Introduction to Robotics
Robots are becoming a big part of today’s lives. From helping in factories to exploring space, they are everywhere. Understanding what robotics is can help see how they shape the world.
Overview of Robotics
Robotics is the science and engineering of creating machines that can perform tasks. These machines, called robots, can be programmed to do almost anything. Some robots look like humans, while others look like machines. The goal of robotics is to build devices that can assist, entertain, or even replace humans in certain tasks.
Suggested Reading: Robotic Process Automation (RPA)
Importance of Robotics in Modern Technology
Robots are essential in today's world. They make work easier and faster. In factories, robots can assemble cars with precision. In hospitals, they can assist in surgeries. In homes, they help with cleaning.
Types of Robotics Technologies
Robots come in many shapes and sizes. Each type has a unique way of helping us. Let's explore the different types of robotics technologies.
Autonomous Robotics
Autonomous robots can think and act on their own. They don't need a human to control them. These robots use sensors and software to navigate and make decisions.
They can be found in driverless cars and robotic vacuum cleaners. Autonomous robots are like self-driving cars that know when to stop and go.
Teleoperated Robotics
Teleoperated robots are controlled by humans from a distance. Think of a drone that a pilot flies from the ground.
These robots are useful in dangerous situations, like exploring underwater or diffusing bombs. The human operator can guide the robot, making it a safe way to handle risky tasks.
Humanoid Robotics

Humanoid robots look and move like humans. They have arms, legs, and sometimes even faces. These robots can help with tasks that require a human touch. Imagine a robot that can walk, talk, and even dance.
Humanoid robots are used in research, entertainment, and even as personal assistants.
Swarm Robotics

Swarm robots work together as a team. They are like a colony of ants, each robot doing its part. These robots can communicate with each other and work together to complete tasks.
Swarm robotics is used in fields like agriculture, where many small robots can plant seeds over a large area.
Collaborative Robots (Cobots)
Cobots are designed to work alongside humans. They are safe and easy to use.
These robots can help with tasks that are too difficult or dangerous for people. For example, in a factory, a cobot might lift heavy objects while a human handles the delicate parts.
Cobots are like helpful teammates who never get tired.
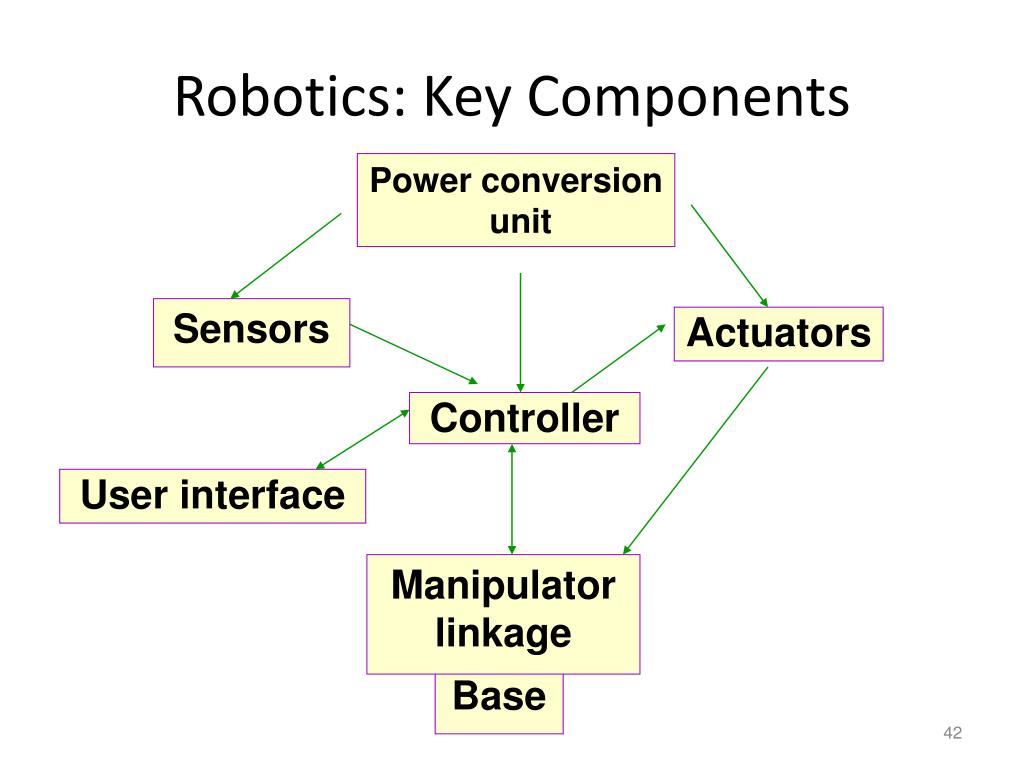
Key Concepts in Robotics
Understanding robotics involves grasping several key concepts. These ideas help us understand how robots work and interact with the world. Let’s break down these concepts into simple terms.
Degrees of Freedom
In the degree of freedom, robotics talks about:
Degrees of Freedom refer to the different ways a robot can move.
Imagine a robot arm. It can move up and down, left and right, and twist around. Each of these movements is a degree of freedom.
The more degrees of freedom, the more flexible the robot.
Kinematics and Dynamics
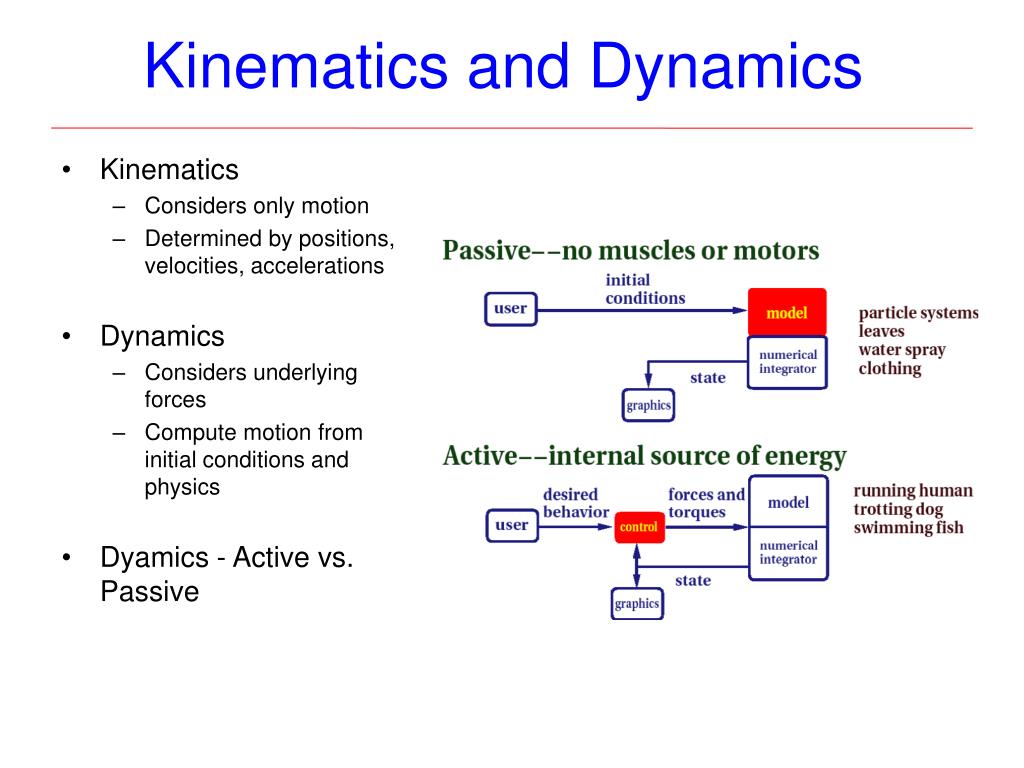
Next concept is kinematics and dynamics:
Kinematics is about how a robot moves. It looks at the position, speed, and acceleration of the robot’s parts without considering the forces causing the movement.
Dynamics goes a step further. It studies the forces that make the robot move. Think of it as the difference between knowing how a car drives and understanding the engine behind it.
Control Systems
Control systems in robotics is:
Control Systems are like the brains of the robot. They decide how the robot moves and reacts.
These systems take inputs (like sensor data) and decide what the robot should do next.
Imagine a thermostat controlling your home’s temperature. It takes the current temperature and adjusts the heating or cooling. Similarly, control systems keep robots functioning correctly.
Human-Robot Interaction (HRI)
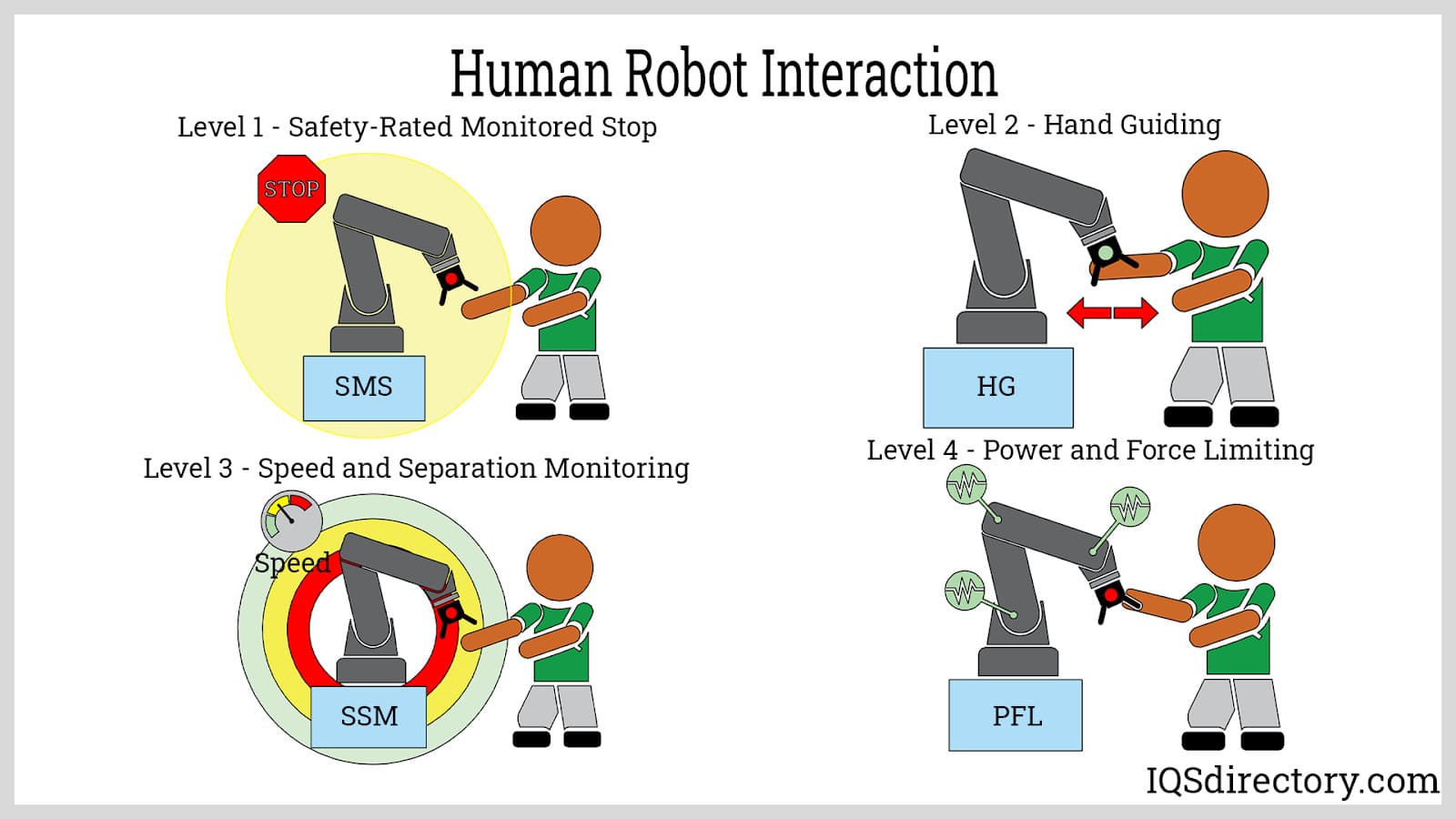
Human-robot interaction includes:
Human-robot interaction (HRI) is about how robots and people work together.
It’s important for robots to be easy and safe to use. HRI studies ways to make this happen.
Picture a robot assistant that understands your voice commands and responds accordingly. That’s HRI in action.
Robot Operating System (ROS)
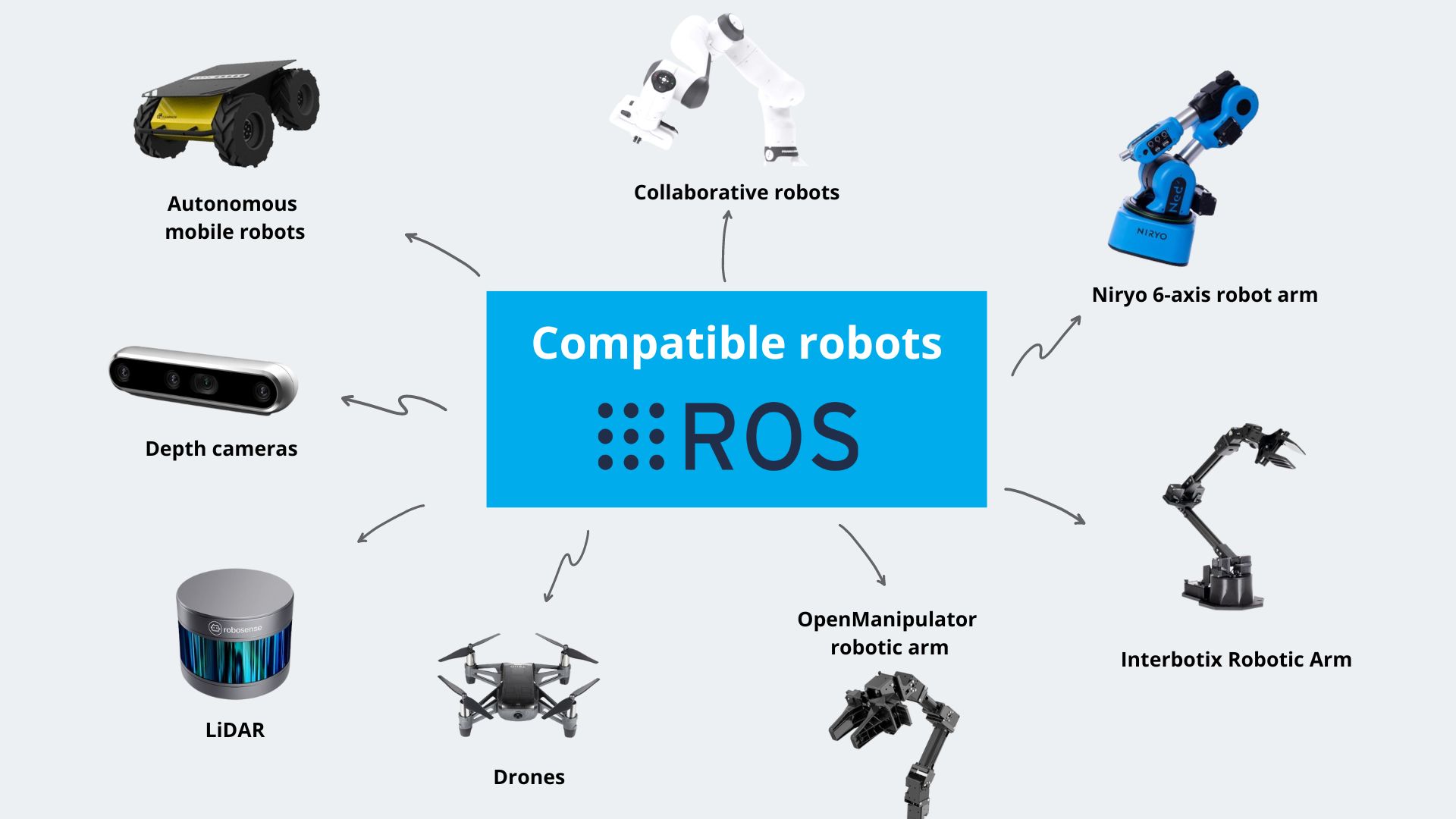
Robot operating system is another key concept that includes: a
Robot Operating System (ROS) is like the software that runs on a computer but for robots.
ROS helps developers build and program robots more easily. It provides tools and libraries to make robots work.
Think of ROS as the Android or iOS of the robot world. It’s a platform that supports many different robots and applications.
Robotics Engineer: Innovating the Future with Automation
A robotics engineer designs, builds, and maintains robots to automate tasks across various industries. They integrate mechanical, electrical, and computer engineering principles to create advanced robotic systems.
Responsibilities of a Robotics Engineer
A robotics engineer designs, builds, and tests robots and robotic systems. They work on creating autonomous machines capable of performing tasks in various industries, from manufacturing to healthcare. Their responsibilities include programming, troubleshooting. They also ensure the efficiency and safety of robotic systems.
Skills and Qualifications of a Robotics Engineer
To excel as a robotics engineer, one must have a strong background in mechanical and electrical engineering, computer science, and programming languages such as Python and C++. Problem-solving skills, creativity, and knowledge of AI and machine learning are essential for developing innovative robotic solutions.
Frequently Asked Questions(FAQs)
What are the main applications of robotics?
Robotics is integral in manufacturing, healthcare, service industries, military, and space exploration. Robots automate repetitive tasks, enhance precision, and operate in hazardous environments.
How is robotics helping in manufacturing?
Robotics improves productivity, efficiency, and safety in manufacturing by automating tasks, such as assembly, welding, and painting, reducing errors and labor costs.
What are the different types of robots?
Types include industrial robots, service robots, mobile robots, collaborative robots, and medical robots, each serving specific applications from production to aiding human activities.
What are the future applications of robotics?
Future applications range from advanced healthcare and assisted living to autonomous transportation, disaster response, and further space exploration technologies.
How is robotics being used in healthcare?
Robots assist in surgeries with high precision, undertake repetitive tasks in labs, enhance patient care with service robots, and support physical therapy and rehabilitation.
What are the safety concerns with robotics?
Safety concerns include potential malfunctions, ensuring human-robot interaction without accidents, and addressing job displacement, requiring new policies and safety standards.
