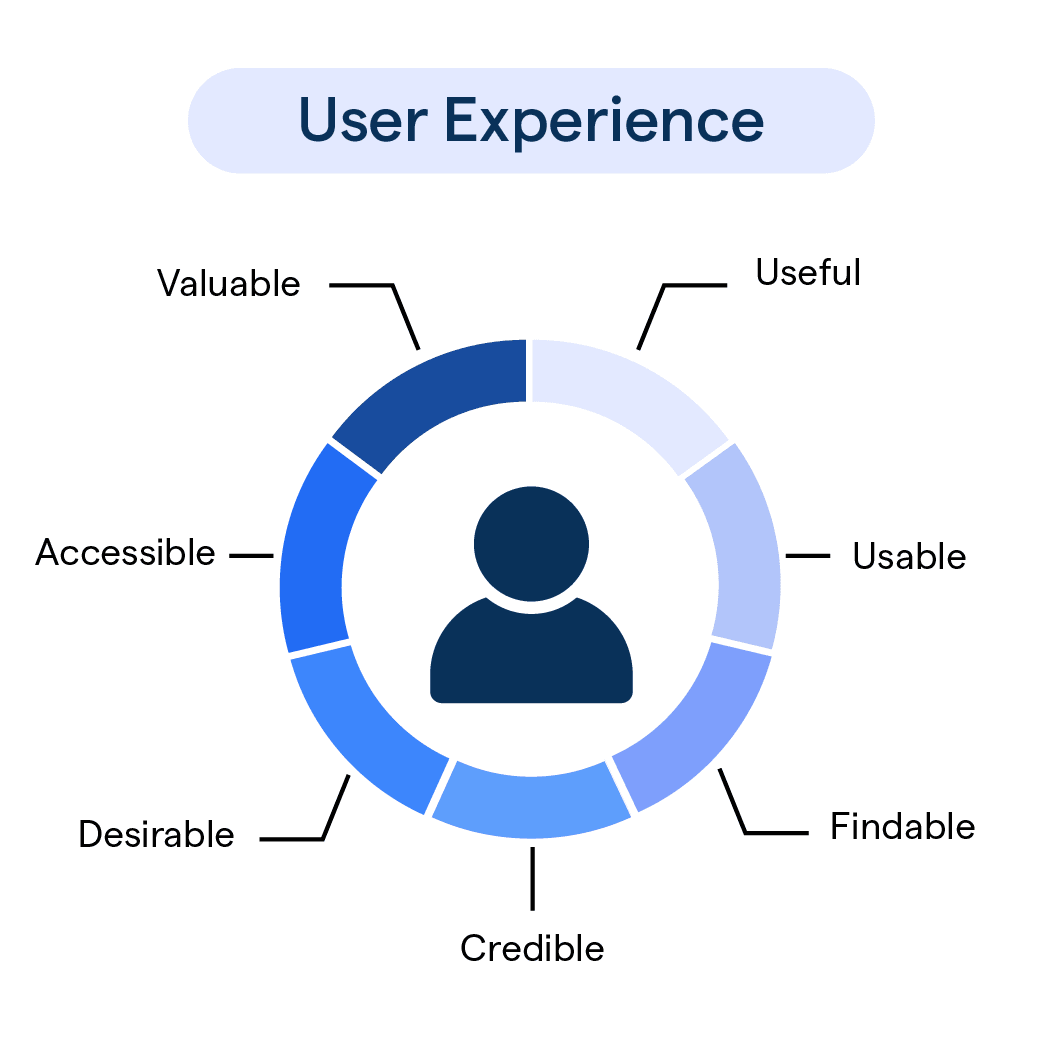
What is User Experience (UX)?
User Experience, or UX, is the overall experience a person has while interacting with a product, service, or system.
It encompasses the user's emotions, perceptions, and responses to the product's usability, functionality, and design. In short, UX is all about how a user feels when using something.
Importance of UX in Design
The importance of UX in design cannot be overstated. A well-designed user experience can make the difference between a successful product and one that falls flat.
By focusing on the user's needs and expectations, designers can create products that are not only functional but also enjoyable to use.
Key Principles of UX
Some key principles of UX design include:
- Put the user first: Understand and prioritize the needs and goals of the target audience.
- Be consistent: Maintain a consistent look and feel across all elements of the design.
- Provide feedback: Give users clear and timely feedback on the results of their actions.
- Keep it simple: Strive for simplicity and minimize complexity whenever possible.
- Focus on usability: Ensure that the product is easy to use and meets the user's needs.
Why is UX Important?
User experience (UX) is the backbone of a product's success. It influences how users interact with a product and shapes their overall perception.
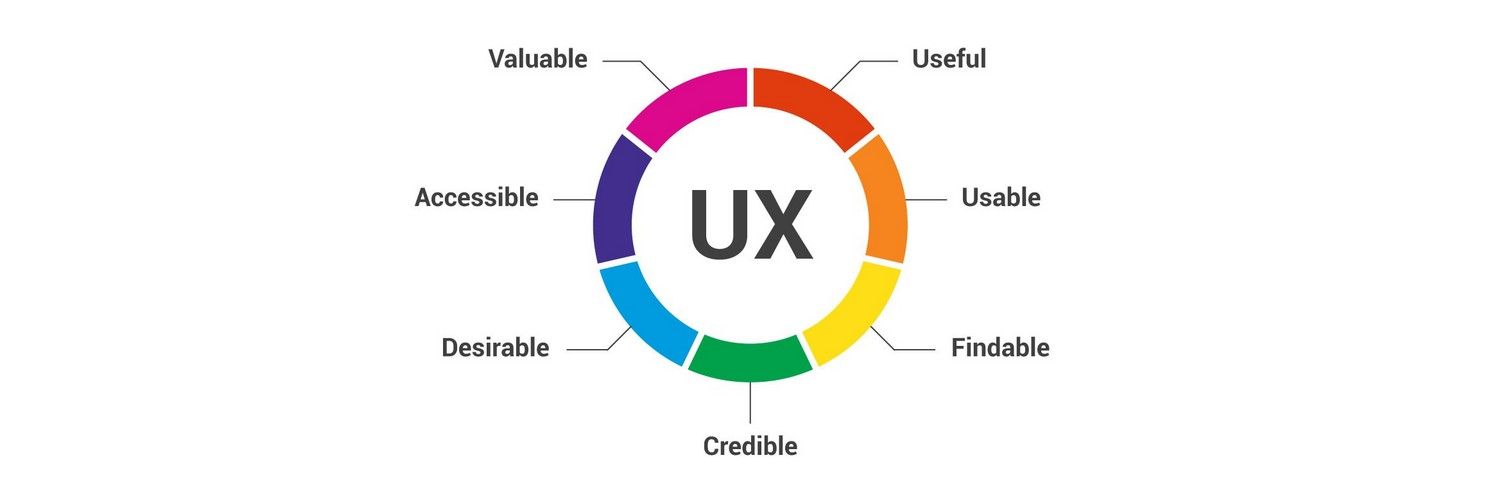
Let’s explore its profound impact on customer satisfaction, brand perception, and business outcomes.
Impact on Customer Satisfaction
A positive user experience leads to increased customer satisfaction. When users enjoy using a product and find it easy to navigate, they are more likely to continue using it and recommend it to others.
On the other hand, a poor user experience can lead to frustration and dissatisfaction, potentially driving customers away.
Influence on Brand Perception
UX plays a significant role in shaping a brand's perception. A well-designed user experience can help create a positive image of the brand, while a poorly designed experience can harm the brand's reputation.
By investing in UX design, companies can ensure that their brand is associated with quality, reliability, and customer satisfaction.
Role in Conversion Rates and Sales
Good UX design can directly impact a company's bottom line by increasing conversion rates and sales.
When users find a product easy to use and enjoyable, they are more likely to complete desired actions, such as making a purchase or signing up for a newsletter. This, in turn, leads to increased revenue and business growth.
Who's on the UX Design Team?
UX design involves a diverse team of experts, each bringing unique skills to create a cohesive user experience. Here are the key roles shaping UX success.
- UX Designers: UX designers take the lead in shaping the user experience. They delve into user research, develop user personas, sketch wireframes, create prototypes, and carry out usability testing to ensure the product aligns with user needs.
- UI Designers: UI Designers specialize in the visual elements of a product like the layout, color schemes, typography, and icons.
It's important to remember that while UI design is a critical part of UX, user experience goes beyond just the visual appeal of a product.
- UX Researchers: UX researchers are detectives of the UX world. They collect and analyze data about users – their needs, preferences, and behaviors.
They use research methods such as interviews, surveys, and usability testing to inform the design process, making sure the product resonates with its users.
- UX Writers: UX writers are the wordsmiths in UX design. They craft the content that users interact with, such as button labels, menu items, and error messages.
They ensure that the language used in the product is clear, concise, and consistent, enabling users to understand and navigate the product seamlessly.
When is UX Design Needed?
UX design isn’t a one-time activity—it’s an ongoing process integrated at various stages of product development and beyond.
During the Product Development Lifecycle
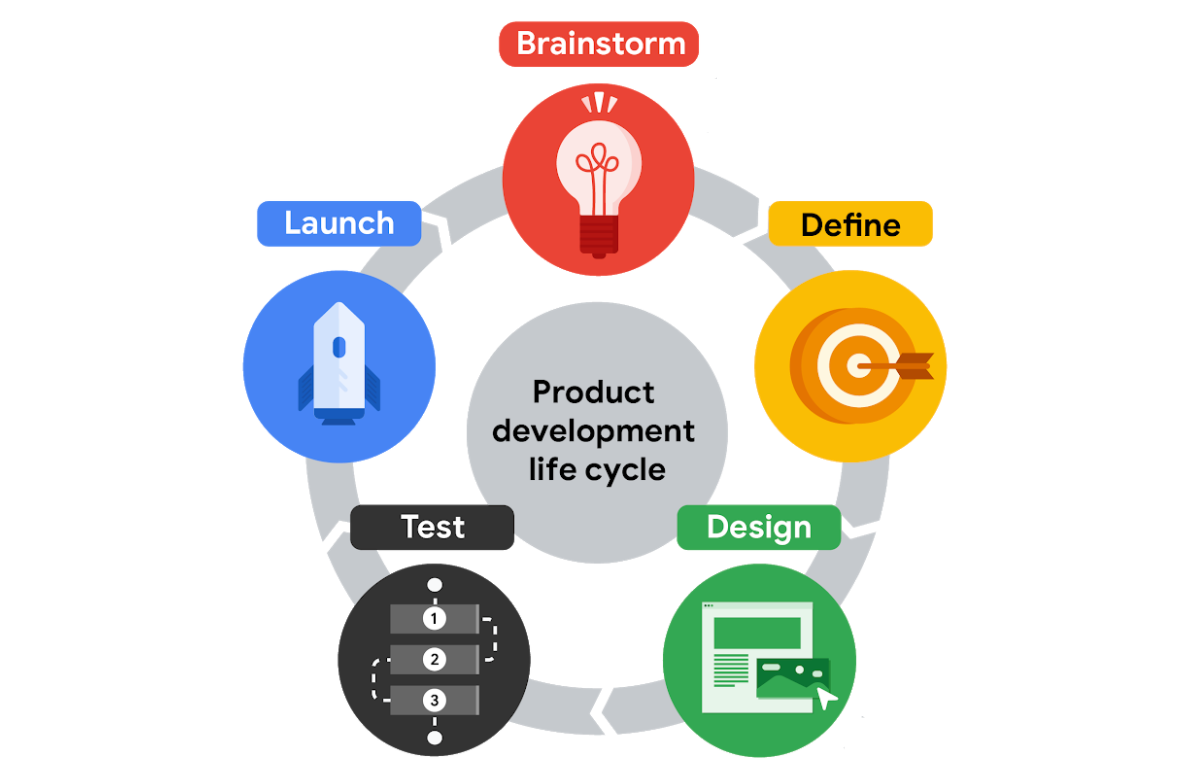
UX design should be integrated throughout the product development lifecycle, starting from the initial idea stage to post-launch maintenance and updates.
By involving UX designers from the outset, you can ensure user needs and expectations are considered at every stage of the development process.
During UX Design Iterations
UX design isn't a one-off process. It's iterative, involving continuous testing, feedback, and refinement.
Designers should regularly test their designs with real users, gather feedback, and make improvements based on their findings. This iterative approach ensures a functional and enjoyable final product.
For Continuous Improvement
Even post-launch, the UX design work continues. Designers should keep an eye on user feedback and analytics data, making updates and improvements as needed to ensure the product remains effective and relevant.
Where does UX Design Happen?
UX design spans across various mediums and contexts, requiring adaptability to cater to diverse platforms and audiences.
For Physical and Digital Products
UX design is relevant for both physical and digital products. While the principles of UX are similar across different products, the specific techniques and tools used may vary depending on whether the product is physical (like a chair) or digital (like a website).
Across Different Platforms
In today's multi-device era, it's critical for UX designers to think about how their designs will operate across different platforms and devices.
This may mean creating responsive designs that adapt to various screen sizes, designing for touch interactions on mobile devices, or considering the unique needs of users with different devices.
Considering Localization and Culture
UX designers should also be aware of the cultural context in which their products will be used.
This might involve localizing design elements to cater to users in different regions, or ensuring that the product is accessible and inclusive to users of diverse backgrounds and abilities.
How to Achieve a Great User Experience?
Creating a great UX requires a thoughtful approach that centers on users and combines design, testing, and consistency.
Use User-Centered Design
User-centered design is a design approach that prioritizes the needs and goals of the target audience.
By involving users in the design process and prioritizing their needs, designers can create products that are both functional and enjoyable.
Conduct Usability Testing
Usability testing is a critical part of the UX design process. It involves observing real users as they interact with a product, helping designers identify usability issues and make improvements based on their findings.
Ensure Accessibility and Inclusivity
An accessible and inclusive user experience means designing products that can be used by people of diverse abilities and backgrounds.
This may involve considering elements such as color contrast, font size, and alternative input methods to make the product accessible to as many people as possible.
Maintain Consistency and Familiarity
Keeping consistency and familiarity in a product's design helps users feel comfortable and confident when using it.
This could involve using consistent colors, fonts, and design elements, as well as sticking to established design patterns and conventions.
Key Elements in UX Design
Several elements come together to form a holistic user experience. Let’s break down the building blocks of great UX design.
- Information Architecture: Information Architecture (IA) pertains to the organization and structure of a product's content. Good IA enables users to find the information they need swiftly and easily, improving the overall user experience.
- Interaction Design: Interaction design focuses on how users interact with a product, such as clicking buttons, scrolling, or swiping. Effective interaction design makes these interactions intuitive, efficient, and enjoyable for users.
- Visual Design: Visual design covers the aesthetic aspects of a product, such as colors, typography, and images. An appealing visual design can enhance the user experience by providing an engaging environment for users.
- Content Strategy: Content strategy involves planning, developing, and managing the content users interact with. It involves creating clear, concise, and consistent messaging that meets user needs and expectations and aligns with the overall goals of the product.
Tools and Techniques in UX Design
UX design relies on various tools and methods to bring concepts to life and refine them through testing and data analysis.
- Wireframing and Prototyping: Wireframing and prototyping are essential tools in the UX design process. Wireframes are simple, low-fidelity blueprints of a product's layout, while prototypes are more detailed and interactive versions for user testing and feedback.
- User Flows and Journey Maps: User flows and journey maps are visual diagrams of the steps users take when interacting with a product.
They help designers understand user navigation and identify potential pain points or areas for improvement.
- UX Metrics and Analytics: UX metrics and analytics involve collecting and analyzing data on user behavior, engagement, and satisfaction.
This data can inform design decisions, measure the success of a product, and pinpoint areas for improvement.
Trends and Best Practices in UX Design
To stay relevant, UX design must balance current trends with timeless principles and draw inspiration from a wealth of resources.
Current UX Design Trends
Staying in tune with current UX design trends can help designers create products that feel modern and relevant.
Some current trends include personalized experiences, voice interfaces, and immersive technologies like virtual and augmented reality.
Timeless UX Principles
While trends come and go, some UX principles are timeless. These include prioritizing the user, striving for simplicity, and focusing on usability and accessibility.
UX Design Resources and Inspiration
There are numerous resources available for UX designers to learn, find inspiration, and stay updated on the latest trends and best practices. These resources range from UX blogs, podcasts, and conferences to vibrant online communities.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is User Experience (UX) Design?
User Experience Design, often abbreviated as UX Design, is about creating user-friendly, efficient, and enjoyable interactions between a user and a product or service.
Why is UX Design Important?
Good UX design enhances user satisfaction. It makes a product easy to use, accessible, and enjoyable, leading to increased engagement, user retention, and conversion rates.
What's the Difference Between UX and UI Design?
UX design focuses on the overall user experience, including the journey and functionality, while UI design is about the visual elements like layout, colors, and typography.
What does a UX Designer do?
A UX Designer researches user needs, develops user personas, creates wireframes and prototypes, conducts usability testing, and continuously refines the product based on user feedback and analytics.
How Can I Improve UX Design?
Improving UX design involves user-centered design, conducting usability testing, ensuring accessibility and inclusivity, maintaining consistency, and continuously learning about UX trends and best practices.