Introduction
Artificial Intelligence (AI) has almost become inseparable from modern business processes. It has already helped to automate several tasks.
However, the latest development that is making several heads turn is the introduction of task-driven autonomous agents. So, what are they and why is the hype around them? Let us understand with the help of an example.
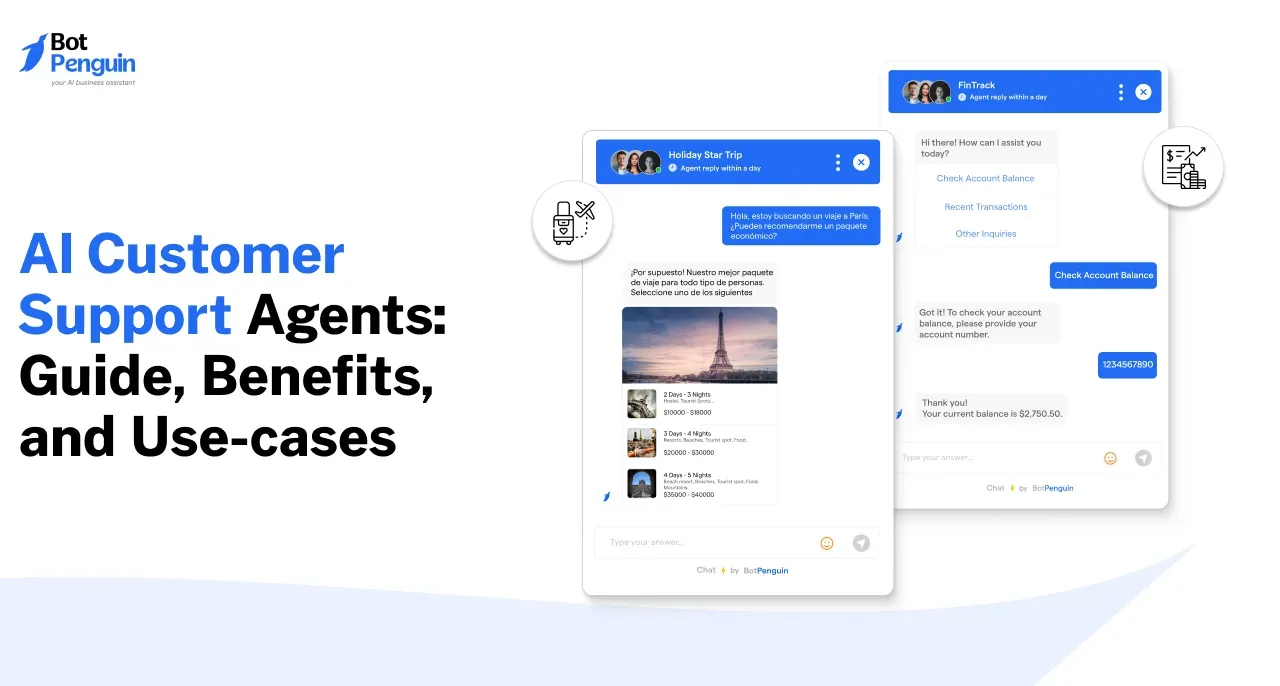
Imagine you are running a travel agency and a customer has booked a flight. Your default response will be limited to confirm the booking.
However, when you use a task-driven autonomous agent, you can enhance the process as it not only confirms the booking but also performs other relevant activities like arranging for hotel accommodation and providing the customer with a curated list of activities to enjoy during their trip.
The best part is that it doesn't require your support for all these activities. This is the power of a task-driven autonomous agent; It not only automates processes but also thinks, decides, and acts to streamline them, thereby making operations more efficient.
So, without further delay, let us learn more about task-driven autonomous agents, and how they are a boon to businesses.
Understanding Task-Driven Autonomous Agents
Task-driven autonomous agents can interpret and execute tasks without constant human intervention. Once they receive an objective, these agents can self-generate tasks, complete the assigned ones, and move on to the next until the objective is fully achieved.
In simple words, task-driven autonomous agents can prioritize a task and execute it to perfection without any guidance. Their actions are repeated until they complete their goal.
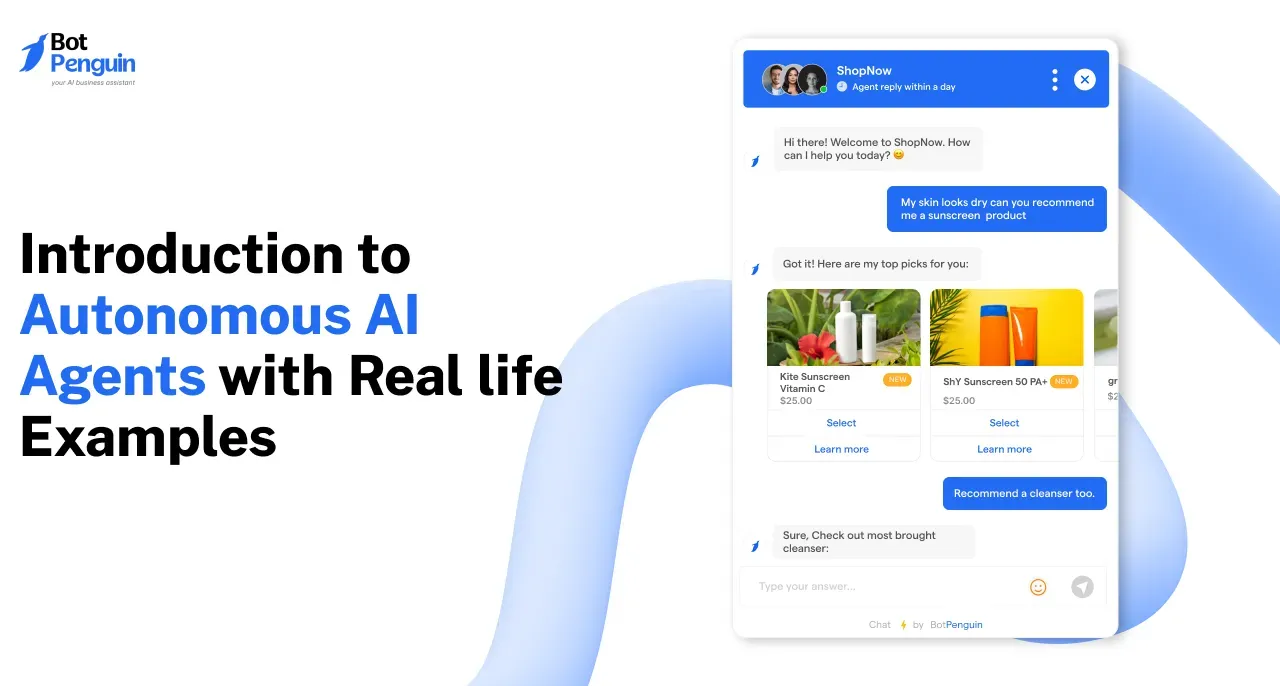
These agents can be designed to perform a variety of tasks from creating a personalized workout plan to providing cooking assistance to even becoming your virtual shopping assistant.
Also, task-driven autonomous agents are not limited to following pre-defined rules. They can function in dynamic environments which can prove to be very helpful in areas like customer service, marketing, sales, etc.
How Do Task-Driven Autonomous Agents Work?
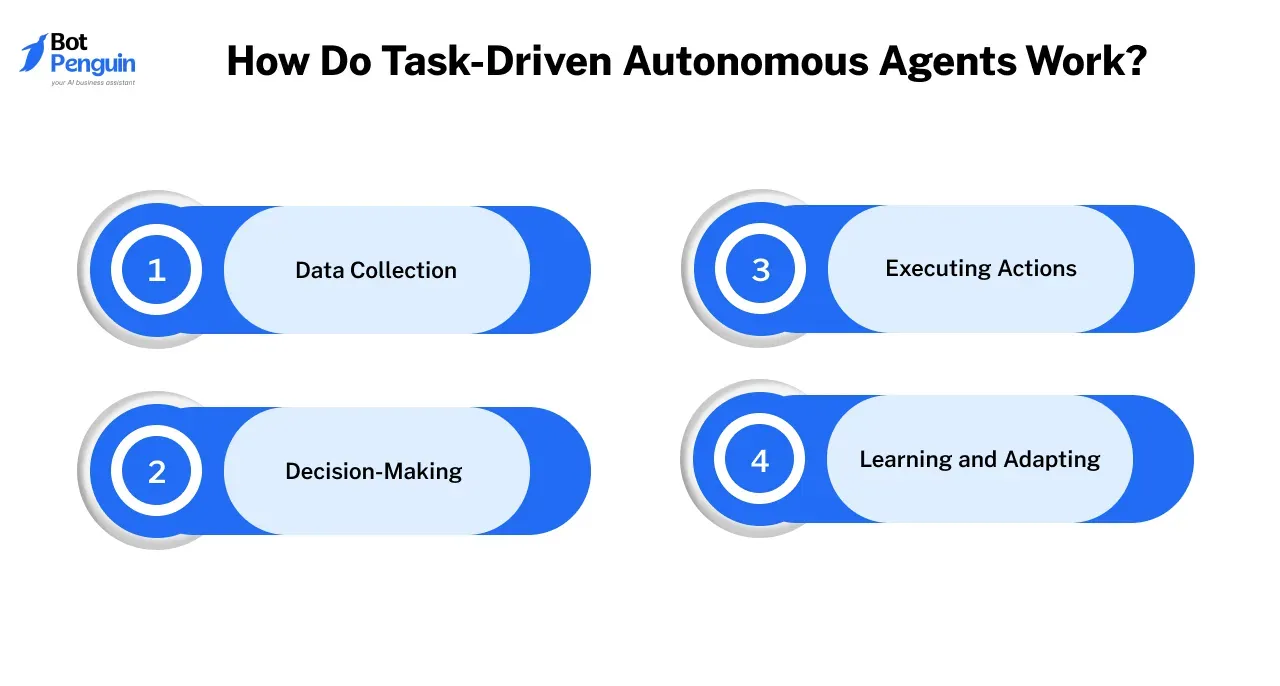
Task-driven autonomous agents operate using a combination of technologies such as machine learning, natural language processing, and real-time data analysis. Let us explore in detail about their working process.
Data Collection
The first step a task-driven autonomous agent does is to collect data from multiple sources like customer conversations, transaction records, and other external databases.
This step is the foundation for the agent to understand the context of each task it receives and to make informed decisions.
Decision-Making
Once the data is collected, the task-driven autonomous agent analyzes it with the help of machine learning algorithms.
It recognizes the patterns in the data, predicts outcomes, and then makes decisions that are in line with its objectives.
Executing Actions
After the task-driven autonomous agent makes its decision, it executes the required actions to obtain the desired results.
This process is designed to be effective, facilitating a smooth and satisfying experience for customers.
Learning and Adapting
A task-driven autonomous agent can learn from every interaction. It constantly updates its knowledge base and fine-tunes its decision-making abilities.
This helps the agents to perform better over time. Also, this adaptive nature helps in managing various tasks and scenarios.
By continuously learning and adapting, task-driven autonomous agents enhance efficiency, improve decision-making, and deliver seamless user experiences, making them invaluable assets across various industries.
How Do Task-Driven Autonomous Agents Differ from Chatbots?
Though a task-driven autonomous agent falls under the category of AI agents, not all AI agents can be considered to be autonomous. Let us probe more on this below.
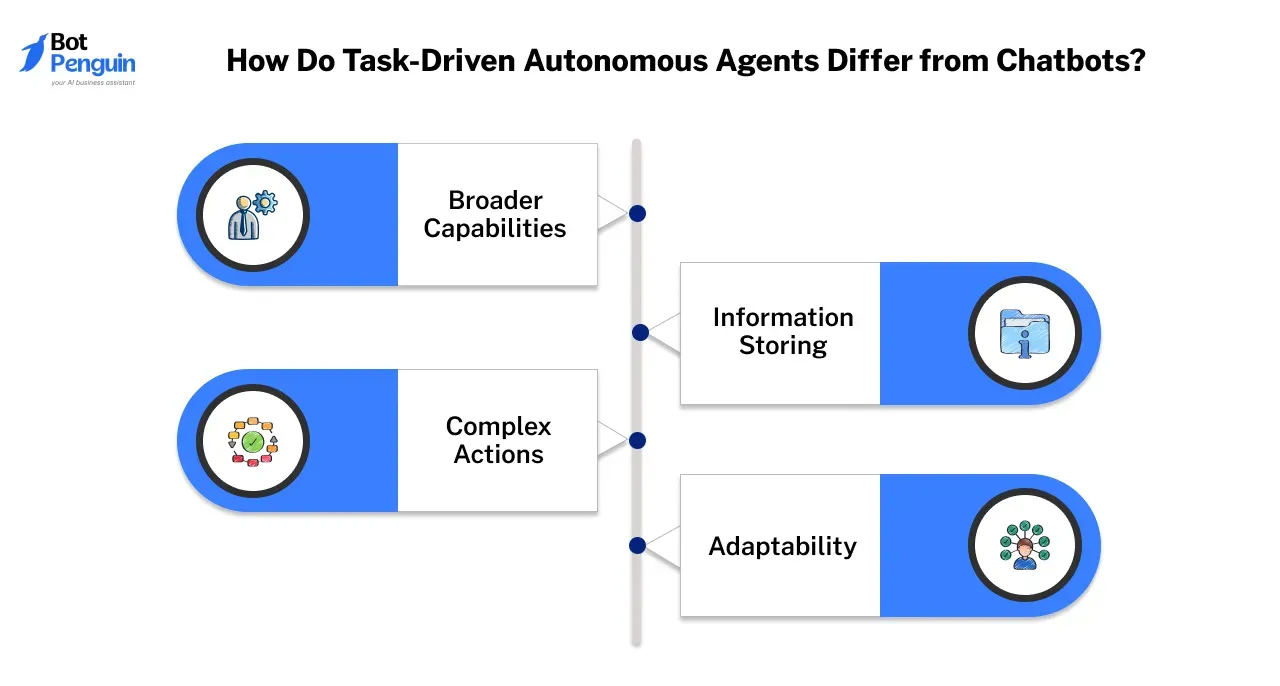
- Broader Capabilities: Chatbots are excellent at responding to user queries and handling specific tasks efficiently. A task-driven autonomous agent, on the other hand, goes a step further by working on multiple tasks based on its objectives and evaluating them before obtaining its goals.
- Information Storing: Traditional chatbots follow scripted responses and do not retain past interactions. In contrast, a task-driven autonomous agent can learn and store the feedback information in its memory, which it can refer to provide the best solution.
- Complex Actions: While chatbots are designed to provide responses based on input, a task-driven autonomous agent can perform complex actions and operations by using tools and memory. It can create tasks, set priorities, and arrange them to complete its goals.
- Adaptability: Chatbots are structured to follow predefined workflows, making them highly reliable for specific use cases. Meanwhile, a task-driven autonomous agent is highly adaptable and can handle dynamic environments efficiently.
Both chatbots and autonomous agents play crucial roles in AI-driven interactions. While chatbots continue to be powerful tools for customer engagement and support, autonomous agents bring in a new level of independence and decision-making.
What are the Types of Autonomous Agents?
There are several types of autonomous agents with each having their own way of working to obtain their goals. Let us explore a few of these common types below.
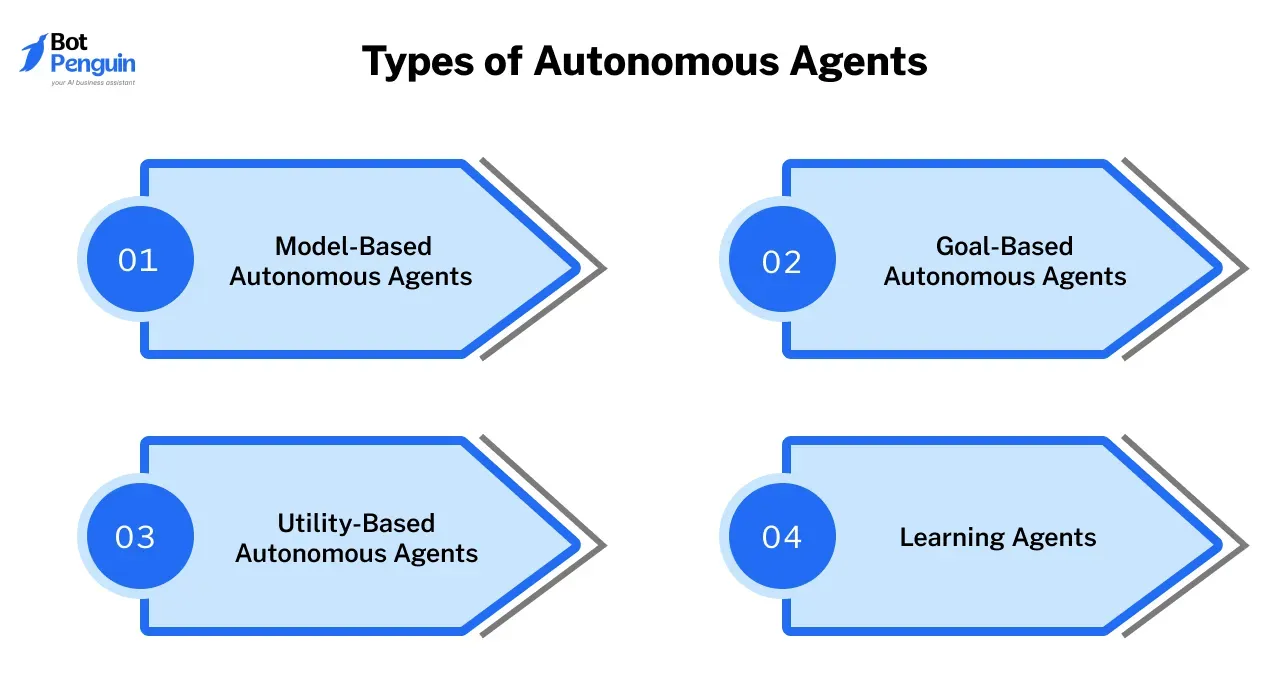
Model-Based Autonomous Agents
These types of agents can not only make decisions by using machine learning but also can learn and adapt over time.
When they are provided with an incomplete dataset, they can intelligently fill in the gaps with predictions based on their past experiences.
Goal-Based Autonomous Agents
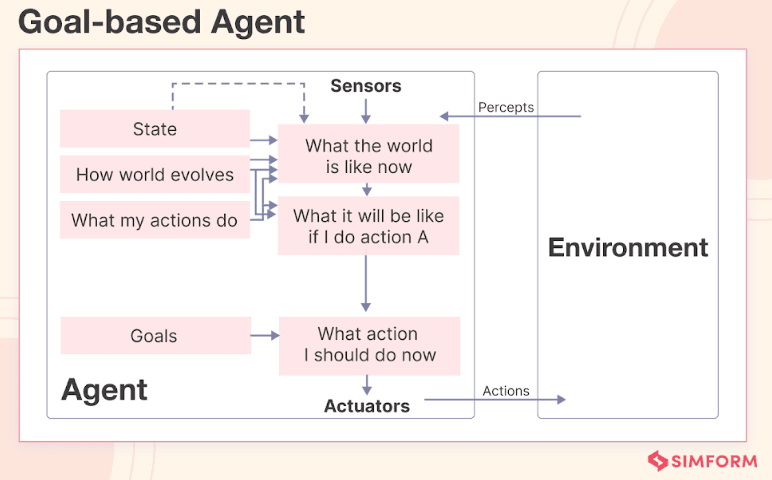
These agents make decisions by analyzing how their specific actions can drive them toward meeting their goals.
They can adapt easily, adjust internally, and respond effectively to changes in objectives or environments.
Utility-Based Autonomous Agents
These agents are similar to goal-based agents. However, a key difference is that utility-based agents evaluate actions by assigning ranks to outcomes based on their ability to meet goals.
They can also optimize their performance according to predefined criteria.
Learning Agents
Learning agents use additional learning algorithms to improve and gain more knowledge about their environment. These agents track their performance and use feedback that can suggest to them how to improve over time.
Understanding these different types of autonomous agents helps in choosing the right one for specific tasks, ensuring smarter decision-making and improved efficiency in various industries.
Advantages of Task-Driven Autonomous Agents
A task-driven autonomous agent is highly adaptive and can execute tasks effectively. Let us find a few of its advantages below.
- Increased Efficiency: A task-driven autonomous agent can automate repetitive tasks and allow employees to focus on more critical responsibilities. This can help in developing effective strategies and improving overall process efficiency.
- Accuracy: It excels in processing data accurately. Hence, it can make effective decisions while encountering specific issues in a dynamic environment. This can also help to minimize potential errors and deliver high-quality results.
- Speed: A task-driven autonomous agent can complete tasks quickly and efficiently. It can process huge amounts of information in a short amount of time and can conclude without any delays.
- Enhanced Customer Experience: When used in customer support, a task-driven autonomous agent can provide personalized and responsive interactions, thereby enhancing customer experience and satisfaction.
By combining speed, accuracy, and adaptability, task-driven autonomous agents enable businesses to optimize workflows, improve decision-making, and deliver exceptional customer experiences.
Applications of Task-Driven Autonomous Agents
A task-driven autonomous agent is so versatile that it becomes inevitable in various fields.
From streamlining customer service to transforming healthcare, it is reshaping industries by performing focused tasks with precision. Below are some of the most impactful applications of these systems.
Customer Service
When a task-driven autonomous agent is used in customer support, it optimizes the process effectively.
Suppose, a customer reports having trouble with their account login, the agent can quickly analyze their account details, check for any recent changes to the password or security settings, and provide the necessary steps to resolve the issue.
This helps the customers to get quick support while allowing human agents to focus on high-priority cases.
Healthcare
Patient experience can be improved greatly with the help of a task-driven autonomous agent. For example, after a patient undergoes surgery, the agent can automatically set up follow-up appointments, and send reminders for post-operative care.
It can also check in with them periodically to ensure they are not experiencing any complications, and in such cases, it can alert the healthcare provider immediately. This can provide timely care while reducing the administrative workload for healthcare professionals.
Sales and Marketing
A task-driven autonomous agent can drive targeted engagement and optimize strategies. If a company has launched a new product, the agent can analyze customer preferences and purchase history to identify those most likely to be interested in that product.
It can then send personalized email recommendations or special offers to them, thereby boosting customer engagement and increasing the chances of conversion.
Supply Chain Management
In this industry, a task-driven autonomous agent can effectively help in inventory management. When there is a shortage of a popular product, the agent can automatically reorder stock from the suppliers before it becomes completely unavailable.
It can also predict demand trends based on past sales records, which helps to maintain the right amount of inventory at the right time. This allows the businesses to operate smoothly and efficiently.
Task-driven autonomous agents are transforming industries by efficiently handling specialized tasks, enhancing productivity, and enabling businesses to deliver better customer experiences and optimized operations.
Challenges and Limitations of a Task-Driven Autonomous Agent
While a task-driven autonomous agent brings many advantages, it also comes with challenges and limitations.
Understanding these issues is crucial for managing expectations and ensuring the effective use of the system. Below are some of the key hurdles the agent faces.
Dependency on Data Quality and Quantity
A task-driven autonomous agent relies heavily on data to function. Poor quality or insufficient data can lead to errors, inefficiencies, or outright failures.
For instance, if this agent is used to recommend products to customers based on their browsing history, but it has been provided with incomplete or inaccurate data, it might suggest the wrong products. This might decrease customer satisfaction which might in turn impact sales.
Ethical Concerns
Ethical concerns are a significant challenge for a task-driven autonomous agent. Bias in data can lead to discriminatory outcomes, while privacy concerns arise when the agent handles sensitive information.
Suppose, the agent is used to screen job applications, but the training data contains biases, it could unfairly favor some candidates over others resulting in discrimination.
Additionally, if it handles sensitive personal data, like medical records, without proper security measures, it could risk exposing private information, raising privacy concerns.
Lack of Adaptability to Unforeseen Scenarios
A task-driven autonomous agent excels at specific tasks but often struggles in unexpected situations, like a delivery robot may not know how to handle a sudden road closure.
This lack of adaptability in such cases can disrupt operations and highlight the limitations of a task-driven autonomous agent compared to human problem-solving abilities.
Suggested Reading:
Detailed Introduction to LLM Powered Autonomous Agents
Maintenance and Cost Issues
Maintaining and updating a task-driven autonomous agent can be expensive and resource-intensive. Regular software updates, troubleshooting, and adapting to new requirements all add to operational costs.
Businesses must weigh these expenses against the efficiency gains to determine the agent’s overall value.
Task-driven autonomous agents undoubtedly offer significant benefits, however, businesses need to address challenges such as data quality, ethical concerns, adaptability, and maintenance costs to ensure they are used effectively and responsibly.
How to Get Started with a Task-Driven Autonomous Agent?
Getting started with a task-driven autonomous agent doesn’t have to be overwhelming. Whether you are an individual, a business, or a developer, there are practical ways to explore and implement this system.
Here is a guide to help you take the first steps.
For Beginners
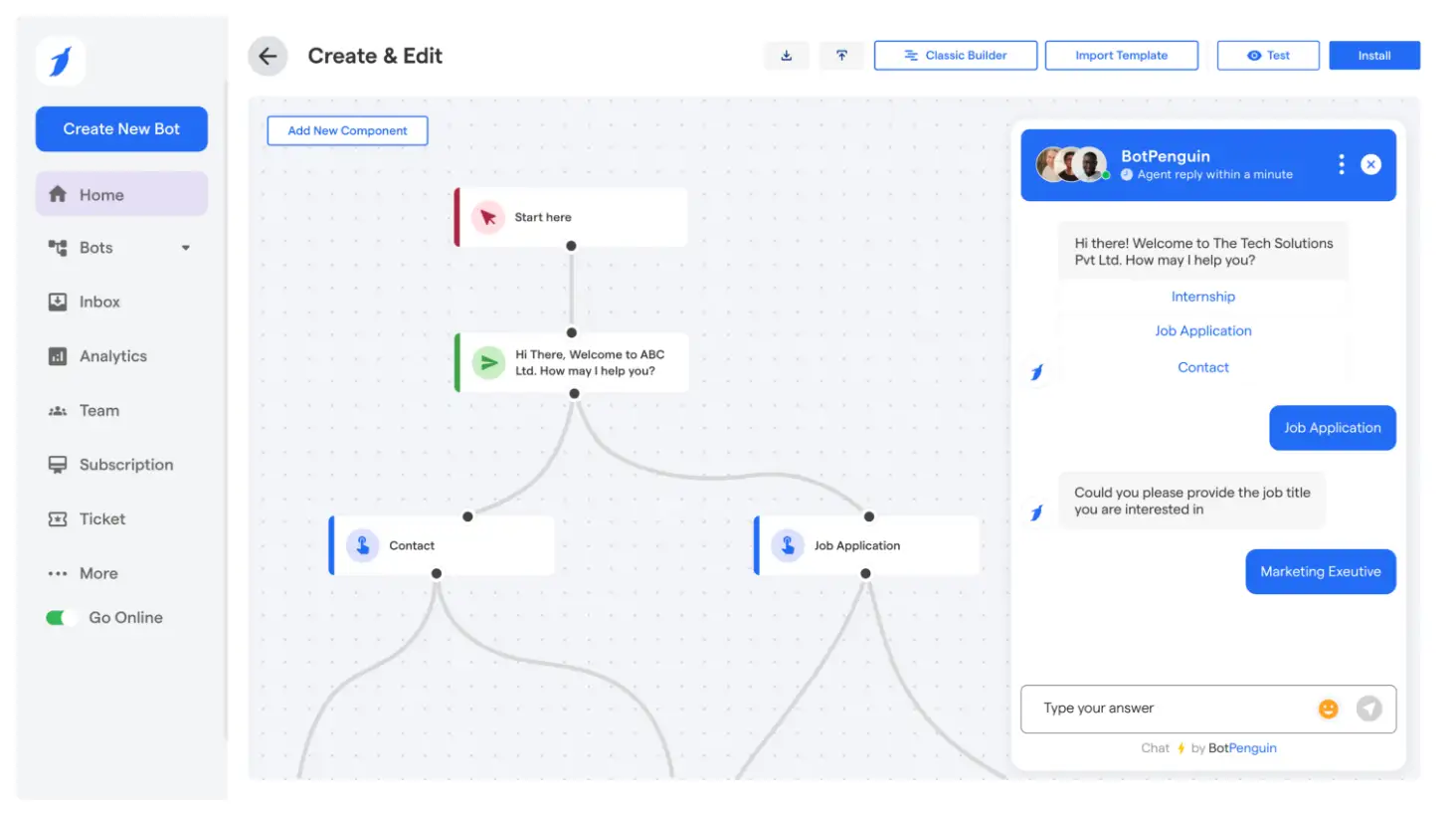
If you are new to task-driven autonomous agents, starting small is the best approach. Experimenting with basic platforms can help you understand their capabilities.
Try platforms like BotPenguin, Dialogflow, or Rasa. These tools allow you to create simple, rule-based bots without requiring coding knowledge.
Explore automation tools like IFTTT or Zapier, which simplify repetitive tasks in personal or professional settings. These steps provide a hands-on introduction and help you grasp how these agents function in real-world scenarios.
For Businesses
Businesses can harness the power of a task-driven autonomous agent to improve efficiency and cut costs. Start small by implementing a chatbot for customer support.
This is a low-risk way to automate responses to common queries while learning about the technology’s impact. Consider process automation tools to handle repetitive tasks like inventory management or data entry.
Evaluate the return on investment (ROI) by identifying specific tasks that consume significant time or resources. This ensures you prioritize automation efforts for maximum benefit.
For Students and Developers
Students and developers can dive deeper into the technical aspects of a task-driven autonomous agent by learning programming and exploring AI frameworks.
Begin with programming basics, especially Python, which is widely used in AI and automation. Study frameworks like TensorFlow, PyTorch, or Rasa to understand how agents are built and trained.
Analyze real-world examples, such as chatbots or delivery robots, to see how theory translates into practical applications. These steps lay the foundation for building more complex and effective agents.
By starting with small, manageable steps and gradually advancing to more complex implementations, anyone, whether a beginner, business, or developer, can effectively explore and harness the power of task-driven autonomous agents to achieve greater efficiency and innovation.
Conclusion
Task-driven autonomous agents are transforming the way we work and interact with technology. Their ability to focus on specific tasks with precision and efficiency makes them invaluable across industries.
For businesses looking to get started with AI-driven automation, BotPenguin is the perfect solution. More than just a chatbot maker, BotPenguin is an AI Agent that understands customer needs, automates interactions, and streamlines workflows across multiple channels.
Whether it is handling customer inquiries, providing smart recommendations, or managing appointments, BotPenguin works seamlessly, reducing costs, improving efficiency, and delivering 24/7 support without requiring technical expertise.
Its no-code interface makes AI accessible to businesses of all sizes, helping them scale effortlessly while enhancing customer engagement.
The journey into task-driven automation starts with the right tools, and BotPenguin is a great place to begin.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
How does a task-driven autonomous agent differ from a general-purpose AI?
A task-driven autonomous agent focuses on specific tasks, optimizing for efficiency and precision, while general-purpose AI, like GPT, is designed for versatility across a wide range of applications and creative problem-solving.
What industries use task-driven autonomous agents?
Industries like customer service, healthcare, logistics, retail, and smart homes use task-driven autonomous agents for automation, improving efficiency, cost reduction, and 24/7 availability.
What are examples of task-driven autonomous agents?
Examples include chatbots for customer support, delivery robots in logistics, virtual health assistants in healthcare, and smart home systems like Alexa or Google Assistant.
Are task-driven autonomous agents capable of working alongside humans?
Yes, task-driven autonomous agents are often designed to work alongside human employees. They handle routine or time-consuming tasks, allowing humans to focus on more complex or strategic activities.
How can I start using a task-driven autonomous agent?
You can begin with simple tools like BotPenguin, an AI agent, and a no-code chatbot maker, or explore platforms like Dialogflow and Rasa to automate specific tasks without needing advanced technical knowledge.