What is a Private Cloud?
A private cloud is a type of cloud computing that delivers similar advantages to the public cloud, including scalability and self-service, but through a proprietary architecture dedicated solely to a single organization.
The Architecture of Private Cloud
The architecture of a private cloud largely depends on its deployment model. It can be hosted on-premises, externally hosted, or a mix of both and can be managed either internally or by a third-party service provider.
Different Types of Private Cloud
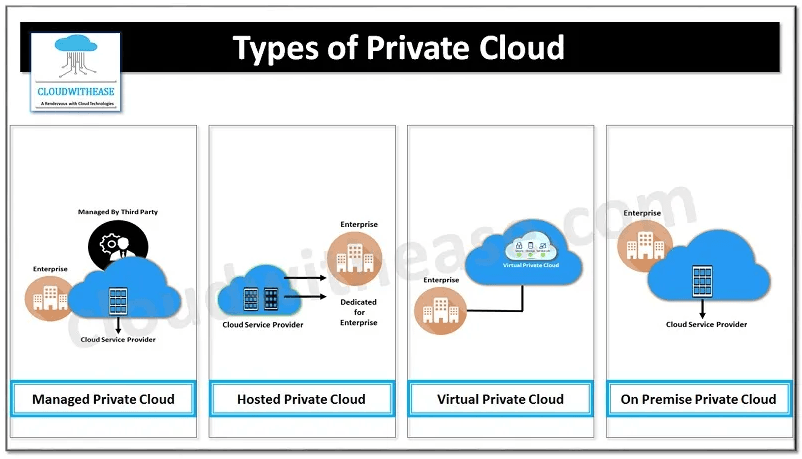
There are two primary types of private cloud: on-premises and externally hosted. The former is hosted within an organization's own infrastructure while the latter is provided by a cloud service provider.
Benefits of Private Cloud
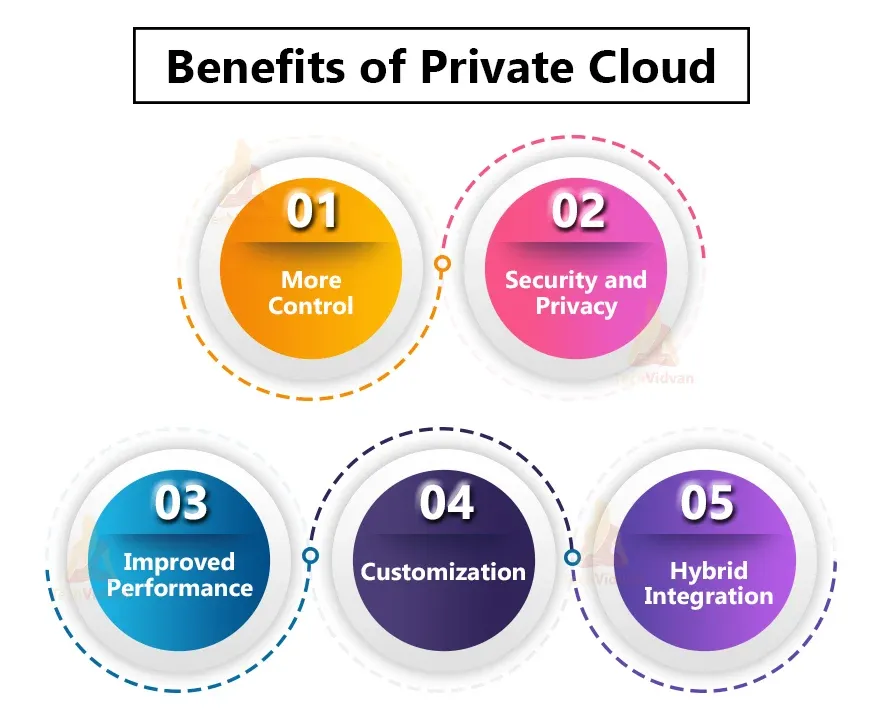
Let us now assess the unique advantages held by private cloud.
Enhanced Security and Privacy
With private cloud, the infrastructure is solely used by a single organization, providing enhanced security, privacy, and control, which is essential for handling sensitive data.
Customization
It allows for significant customization to match specific business requirements. Organizations have the freedom to tailor their environments to their specific needs.
Cost Efficiency
While private cloud can be more expensive initially, it can provide significant cost efficiencies in the long run, especially for businesses with predictable and steady demand for computing resources.
High-Level Control
With private cloud, organizations maintain a higher level of control over their cloud environment. They can decide the update cycle, the system's configurations and the security settings.
Challenges with Private Cloud
Despite its benefits, private cloud presents some challenges that businesses must be aware of.
- Higher Initial Costs: The initial costs of setting up a private cloud environment, including purchasing hardware and hiring dedicated IT personnel, can be considerably high.
- Maintenance Responsibility: The organization or the hired third-party are responsible for the constant maintenance, update, and security of the private cloud.
- Inflexibility: Private clouds are less flexible than public clouds in terms of capacity usage, especially for businesses with highly variable workloads.
- Dependency: There is a potential dependence on legacy systems, which can create transition challenges when migrating to a private cloud environment.
Difference Between Private Cloud and Other Types
Understanding how private cloud differs from other types of cloud services can help businesses decide the best fit.
Private Cloud vs Public Cloud
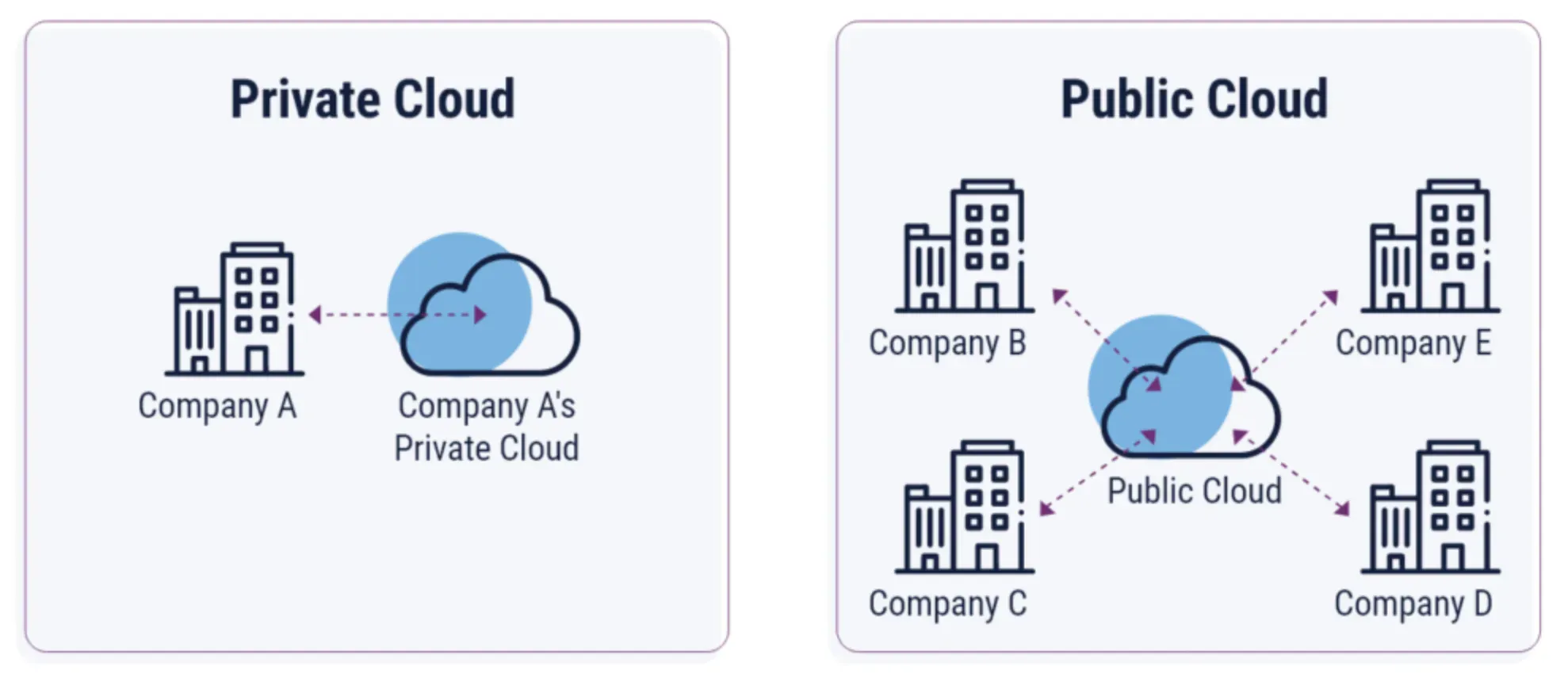
Unlike a public cloud, which serves multiple organizations, a private cloud is exclusive to one organization, providing more control and privacy.
Private Cloud vs Hybrid Cloud
A hybrid cloud model blends the use of private and public clouds. Organizations use the private cloud for sensitive tasks and the public cloud for high-volume, less sensitive tasks.
Private Cloud vs Multi-Cloud
While private cloud involves single-cloud environment, multi-cloud is the use of multiple cloud services from different vendors to accomplish diverse tasks.
Private Cloud vs Community Cloud
A community cloud serves an exclusive group of organizations with similar cloud requirements, unlike a private cloud that serves just one organization.
Use Cases of Private Cloud
To understand the practicality of private cloud, let's consider some of its common use cases.
- Large Enterprises: Large enterprises with sufficient resources and expertise leverage private cloud to gain complete control over their sensitive data.
- Regulated Industries: Highly regulated industries such as finance, healthcare, and government often use private cloud due to compliance regulations around data privacy.
- High-Performance Computing: For high-performance computing tasks that require extensive processing power, a private cloud can offer the needed customizable and dedicated resources.
- Software Development: In software development, private cloud provides a controlled and secure environment for development, testing, and deployment of software.
Managed Private Cloud
In the context of private cloud, there is another significant term: managed private cloud. Let's explore it further.
What is Managed Private Cloud?
Managed private cloud refers to a private cloud environment, where everyday operations like system performance monitoring, patch management, and backup services are handled by a third-party service provider.
Benefits
Managed private cloud unburdens businesses from daily IT management tasks, giving them more time to focus on strategic initiatives, it also ensures the private cloud is optimized for performance and security.
Service Level Agreement (SLA)
An SLA is a critical part of a managed private cloud. It outlines the services a provider will offer and their benchmarks.
Different Operations
Managed private cloud operations can include patch management, systems monitoring, backup and restore, and application performance monitoring, amongst others.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is the difference between private cloud and public cloud?
Private cloud is dedicated to a single organization, offering more control and customization, while public cloud is shared by multiple users and offers scalability and cost-efficiency.
How does private cloud ensure security and privacy?
Private cloud provides a dedicated and isolated environment accessed through secure network links, ensuring that sensitive data is protected from unauthorized access.
Can a small business benefit from private cloud?
Yes, small businesses can benefit from private cloud as it offers cost-effective solutions, enhanced security, and flexibility to scale their infrastructure according to their needs.
Is private cloud more expensive than public cloud?
Private cloud can have higher upfront costs due to infrastructure setup, but long-term costs can be lower. Assessing cost benefits should consider factors like usage patterns, scalability needs, and resource utilization.
Can I have a hybrid cloud with private cloud?
Yes, hybrid cloud combines private and public cloud environments, allowing organizations to utilize the benefits of both. It offers scalability, flexibility, and control over data placement, based on specific requirements.