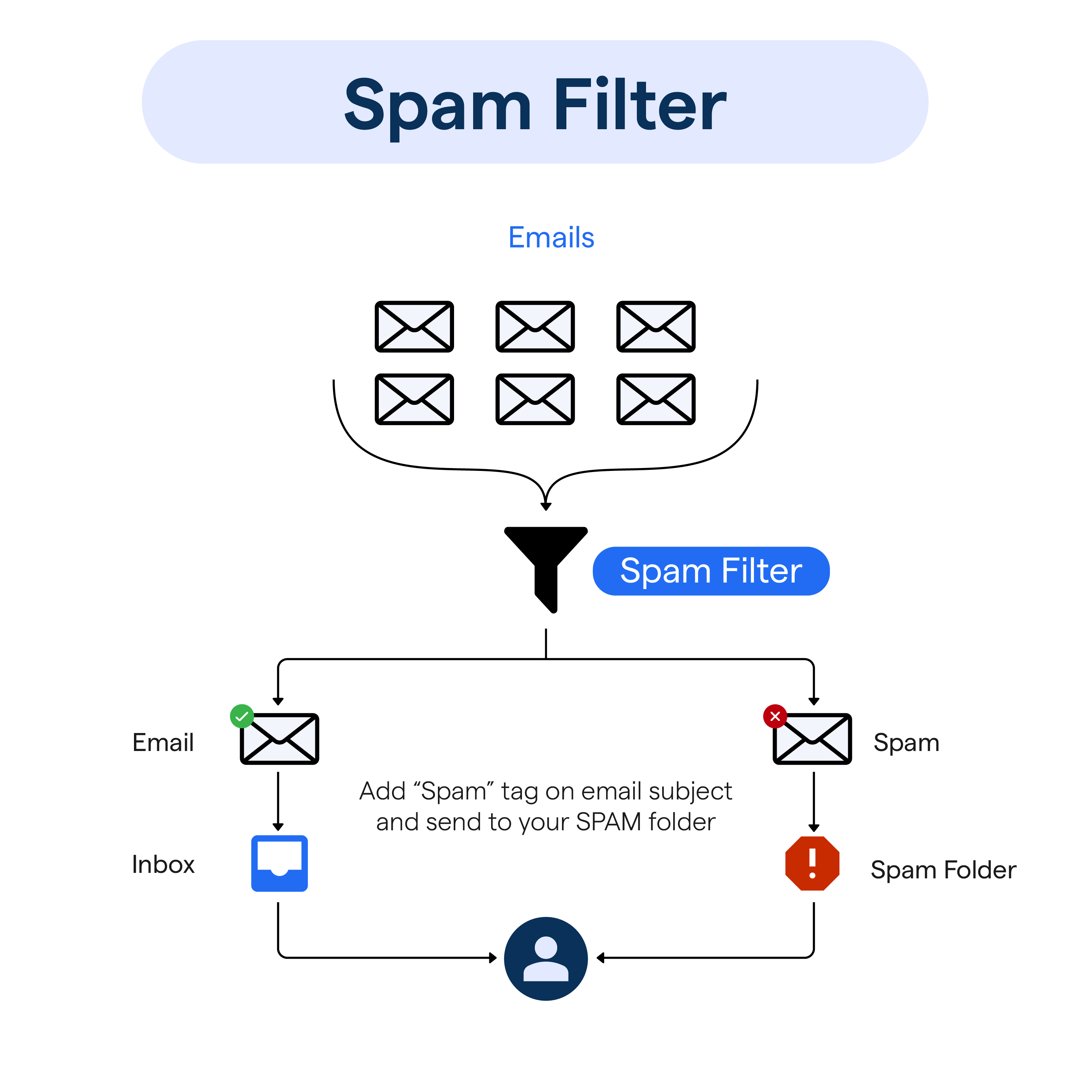
What is a Spam Filter?
Spam filters work by applying scrutiny through a set of protocols, in order to identify spam emails.
These protocols can involve various checks, including "watching" for certain words or phrases, observing senders' reputations, and detecting the mass distribution of identical messages, among other tactics.
Importance of Spam Filters
The consequence of a world without spam filters hardly needs explaining. Considering that more than half of all global email is spam, those unsolicited emails would make finding genuine emails laborious without efficient spam filtering.
Types of Spam Filters
There are several types of spam filters, each utilizing different strategies and technologies for flagging spam.
This includes content filters, header filters, general blacklist filters, rule-based filters, and more.
How Spam Filters Work
An email moves through multiple stages before landing in a user's inbox or the spam folder.
From analyzing the sender’s reputation to evaluating the email content and recipient interaction, every aspect plays a role.
Why Use Spam Filters?
Ever wondered why spam filters come in handy? Here's your answer.
Protects Against Malicious Content
Cybercriminals often use spam emails to spread malware. Spam filters can detect such malicious emails and prevent them from reaching the user’s inbox.
Saves Time and Resources
By identifying and separating spam from legitimate emails, spam filters save the user’s time and maintain the efficiency of their email management.
Preserves Server Space
Preventing spam emails from clogging the user's inbox indirectly preserves server space, leading to better overall performance of the email system.
Enhances Email Security Standards
Spam filters are an essential tool in the box of email security procedures, alongside antivirus software and firewall security.
Supports Compliance Regulations
For businesses, spam filters help in adhering to compliance regulations by preventing confidential information from getting compromised through spam emails.
Who Uses Spam Filters?
Any business or individual who regularly communicates via email will benefit greatly from spam filters.
Businesses and Organizations
Large corporations, SMEs, and non-profit organizations can use spam filters to protect their email communications from unwanted and potential phishing threats.
Email Service Providers
Email service providers like Gmail or Yahoo employ extensive spam filtering to protect their millions of users from the deluge of spam emails sent each day.
E-commerce Websites
E-commerce businesses often use spam filters to protect themselves and their customers from pesky, unwanted advertisements, and malicious content.
Internet Service Providers
ISP's deploy spam filters at the server level to block spam for all users in their network, improving Internet security.
Individuals
For individual email users, setting a spam filter is crucial in maintaining their inbox sanity and keeping cybersecurity threats at bay.
Where are Spam Filters Used?
From servers to individual mailboxes, spam filters find usage in various environments to enhance email security.
Server-Level Filtering
Spam filters can be used right at the entry stage, i.e., the mail server. Enterprise email servers often have spam filters to prevent malicious emails from getting into the network.
Email Client Filters
Email clients, like Outlook or Thunderbird, also have built-in spam filters. The user can adjust these filters as per their requirements for an individual mailbox.
Third-party Spam Filters
There are also specialized third-party applications, which can scan the emails in your inbox for spam. They can be used in addition to your email client's spam filter for extra protection.
Cloud-based Spam Filters
Cloud-based spam filters are a newer proposition offering extra convenience, capacity, and utility. They filter email before it is delivered to a user's email server.
Gateway Filters
These are hardware filters installed between the business network and the Internet Service Provider. They filter all incoming and outgoing network traffic, including emails.
When to Use Spam Filters?
Spam filters are always working in the background to protect your inbox. But there are specific scenarios where their role becomes even more crucial.
Receiving Bulk Unsolicited Emails
When you start receiving a high volume of unsolicited emails, this indicates it's time for a spam filter action.
Increased Phishing Threats
As cyber threats increase or become more sophisticated, the need for an effective spam filter becomes pressing.
Setting Up a New Email System
When setting up a new email system or server, it's a best practice to install and correctly configure spam filters right from the outset.
Regulation Changes
When privacy or security regulations change, businesses must tweak their spam filter settings to stay compliant.
Seasonal Malware Attacks
During certain seasons or events, spam and malware attacks tend to increase. For these periods, paying extra attention to spam filter performance is advised.
How to Implement Spam Filters?
For email users, implementing spam filters is usually straightforward. However, for businesses or server setups, some caution is necessary.
Check Current Filters
Check whether your email client or server already has a spam filter, and understand what it’s blocking.
Configure the Spam Filter
Set the filter rules as per your requirements. It could be as simple as marking certain sender's emails as spam or implementing complex filtering rules.
Train the Filter
Many spam filters are trainable. By marking messages as spam or not spam, the filter's effectiveness can improve over time.
Regularly Review Filter Performance
Check your spam folder regularly for any genuine emails marked as spam. Update your spam filter rules accordingly.
Employ Additional Layers of Security
Combine spam filters with antivirus software and firewall security for comprehensive protection against cyber threats.
Best Practices in Using Smart Responses
Before we journey through the best practices, remember this: the successful implementation of smart responses hinges on an understanding of the right methodology and avoiding common missteps.
Designing User-Friendly Conversations
Design user interactions as you would design a conversation with a friend. Keep smart responses human-like, engaging, and easy to understand. Technical jargon or overly formal language can confuse or frustrate users.
Offering Multichannel Support
Smart responses should be available across all customer touchpoints. Whether it's your website, mobile app, email, or social media, the user should be able to access the same level of service.
Maintaining Contextual Understanding
Ensuring smart responses remember previous user interactions and maintain a contextual understanding throughout a conversation helps create a smoother user experience. A system failing to recall previous inquiries or details can create frustration.
Implementing Escalation Procedures
There will inevitably be instances when a chatbot can't solve a query. A well-defined process must be set for escalating such conversations to live agents without causing any inconvenience to the user.
Ensuring Privacy and Security
As smart responses handle customer queries, they invariably deal with personal data. Ensuring the highest level of data privacy and security is an absolute must to maintain user trust and comply with regulations.
Challenges in Implementing Smart Responses
We are now shifting gears to talk about the roadblocks you might face with smart responses. Each challenge offers an opportunity to optimize your AI strategy.
Handling Misinterpretations
Despite advancements, smart responses may sometimes misinterpret user queries or intentions. This can lead to incorrect responses, causing user frustration and tarnishing the service experience.
Maintaining Up-to-date Information
Keeping the smart response system up-to-date with latest product updates, business rules, or regulatory changes is a significant challenge, especially for dynamically changing businesses.
Managing User Expectations
Managing user expectations is crucial. If users believe the chatbot can solve all issues (regardless of complexity), they may feel let down when it can't. Clearly defining what the chatbot can and can't do helps set realistic expectations.
Dealing with Sarcasm or Anger
While AI has improved significantly, it still finds understanding emotions, particularly negative ones or sarcasm, challenging. Dealing with an upset customer or handling a sarcastically phrased query is often better suited for human agents.
Implementing Advanced Features
Implementing features like sentiment analysis, user emotion detection, or predictive responses can be technically challenging and resource-intensive for several businesses.
Examples of Smart Responses
There’s no better way to understand smart responses than real-life examples that illustrate their potential in action.
eCommerce Customer Support
Consider an eCommerce platform where a user asks, "Can I return my order?" The smart response might be, "Yes, you can return your order within 30 days of purchase. Would you like help with the return process?"
Online Food Delivery
In an online food delivery app, if a user asks, "Where is my order?" the smart response might be, "Your order is on its way and will reach you in approximately 10 minutes. Would you like to track it on the map?"
Banking Support
In digital banking, a user might ask, "What's my account balance?" The smart response, ensuring utmost data security, might be, "Your current account balance is $5,230. Do you need help with any other banking services?"
Virtual Personal Assistant
In a virtual personal assistant scenario, if a user asks, "What's on my schedule today?" The smart response could be, "You have a team meeting at 10 AM, a dentist appointment at 2 PM, and dinner with Sara at 7 PM. Would you like reminders for these?"
Social Media Marketing
In a social media marketing scenario, a user might ask, "What's this product made of?" The smart response could be, "This product is made of 100% organic cotton. Would you like to know more about its sustainability practices?"
Trends in Spam Filtering
Like any technology, spam filtering sees continuous evolution. Here are a few trends shaping its future.
Machine Learning
Machine learning models are being utilized more to improve spam filter performance and deal with ever-more sophisticated spamming techniques.
Reputation-based Filtering
This technique is gaining popularity. It focuses on the sender's reputation instead of the email content for filtering spam.
Cloud-based Filters
Cloud-based filters are becoming the norm, due to their increased capacity and because they can be more effective at catching spam before it reaches the client's network.
Integration with Other Security Measures
Spam filters are increasingly being integrated with other security systems, like IDS/IPS, for a more comprehensive security approach.
Real-time Blacklist Providers
These services provide real-time information about IP addresses known to send spam, helping improve spam filter effectiveness and speed.
That's about it! One person’s annoyance may seem trivial, but multiply that across billions of people using email around the world, and you can see why spam filtering is an ever-evolving, crucial part of the modern online ecosystem.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
How do Spam Filters identify Unwanted Emails?
Spam filters use algorithms to identify patterns common in spam emails, such as specific keywords, sender reputation, and unusual sending behavior.
Can a Spam Filter be too aggressive?
Yes, overly aggressive spam filters can mistakenly categorize legitimate emails as spam, a situation known as a false positive.
What's the role of Machine Learning in Spam Filtering?
Machine learning improves spam filters by enabling them to learn from patterns in data and adapt to new types of spam over time.
Why should I regularly check my Spam Folder?
Regular checks can catch legitimate emails that were incorrectly marked as spam, ensuring you don't miss important communications.
Are Spam Filters Different across Email Providers?
Yes, different email providers may use various filtering techniques and algorithms, leading to differing effectiveness and rates of false positives/negatives.