Most businesses already automate tasks, just not in a structured way. Spreadsheets, manual approvals, follow-ups, and handoffs quietly run daily operations.
As teams scale, these task-level workarounds start to fail. Delays increase, errors multiply, and automation tools added too early often create more complexity. AI task automation adds another layer of confusion when it is treated as a shortcut instead of a progression.
This guide explains task automation step by step. It covers what a business task is, how task automation works, where task automation tools fall short, and when AI task automation becomes necessary to scale without breaking operations.
What is a Business Task and Why Automation Starts Here
Automation works only when the unit of work is clearly defined. That unit is the business task.
What Qualifies as a Business Task
A business task is a single, repeatable action triggered by an event and completed when a clear outcome is achieved.
Examples include assigning a lead, approving a request, or updating a record. Tasks are predictable, trigger-based, and outcome-driven, which makes them suitable for automation.
Tasks vs Workflows vs Processes
A task is one action. A workflow is a sequence of tasks. A process is a broader system that may span teams, tools, and time.
Automating workflows or processes without isolating individual tasks often leads to rigid systems and fragile automation.
Why Automation Must Start at the Task Level
Starting at the task level provides control and clarity. Tasks are easier to standardize, measure, and optimize.
This granularity makes automation easier to scale without introducing unnecessary complexity.
What is Task Automation
Task automation is the use of software to execute repeatable business tasks when specific conditions are met automatically.
It focuses on removing routine, predictable work from day-to-day operations so teams can move faster and work more consistently.
Problems Task Automation Solves
- Manual effort: Repetitive tasks consume time and attention that could be spent on higher-value work.
- Delays and inconsistencies: Manual handoffs depend on availability and memory, leading to uneven execution.
- Human error: Tasks involving data entry or multiple steps are prone to mistakes when handled manually.
What Task Automation Does Not Replace
Task automation does not replace strategic decision-making or human judgment in complex scenarios.
It supports teams by handling predictable execution, not by making critical business decisions.
How Does Task Automation Work Step by Step
Task automation works by moving a task through a simple chain: a trigger happens, rules decide what to do, systems execute the action, and humans step in only when needed.
This structure is why automation can speed up work without sacrificing control.
Triggers and Events
A trigger is the moment that starts the automation. Triggers can be manual or automated.
- Manual triggers: Happen when someone clicks a button, submits a form, or selects an option like “approve” or “assign.”
- Automated triggers: Happen when a system detects an event, such as a new lead being created or an invoice becoming overdue.
Common triggers include:
- A customer submits a form or message
- A ticket is created or updated
- A lead enters a specific pipeline stage
- A payment fails or succeeds
- A deadline is reached
Rules and Conditions
Once the trigger fires, the system checks rules and conditions. These rules are the logic that determines what should happen next. They are usually deterministic, meaning the same input should lead to the same output.
Examples include:
- If the lead is from a specific country, route to the right sales rep
- If the ticket includes a billing keyword, tag it as billing
- If a customer is a high priority, mark the case urgent
System Actions and Execution
After rules decide the path, automation performs the action across tools.
Typical actions include:
- Data updates like updating a CRM field, changing ticket status, adding tags, or logging a note
- Notifications and handoffs like sending an email or WhatsApp update, alerting a team in Slack, assigning ownership, or creating a follow-up task
Human Review and Exception Handling
Even good automation needs oversight. Human review is used when the system detects uncertainty, risk, or exceptions.
Escalation scenarios include:
- Missing or conflicting information
- Requests involving refunds, disputes, or compliance
- High-value deals that need approval
- Situations where the automation confidence is low
This is how task automation stays fast while still remaining safe and reliable at scale.
What are Task Automation Tools and What Do They Do
Task automation tools are software platforms that automatically execute repeatable tasks when predefined conditions are met.
They turn task automation logic into action by handling routine work such as assignments, updates, notifications, and follow-ups.
These tools focus on consistent execution rather than decision-making, making them a practical starting point before adopting AI task automation.
Core Capabilities of Task Automation Tools
Most task automation tools are built around a few essential capabilities:
- Workflow builders that allow users to define how a task moves from trigger to completion using rules and step-by-step logic.
- Triggers and integrations that connect the tool with other systems so tasks can start based on events like form submissions, status changes, or data updates.
Common Types of Task Automation Tools
Task automation tools generally fall into these categories:
- Workflow automation platforms that manage rule-based task execution across connected systems.
- RPA-style tools that automate tasks by mimicking human actions within user interfaces.
- No-code automation tools that help non-technical users build simple automations quickly.
Some platforms add limited AI features and are often positioned as AI tools for automating tasks, though most still rely on predefined rules.
Where Task Automation Tools Work Best
Task automation tools work best for low-variability tasks and stable, predictable processes, where consistent inputs lead to consistent outcomes.
Limitations of Traditional Task Automation
Traditional task automation is effective for simple, predictable work, but its limitations become clear as operations grow more complex.
Most task automation tools rely on fixed rules, which makes them difficult to adapt when inputs, exceptions, or business needs change.
Rigid Workflows and Rule Explosion
Rule-based automation depends on predefined paths. As new scenarios appear, more rules are added to handle them.
Over time, this creates maintenance overhead and tightly coupled workflows. Small changes can cause failures elsewhere, making automation fragile at scale.
Poor Exception Handling
Traditional task automation struggles with edge cases that fall outside predefined logic.
When inputs are incomplete or ambiguous, automations fail silently or require manual intervention, reducing efficiency. As exceptions increase, teams spend more time managing automation than benefiting from it.
Scaling and Governance Challenges
As multiple teams adopt task automation tools, tool sprawl becomes common. Automations are created in isolation, with limited visibility into ownership, performance, or impact. Without governance, automation becomes difficult to manage, audit, and scale safely.
These limitations are not flaws in automation itself, but signs that rule-based task automation has reached its ceiling and needs a more adaptive approach.
What is AI Task Automation
AI task automation enhances traditional task automation by allowing systems to understand context and make decisions, not just follow rules.
Instead of relying only on predefined logic, AI uses patterns and learning to handle tasks when inputs are variable or incomplete.
Unlike rule-based task automation tools, AI task automation can work with unstructured data such as text, intent, or sentiment.
This reduces the need for constant manual intervention when exceptions occur. As a result, AI tools for automating tasks can complete more work autonomously while escalating only when confidence is low or risk is high.
AI task automation does not replace human judgment or existing automation. It extends them by making task execution more adaptive and resilient as complexity grows.
How Does AI Task Automation Work
AI task automation works as a layered system where understanding comes first, decisions follow, execution happens across tools, and humans step in only when required.
Instead of relying on fixed rules, it evaluates context at every stage, which allows automation to function reliably in real operational environments.
Step 1: Input Interpretation
- Inputs arrive from forms, messages, tickets, or system events
- AI identifies intent, key data points, and priority
- Unstructured inputs, like text or mixed information,n are processed without requiring rigid formats
This step allows automation to start even when data is incomplete or inconsistent.
Step 2: Contextual Decision Evaluation
- The system evaluates intent, urgency, historical patterns, and confidence
- Decisions are based on probability and relevance, not only predefined rules
- Multiple factors are assessed together instead of simple if conditions
This is where AI task automation moves beyond traditional task automation tools.
Step 3: Task Execution Across Systems
- Actions are carried out through connected systems and integrations
- Common actions include record updates, routing, notifications, and follow-ups
- Execution remains structured even though decisions are adaptive
Most AI tools for automating tasks reuse existing automation infrastructure at this stage.
Step 4: Confidence-Based Escalation
- High-confidence tasks are completed automatically. Low-confidence or high-risk tasks are routed for human review
- Oversight is applied only where it adds value
This ensures control without slowing down routine execution.
AI task automation works by adding intelligence before execution, allowing automation to scale while remaining accurate, controlled, and measurable.
Task Automation Tools vs AI Task Automation
As automation matures, the key question is no longer whether to automate, but how.
Understanding the difference between traditional task automation tools and AI task automation helps teams choose the right approach based on complexity, scale, and variability.
Traditional task automation tools work well when processes are consistent and outcomes are predictable. AI task automation becomes necessary when variability increases, and decision points cannot be reliably handled by rules alone.
Choosing between them is not about replacing one with the other, but about applying the right level of intelligence where complexity demands it.
Benefits of AI Task Automation
AI task automation delivers value where traditional task automation tools begin to struggle.
Adding context awareness and adaptive decision making improves both operational efficiency and reliability as complexity increases.
Handles Variability Without Constant Rework
AI task automation can manage changing inputs, incomplete data, and unstructured information without requiring new rules for every scenario.
This reduces the need for frequent manual updates and ongoing rule maintenance.
Reduces Manual Intervention
Tasks that previously required human review due to exceptions can often be completed autonomously.
Human involvement is reserved for low confidence or high-risk situations, which improves focus and productivity.
Improves Speed and Consistency
Decisions and actions happen in real time once inputs are received.
This removes delays caused by handoffs, availability, or prioritization issues, while maintaining consistent execution across tasks.
Scales Without Increasing Complexity
As volume grows, AI task automation does not rely on adding more rules or workflows. This makes it easier to scale operations without increasing system fragility or operational overhead.
Enhances Decision Quality Over Time
AI tools for automating tasks learn from historical outcomes and feedback. This allows decision accuracy to improve gradually, leading to better task routing, prioritization, and execution.
AI task automation allows businesses to automate not just execution, but decision points, making automation more resilient as operations grow.
How to Get Started With AI Task Automation
Getting started with AI task automation does not require replacing existing systems or automating everything at once.
The most effective approach is incremental, focused, and grounded in operational reality.
Start With High-Friction Tasks
Begin by identifying tasks that frequently slow teams down due to variability, manual review, or repeated exceptions.
These are often tasks where traditional task automation tools already exist but require constant human intervention.
Define Decision Boundaries Clearly
Before introducing AI, define where automated decisions are acceptable and where human approval is required.
Clear boundaries ensure AI task automation operates within safe and measurable limits from the start.
Use AI Alongside Existing Automation
AI task automation works best when layered on top of existing task automation.
Let AI handle interpretation and decision-making while execution continues through current systems and integrations.
Monitor Confidence and Outcomes
Track where AI completes tasks autonomously and where escalation occurs. Reviewing these patterns helps refine confidence thresholds and improve reliability over time.
Expand Gradually Based on Results
Once AI task automation proves reliable in one area, extend it to similar tasks with higher volume or complexity. Scaling should be driven by performance data, not assumptions.
A successful start focuses on control first, learning second, and scale last.
How Can Businesses Measure the ROI of AI Task Automation
Measuring the ROI of AI task automation requires focusing on operational impact, not just cost savings.
Because AI task automation affects both execution and decision making, ROI should be evaluated across efficiency, quality, and scalability.
Measure Time Saved Per Task
Start by comparing how long a task took before automation versus after AI task automation.
This includes time spent on manual execution and time spent reviewing exceptions. Reduced handling time is often the fastest and clearest ROI indicator.
Track Reduction in Manual Intervention
One of the biggest gains from AI task automation is fewer escalations. Measure how often tasks required human involvement before and after automation.
A steady decline shows that AI tools for automating tasks are handling variability effectively.
Monitor Error and Rework Rates
Errors caused by manual execution or incorrect routing create hidden costs.
Track reductions in rework, corrections, or customer follow-ups after automation is introduced. Improved accuracy directly contributes to ROI.
Evaluate Throughput and Capacity Gains
AI task automation allows teams to handle more volume without adding headcount. Compare task completion rates and workload per employee to understand how automation increases operational capacity.
Connect Outcomes to Business Metrics
Finally, link automation performance to business results such as faster response times, improved customer satisfaction, or reduced operational costs. ROI becomes clear when automation outcomes align with measurable business goals.
Effective ROI measurement focuses on sustained efficiency and scalability, not short-term automation wins.
Common Task Automation Tools Used by Businesses
Once organizations understand how task automation works and where its limitations appear, the next step is choosing the right tools.
Different task automation tools serve different purposes depending on task complexity, system maturity, and variability. Most businesses use a combination of these tools as they move from basic automation toward AI task automation.
Workflow Automation Tools
Workflow automation tools are designed to automate rule-based tasks across connected applications using triggers and actions.
They focus on predictable execution rather than contextual decision making, making them suitable for structured and repeatable workflows.
These tools are commonly used for lead routing, record updates, notifications, and simple task orchestration across multiple systems.
They perform best when inputs are structured, rules are stable, and outcomes are consistent, which makes them a foundational layer before moving toward AI task automation.
RPA Task Automation Tools
RPA task automation tools automate tasks by mimicking human actions inside software interfaces. They interact with screens, fields, and buttons, which makes them useful when direct integrations are unavailable.
RPA tools are commonly used for legacy systems, repetitive administrative work, and interface-level automation. They are effective for structured tasks but require ongoing maintenance as interfaces or layouts change.
AI Task Automation Tools
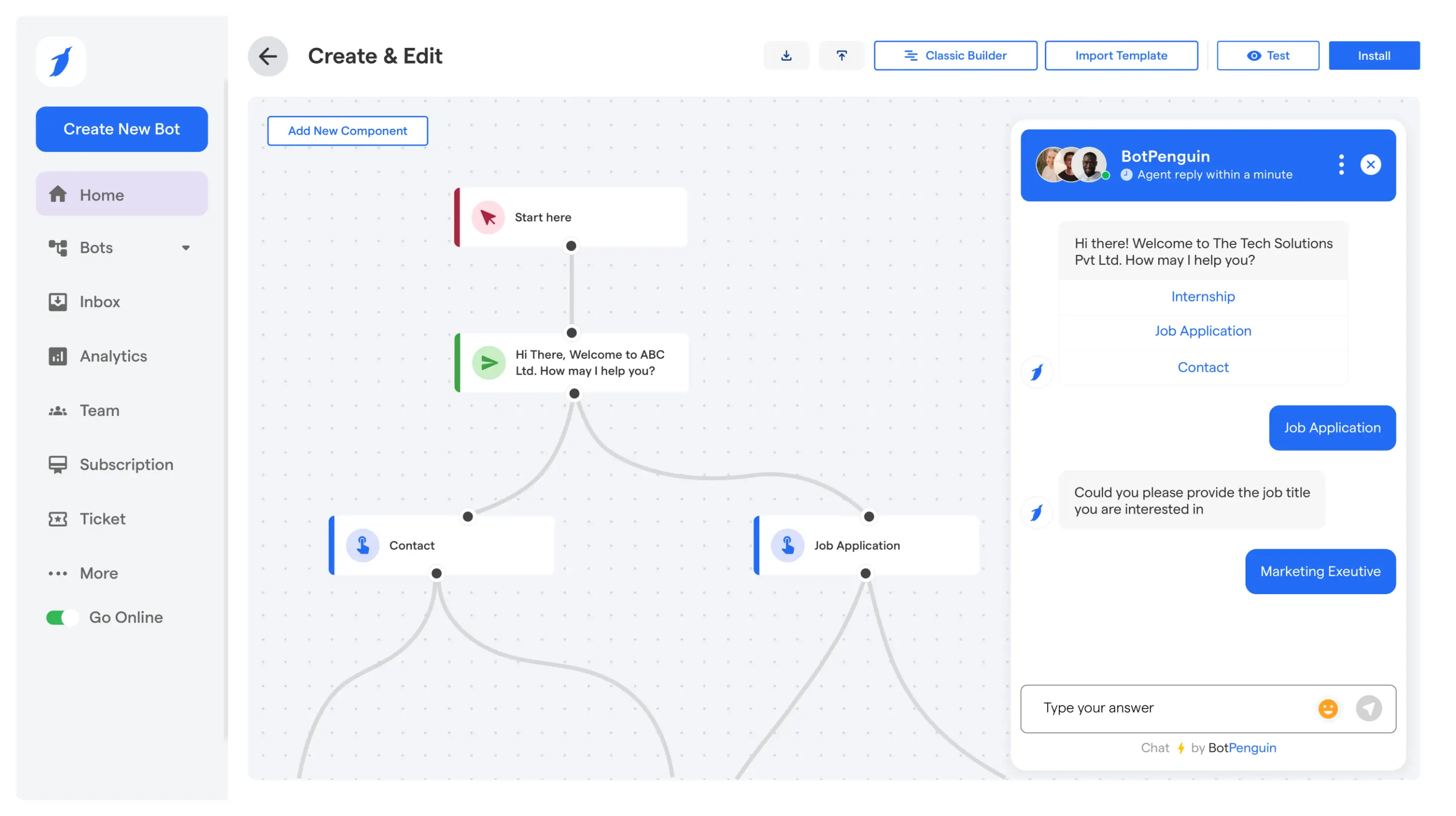
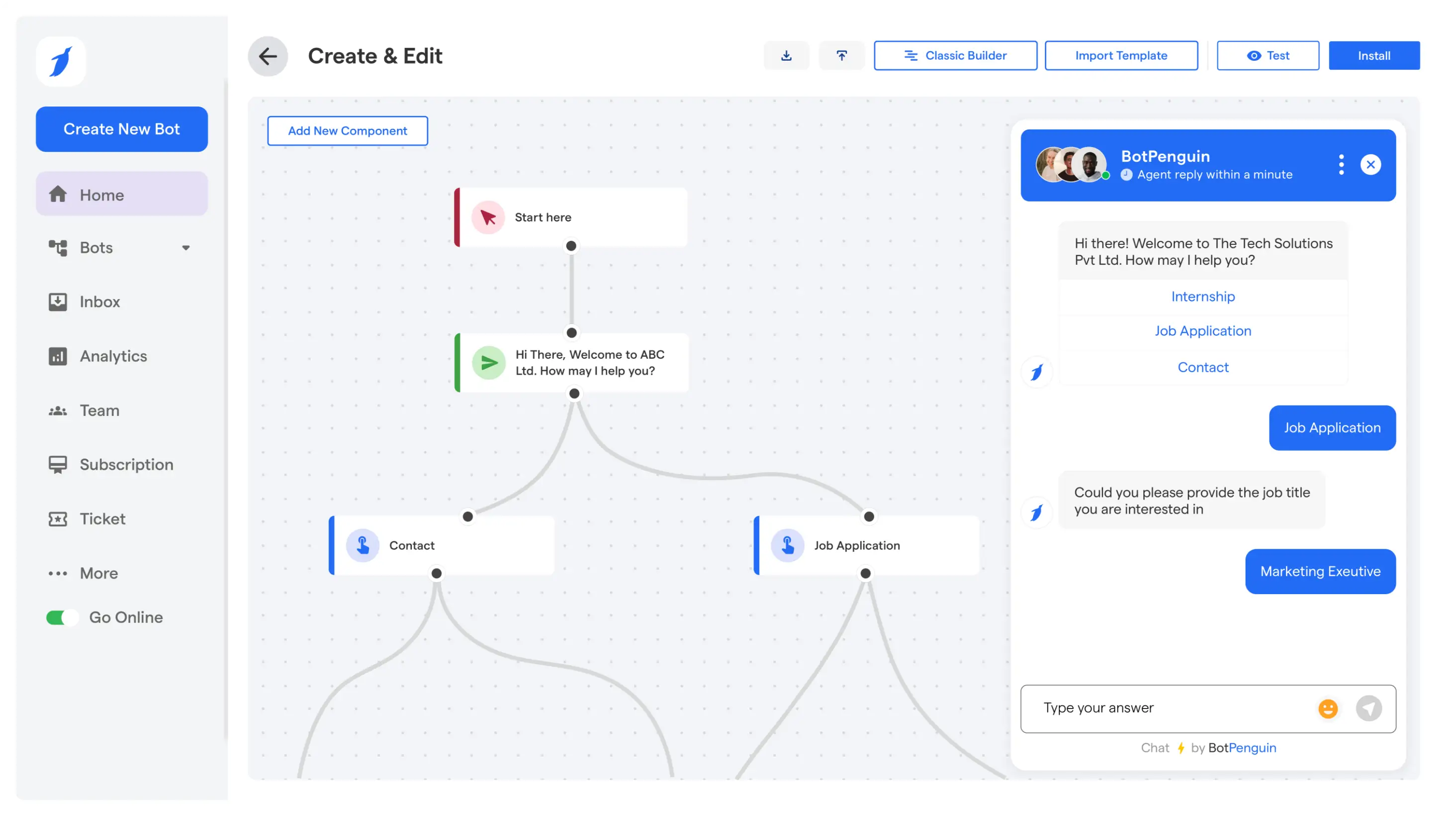
AI task automation tools introduce context awareness and decision-making into automation. Instead of executing tasks only through predefined rules, these tools evaluate intent, confidence, and relevance before acting.
These AI tools for automating tasks handle intent detection, task routing, escalation, and execution across customer-facing and internal workflows.
They are most effective when variability, volume, and decision complexity make rule-based task automation tools insufficient.
AI Task Automation Tool That Businesses Can Deploy in 24 Hours
AI task automation becomes valuable only when it fits naturally into how businesses already communicate, sell, and support customers.
Platforms like BotPenguin focus on embedding AI task automation directly into everyday business workflows across chat, messaging, and internal systems.
Instead of treating automation as a backend project, BotPenguin brings AI task automation closer to real operational touchpoints where tasks actually originate.
AI Agents Across Business Workflows
BotPenguin enables AI task automation through AI agents deployed across multiple channels and use cases.
👉 What this looks like in practice:
- AI agents handle tasks across website chat, WhatsApp, Instagram, and other messaging channels
- Tasks such as lead qualification, ticket creation, routing, follow-ups, and status updates are managed end-to-end
- AI agents adapt responses and actions based on user intent, conversation context, and confidence
📌 Impact: tasks move forward automatically from conversations without manual handoffs.
Integration With Existing Systems 🔗
A major strength of BotPenguin is its ability to work with existing business tools rather than replace them.
📌 Impact: AI task automation extends current task automation tools instead of adding a disconnected layer.
Visibility, Control, and Governance
For AI task automation to scale safely, teams need visibility and control. BotPenguin provides clear oversight into how tasks are handled.
👉 Governance capabilities include:
- Confidence-based escalation to human agents
- Clear tracking of task triggers, decisions, and outcomes
- Centralized management of AI agents and workflows
- Defined ownership across teams
📌 Impact: AI tools for automating tasks remain transparent, auditable, and trusted by teams.
Quick Snapshot 📊
Platforms like BotPenguin make AI task automation operational by connecting intelligent decision making directly to customer conversations and internal systems, without sacrificing control or visibility.
Final Thoughts
Task automation is not just about speeding up work. It is about creating consistency and reliability in how tasks are executed across an organization.
When task automation is introduced without clarity, or when task automation tools are applied too early, complexity often increases instead of efficiency.
Traditional task automation tools remain effective for stable, predictable tasks. As variability, exceptions, and decision points increase, AI task automation becomes necessary to maintain accuracy and control.
This is where AI tools for automating tasks add value by handling context, reducing manual intervention, and improving decision quality over time.
The most effective automation strategies combine task automation and AI task automation in the right sequence. When applied thoughtfully, they help businesses scale operations without constant rework, fragile workflows, or loss of visibility.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
How Does Task Automation Impact Cross-Team Collaboration in Growing Businesses
Task automation improves coordination by standardizing handoffs between teams, reducing dependency on manual follow-ups, and improving visibility across shared operational tasks.
When Do Task Automation Tools Become Difficult to Manage at Scale
Task automation tools become harder to manage when rule sets grow rapidly, ownership is unclear, and multiple teams create automations without centralized governance.
Can AI Task Automation Work Alongside Legacy Systems Without Replacements
Yes. AI task automation can sit on top of existing systems, handling decision logic while execution continues through legacy tools and integrations.
What Security Considerations Should Businesses Evaluate Before Using AI Tools for Automating Tasks?
Businesses should review data access controls, audit logs, escalation rules, and compliance handling to ensure AI tools for automating tasks operate within governance and security boundaries.
How Does AI Task Automation Affect Operational Costs Over Time
AI task automation typically lowers long-term costs by reducing manual intervention, limiting rework, and allowing teams to handle higher volume without proportional headcount growth.
How Does BotPenguin Support AI Task Automation Across Customer-Facing Workflows?
BotPenguin enables AI task automation by turning conversations into structured tasks, routing actions across systems, and providing visibility and control over automated execution.