What is Information Retrieval?
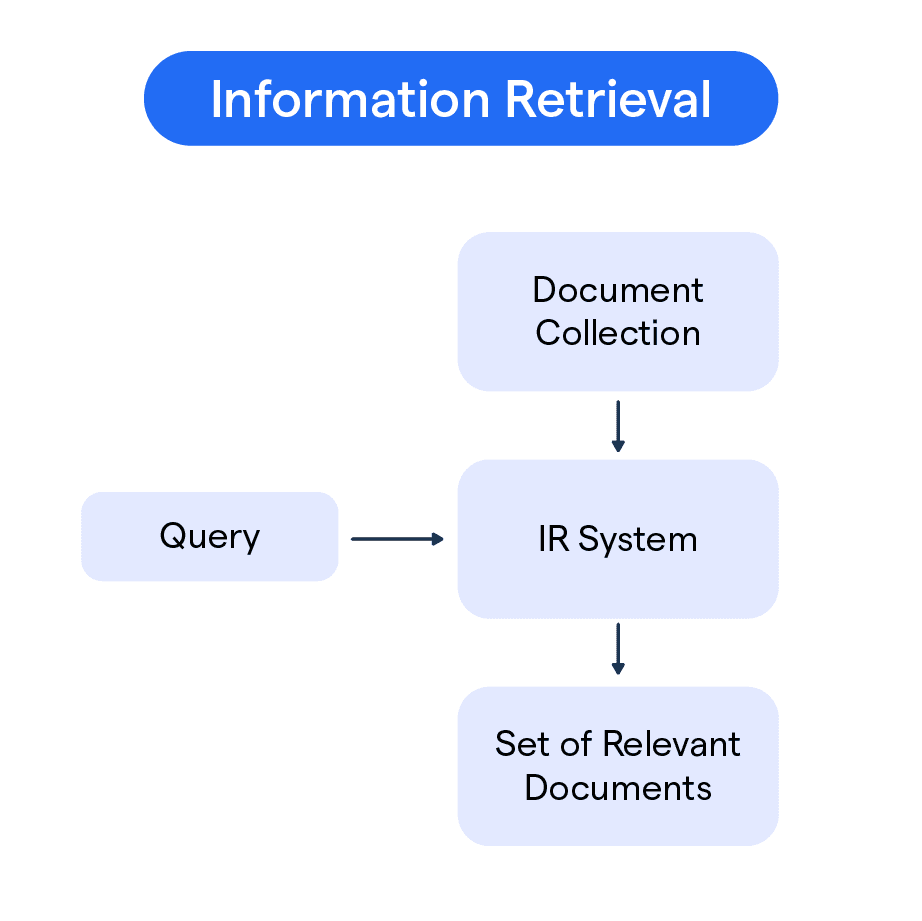
Information retrieval is the science of searching for and extracting information from large collections of unstructured data.
It involves developing methods and systems to efficiently find relevant information from within large document repositories, databases, and networks.
At the core of information retrieval is indexing - using metadata and descriptors to represent information making it easily searchable.
Retrieval then operates over these indexes to serve user search queries by ranking and returning relevant results.
Key components of an information retrieval system include:
- The document corpus or database being searched
- Indexing methodology to create searchable representations
- Query syntax and semantics for expressing user information needs
- Matching and ranking algorithms to compare queries with indexed data
- User interaction models to request, refine, and present results
Optimizing speed, accuracy and relevance are major focuses in information retrieval research and technology. Common applications include web search engines, legal and medical databases, enterprise document management, and social media monitoring.
As data volumes grow exponentially, continuous innovation in information retrieval is crucial for efficiently connecting users to the precise information they need from massive, unstructured data troves.
In summary, information retrieval enables pinpoint searching within huge datasets by utilizing metadata, analytics, and algorithms to uncover relevant content.
Components of Information Retrieval
Now that we understand the process let's explore the key components that makeup Information Retrieval.
In this section, we'll discuss the core components of Information Retrieval (IR), an essential field in computer science dedicated to the organization, retrieval, and presentation of information.
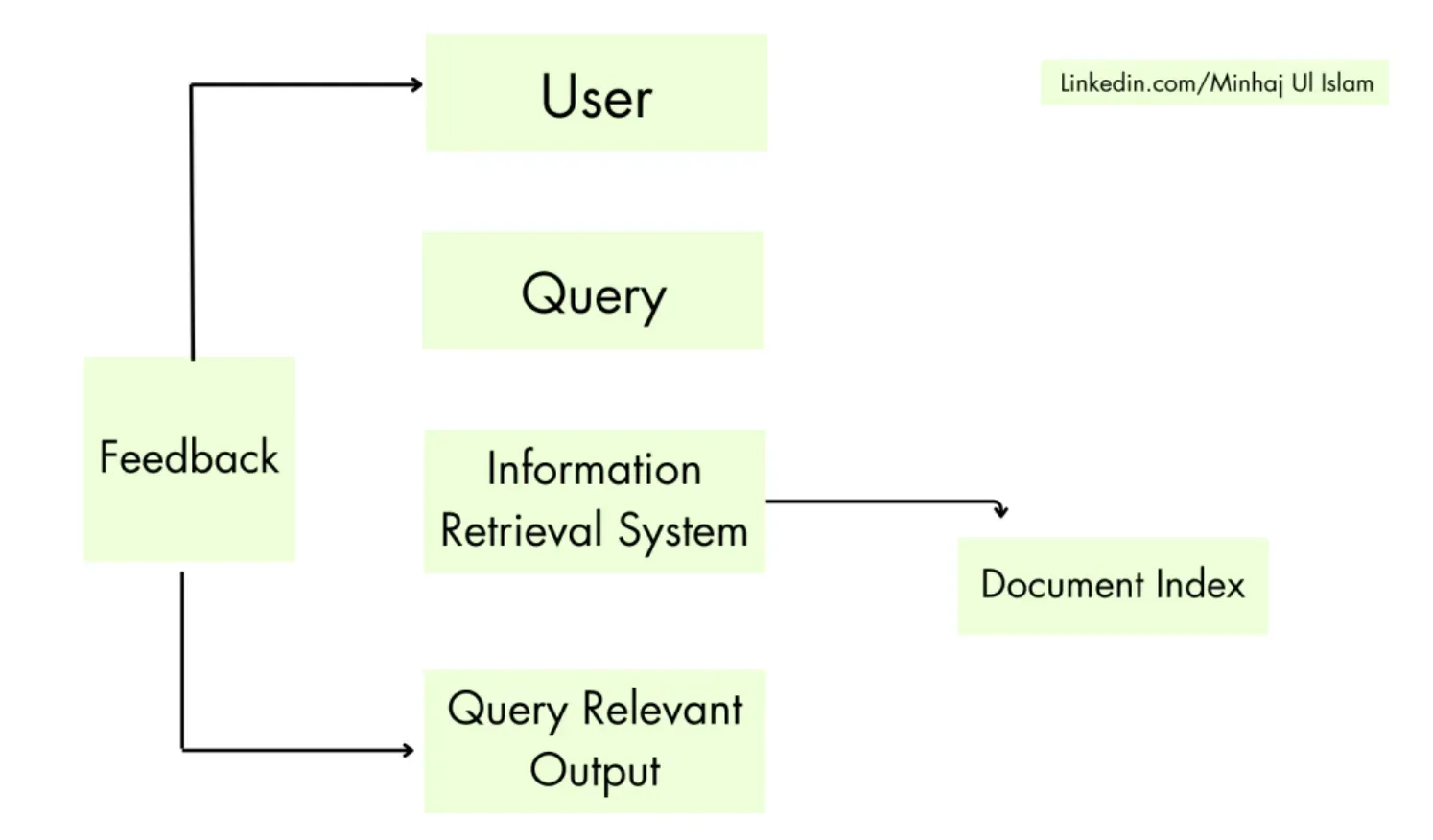
Document Representation
Document representation involves organizing and formatting documents to make the contained information easily accessible.
This can involve indexing, categorizing, or summarizing content, essentially creating structured metadata from unstructured data.
Indexing
Indexing in information retrieval refers to creating a data structure (index) that makes the retrieval of data more efficient.
It involves the use of techniques like hash tables, B-trees, or inverted indices, which allow for faster access to the documents.
Query Processing
Query processing is a pivotal component that manages and interprets user queries, translating them into a form that can be compared against the indexed documents.
This process often entails understanding the user's intended meaning, recognizing keywords, and handling ambiguity in the query.
Searching and Matching
This involves using the processed query to sift through the indexed documents to find relevant matches. The search algorithm can use various strategies, like Boolean retrieval, vector space models, or probabilistic models, depending on the architecture of the IR system.
Ranking and Relevance
Once matches have been found, the system must decide which are most relevant to the user's query. This is usually done through a ranking mechanism that orders results based on specific parameters.
The exact ranking algorithm is generally designed to reflect the specific needs and contexts of the users.
Techniques and Methods in Information Retrieval
Now that we have a good grasp of the components let's explore some techniques and methods used in Information Retrieval.
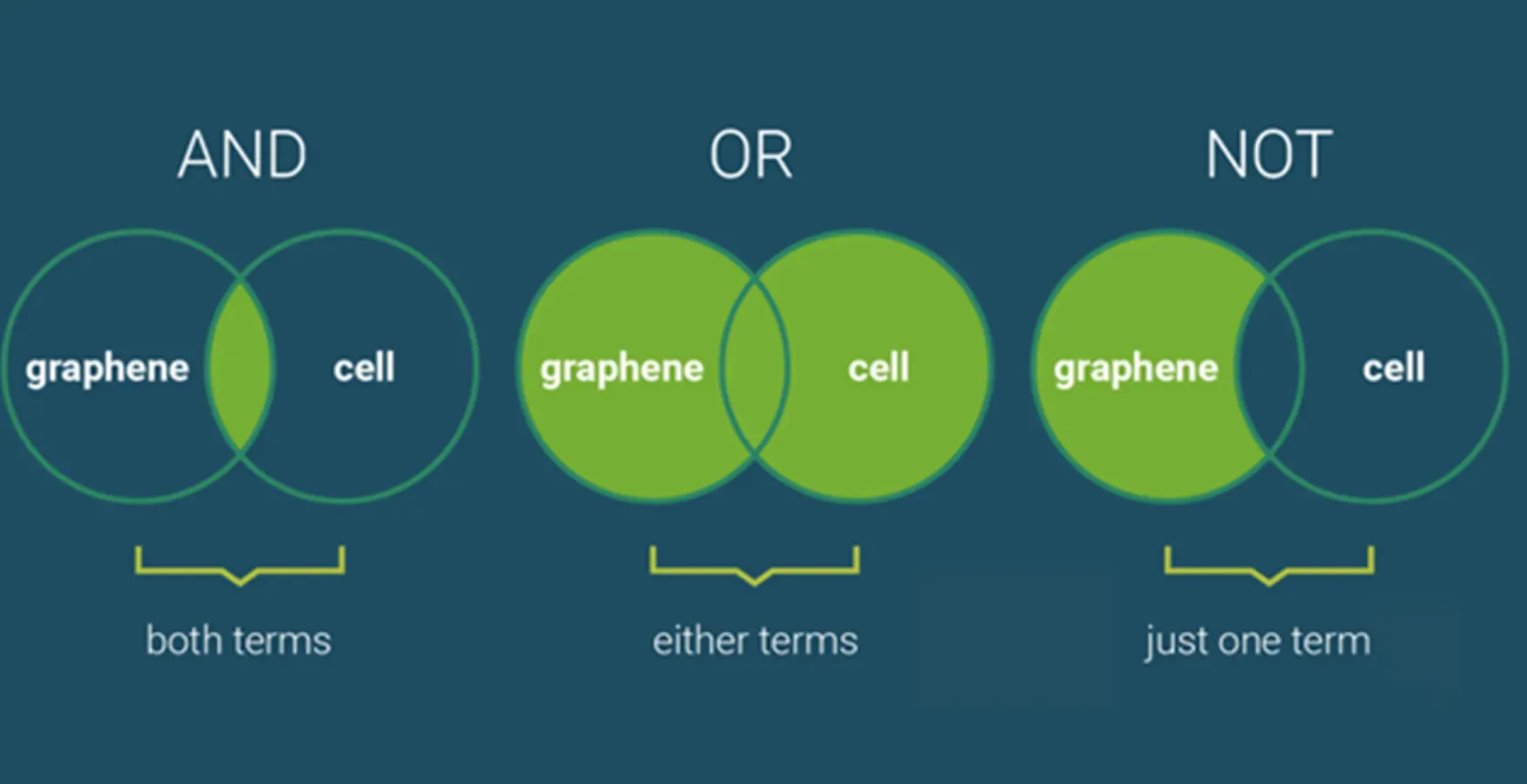
Boolean Query Processing
Boolean query processing is a simple yet effective method where data is retrieved based on boolean expressions (AND, OR, NOT operators), which help filter information effectively.
Vector Space Model
The vector space model is a robust technique used in information retrieval.
It involves the representation of text documents as vectors in multi-dimensional space, facilitating the comparison and sorting of said documents.
Fuzzy Retrial Models
Fuzzy retrieval models handle uncertain or vague queries effectively.
They apply fuzzy logic to interpret and retrieve the most relevant information that aligns closely with the intent of ambiguous queries.
Probabilistic Models
Probabilistic models utilize statistical methods to rank the relevance of documents.
They leverage probabilities to address uncertainties present in user queries and available information.
Latent Semantic Indexing (LSI)
Latent Semantic Indexing uses singular value decomposition to identify the relationships among words and concepts contained in an unstructured collection of text, improving the retrieval of conceptual information.
Hypertextual Information Retrieval
Hypertextual information retrieval encompasses techniques that exploit the unique features of hypertext documents (like links) to improve information retrieval, especially relevant in web search engines.
Multilingual Information Retrieval
Multilingual information retrieval systems prioritize translating the query or the text databases (or both) to facilitate retrieval across multiple languages.
Use of Metadata in Information Retrieval
Metadata enhances the retrieval of information. By applying tags or additional contextual information to documents, it increases the precision of retrieval systems.
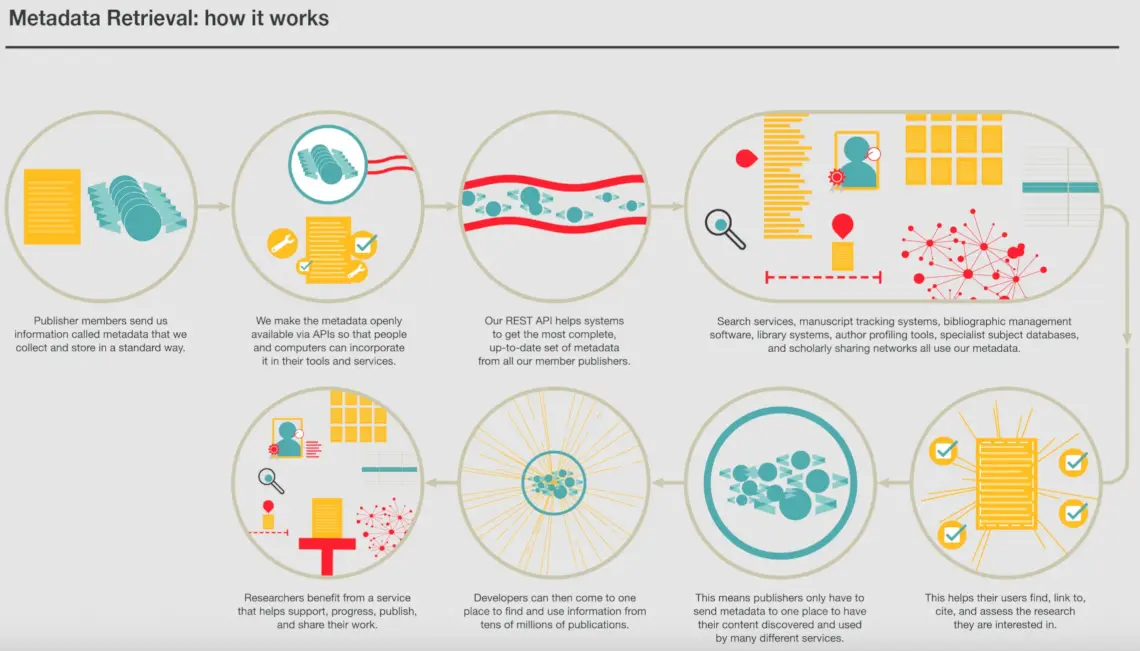
Social Tagging and Folksonomies
Social tagging involves users labeling and sharing content, while folksonomies are a type of decentralized classification system.
Both play significant roles in user-generated categorization and organization, enhancing information retrieval.
Suggested Reading:
Pattern Matching
Neural Network-Based Retrieval Models
Marrying information retrieval with machine learning, these models use neural networks to improve the retrieval system's performance.
They are particularly advantageous in processing large-scale and complex information databases.
Applications of Information Retrieval
Information Retrieval finds its applications in various areas. Let's take a look at some of them:
Applications of Information Retrieval
In this section, we'll explore the wide-ranging applications of information retrieval, demonstrating its value across various industries and contexts.
Search Engines
Potentially the most ubiquitous application, search engines like Google extensively use information retrieval algorithms to scan the internet and present relevant search results to users.
Digital Libraries
Digital libraries leverage information retrieval to help users find books, articles, and other resources among vast collections of digital materials.
eCommerce Platforms
eCommerce platforms such as Amazon utilise information retrieval to provide product recommendations based on users' search history and preferences, enhancing overall shopping experience.
Social Media Platforms
Social media platforms like Facebook apply information retrieval to filter and present the most relevant content in users' feeds, which includes posts, advertisements, and suggested friends.
Enterprise Search Systems
Large organizations use enterprise search systems to help employees locate and retrieve relevant information from vast internal databases, improving operational efficiency.
Email Filters
Email platforms use information retrieval to filter and categorize incoming emails, distinguishing between relevant emails, junk mail, and spam.
Music and Movie Recommendation Services
Streaming services like Spotify and Netflix deploy information retrieval to provide personalized recommendations and enhance users' entertainment experience.
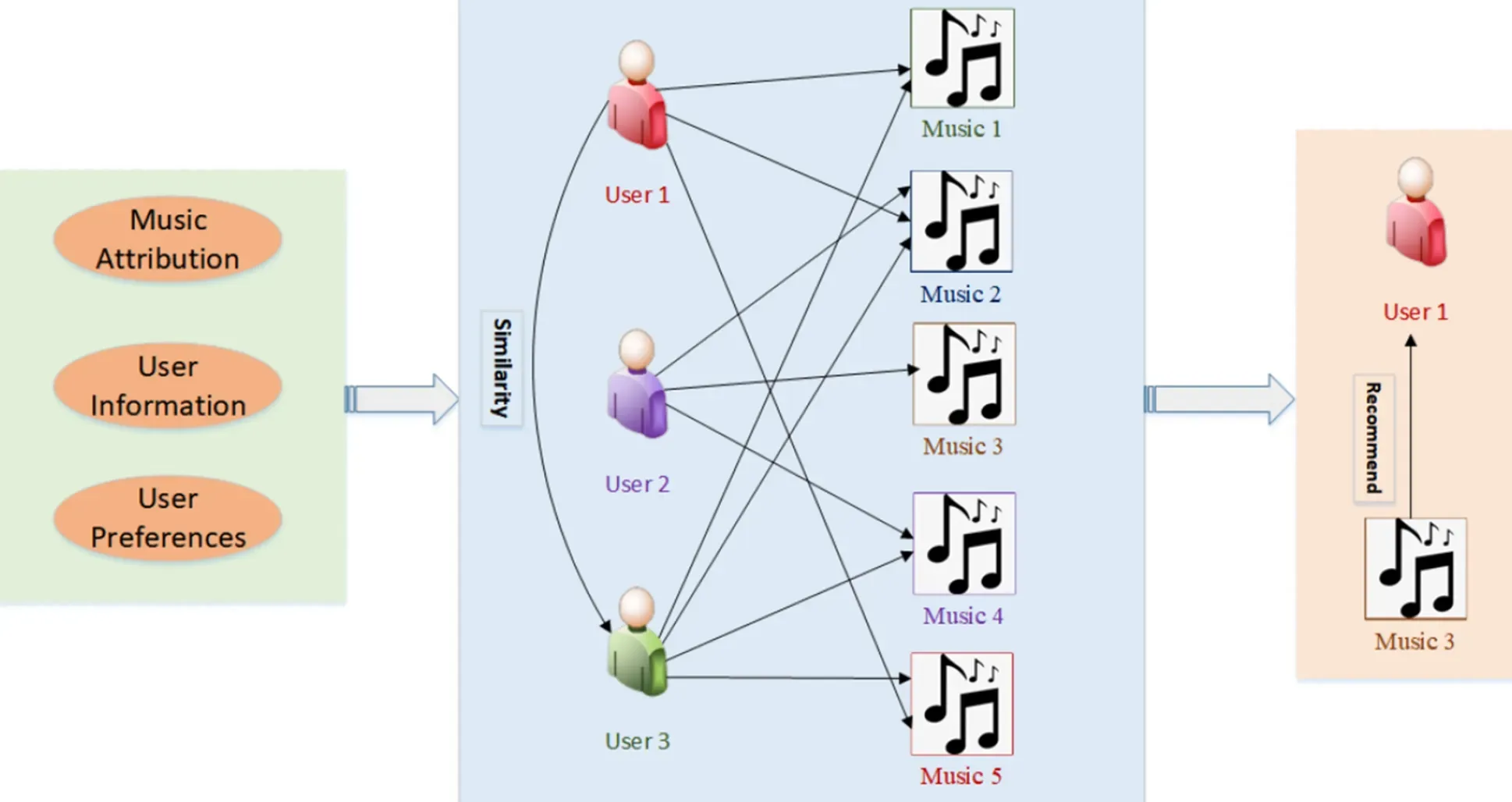
Financial Market Analysis
In finance, information retrieval supports market analysis by extracting relevant information from a myriad of financial documents, assisting in decision-making.
Healthcare and Medical Research
In the healthcare sector, information retrieval aids in sifting through massive medical databases to fetch patient information or to aid in medical research.
Legal Information Search
Information retrieval is pivotal in legal scenarios, enabling law professionals to find relevant precedents, laws and documents needed for case building.
With such diverse applications, information retrieval has a transformative impact on how information is accessed, processed, and utilized, thereby shaping our digital experience.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is Information Retrieval (IR)?
Information Retrieval (IR) is a field focused on finding relevant data within massive databases or other structured and unstructured data sources.
How does an Information Retrieval (IR) system work?
An IR system locates and retrieves data relevant to a user query by using sophisticated algorithms that index and search databases.
What are the applications of Information Retrieval (IR)?
IR has wide-ranging applications, from web search engines to digital libraries to e-commerce product recommendations and even medical databases.
How does Information Retrieval differ from Data Mining?
While both handle large data sets, Information Retrieval focuses on finding and obtaining relevant data, whereas Data Mining is about discovering patterns within the data.
How important is Information Retrieval in today's digital landscape?
In our data-driven world, IR is vital. It helps users sift through the vast realm of data, delivering needed information quickly and accurately