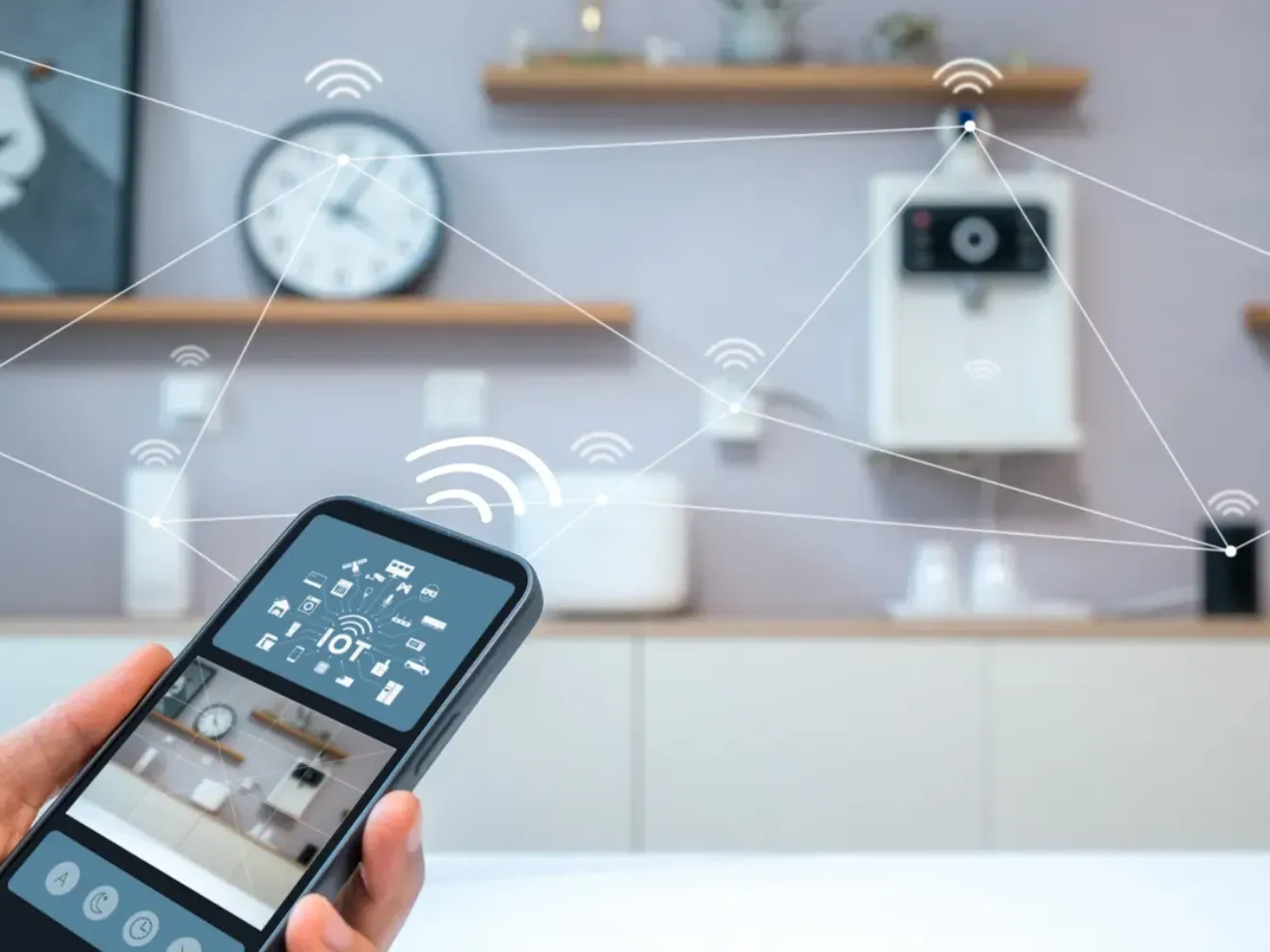

Smart home automation systems, such as connected lighting, heating, and security systems, employ HCI strategies to provide a seamless user experience.
With the help of applications, graphical user interfaces, voice controls, or touch panels, homeowners can efficiently manage and interact with their smart home's connected infrastructure.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is HCI?
HCI stands for Human-Computer Interaction, a multidisciplinary field concerned with the design, evaluation, and implementation of interactive computing systems.
It focuses on understanding and improving the interaction between humans and computers to enhance usability, user experience, and overall system effectiveness in various contexts.
How does Human-Computer interaction impact user experience?
Human-computer interaction plays a crucial role in shaping user experience by considering factors like ease of use, efficiency, and satisfaction in designing interactive systems.
What are the major principles of user-centered design in Human-Computer interaction?
User-centered design in Human-Computer interaction follows principles like conducting user research, involving users throughout the design process, and iterating based on feedback to create more usable and effective systems.
How do cognitive processes influence Human-Computer interaction?
Cognitive processes like perception, attention, memory, and problem-solving affect how humans interact with computers.
Understanding these processes helps designers create interfaces that support users' mental abilities and limitations.
What ethical considerations are important in Human-Computer interaction?
Ethical considerations in Human-Computer interaction involve protecting user privacy, addressing biases in algorithms, ensuring accessibility for all users, and designing inclusive and responsible systems that adhere to ethical standards.
How can Human-Computer interaction improve efficiency and productivity?
Improving Human-Computer interaction can lead to increased efficiency and productivity by streamlining tasks, reducing cognitive load, providing intuitive interfaces, and optimizing user workflows.