Introduction
A few years back, if someone had told you that machines could understand, and act based on your needs without your guidance, would you have believed it? Fast forward and arrive at the present, you will find that this is a reality.
Autonomous AI agents have well-established their place in various industries helping them in many ways.
Be it customer support where you can find these autonomous agents dealing with complex queries at ease, or in the supply chain where they are optimizing processes, they are definitely taking businesses to greater heights by making them smarter, and highly adaptable.
In this guide, we will explore how these agents work, their practical applications, and what this means for the future. Along the way, you will see surprising examples of AI shaping our world. By the end, you might question who or what is really in control.
What are Autonomous AI Agents?
Autonomous AI agents are intelligent systems that operate independently. They are not bound by constant human input.
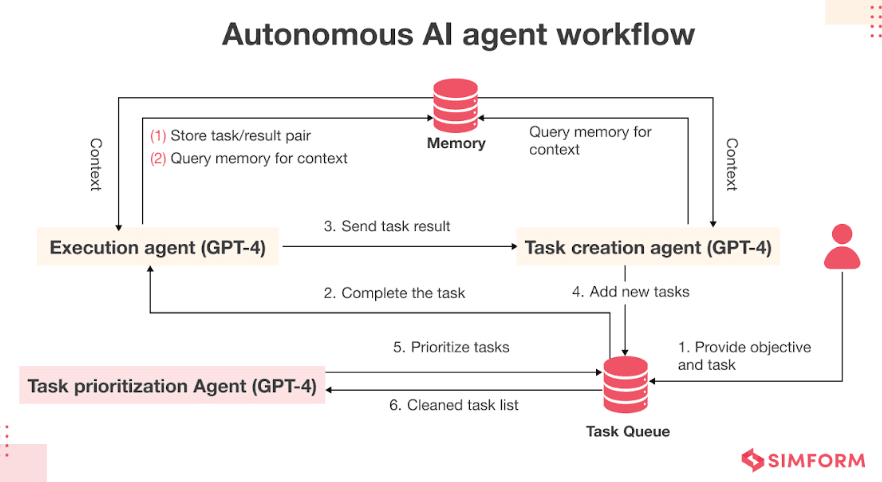
Instead, they analyze data, make decisions, and act to achieve predefined goals. Unlike traditional software, these agents are dynamic and capable of adapting to new challenges.
For example, a self-driving car is an autonomous agent in AI. It observes its surroundings, decides the best route, and navigates safely—all without human control. These systems combine advanced algorithms, machine learning, and decision-making models to perform tasks with minimal intervention.
Another good example will be OTT apps. When you open them, you can find suggestions on shows based on your previous preferences.
Who do you think is responsible for this activity? Undoubtedly, it is the work of AI autonomous agents. These automatic recommendations will save you time from searching for new shows.
Key Features of Autonomous AI Agents
While the excellent capabilities of autonomous AI agents are well-known, it is now time to explore their key features below.
- Autonomy: AI autonomous agents can make decisions and act independently without constant manual interference.
For example, chatbots handle customer queries without a human operator.
- Perception: These autonomous agents can identify and gather data from their environment like input mechanisms, sensors, and cameras.
For example, self-driving cars can recognize obstacles, traffic signals, and pedestrians using sensors and cameras.
- Action: Once the autonomous AI agents identify information, they can respond accordingly. For example, these agents in email systems can sort incoming emails into categories like promotions, and primary inbox, responding to organizational requirements without human supervision.
- Goal-Centered Behavior: Autonomous AI agents are designed to accomplish specific goals. For example, when an autonomous agent is used in inventory systems, it will automatically restock products when there is a shortage to ensure uninterrupted supply chain operations.
With these key features, autonomous AI agents are transforming industries by streamlining processes, enhancing efficiency, and reducing the need for constant human intervention.
Types of Autonomous AI Agents
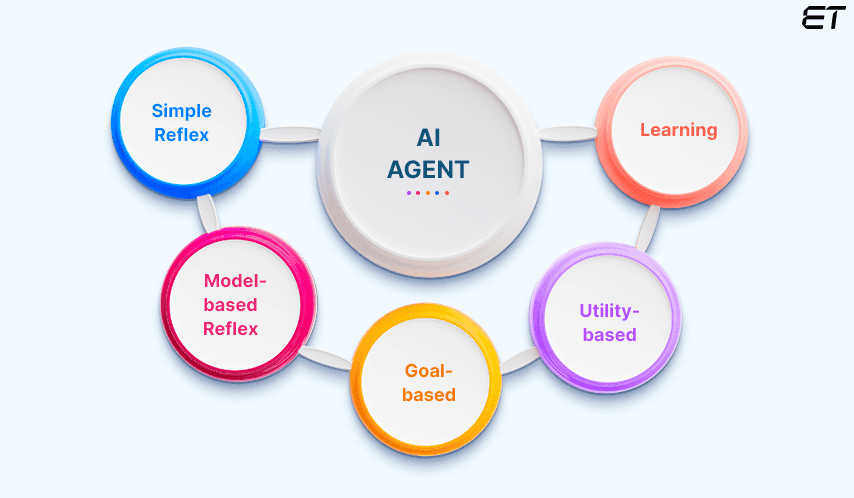
Autonomous AI agents come in various forms, each designed to tackle unique challenges. From digital problem solvers to robots and hybrid systems, these agents showcase the versatility of modern AI.
Let us dive into the main types of these agents and their capabilities.
Utility-Based Agents
Utility-based agents evaluate the possible outcomes of their actions and make decisions accordingly. They choose the actions that maximize overall utility. The goal is to strike the right balance for the best overall performance.
They can be used in complex decision-making processes like medical treatment selection, risky investment choices, etc. These agents use a mathematical utility function that evaluates every option and ranks them as per the most appropriate results.
For example, these utility-based agents when used in financial markets can evaluate, analyze, and forecast trends, and market dynamics and help to execute trades accordingly.
Goal-Based Agents
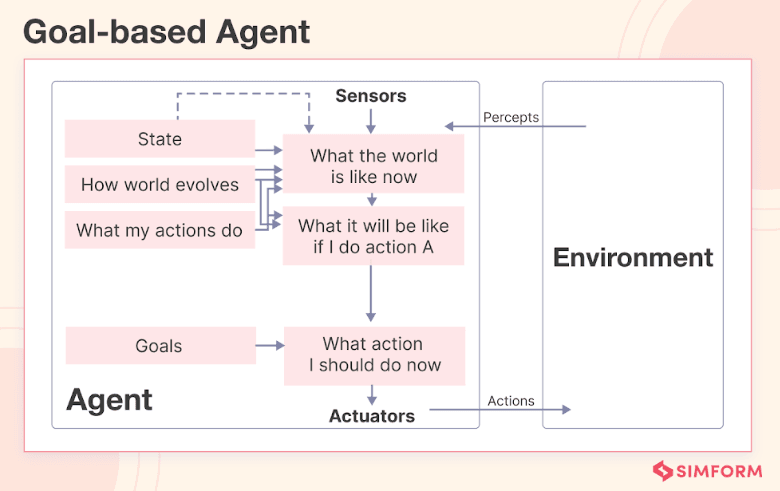
Goal-based agents execute tasks to fulfill particular objectives. They analyze the task and find the best solution to conveniently achieve goals. One of the best areas where you can use these agents is in project management.
They assist teams in coordinating, tracking, and prioritizing tasks and achieving project goals efficiently. These agents can analyze project data, suggest task assignments, or highlight potential delays in project milestones, ensuring teams meet deadlines effectively.
Model-Based Reflex Agents
Model-based reflex agents observe the environment, develop an internal representation (model), and then make informed decisions based on that representation.
A practical application where you can see these agents in action is in autonomous vehicles. The vehicles depend on these models to navigate the roads safely.
The vehicles use sensors and cameras to gather real-time information, process it, and decide their way of driving. It can either be to adjust their speeds, switch lanes, or avoid obstacles based on their internal model of the road conditions.
Learning Agents
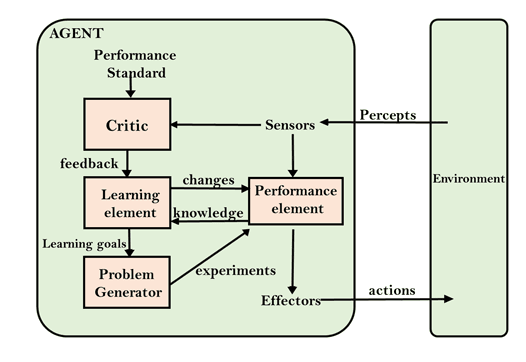
Learning agents can enhance their performance over time by learning from feedback.
Using machine learning algorithms, they can adapt and boost their decision-making abilities as they interact with their environment. A good example to understand these learning agents are apps like Netflix and Spotify.
They analyze your behavior, and preferences and suggest shows, movies, or music based on your previous interests. These learning agents constantly fine-tune their suggestions as they collect more user data.
Hierarchical Agents
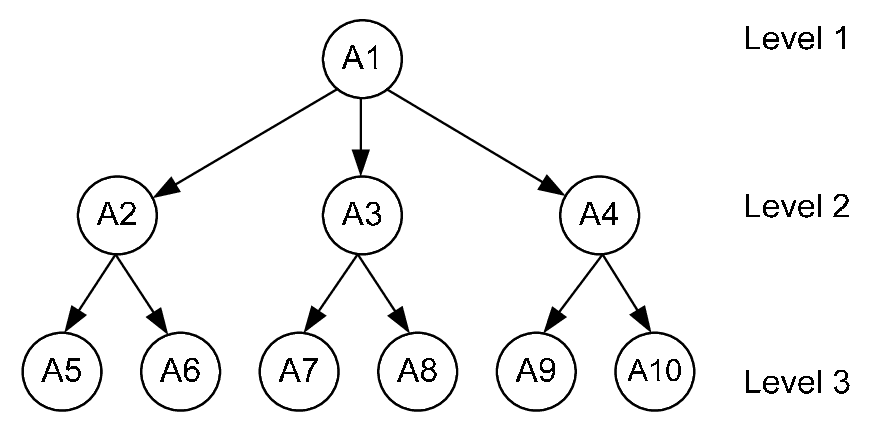
Hierarchical agents split tasks into smaller, achievable sub-tasks and handle them across various levels of complexity.
Due to this splitting of tasks, these agents can manage complex workflows and coordinate several operations simultaneously. You can take the example of air traffic control systems where these agents monitor and manage aircraft movements.
They process real-time data and provide flight paths, avoid collisions, and ensure there is sufficient distance between flights. This helps the operations to run smoothly even during peak seasons.
With their diverse capabilities, these different types of autonomous AI agents are changing the future of industries, improving efficiency, and handling complex problems with precision and adaptability.
Practical Examples of Autonomous AI Agents
Autonomous AI agents are already shaping the world around us, offering solutions across various fields. They operate independently, making decisions and performing tasks that once required human effort.
From answering questions to diagnosing diseases, driving cars, building products, and detecting financial fraud, their influence is vast. Here is a closer look at some of their applications across industries.
Customer Service
In customer service, autonomous AI agents have transformed how businesses interact with their customers.
They can provide instant responses, manage large volumes of inquiries, and handle repetitive tasks like account management or FAQs. These autonomous agents in AI function round the clock, reducing the need for human intervention.
For example, e-commerce companies use chatbots to assist customers with tracking orders, recommending products, or processing refunds. Advanced chatbots can even escalate issues to human agents when needed, ensuring seamless customer service.
A good example is BotPenguin, which can automate customer service tasks. It operates independently to provide instant responses to customer inquiries, manage orders, and resolve issues without human intervention.
This AI-powered chatbot can handle a variety of tasks, such as offering product recommendations, processing refunds, and escalating complex issues to human agents when needed.
Its ability to offer seamless assistance makes it a powerful example of how autonomous AI agents are transforming customer service and enhancing user experiences.
Healthcare
In healthcare, autonomous AI agents are revolutionizing patient care. IBM Watson Health is a prominent example, analyzing medical records, test results, and research data to assist doctors in diagnosing conditions and recommending treatment plans.
These autonomous agents in AI excel at identifying patterns in complex datasets, enabling early detection of diseases like cancer or heart conditions.
For example, Watson’s oncology tools have been used to provide evidence-based treatment recommendations, helping healthcare professionals make more informed decisions.
Also, robots like the da Vinci Surgical System are physical autonomous agents that enhance surgical precision.
While a surgeon guides the robot, AI provides real-time feedback to optimize movements and reduce errors. These systems are commonly used for procedures requiring high precision, such as cardiac surgery or prostatectomy.
Such applications of autonomous agents AI improve patient outcomes by minimizing invasiveness, reducing recovery time, and lowering risks associated with human error.
Suggested Reading:
A Comprehensive Guide to AI Agentic Workflow for Businesses
Transportation
Autonomous vehicles are one of the most transformative applications of autonomous AI agents. Companies like Waymo lead the way, developing self-driving cars that navigate roads using advanced machine learning, sensors, and decision-making algorithms.
These cars are equipped to identify pedestrians, traffic signals, and obstacles in real-time, ensuring safety while reducing the need for human drivers.
In cities where Waymo operates, people can already hail rides in fully autonomous vehicles, signaling the beginning of a new transportation era.
Delivery drones are another application of physical autonomous agents in AI. Companies like Zipline use drones to deliver medical supplies to remote areas, where traditional logistics are challenging.
These drones operate independently, following pre-set routes and making adjustments based on environmental factors like wind or rain.
Manufacturing
In manufacturing, robots have long been essential, but autonomous AI agents are pushing their capabilities further. These robots are not just pre-programmed machines; they learn and adapt to tasks over time, ensuring higher efficiency and fewer errors.
For example, they inspect parts for quality, identify defective products, and adjust their processes based on real-time feedback. This adaptability makes them indispensable in industries like electronics and automotive manufacturing.
Fanuc’s robots are leading examples of autonomous agents in AI. Used extensively in the automotive industry, they assemble car parts, weld components, and even test vehicle durability. By integrating AI, these robots optimize production workflows, predict maintenance needs, and minimize downtime.
Finance
Financial systems rely on autonomous AI agents to analyze vast datasets for anomalies that may indicate fraudulent activities. These systems work in real-time, flagging suspicious transactions for further investigation.
For example, AI-driven fraud detection tools analyze spending patterns and alert banks if unusual activity occurs on an account. This application of autonomous agents AI ensures better security for customers and businesses.
A real-time example is JPMorgan Chase which employs AI-powered trading platforms as autonomous agents to automate trading decisions.
These platforms monitor market conditions, analyze risks, and execute trades without human input. This automation not only speeds up transactions but also reduces human bias and error in decision-making.
Additionally, JPMorgan’s Contract Intelligence platform uses AI to analyze legal documents, saving countless hours of manual review while ensuring accuracy.
From healthcare to finance, autonomous AI agents are already making a significant impact, enhancing efficiency, accuracy, and safety.
Benefits of Autonomous AI Agents
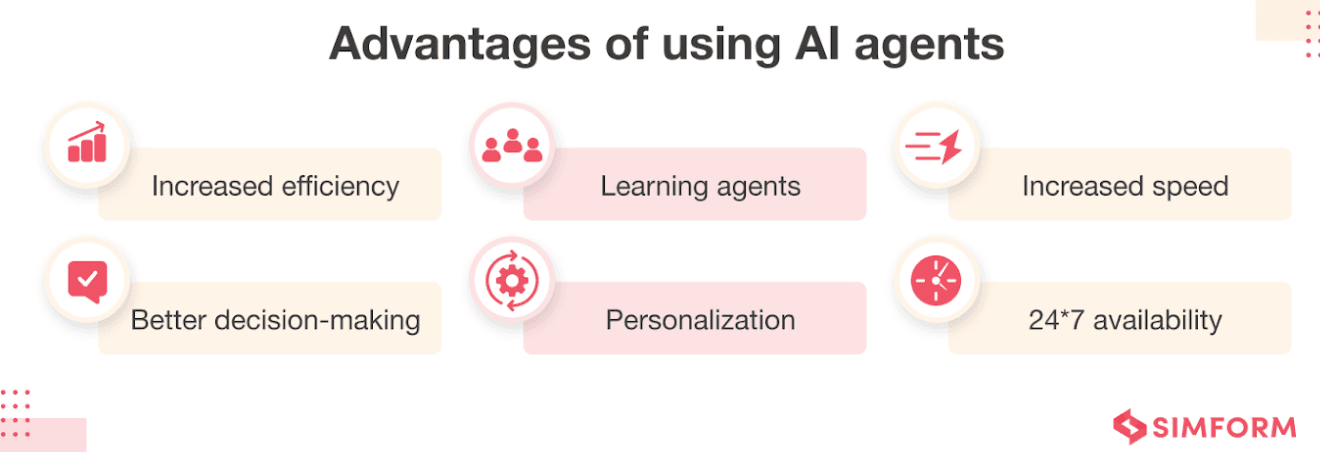
Autonomous AI agents are transforming industries with their ability to work efficiently and independently.
They bring a host of advantages, making processes faster, more accurate, and cost-effective. Let us explore the key benefits of these intelligent systems.
Increased Efficiency
One of the most significant advantages of autonomous AI agents is their ability to perform tasks with remarkable speed and precision.
They analyze large datasets, make decisions, and execute actions faster than humans. For example, in logistics, autonomous agents optimize delivery routes in real-time, saving time and fuel.
By eliminating delays caused by manual intervention, autonomous agents streamline workflows, allowing businesses to operate at peak efficiency.
Cost Reduction
AI autonomous agents reduce costs by automating repetitive and time-consuming tasks. In manufacturing, robots replace manual labor for tasks like assembly or quality checks, cutting labor costs while increasing production rates.
Moreover, autonomous agents in AI improve resource management. They minimize waste by predicting maintenance needs, reducing downtime, and ensuring optimal usage of materials and energy.
Suggested Reading:
AI Customer Support Agents: Guide, Benefits, and Use-cases
Informed Decision-Making
Autonomous AI agents can analyze huge amounts of data and generate useful insights that can help in making informed decisions.
They can be used in various industries like stock trading, supply chain, etc., where these agents provide real-time recommendations by analyzing data patterns, resulting in enhanced decisions.
Improved Customer Experience
Unlike humans, autonomous AI agents can work continuously without breaks. This 24/7 availability is a game-changer for industries like customer service, where chatbots and virtual assistants handle queries at any time of the day.
For example, a chatbot powered by autonomous agents AI resolves customer issues in real-time, providing round-the-clock support. This constant availability enhances user satisfaction while ensuring uninterrupted business operations.
Reducing Human Error
Humans are prone to errors, especially in monotonous or high-pressure tasks. Autonomous agents in AI eliminate these mistakes by relying on data-driven algorithms.
For example, in healthcare, autonomous AI agents analyze medical data with high accuracy, reducing diagnostic errors. Similarly, in finance, AI systems detect fraudulent transactions without missing critical details, ensuring reliability and security.
With their ability to work independently and efficiently, autonomous AI agents are helping businesses implement faster processes, achieve cost savings, and enhance accuracy, all while improving customer experiences and reducing human error.
Challenges and Concerns of Autonomous AI Agents
While autonomous AI agents bring incredible benefits, they also come with challenges and concerns that need addressing.
Ethical dilemmas, technical limitations, and societal impacts are significant areas of focus. Let us break down these challenges to understand their implications better.
Bias in Decision-Making
AI autonomous agents can unintentionally adopt biases present in their training data.
For example, hiring systems powered by autonomous agents in AI may unfairly favor certain demographics if the dataset used is biased. Ensuring fairness and neutrality in decision-making is a critical challenge.
Privacy Issues
Autonomous agents AI often require vast amounts of personal data to function effectively. Virtual assistants or chatbots, for instance, collect user information to provide personalized services.
This raises concerns about data misuse, security breaches, and a lack of transparency in how information is stored and used.
Handling Unexpected Scenarios
Even the most advanced autonomous AI agents struggle with unpredictable or rare situations.
For example, self-driving cars may fail to respond appropriately to unusual road conditions, posing safety risks.
Reliability in Critical Tasks
In critical industries like healthcare, autonomous agents must perform flawlessly. However, reliance on AI can lead to catastrophic consequences if these systems fail during surgeries or emergency diagnoses.
Building robust, fail-safe systems is a technical hurdle that developers must overcome.
Societal Impacts
One of the most debated concerns around autonomous agents is job displacement.
As automation replaces repetitive tasks, workers in industries like manufacturing, logistics, and customer service face job losses. While these changes create new opportunities, they also require significant reskilling efforts.
While autonomous AI agents offer immense benefits, addressing challenges such as bias, privacy concerns, and the potential societal impact of job displacement is crucial to ensure their responsible and effective deployment.
Ethical and Legal Implications
As autonomous AI agents continue to expand their role in society, ethical and legal questions are becoming increasingly important.
Clear regulations are essential to balance innovation with safety, ensure fairness, and hold these systems accountable for their actions.
The Need for Regulations
Governments and organizations are recognizing the need to regulate autonomous agents AI to address issues like privacy, bias, and accountability.
For example, the European Union has proposed the AI Act, which aims to create a legal framework for the safe and transparent use of autonomous agents in AI. Such initiatives strive to establish boundaries while encouraging innovation.
Balancing Innovation and Safety
Developing policies for autonomous AI agents requires a careful balance between fostering innovation and mitigating risks.
Too much regulation can stifle creativity, while too little can lead to misuse or harm. The challenge lies in creating standards that adapt as technologies evolve.
Ensuring Fairness and Accountability
Ethical AI must be fair and unbiased. Developers of autonomous agents must prioritize transparency and create mechanisms to audit decisions.
Accountability is crucial, especially when these systems operate in critical sectors like healthcare or finance. If an autonomous agent fails, clear guidelines must determine who is responsible.
As the role of autonomous AI agents grows, it is essential for businesses to establish clear regulations and ethical standards to ensure they are used safely, fairly, and responsibly.
Getting Started with Autonomous AI Agents
Getting started with autonomous AI agents can feel overwhelming, but the process is simpler than it seems.
Whether you are a beginner exploring AI, a business looking to streamline tasks, or a developer building intelligent systems, there are accessible tools and steps to get you started.
For Beginners
If you are new to autonomous agents AI, start small. Tools like ChatGPT or voice assistants such as Siri and Alexa are great introductions. These systems provide a glimpse into how autonomous AI agents operate in the digital realm.
For a hands-on experience, explore open-source projects like AutoGPT. These platforms allow you to experiment with building autonomous agents for tasks like summarizing documents or automating workflows. They are beginner-friendly and require minimal technical expertise.
For Businesses
Businesses can benefit greatly from autonomous agents in AI by automating repetitive or resource-intensive tasks. Start by identifying areas like customer service, data analysis, or inventory management that could be streamlined.
Once you have identified the tasks, research platforms, or vendors that specialize in autonomous AI agent solutions, tools like Salesforce Einstein for customer relationship management or RPA (Robotic Process Automation) software can bring immediate efficiency to your operations.
For Developers
Developers interested in creating autonomous agents should begin by learning AI frameworks like TensorFlow or PyTorch. These tools provide the foundation for designing, training, and deploying intelligent systems.
Start with small projects, such as building a chatbot or a recommendation engine. These simple systems will help you understand the core mechanics of autonomous agents in AI. As you gain confidence, you can tackle more complex applications like self-learning agents or robotics.
By taking small steps and using the right tools, beginners, businesses, and developers can easily start their journey with autonomous AI agents, unlocking the potential to enhance efficiency, improve services, and build intelligent systems.
The Future of Autonomous AI Agents
The future of autonomous AI agents is poised to bring transformative changes across industries and everyday life.
From personalized interactions to collaborative technologies, these systems will continue to evolve, integrating more deeply into our world. Let us explore key trends, emerging areas, and long-term predictions for their impact.
Trends
As technology advances, autonomous agents AI will become more tailored to individual needs.
Virtual assistants will anticipate user preferences, offering highly personalized recommendations and solutions.
Emerging Areas
The use of autonomous agents in AI is expanding into creative domains like writing, design, and music. AI systems are already generating articles, composing songs, and designing graphics, pushing the boundaries of creativity.
In manufacturing, collaborative robots or “cobots” are redefining workflows. These autonomous AI agents work alongside humans, enhancing productivity while ensuring safety in shared spaces.
Long-Term Predictions
In the future, autonomous agents will seamlessly integrate into daily activities, from managing smart homes to assisting with healthcare. Their presence will become as common as smartphones are today.
The relationship between humans and autonomous agents in AI will grow into a partnership. These systems will complement human decision-making rather than replace it, creating a balanced collaboration.
As autonomous AI agents continue to advance, they will become an integral part of our everyday lives, offering personalized experiences, boosting creativity, and transforming industries.
Conclusion
Autonomous AI agents are transforming the way we live and work, offering unparalleled opportunities for efficiency, innovation, and growth.
They help businesses streamline operations, improve customer service, and tackle complex challenges with ease. Whether it’s a chatbot resolving queries or a robot automating a factory line, these systems are shaping the future.
For businesses ready to explore the possibilities, tools like BotPenguin provide a great starting point.
As a no-code AI chatbot maker, BotPenguin empowers businesses to create intelligent chatbots quickly and effectively. By automating customer interactions, it enables organizations to enhance engagement and focus on what truly matters.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
How do autonomous AI agents work?
Autonomous AI agents follow a process of perception (data gathering), decision-making (analyzing and choosing actions), and execution (performing tasks), supported by technologies like machine learning, NLP, and robotics.
What are some practical examples of autonomous AI agents?
Examples include chatbots like Alexa, self-driving cars such as Waymo, surgical robots, factory automation tools, and fraud detection systems in finance.
What industries benefit most from autonomous AI agents?
Industries like healthcare, manufacturing, transportation, customer service, and finance benefit greatly by automating tasks, improving efficiency, and reducing human error.
What are the challenges of using autonomous AI agents?
Challenges include ethical concerns like bias, technical limitations in handling unexpected scenarios, and societal impacts like job displacement and over-reliance on technology.
How can businesses get started with autonomous AI agents?
They can start by identifying tasks for automation, exploring platforms like BotPenguin for chatbots, and integrating suitable AI tools into their workflows.