Most customer service failures are not caused by a lack of effort. They happen because businesses respond in the wrong place.
Salesforce reports that 73% of customers expect companies to understand their needs and expectations, yet many businesses still rely on slow, channel-limited support models. When
customers cannot get timely responses through digital touchpoints, dissatisfaction builds quietly, and churn increases.
This shift has changed how modern businesses approach support. Phone-first models no longer match customer behavior. Digital, always-available service has become the baseline expectation.
That change defines digital customer service.
This guide explains what digital customer service means today, why it matters for retention and efficiency, and how businesses apply it across channels using practical strategies and real-world examples.
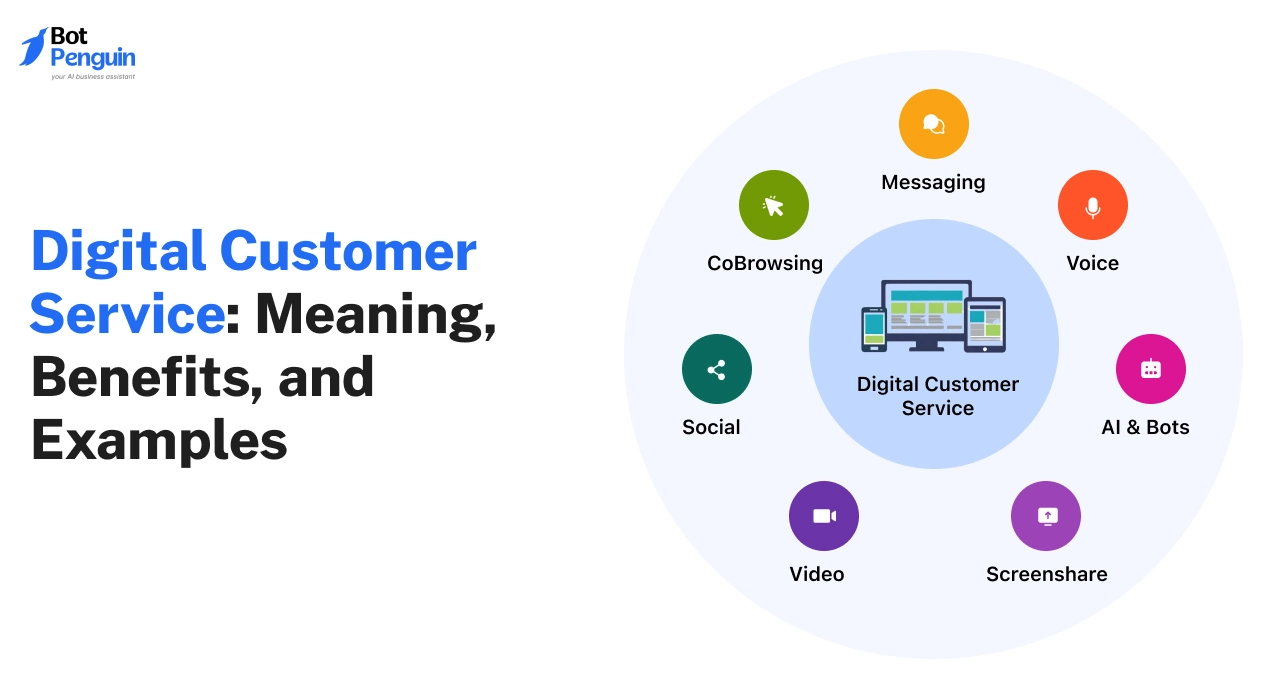
What is Digital Customer Service?
Digital customer service refers to supporting customers through channels such as live chat, messaging apps, email, social media, and self-service tools.
It enables faster responses, supports higher volumes, and maintains consistent experiences by combining automation, AI, and human assistance.
In practical terms, this could mean handling order updates through a messaging app, resolving common billing questions through automated chat, or routing complex issues to agents with full conversation context. Each interaction is designed to reduce wait time and limit unnecessary handoffs.
First, let's understand how it is different from traditional customer service.
Digital Customer Service vs Traditional Customer Service
Once what is digital customer service is clear, the difference between modern and legacy support models becomes easier to evaluate.
The contrast is not limited to channels alone. It affects response speed, operational capacity, and cost structure. Understanding these differences helps teams decide when digital-first models are necessary and where traditional methods fall short.
Key Differences Explained
In day-to-day operations, this difference is visible quickly. A customer checking delivery status through chat receives an immediate response.
In a phone-based model, the same request adds to call queues and agent workload. Over time, this gap compounds across thousands of interactions.
From a planning perspective, a digital customer service strategy allows support teams to design workflows around volume, not availability.
Channels are chosen based on customer behavior, not internal limitations. This is where digital customer service channels become a structural advantage rather than an optional upgrade.
These contrasts explain why many teams move away from traditional support as demand grows. The business impact becomes clearer when we examine why digital customer service matters for modern organizations, as addressed next.
What are the Benefits of Digital Customer Service?
The differences between modern and traditional support models lead to measurable outcomes. Once teams move away from phone-centric workflows, the impact shows up in speed, cost control, and experience quality.
These benefits are the reason digital customer service has become a core operational priority rather than an optional improvement.
Faster Response and Resolution Times
Digital channels reduce wait time at the first point of contact. Automated replies handle common questions instantly, while routing rules send complex issues to the right agent.
A customer asking about account access via chat receives guidance within seconds, rather than waiting in a call queue. Faster responses also shorten overall resolution time by keeping conversations focused and contextual.
Scalable Support Without Increasing Headcount
As interaction volume grows, traditional models require more agents. Digital systems scale differently. One automated workflow can resolve thousands of repetitive requests daily.
This allows teams to manage growth without expanding support staff at the same pace. A well-planned digital customer service strategy shifts agent effort toward high-value issues rather than routine queries.
Consistent Omnichannel Customer Experience
Customers rarely stay on one channel. They might start with chat, continue via email, and follow up via messaging apps.
79% of customers expect consistent interactions across departments, yet 55% say they feel they're communicating with separate departments rather than one company. (Source: Salesforce)
Digital platforms maintain context across touchpoints, preventing customers from repeating information. This consistency across digital customer service channels reduces friction and improves service reliability across the entire journey.
Improved Customer Satisfaction and Retention
Quick answers and fewer handoffs directly affect satisfaction. Customers value clarity and timely updates more than channel choice. When issues are resolved without delay, trust increases.
Over time, this leads to higher retention and fewer escalations, especially for support-heavy products and services.
Actionable Insights from Customer Conversations
Every digital interaction generates structured data. Support teams can analyze recurring issues, response performance, and customer sentiment.
These insights help improve workflows, product decisions, and knowledge content. Understanding patterns in conversations also clarifies what is working and where support needs adjustment.
Together, these benefits explain why businesses adopt digital models early in their growth cycle. The next step is to understand which channels enable these outcomes and how each channel fits within a modern support setup.
Digital Customer Service Channels Explained
The benefits of digital support only materialize when the right channels are used for the right purpose. Each channel plays a distinct operational role.
Together, they form the execution layer of a digital customer service strategy, shaping how quickly issues are resolved and how consistently customers are supported.
1. Live Chat and Website Messaging

Live chat is used during high intent moments such as product evaluation, onboarding, or checkout.
Customers initiate conversations when they face friction and expect immediate guidance.
How it Works in Practice
A visitor encountering friction on a pricing or signup page starts a chat and receives instant guidance.
Agents see page context and past interactions, which shortens resolution time. Asynchronous messaging allows replies without forcing customers to stay online.
Operational Value
- Immediate engagement
- Lower abandonment
- Fewer repeated questions
2. Messaging Apps: WhatsApp, Instagram and Facebook
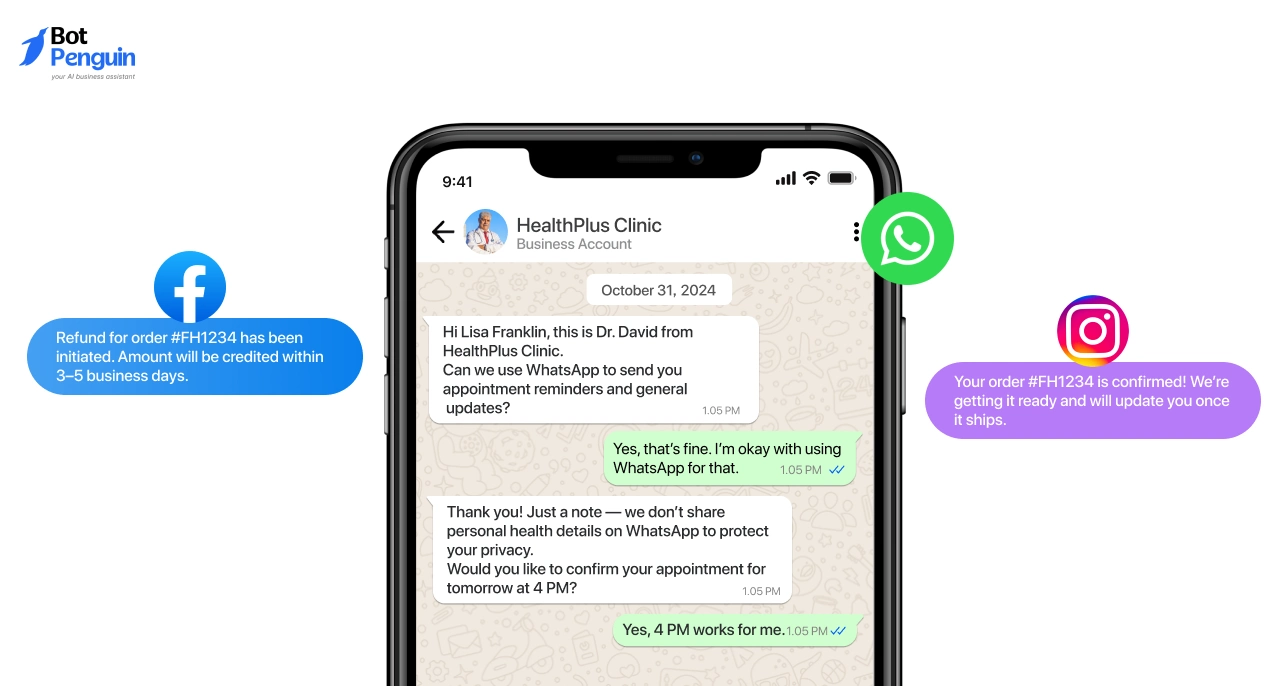
Messaging apps support ongoing conversations and transactional updates. Customers use these channels for order status, appointment confirmations, and short follow up questions.
How it Works in Practice
Customers check order status, confirm appointments, or ask quick questions through familiar apps.
Automated responses handle common requests while agents step in when context or judgment is required.
Operational Value
- High open rates
- Faster acknowledgment
- Lower support effort per interaction
3. Email and Ticket-Based Support
Email and ticket systems are suited for structured issues that require tracking, prioritization, and documentation.
This includes billing issues, account changes, and service requests.
How it Works in Practice
A customer submits a billing or account issue once. The ticket captures details, assigns priority, and tracks progress.
Automated confirmations reduce follow-ups while agents focus on resolution.
Operational Value
- Clear ownership
- Predictable workflows
- Better SLA management
4. Social Media Customer Support
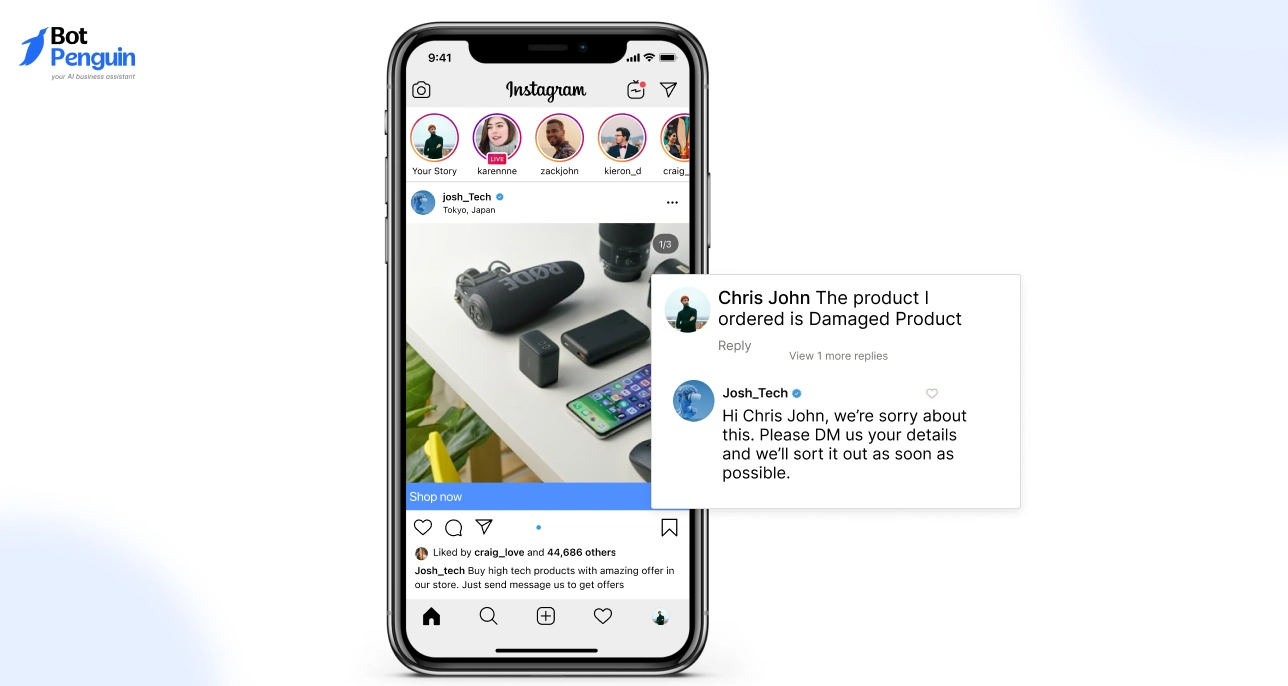
Social platforms handle both private concerns and public feedback.
Customers often raise issues through comments or direct messages, especially when responses are delayed elsewhere.
How it Works in Practice
Customers raise issues through comments or direct messages. Quick responses prevent escalation and protect brand credibility.
Patterns in public queries highlight gaps in product or communication.
Operational Value
- Reputation control
- Early issue detection
- Faster response visibility
5. Self-Service Portals and Knowledge Bases
Self-service tools address repeated questions and allow customers to resolve issues independently. FAQs and guides are available at all times and often deliver faster resolution than live support.
How it Works in Practice
Customers search FAQs or guides to resolve issues without contacting support. Well-structured content often delivers faster resolution than live interaction and reduces inbound volume.
Operational Value
- Lower ticket load
- Always available support
- Better agent focus
Each of these touchpoints answers a different customer need.
The next section explains how automation and AI connect these channels into a system that reduces effort while maintaining service quality.
Role of Automation and AI in Digital Customer Service
The channels outlined earlier create access. Automation and AI determine how efficiently that access is managed. Without automation, digital channels behave like faster versions of email.
With the right systems in place, they become structured, responsive, and scalable. This is where digital customer service moves from availability to operational control.
What is Automated Digital Customer Service?
Automated digital customer service refers to handling customer requests through predefined workflows, AI-based systems, and intelligent routing across digital channels.
It enables instant responses for common needs, consistent handling of requests, and escalation to human agents when complexity increases. Automation ensures support remains responsive even during high-volume periods.
In practice, this includes auto replies for order status, guided flows for account issues, and smart routing based on intent and urgency.
Automation does not replace agents. It filters and prepares conversations so agents work with context, not guesswork.
AI Chatbots vs Rule-Based Automation
AI chatbots are suited for open-ended questions where intent may vary. Rule-based systems work well for predictable flows like form submissions or basic confirmations.
Most mature teams use both as part of a broader digital customer service strategy.
When Automation Works Best vs When Humans are Needed
Automation performs best when questions are repetitive, time-sensitive, or informational. Examples include delivery updates, password resets, and appointment confirmations.
These interactions benefit from speed and consistency more than human judgment.
Human agents are essential when issues involve exceptions, emotional context, or decision-making. Billing disputes, account changes, and service complaints require understanding beyond predefined logic. Automation supports these cases by collecting details before handoff, reducing resolution time.
Used correctly, automation increases capacity without sacrificing quality. It allows teams to scale across digital customer service channels while reserving human effort for situations where it has the most impact.
This balance between automation and human support sets the foundation for building a structured service model. The next section explains how teams translate these capabilities into a practical implementation strategy.
Digital Customer Service Strategy
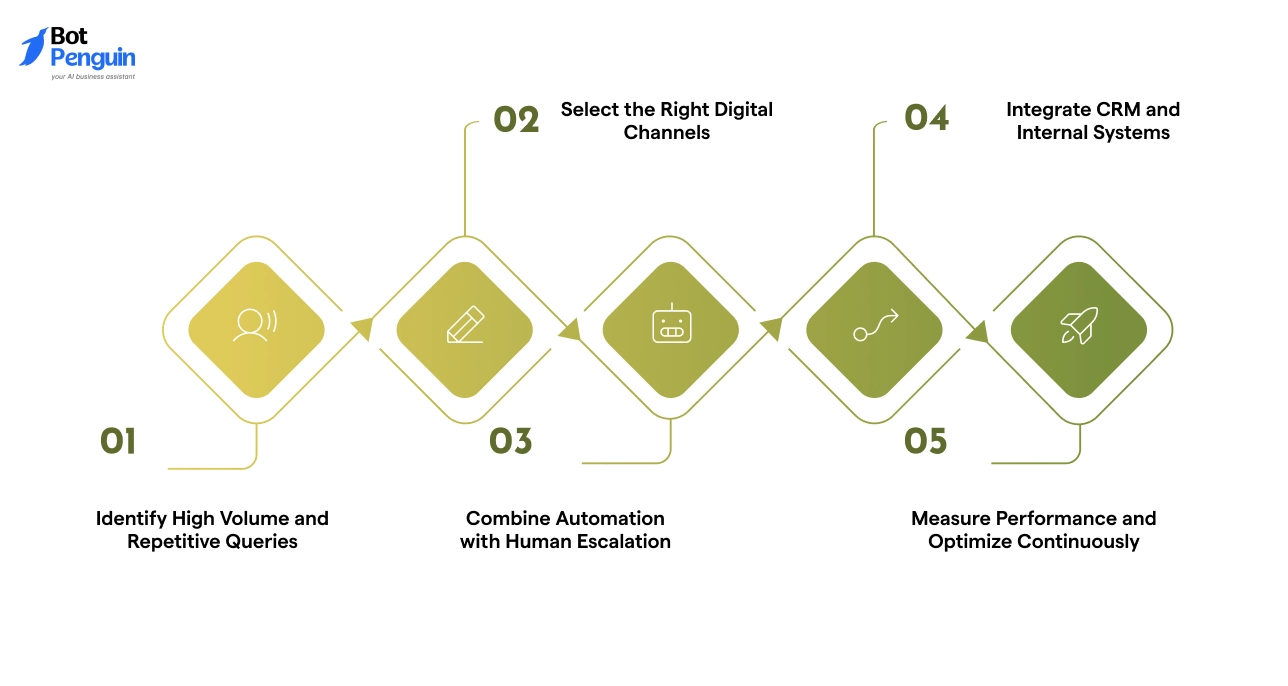
Automation and channels only deliver value when they are applied with structure. Without a clear plan, digital support becomes fragmented and difficult to scale.
A strong digital customer service strategy focuses on prioritization, channel intent, and continuous improvement. The steps below outline how mature teams design support models that perform consistently as demand grows.
Step 1: Identify High Volume and Repetitive Queries
Start by reviewing recent support conversations. Look for questions that appear frequently and follow predictable patterns. Examples include order status, password resets, billing dates, or appointment confirmations.
These interactions consume time but add limited value when handled manually. Identifying them creates the foundation for efficient automation.
Step 2: Select the Right Digital Channels
Not every query belongs on every channel. High urgency questions work better on chat or messaging apps. Detailed issues may require email or ticket based handling.
Channel selection should reflect customer behavior and query type, not internal preference. Aligning use cases with digital customer service channels reduces friction and improves response quality.
Step 3: Combine Automation with Human Escalation
Automation should handle the first layer of interaction. It collects context, validates intent, and resolves simple requests. When complexity increases, conversations must move to human agents without restarting the process.
This approach preserves speed while ensuring accountability. Teams that balance automation and escalation scale faster without lowering service standards.
Step 4: Integrate CRM and Internal Systems
Support conversations gain value when connected to customer data. Integrating CRM, order systems, and internal tools allows agents to view history, status, and previous interactions in one place.
This prevents repeated questions and shortens resolution time. Integration also enables consistent handling across channels within a unified digital customer service model.
Step 5: Measure Performance and Optimize Continuously
Strategy does not end at deployment. Teams should track response time, resolution rate, and customer satisfaction across channels.
Data patterns highlight gaps in workflows and content. Regular reviews help refine automation, update routing rules, and improve overall efficiency.
A structured strategy turns digital support into a predictable system rather than a reactive function. With this foundation in place, real-world examples show how different industries apply these principles at scale, which is explored next.
What are the Examples of Digital Customer Service?
Once a strategy is defined, its value becomes visible only when applied to real operating environments.
Different industries face different customer expectations, volumes, and constraints, yet the underlying principles of digital customer service remain consistent.
The following examples show how businesses apply these principles in practical, industry-specific scenarios.
SaaS Example: Onboarding and Technical Support
SaaS businesses receive a high volume of questions during onboarding and early product use. Users often ask about account setup, feature configuration, integrations, and permission settings.
Digital support handles these requests through in-app chat, contextual help content, and automated guidance tied to user actions.
Simple setup questions are resolved instantly through automation, while technical issues are routed to specialists with access to account history and usage data.
This structure reduces resolution time, improves activation rates, and allows support teams to scale without increasing headcount.
Ecommerce Example: Order Tracking and Returns
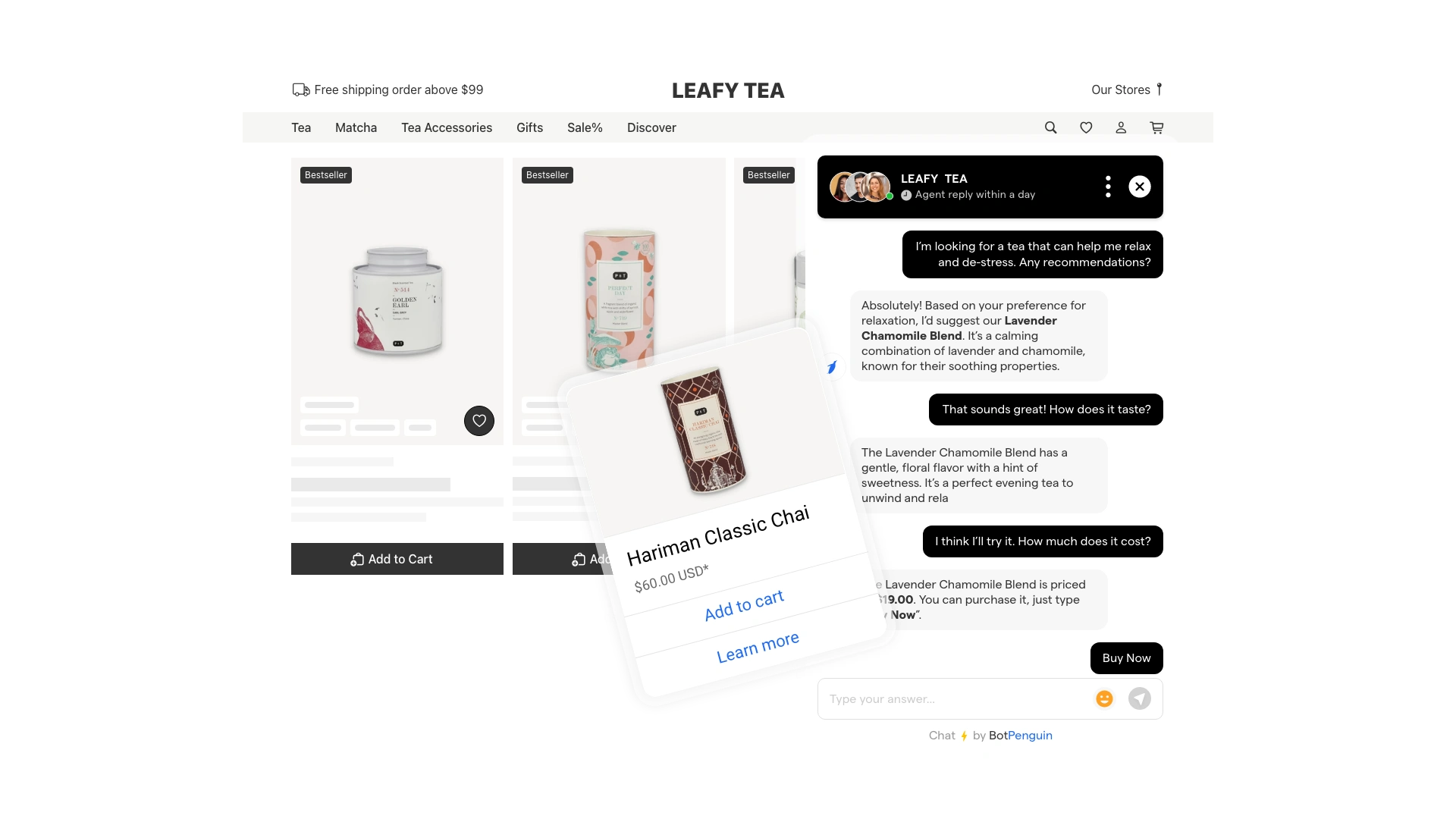
Ecommerce support is driven largely by transactional requests, including order tracking, delivery updates, cancellations, and returns.
Messaging-based support provides real-time updates that customers actively engage with, especially during peak shopping periods.
Automated workflows handle status checks and return eligibility, while exceptions such as delayed shipments or address changes are escalated to agents.
This use of digital customer service channels keeps response times predictable and prevents support queues from growing during high-demand cycles.
Healthcare Example: Appointment and FAQ Automation
Healthcare providers receive repeated inquiries about appointment scheduling, preparation instructions, clinic timings, and insurance documentation. Digital systems manage these through chat-based scheduling, automated reminders, and structured FAQs that are accessible at any time.
When conversations involve medical context or patient-specific details, they are routed to the appropriate staff member, with the relevant information already captured.
This model improves patient accessibility while reducing administrative burden and maintaining compliance standards.
Education Example: Student Support at Scale
Educational institutions support students across admissions, coursework, examinations, and administrative processes. Digital channels centralize these interactions and route questions based on category and urgency.
Automation addresses common queries about deadlines, account access, and course materials, while advisors focus on academic guidance and financial support. Conversation data helps institutions identify recurring issues and refine communication across departments.
These examples show how digital customer service adapts to industry needs without changing its core purpose.
The next section addresses the common challenges teams face when implementing these models and outlines how to address them effectively.
What are the Common Challenges in Digital Customer Service?
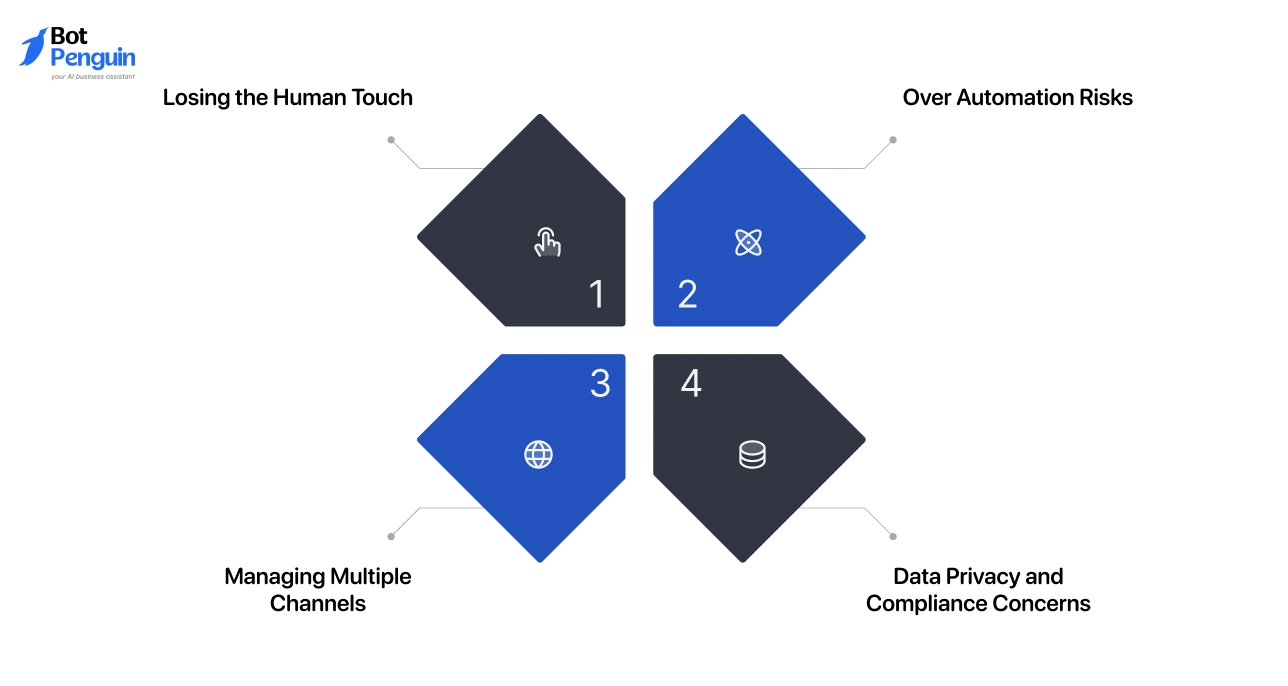
As teams move from planning to execution, recurring concerns tend to surface. These challenges appear when digital support begins to scale and customer expectations increase.
Addressing them early is critical for building a stable digital customer service model that delivers consistency without operational strain.
Losing the Human Touch
A common concern is that digital interactions feel impersonal over time. This typically occurs when automation is applied without context or escalation logic.
For example, a customer raising a billing issue may receive generic replies that ignore past conversations. The issue is not automation itself, but the lack of a seamless handoff to a human agent when judgment or reassurance is required.
Well-structured workflows preserve empathy by ensuring conversations move to agents with full context when complexity increases.
Over Automation Risks
Automation creates problems when it is applied without prioritization. Not every request should follow an automated path.
Complex cases, such as refund disputes or account modifications, often require explanation and decision-making. Forcing these through rigid flows increases frustration and resolution time.
A defined digital customer service strategy sets clear boundaries for automation and protects the overall experience.
Managing Multiple Channels
As support expands across chat, messaging apps, email, and social platforms, visibility becomes harder to maintain.
Without centralized tracking, conversations fragment and responses become inconsistent. A customer may receive different answers across channels for the same issue, creating confusion and repeated contact.
Centralized routing and shared history are essential for managing digital customer service channels with accuracy and accountability.
Data Privacy and Compliance Concerns
Digital interactions generate large volumes of customer data, including personal details and transaction history.
If this data is stored without proper controls, compliance risks increase. For instance, unsecured chat logs may expose sensitive information or violate retention policies.
Strong access controls, encryption, and data governance must be embedded into digital support systems from the start.
These challenges highlight why successful implementation depends on more than individual tools.
The next section focuses on how businesses evaluate platforms and capabilities to address these risks while supporting growth and scale.
Choosing the Right Digital Customer Service Platform
The challenges outlined earlier make one point clear. Tools determine outcomes. Even a well-planned approach fails if the platform cannot support scale, visibility, and control.
Choosing the right system is where digital customer service shifts from concept to execution, and where long-term efficiency is either enabled or limited.
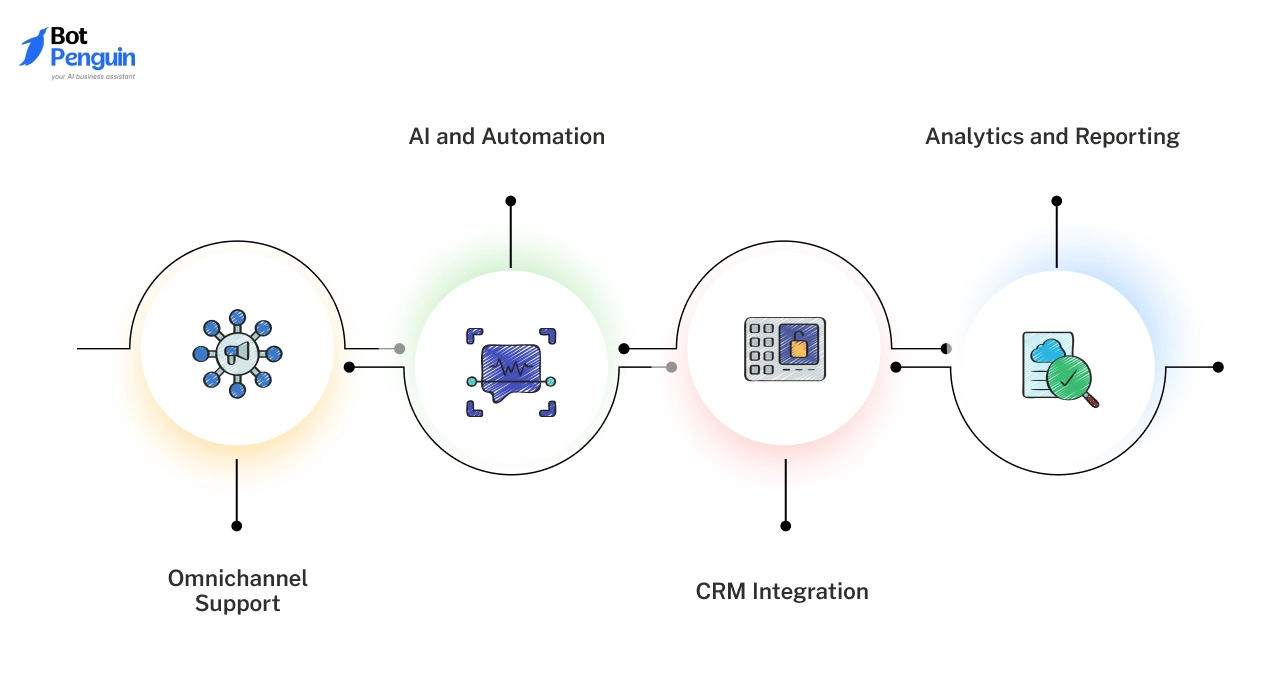
Omnichannel Support
A platform should unify conversations across chat, messaging apps, email, and social channels into a single interface.
This ensures customers receive consistent responses regardless of where they reach out. Without this, teams struggle to manage digital customer service channels as volume increases.
AI and Automation
Automation should go beyond basic replies. Look for intent detection, guided workflows, and intelligent routing that reduce manual effort while preserving context.
This capability directly supports faster resolution and predictable service levels.
CRM Integration
Customer data must be available during every interaction.
Integration with CRM and internal systems allows agents to view history, account status, and previous conversations in real time. This reduces repeated questions and shortens resolution cycles.
Analytics and Reporting
Visibility into response times, resolution rates, and conversation trends is essential.
Reporting helps teams identify gaps, refine workflows, and measure the effectiveness of their digital customer service strategy over time.
Building a Digital First Customer Service Model
At its core, digital customer service delivers faster resolution, predictable costs, and consistent experiences across touchpoints. When implemented correctly, it reduces customer friction and provides support teams with a clear structure for operating at scale.
A strong digital customer service strategy aligns channel selection, automation depth, and human involvement around measurable outcomes. Workflows respond to intent and urgency rather than to agent availability, improving reliability during growth and peak demand.
Future readiness depends on adaptability. Customer behavior continues to shift across messaging platforms, self-service tools, and real-time interactions. Systems built around flexible digital customer service channels can evolve without constant process redesign.
How BotPenguin Supports Scalable Digital Customer Service
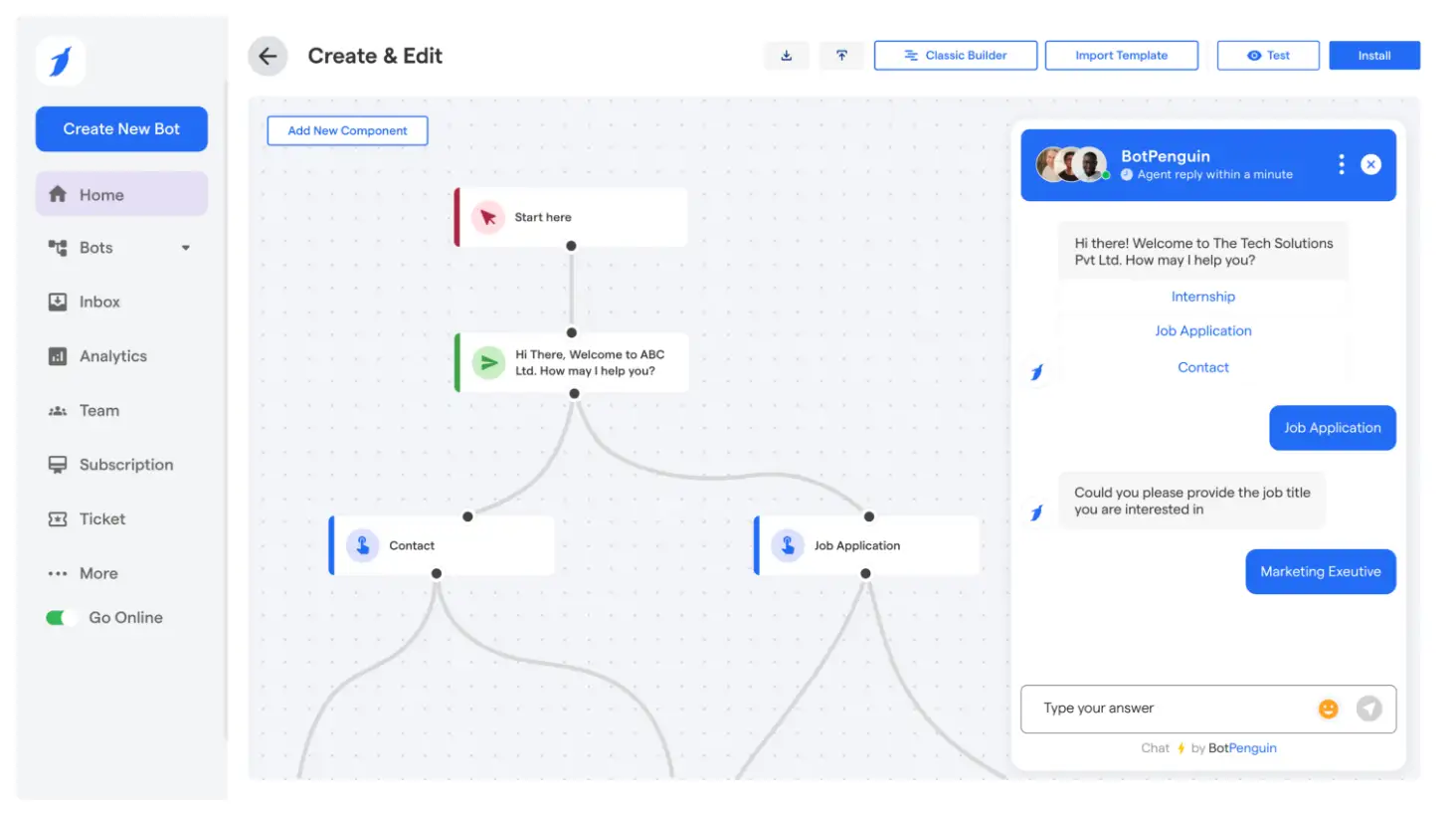
Platforms like BotPenguin are built to support this model in practice. By combining AI-driven automation, omnichannel conversation management, and CRM level context, teams can handle high interaction volumes without reducing response quality.
BotPenguin automates repetitive requests, escalates complex issues with context, and provides unified visibility across channels. This helps businesses maintain consistency as demand grows while retaining control over performance and outcomes.
For teams moving from evaluation to execution, choosing a platform designed for modern support models is a practical step toward sustainable, scalable digital customer service.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Is Digital Customer Service Suitable for Small Businesses?
Yes. Small teams benefit significantly because digital models reduce manual workload and support growth without immediate hiring.
Automation handles frequent requests, while agents focus on higher-value conversations. This allows smaller businesses to deliver reliable support without enterprise-level staffing or infrastructure.
How Does Digital Customer Service Support Omnichannel CX?
Digital support connects conversations across multiple channels into a single operational view. Customers can switch between chat, email, or messaging apps without restarting the conversation.
This continuity improves the customer experience and helps teams manage digital customer service channels with consistent responses and shared context.
How Do You Measure Digital Customer Service Success?
Success is measured using response time, resolution time, customer satisfaction, and interaction volume handled through automation.
Additional indicators include reduced ticket backlog and lower cost per interaction. These metrics help refine workflows and improve the overall digital customer service strategy.
How BotPenguin Fits into Digital Customer Service Adoption
BotPenguin supports modern support models by combining AI-driven automation, omnichannel conversation handling, and system integrations in one platform.
It helps teams automate repetitive requests, route complex issues to agents, and maintain visibility across interactions.
This enables businesses to apply the principles discussed throughout this guide in a structured and scalable way, aligning daily support operations with long-term customer experience goals.
What is Digital Customer Service Designed to Replace?
Digital customer service replaces phone first and email heavy support models by shifting customer interactions to digital touchpoints that support faster handling and higher volumes.