Agent Interface
Agent Interface is a computer program or software system that interacts with other software agents or environments.
It facilitates transactional communication, directing command controls, and provides sensory feedback. These make up the fundamental layers of interaction in different systems, especially those automation-driven.
Origin and Evolution
The concept of Agent Interface began with the initiation of computer science itself.
It has evolved from basic command-line interfaces (CLI) to highly sophisticated and intuitive graphical user interfaces (GUI) and interactive voice response (IVR) systems.
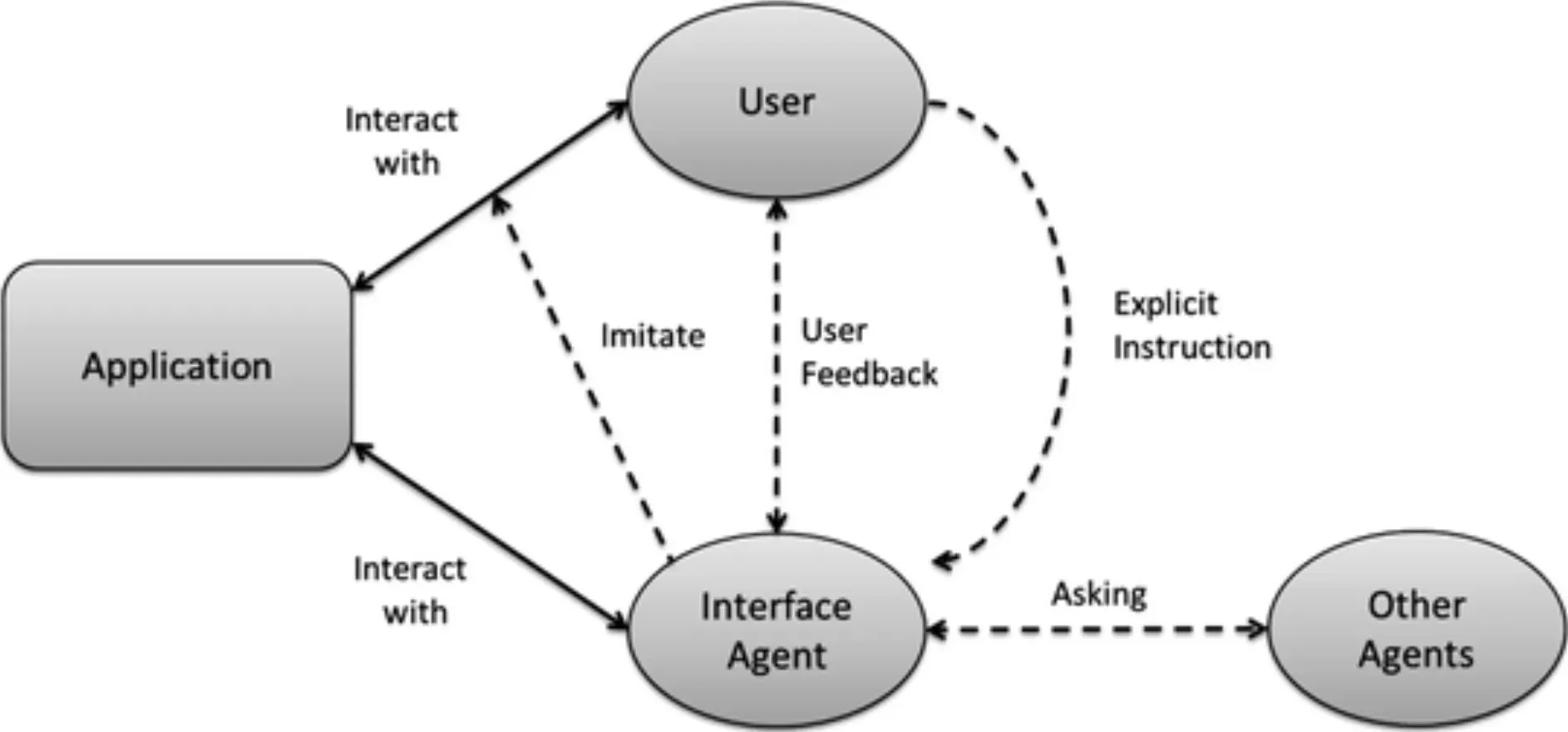
Role in Software Systems
In software systems, an Agent Interface serves as the central access point, coordinating and navigating interactions. It is critical to seamless system operations and user experiences.
Agent Interface and User Experience
Despite being behind-the-scenes, an Agent Interface significantly impacts user sensory experience.
A properly designed, efficient, and intuitive agent interface can lead to a more enjoyable and productive user experience.
Components of an Agent Interface
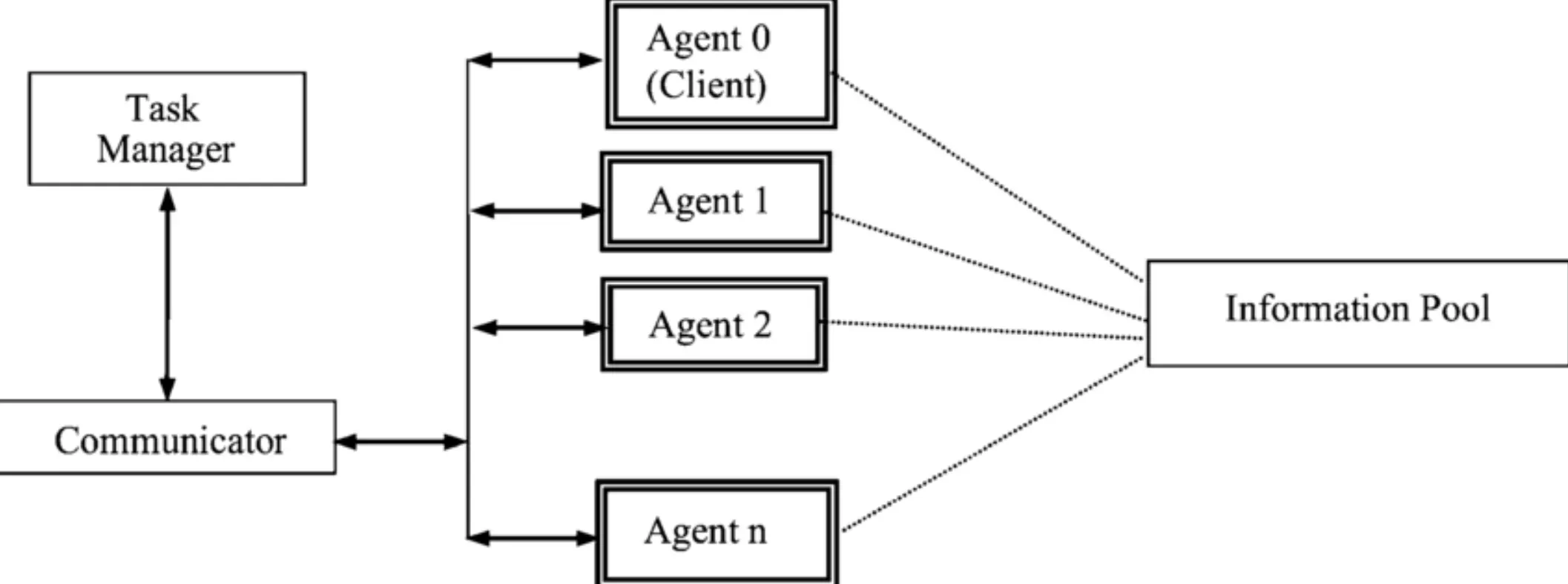
- Interaction Methods: These include various forms of input, such as text commands, mouse clicks, touch gestures, or voice commands, that allow users to engage with systems and software.
- Feedback Mechanisms: Feedback mechanisms refer to the ways systems respond to user input. This can range from simple text responses, graphical representation to auditory sounds and tactile feedback.
- Control Measures: Control measures include sophisticated features like error detection, data validation, data encryption and security protocols, which help ensure accurate and safe transaction of data.
- User Interface (UI): UI represents the visual, auditory, and tactile elements that users directly interact with in a software system. An effective User Interface (UI) is intuitive, efficient, and enjoyable to use, working hand in hand with the agent interface.
Types of Agent Interface
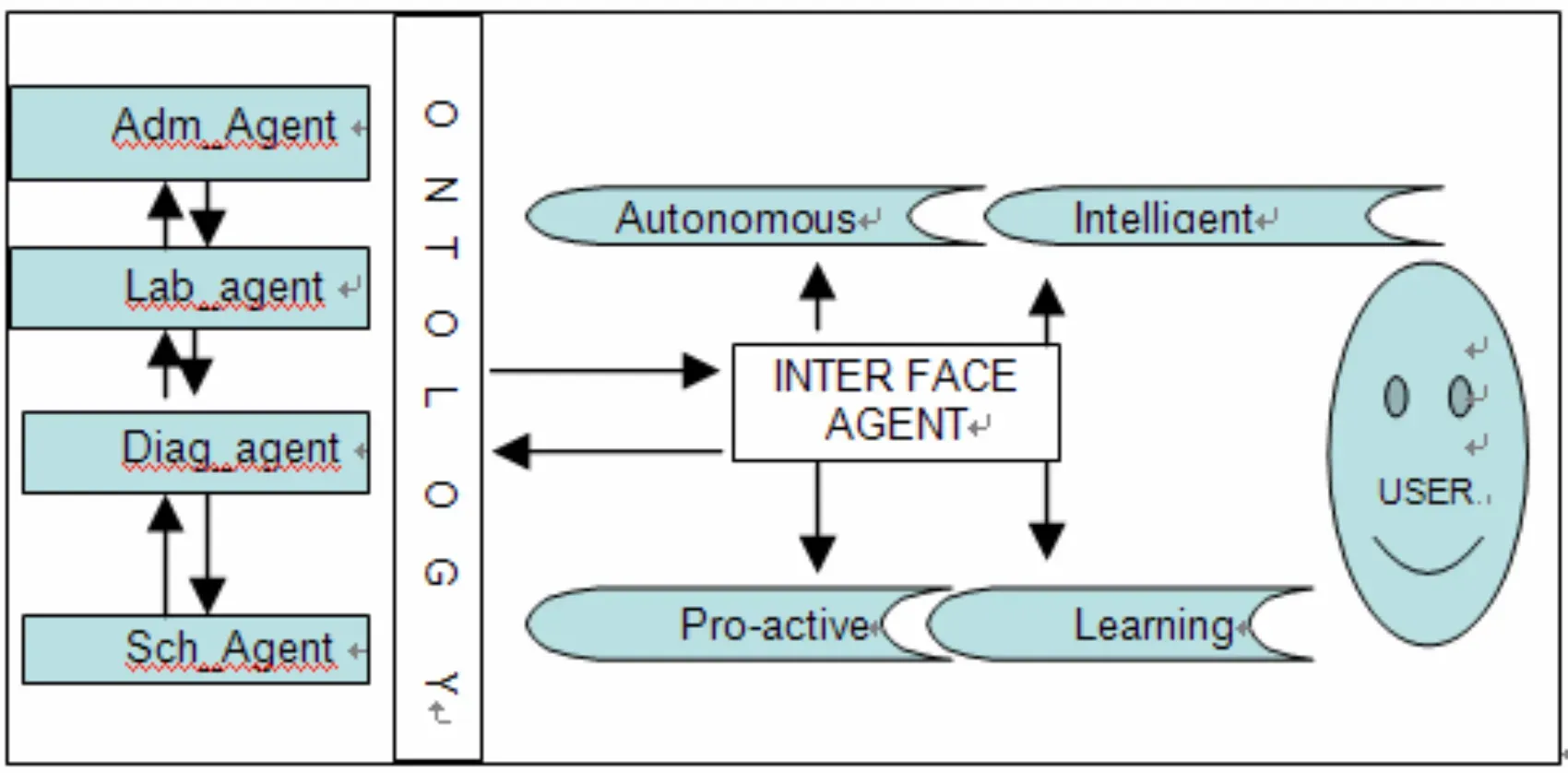
Text-based Interfaces
The simplest form. Users enter commands via keyboard to interact. Commonly seen in command-line interfaces.
Graphical User Interfaces (GUI)
These interfaces allow visual interactions via graphical icons and visual indicators.
Most modern software utilizes sophisticated Graphical User Interfaces (GUIs), making interaction more intuitive for users.
Interactive Voice Response (IVR) Systems
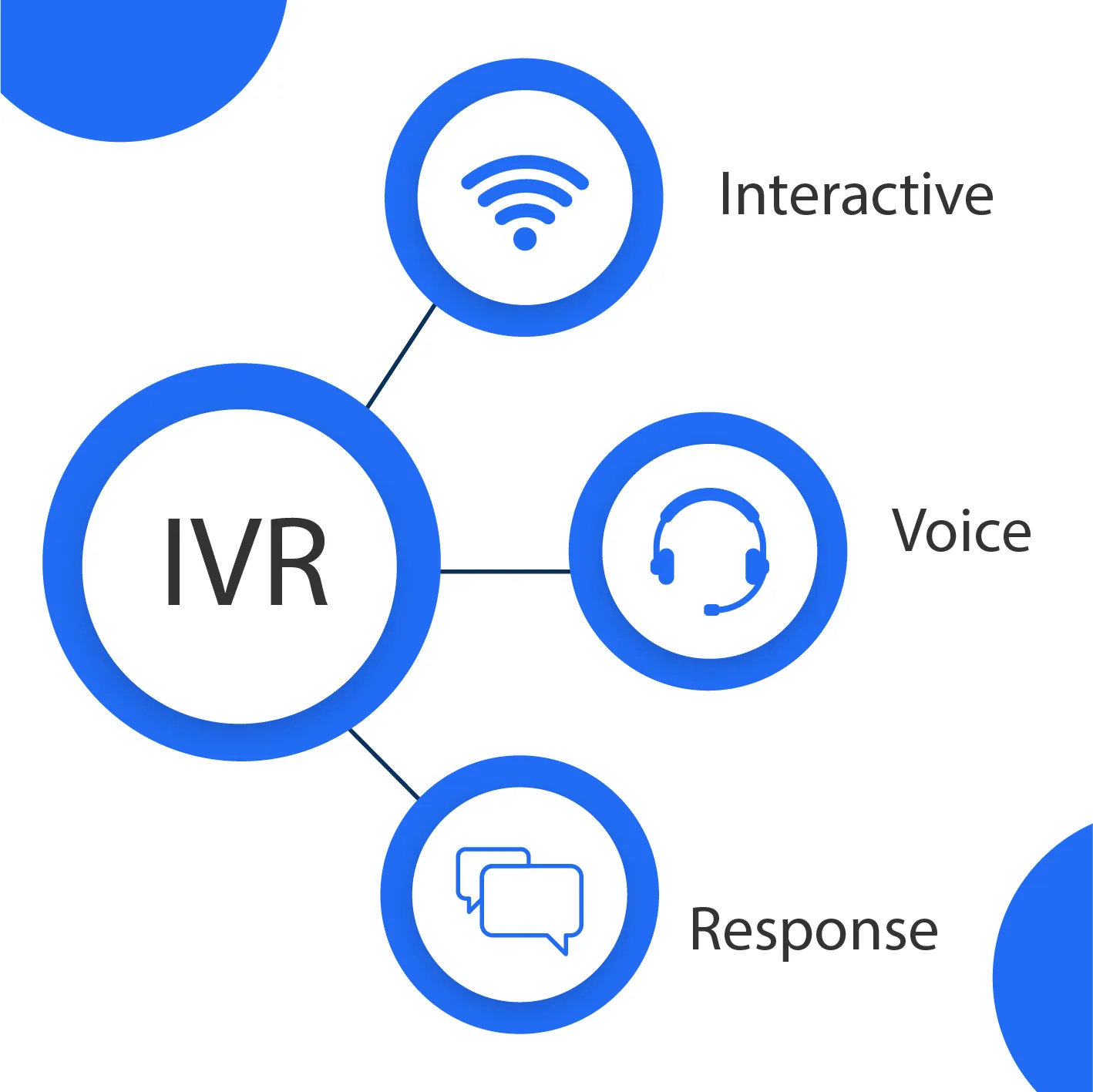
Utilized in telecommunication and call center technology, these interfaces allow interaction via spoken commands, providing auditory responses to users.
Gesture-based Interfaces
Emerging with development in technology, these interfaces respond to physical gestures. Commonly seen in gaming, virtual reality, and augmented reality applications.
Role in Robotics and AI
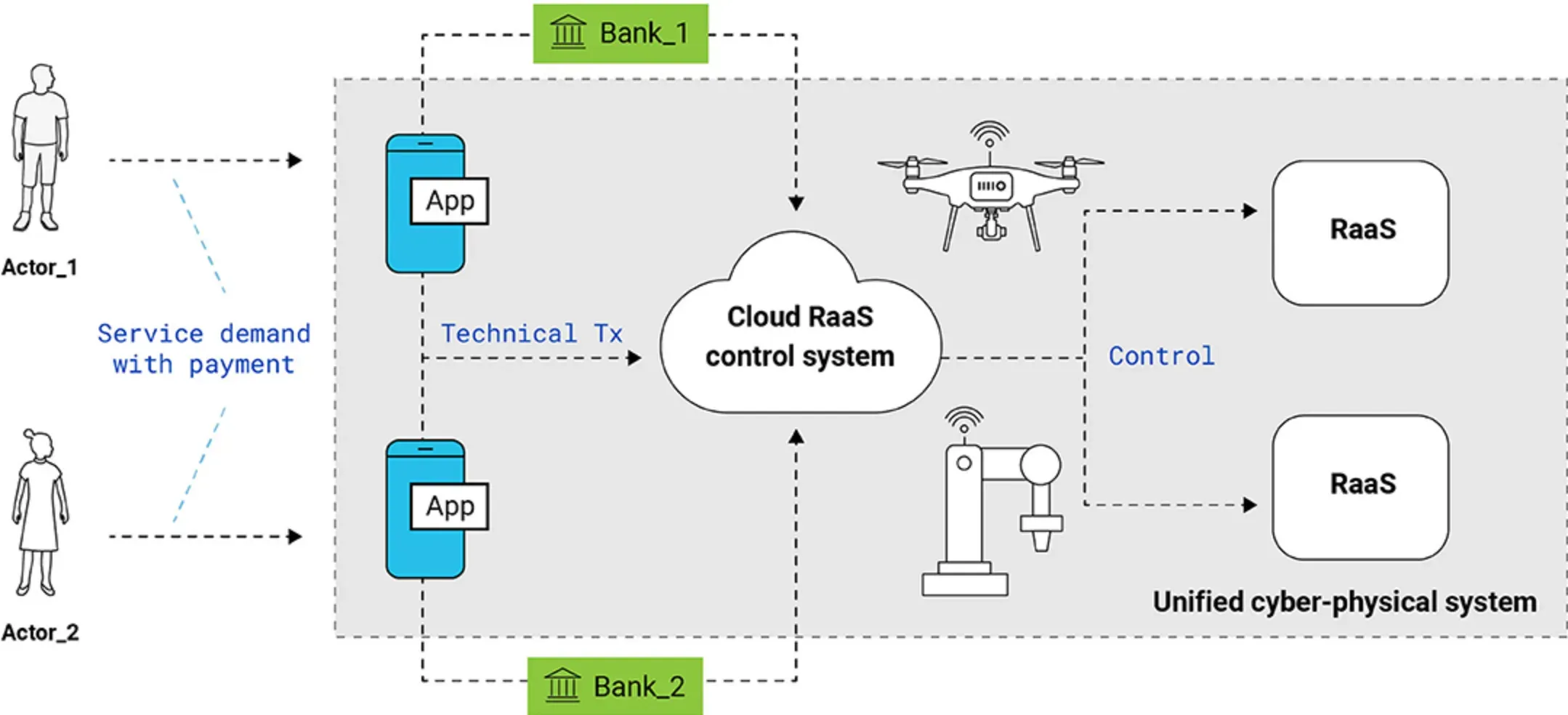
- Control of Robotic Systems: Agent Interfaces play an instrumental role in robotics. They aid in delivering control commands, signal processing, and sensory feedback in real-time robotic operations.
- Autonomous Microservices: Many Artificial Intelligence (AI) systems employ agent interfaces. These interfaces enable autonomous microservices to communicate with each other, provide status updates, and execute commands.
- AI Assistants: AI-driven assistants like Siri, Alexa, and Google Assistant utilize sophisticated agent interfaces, enabling them to receive, interpret, and respond intelligently to user queries.
- Machine Learning: Agent interfaces in machine learning systems are designed to facilitate data gathering for training algorithms, iterative learning processes, and refined prediction models.
Agent Interface in the IT sector
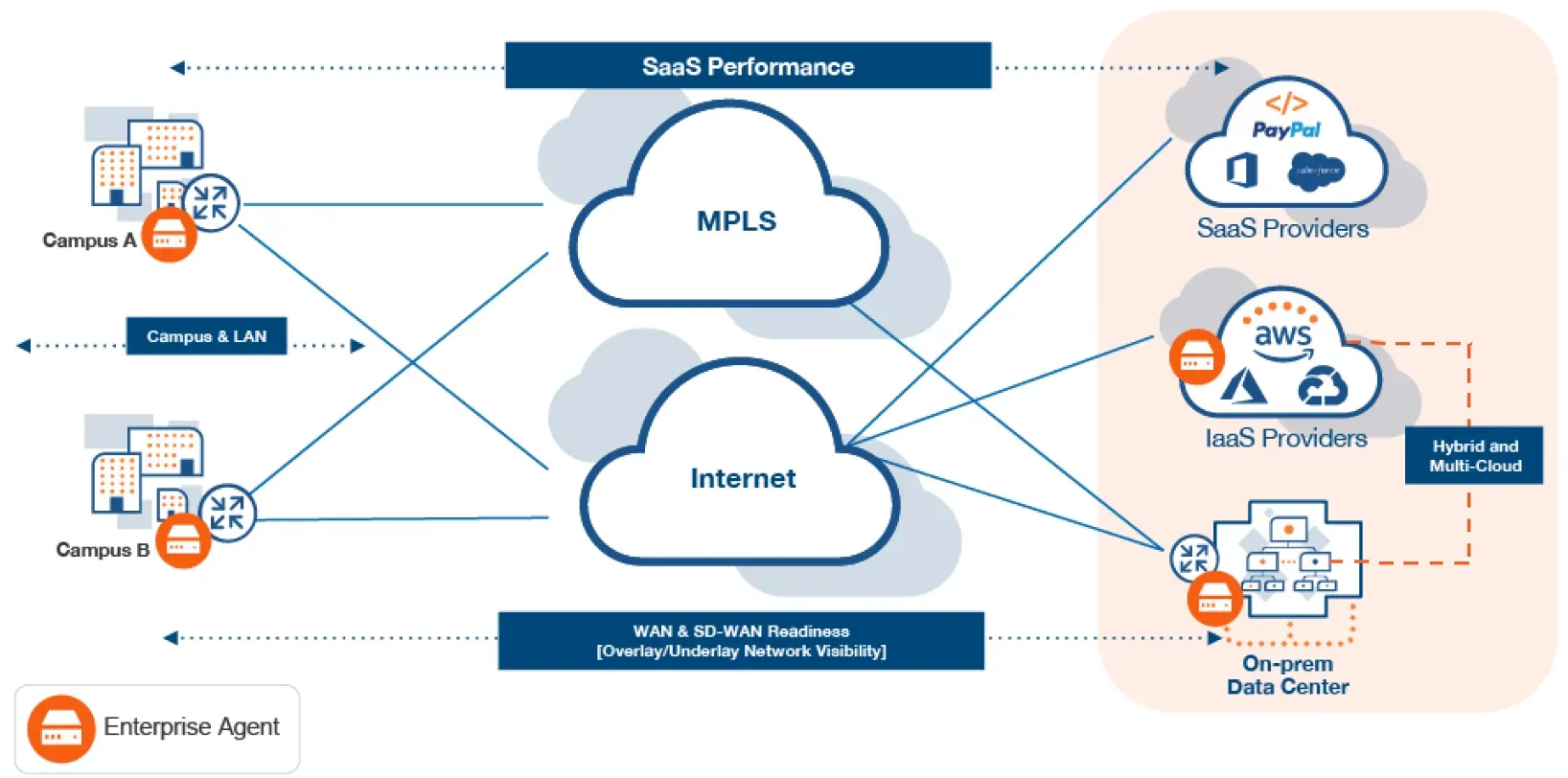
- IT Service Management (ITSM): ITSM employs agent interfaces to control various software agents, making service delivery more consistent, efficient, and automated.
- Network Management: Agent interfaces in network management software help monitor and control network elements, handle alerts, and enable automated responses to varying network scenarios.
- Software Development: Most Integrated Development Environments (IDEs) utilize agent interfaces for developers to interact with the software, simplify code writing, debugging, and testing.
- Data Management: Data-driven sectors such as databases, big data, and business intelligence use agent interfaces for successful transaction, manipulation, and presentation of data.
Design Principles for Agent Interface
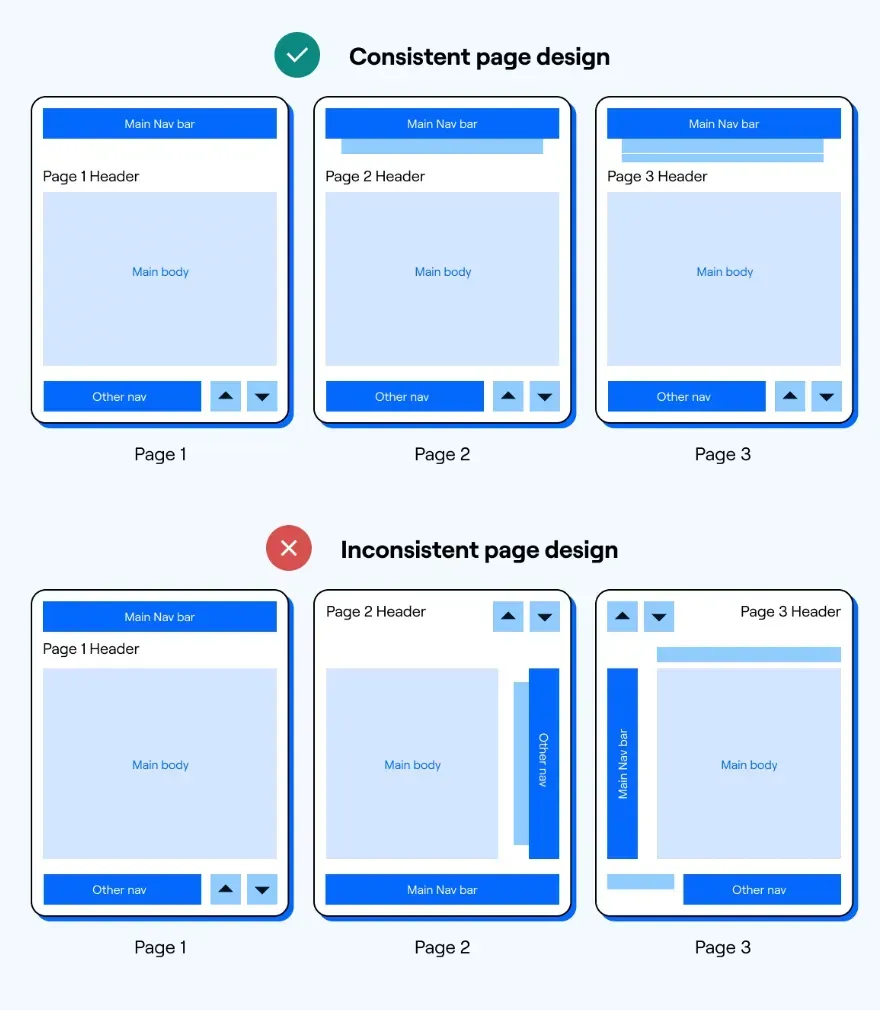
- User-Centric Design: The design of an agent interface should prioritize the audience's experiences and expectations. It should be intuitive, efficient, and accommodating different user skill levels.
- Consistency Matters: Consistency in the design, whether in configurations, command interfaces, or visual elements, helps users learn and operate the system faster without confusion.
- Quick and Responsive: A high-quality agent interface must cater to smooth interaction, quick command execution, instant feedback, and handle multiple tasks concurrently.
- Accommodating Evolving Technological Trends: As technology continues to evolve, so should agent interfaces. Incorporating the latest trends in interfaces, such as Big Data, AI, Machine learning, and VR, can significantly improve user engagement.
Challenges with Agent Interface
Complexity Management
As software systems grow more complex, so does the design and management of Agent Interfaces. Balancing complexity, functionality, and user experience can be a challenging task.
Integration with Multiple Systems
Integrating different system interfaces, each with unique requirements, can be tricky. Seamless interaction without compromising data security and integrity is key.
Dealing with Technology Changes
With the rapid evolution of technologies, interface design should consistently adapt to meet user expectations and accommodate emerging technological trends.
Security Concerns
Data security and privacy concerns are of the utmost importance, especially with increasing data breaches and cyber threats. Implementing robust security protocols within agent interfaces is critical.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is an Agent Interface?
An Agent Interface is a medium for interaction between computer systems or software environments, allowing command input, control operations, and providing sensory feedback.
Why is the Agent Interface important?
Agent Interfaces are essential for facilitating user engagement with software systems, driving command-control operations, and managing interactive responses within a system.
What are the components of an Agent Interface?
An Agent Interface consists of various interaction methods, feedback mechanisms, safety control measures, and a user interface.
How has the Agent Interface evolved with technology?
Agent Interfaces have progressed from basic text-based interfaces to graphical and voice interfaces, even to gesture-based systems in AI, VR, and gaming applications.
What challenges can one face with Agent Interfaces?
Maintaining simplicity in the face of growing complexity, integrating multiple systems, coping with rapid technology changes, and ensuring data safety are significant challenges with Agent Interfaces.