What is Robotic Process Automation (RPA)?
Robotic Process Automation (RPA) is an emerging technology that automates repetitive and rule-based tasks, allowing organizations to streamline their operations and improve efficiency. By using software robots or "bots," RPA mimics human actions within a digital system to execute tasks like data entry, data validation, and data extraction.
AI robotics process automation offers several benefits, including increased productivity, improved accuracy, reduced costs, efficiency of repetitive tasks, and enhanced customer experience.
In this comprehensive glossary page, we will explore the ins and outs of RPA and provide you with in-depth knowledge to help you navigate this exciting field.
What are the Benefits of Robotic Process Automation (RPA)?
Robotic Process Automation (RPA) streamlines repetitive tasks, enhances efficiency, and reduces operational costs. This section explores its key benefits, highlighting how RPA transforms business processes and boosts productivity across various industries.
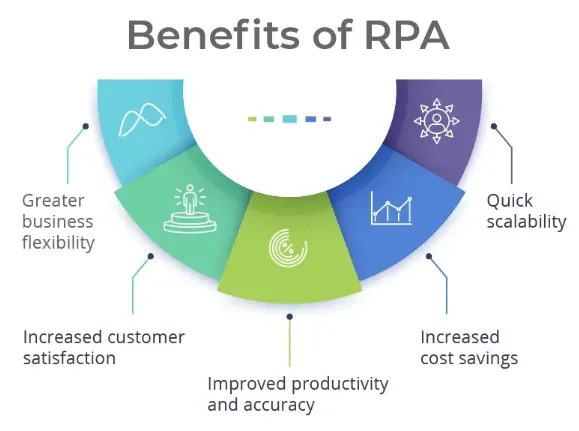
Increased Productivity
AI robotics process automation simplifies and accelerates task execution, allowing organizations to accomplish more with fewer resources. Automating the efficiency of repetitive tasks allows employees to focus on more strategic, creative, and customer-centric endeavors.
Enhanced Efficiency
The implementation of Robotic Process Automation (RPA) reduces the potential for errors in tasks. Unlike humans, robots are immune to fatigue and are less likely to make mistakes, resulting in greater efficiency and the delivery of higher-quality results.
Improved Compliance
Robotic Process Automation (RPA) ensures that all tasks are performed with efficiency to the specified rules and regulations. It keeps a detailed log of every action that can be reviewed for compliance purposes, increasing transparency and accountability.
Cost Savings
With the automation of repetitive tasks, AI robotics process automation can significantly reduce operational expenditure. With decreased reliance on manual input, organizations can direct funds saved from labor costs to other strategic and growth-focused areas.
Scalability
One of the significant benefits of RPA is its scalability. As business requirements change or volumes increase, RPA systems can be easily adjusted, scaled up, or scaled down, thereby providing a highly flexible solution to meet evolving business demands.
How does Robotic Process Automation (RPA) Work?
Robotic Process Automation (RPA) simplifies workflows by automating repetitive tasks and mimicking human interactions with software bots to enhance efficiency.
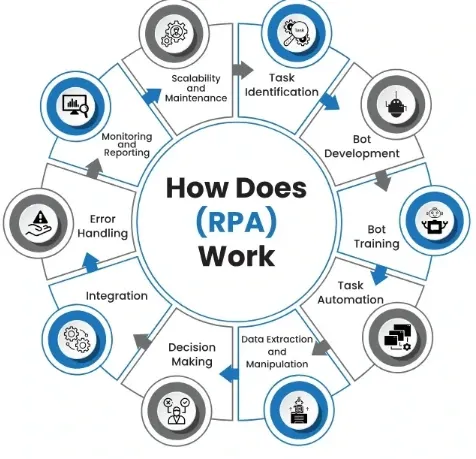
Understanding the Process
AI robotics process automation works by automating rule-based and repetitive tasks, effectively mimicking how humans interact with software bots. By observing existing workflows, RPA software bots can identify patterns and streamline processes without modifying underlying systems.
Identifying Suitable Tasks
To implement RPA, tasks need to be assessed for suitability. Ideal tasks are rule-based, structured, repetitive, and have a low rate of exceptions. Examples include data entry, data validation, and report generation.
Designing Automation Rules
Once suitable tasks have been identified, AI robotics process automation developers define the automation rules by creating a detailed workflow or process map. This map outlines each step that the AI robotics process automation software bots will execute, including decisions, actions, and interactions with various applications.
Developing and Testing RPA Bots
RPA developers use a specialized software platform to create and configure the robots that will automate the tasks. These software bots are then thoroughly tested to ensure they perform the desired actions accurately and efficiently.
Monitoring and Optimization
After deploying RPA software bots, they are monitored to assess their performance, identify any areas for improvement, and ensure they adapt to any changes in the operating environment. This ongoing process helps to maintain efficiency and optimize the benefits of RPA.
What are the Types of Robotic Process Automation (RPA)?
Robotic Process Automation (RPA) has different types of automation for different use cases. This section explores its various types and applications.
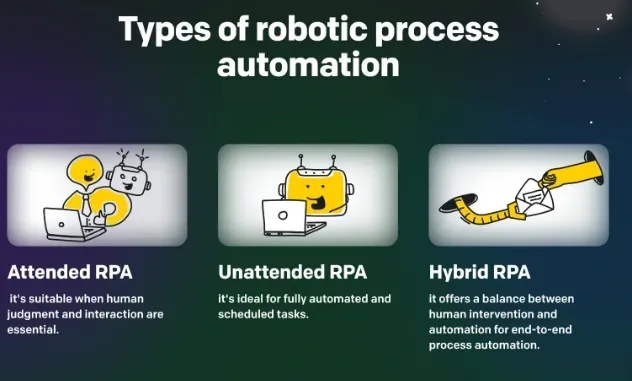
Attended RPA
Attended RPA works in collaboration with human operators. It assists employees by automating repetitive tasks, such as data input, while allowing them to retain control and decision-making authority.
Unattended RPA
Unattended RPA operates without human intervention. It performs repetitive tasks independently, often running in the background, making it ideal for automating processes that require continuous execution, such as report generation or data reconciliation.
Hybrid RPA
Hybrid RPA combines the features of both attended and unattended RPA. It allows human operators to intervene when necessary while also automating tasks that can run in the background.
Applications of Robotic Process Automation (RPA)
Robotic Process Automation (RPA) streamlines business processes, enhancing efficiency, accuracy, and productivity across various industries through automation technologies. So here are the applications of AI robotics process automation:
Streamlining Business Processes
Robotic process automation (RPA) can help businesses achieve operational efficiency by automating rule-based, repetitive tasks. With RPA, organizations can optimize workflows, reduce human error, and reduce time-consuming manual processes.
Boosting Customer Service
AI robotics process automation tools enhance customer service by automating key aspects, such as responding to common inquiries, tracking order statuses, or sending notifications.
These automated solutions can help resolve customer issues more quickly, improving satisfaction and building stronger relationships.
Enhancing Data Management and Analytics
Robotic Process Automation (RPA) simplifies the process of collecting, storing, and retrieving data, making it easier for organizations to manage and analyze large data sets.
Automating these tasks reduces the likelihood of errors and ensures that data analysts can focus on generating insights and driving informed decision-making.
Supporting Compliance and Risk Management
In highly regulated industries, AI robotics process automation plays a crucial role in ensuring compliance with regulatory requirements by automating specific reporting tasks and data collection.
By accurately processing and recording required information, businesses can minimize the risk of non-compliance penalties.
Increasing Scalability and Flexibility
Robotic Process Automation (RPA) allows organizations to scale up their operations quickly, adjusting the number of automated processes as needed to respond to changing demands.
This increased flexibility enables businesses to adapt more efficiently, improve reaction times, and maintain a competitive edge in their industry.
How to Implement Robotic Process Automation (RPA)?
To get the most out of Robotic Process Automation (RPA) a proper implementation process should be followed. This section explores effective implementation strategies for RPA success.
Identify Opportunities for Automation
Your first step to implementing Robotic Process Automation (RPA) should be identifying repetitive tasks that are high volume in nature, prone to errors, and demand a lot of your team's time. These tasks are ideal candidates for automation.
Choose the right RPA Tool
There's a wide range of AI robotics process automation tools available, each with its strengths and weaknesses. Evaluate them carefully. Consider aspects such as ease of use, scalability, AI capabilities, reporting features, and costs.
Design and Test the Process
After choosing the tool, outline your process. Define the steps clearly. Then design it in the Robotic Process Automation (RPA) tool, followed by a thorough testing phase to ensure efficiency and accuracy.
Employee Training and Change Management
Implement training sessions for employees to ensure they understand how to work with the new open source technology. It's also important to manage the change effectively to help your team adapt and transition smoothly.
Monitor and Improve
Once AI robotics process automation is live, continue to monitor processes. Gather feedback, learn from it, and make necessary changes to improve the system over time. Remember, the goal of AI robotics process automation is continuous improvement and efficiency.
What are the Tools and Technology of Robotic Process Automation (RPA)?
Robotic Process Automation (RPA) utilizes advanced tools and technologies to automate repetitive tasks, enhancing efficiency and accuracy across industries.
Popular Robotic Process Automation Tools
Several tools are available for RPA development and deployment. UiPath Studio, Automation Anywhere Enterprise, and Blue Prism are leading platforms that offer user-friendly drag-and-drop interfaces, visual process designers, and advanced functionality for building bots.
The Evolution of Robotic Process AutomationTechnology
AI robotics process automation open source technology is always advancing, and developments such as cognitive automation, machine learning algorithms, and natural language processing allow bots to perform more complex and intelligent tasks, raising the bar for process automation capabilities.
Open Source Robotics Process Automation Alternatives
Open source robotics process automation tools, like Robot Framework and Selenium, offer flexibility and customization for organizations seeking alternative options.
These free and open source robotics process automation tools have thriving communities. These open source robotics process automation provide additional resources for refining and expanding automation strategies.
Cognitive Automation in Robotic Process Automation
Incorporating AI-powered cognitive automation into RPA allows bots to understand and analyze unstructured data, learn from experience, and make informed decisions. This significant leap in functionality enables businesses to automate a greater range of processes, including those that depend on human expertise.
Cross-Industry Robotic Process AutomationApplications
Thanks to the versatility and adaptability of RPA technology, it can be applied across a wide range of industries, including finance, healthcare, insurance, and more.
From automating data entry tasks to providing intelligent customer support, AI robotics process automation has emerged as a transformative force in the business world.
Frequently Asked Questions(FAQs)
What does Robotic Process Automation (RPA) do?
RPA is a technology that uses software bots to automate repetitive tasks. It mimics human actions within a digital system, improving efficiency and accuracy in business processes.
How does Robotic Process Automation (RPA) benefit organizations?
RPA increases productivity, reduces costs, improves accuracy, and enhances customer experience by automating repetitive tasks, reducing errors, and providing better visibility into business operations.
Are there any categories of Robotic Process Automation (RPA)?
There are three categories or types of RPA: attended RPA, which collaborates with human operators. Next is unattended RPA, which operates without human intervention; and hybrid RPA, a combination of attended and unattended.
What are some typical use cases of Robotic Process Automation (RPA)?
RPA is used in various industries for tasks such as invoice processing, customer onboarding, claims processing, inventory management, and call center operations.
How can organizations ensure data security in Robotic Process Automation (RPA)?
To ensure data security in RPA, organizations should implement role-based access control, encryption, auditing, monitoring, and regular security assessments.