What is Experience Design (XD)?
Experience Design, commonly abbreviated as XD, is an approach to design that focuses on creating enjoyable and meaningful user experiences.
It involves designing products, services, processes, environments, and interactions with a deep understanding of human behavior, emotions, and needs. In experience design, the goal is to not only meet user expectations but also to exceed them by delivering exceptional experiences that evoke positive emotions and build lasting connections.
Why is Experience Design Important?
Experience Design holds a great significance in providing users with a meaningful experience. Below mentioned is why it is important -

- Importance of focusing on customer and user experiences
In a crowded marketplace, businesses need to differentiate themselves by prioritizing user-centric design and delivering exceptional experiences that meet and exceed customer expectations.
- Impact on customer satisfaction and loyalty
When users have positive experiences with a product or service, they are likelier to become loyal customers and advocates. By focusing on experience design, businesses can build long-term relationships with their customers.
- Relationship between usability and emotions
Usability ensures products or services are easy to use, but experience design takes it a step further by considering emotions and the overall feeling users have when interacting. Emotions heavily influence user behavior and perception of a brand.
- Creating positive feelings and emotions in users
Experience Design aims to evoke positive emotions such as joy, delight, and satisfaction in users. By considering the emotional impact of interactions, businesses can create memorable experiences and build emotional connections.
- Driving business growth through experience design
Exceptional experiences set businesses apart from competitors, attract new customers and increase sales. Focusing on user experiences can drive customer loyalty, reduce churn rates, and increase customer lifetime value, leading to business growth.
Is Experience Design the Same as UX?
While Experience Design has some similarities with User Experience (UX) design, they are not exactly the same.
UX design focuses on the usability and functionality of a product or service, ensuring that it meets user needs and goals.
On the other hand, Experience Design takes a more holistic approach, encompassing not only usability but also emotional and sensory aspects that contribute to the overall experience.
What is an Experience Design Strategy?
An Experience Design Strategy is a plan that aligns experience design efforts with business goals. It involves:
- Understanding the target audience
To create exceptional and relevant experiences, businesses must have a deep understanding of their target audience's needs, preferences, and behaviors.
- Analyzing competitors
Analyzing the competition provides insights into how other businesses approach experience design, what works, and what doesn't.
- Creating a data-driven experience model
By using data to inform decision-making, businesses can develop an experience model that reflects customer needs, expectations, and preferences.
- Mapping the customer journey
Mapping how customers interact with a product or service is essential to identifying pain points and areas for improvement.
- Identifying customer segments
Breaking the customer base into segments allows businesses to tailor experiences to specific groups, increasing relevance and impact.
- Developing guidelines for consistent and exceptional experiences
By creating guidelines, businesses can consistently deliver exceptional experiences across all touchpoints.
What is Customer Experience (CX) Design?
Customer Experience (CX) Design is closely related to Experience Design. It focuses on optimizing the end-to-end journey of customers across all touchpoints, both online and offline. CX design emphasizes customer-centered strategies, tailored experiences for individual customers, and building strong relationships to foster loyalty and advocacy.
Who Benefits from Experience Design?
Experience Design benefits various stakeholders. Businesses across industries can gain a competitive edge and drive growth by prioritizing user experiences.
- Customers and users benefit from products and services that are intuitive, engaging, and tailored to their needs.
- Designers and developers involved in the design process gain insights, inspiration, and methodologies to create exceptional experiences.
- Stakeholders and decision-makers in organizations benefit from improved metrics, customer satisfaction, and brand loyalty.
Where is Experience Design Applied?
Experience Design is applied in a wide range of industries. It has transformed the way businesses approach design in sectors such as e-commerce and retail, logistics, ed-tech, travel and hospitality, insurance and banking, government, and even real estate.
From creating seamless online shopping experiences to designing innovative educational platforms, experience design plays a vital role in enhancing user experiences across diverse fields.
How to Implement Experience Design?
Implementing Experience Design involves several key steps:
- Understanding customer needs and aligning them with business objectives is crucial.
- Collecting both qualitative and quantitative data enables businesses to gain insights into user behavior and preferences.
- Conducting research and analysis, mapping the customer journey, and identifying gaps in the experience all contribute to a robust experience design process.
- Regularly gathering feedback and involving all teams and stakeholders ensure that the experience model evolves and improves continuously.
Key Principles of Experience Design
Several key principles guide the implementation of Experience Design:
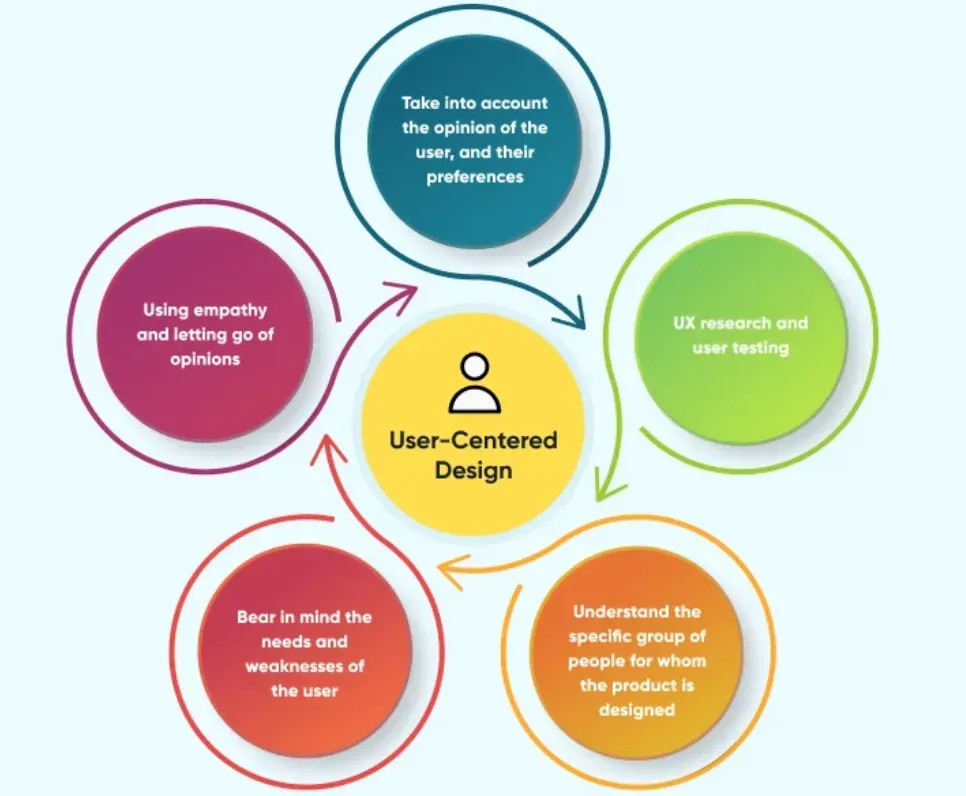
- Designing for emotions and user needs
Emotional aspects play a significant role in shaping user experiences. Designing with empathy, understanding, and addressing user needs and desires leads to more engaging and satisfying experiences.
- Providing seamless and convenient experiences
By reducing friction, simplifying interactions, and ensuring consistency across touchpoints, businesses can provide seamless and convenient experiences that users appreciate.
- Personalizing experiences for individual customers
Tailoring experiences to individual preferences and characteristics enhances user satisfaction and creates a sense of personal connection.
- Applying human-centered design principles
Understanding and empathizing with the end-users allows designers to create intuitive, user-friendly interfaces and interactions.
- Continuously gathering feedback and improving experiences
Collecting user feedback and conducting regular evaluations enable businesses to identify areas for improvement and drive iterative enhancements in the experience design process.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Can Experience Design be applied to any industry or business?
Yes, experience design can be applied to any industry or business, as it focuses on understanding and improving the experiences of customers or users, regardless of the product or service offered.
How do you measure the success of Experience Design?
The success of Experience Design can be measured through various metrics such as customer satisfaction scores, Net Promoter Score (NPS), customer retention rates, conversion rates, and revenue growth.
What is the role of empathy in Experience Design?
Empathy is essential in Experience Design as it helps designers understand and connect with users on a deeper level, leading to the creation of more meaningful and empathetic experiences that meet their needs and desires.
How does technology impact Experience Design?
Technology plays a significant role in Experience Design, as it enables the creation of innovative and immersive experiences. It can enhance personalization, convenience, and speed, contributing to overall user satisfaction.
Is Experience Design a one-time effort or an ongoing process?
Experience Design is an ongoing process that requires continuous refinement and improvement. It involves gathering feedback, analyzing data, and iterating on the design to adapt to changing customer needs and market demands.