Introduction
Over 70 percent of customer queries are now handled without a human when chatbot assistants are set up correctly.
Yet many teams still struggle to get consistent results from them.
The issue is rarely the AI itself. It is how the assistant is created and used.
This guide is written to close that gap. It is a how to use chatbot assistant guide focused on practical steps, not theory.
You will learn how to create a chatbot assistant using BotPenguin, set it up with clear intent, deploy it on the right channels, and use it daily.
It also shows how to improve the assistant after launch, based on real conversations, without hype or technical overload.
What a Chatbot Assistant Does in Real Life
A chatbot assistant handles conversations that would otherwise need human time.
It answers common questions. It guides users to the right next step. It collects details without friction.
It can even trigger actions like creating a ticket or booking a meeting. This how to use chatbot assistant guide focuses on these real moments, not abstract capabilities.
Think of a visitor asking about pricing at midnight. Or a customer checking an order update. Or a lead wanting a quick demo link.
A chatbot assistant steps in, responds instantly, and keeps the interaction moving forward.
That is the real job of a chatbot assistant.
Chatbot Assistant vs Traditional Chatbots
Traditional chatbots and chatbot assistants are built for very different types of conversations.
The table below compares them based on their performance in real-world scenarios.
This table makes clear why setup and usage feel different. Traditional chatbots depend on perfect paths. Chatbot assistants depend on clear intent and context.
This distinction is central to modern how to use AI chatbot assistant guide approaches.
Once this difference is clear, it becomes easier to decide where chatbot assistants fit best and how they should behave across different channels.
Where Chatbot Assistants Are Commonly Used
Chatbot assistants appear where conversations already happen.
- On websites, they guide visitors, answer questions, and capture leads.
- On WhatsApp and Instagram, they handle quick queries, updates, and follow-ups in a familiar format.
- Internal teams use them too. Support agents rely on assistants to draft replies or pull information fast. Sales teams use them to qualify leads before a call.
Each channel has a different intent. Website visitors explore. Messaging users expect speed. Internal users want efficiency.
Knowing this shapes AI chatbot assistant strategies across platforms.
Before building one, it helps to pause and consider goals, users, and context. That groundwork comes next.
Getting Ready Before You Use a Chatbot Assistant
A chatbot assistant is flexible but still requires direction. This is where many projects go wrong.
Good results start before anything is built. You need to know what problem the assistant should solve, whom it should speak with, and what information it should rely on.
This how to use chatbot assistant guide treats preparation as part of the build, not a separate step.
Without clarity, even the best tools struggle. With it, setup becomes faster and decisions feel obvious.
Defining the Goal of Your Chatbot Assistant
A chatbot assistant should have a clear initial task. Trying to make it handle support, sales, onboarding, and updates on day one usually creates confusion.
For example, a small ecommerce team might begin with questions about order tracking and delivery.
A SaaS company might focus on demo requests and pricing queries. Both are valid. What matters is focus.
When the goal is clear, instructions become simpler, and conversations feel natural. This clarity is central to scalable chatbot assistant practices.
You can always expand later, once real usage shows what else the assistant should handle.
Choosing the Right Channel to Deploy
Where the chatbot assistant lives matters as much as what it does.
Users behave differently across channels. Website visitors explore and compare. WhatsApp users expect fast, short replies.
Instagram users often ask quick questions before taking action. The same assistant must adapt to these contexts.
Platforms like BotPenguin make this easier by allowing a single assistant to work across channels from a single setup.
This flexibility supports modern AI chatbot assistants without forcing duplicate work.
With goals set and channels chosen, the actual build becomes far more straightforward.
The next step is turning these decisions into a working assistant, one piece at a time.
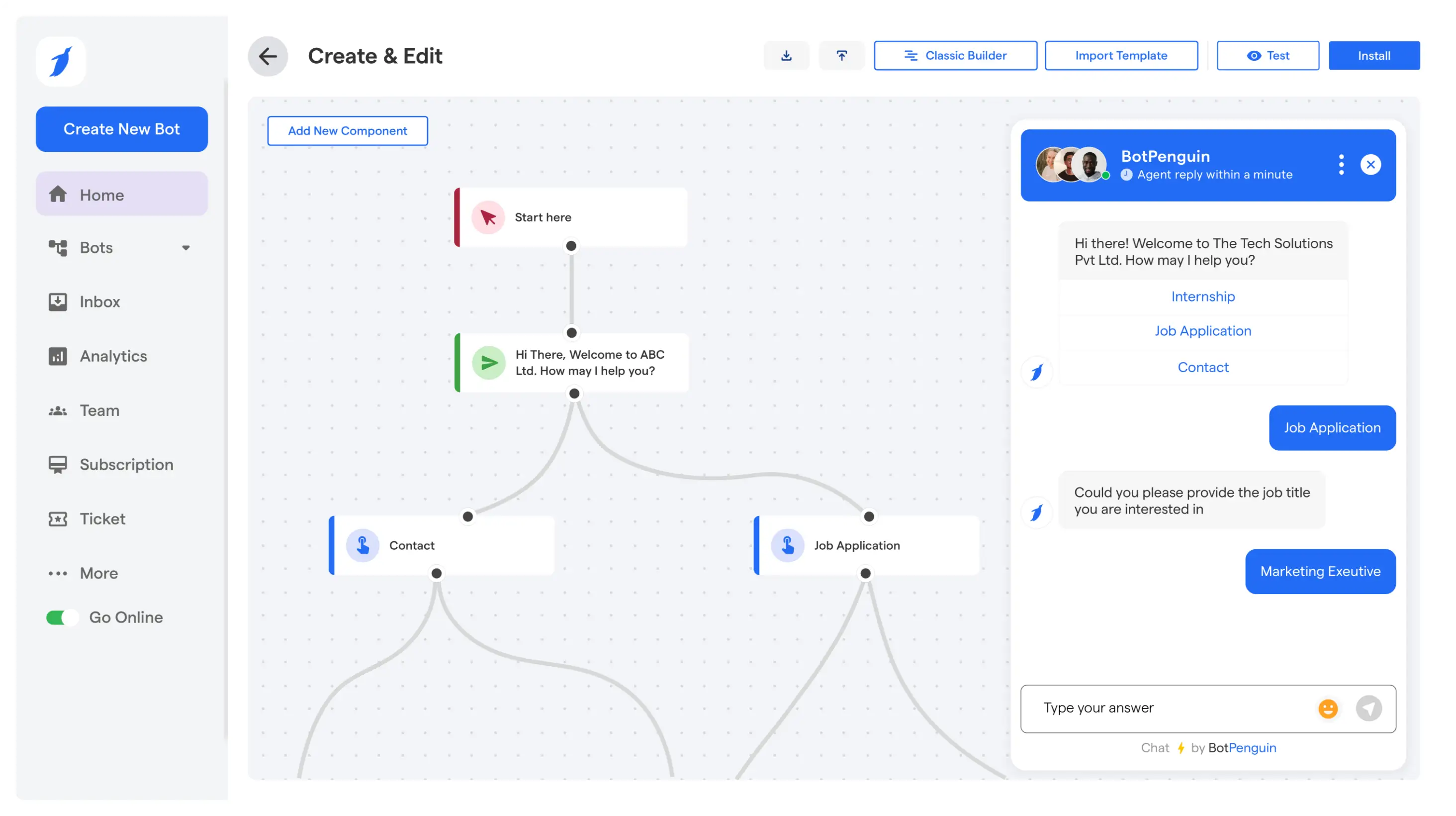
Step-by-Step Setup of a Chatbot Assistant Using BotPenguin
This is the main part of the how to use chatbot assistant guide. It outlines steps to build the assistant so it feels usable from day one.
No code tools like BotPenguin keep this process structured. With an easy-to-use interface and team support, you can launch your chatbot assistant within hours. Let’s see how!
Defining the Assistant’s Role
Start by logging into BotPenguin using Google or Facebook. Once you are in, choose the platform where you want the assistant to run.
This could be your website, WhatsApp, Facebook, Telegram, Instagram, or MS Teams.
Next, pick a business goal. This is where the role becomes clear. Choose from lead generation, customer support, appointment booking, marketing automation, ecommerce, or a custom goal.
This choice is not just a label. It shapes how the assistant behaves and what it prioritizes.
After that, you can select a bot template from BotPenguin’s pre-made options. Templates speed up the process when you need a proven structure.
If your use case is unique, you can skip templates and build a custom assistant from scratch.
Role clarity at this stage keeps the assistant focused and prevents messy conversations later.
Setting Tone and Personality
Once the role is set, define how the assistant should sound. Tone affects trust more than people expect.
For example, a WhatsApp assistant for order updates should reply fast and simple. A website assistant handling pricing questions can be slightly more detailed and guiding.
With BotPenguin, you can shape this through configuration choices and behavior settings.
Keep replies short. Use simple words. Avoid long paragraphs. This is where you need to align the assistant’s voice with the channel and the job.
Training the Chatbot Assistant
Now you configure the bot. This is where the assistant learns what to say and how to handle common situations.
In BotPenguin, configuration includes editing the chat flow, training the assistant on your data, designing the look and feel, and installing it on the chosen platform. If you started with a template, you will now customize it to match your business.
If you went custom, this is where you build the core conversation paths and responses.
Training should be focused. A lead generation assistant needs pricing, use cases, and booking steps.
A support assistant needs policies, troubleshooting steps, and escalation rules.
Do not aim for perfection here. Aim for coverage of the top questions. You can refine later based on real chats.
What Data to Use for Training
Use data that answers real customer questions.
Good sources include FAQs, help center articles, product pages, shipping and return policies, and onboarding guides.Keep it up to date and easy to read.
Remove internal shorthand and confusing phrasing. For example, if your refund policy spans three pages, consolidate it into a single, clean reference.
This reduces wrong answers and keeps the assistant consistent.
Clean training inputs are a big part of this how to use chatbot assistant guide working well in real conversations.
Connecting Tools and Systems
Next comes advanced settings. This is where the assistant becomes more than a chat box.
In BotPenguin, advanced configuration includes bot behavior settings, pre-built settings, and third-party app integrations.
This is where you connect CRMs, calendars, ticketing tools, and automation platforms.
If a user requests a demo, the assistant can capture the details and enter them into your CRM.
If a user reports an issue, it can create a ticket and route it to the right team.
After that, test the assistant. Ask messy questions like a real user would. Try short messages. Try vague messages.
Then adjust behavior settings until responses feel clear.
Finally, deploy.
Once it is live, the work shifts from building to using it daily, spotting gaps, and improving based on what users actually ask.
That is the natural next step in any how to use ai chatbot assistant guide that is built for real outcomes.
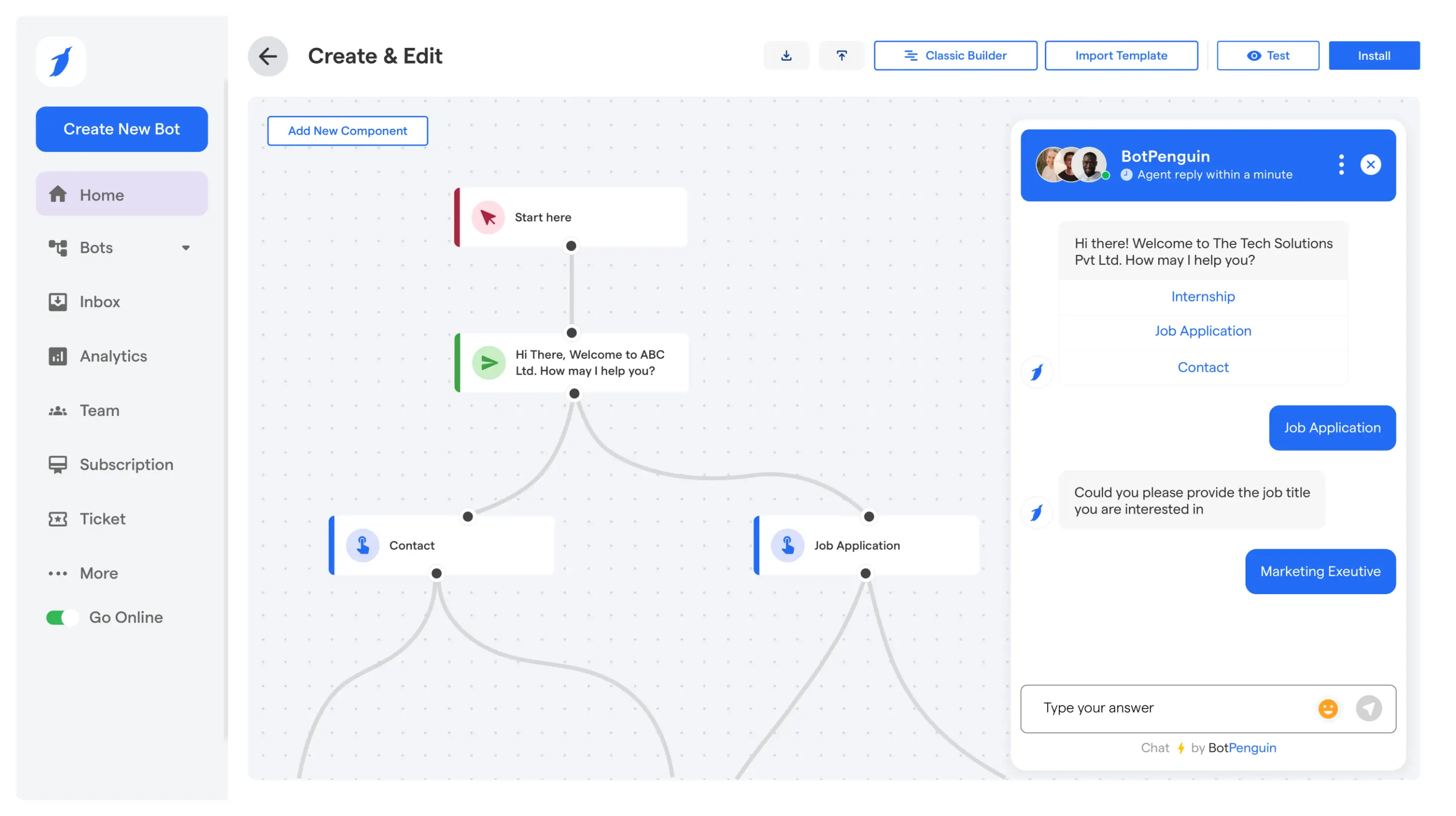
How to Use a Chatbot Assistant Day to Day with BotPenguin
A chatbot assistant is not something you set up and forget. It becomes part of daily operations.
In BotPenguin, teams use the dashboard to see live conversations, review past chats, and step in when needed.
Over time, patterns start to appear. You see what users ask most. You see where the assistant performs well and where it hesitates.
This how to use chatbot assistant guide treats daily usage as an ongoing process. The goal is simple.
Let the assistant handle routine work. Let humans focus on cases that need judgment.
Handling Customer Questions Automatically
Most daily conversations are predictable. Order status. Pricing. Working hours. Basic how-to questions.
BotPenguin handles these automatically using the training and behavior settings you configured earlier. A user asks a question.
The assistant responds instantly, regardless of time or channel.
There is no waiting. No ticket queue.
For example, a customer checking delivery status late at night gets an answer without involving support. Multiply this across hundreds of conversations, and the workload drops fast.
Capturing and Qualifying Leads
Not every conversation is supportive. Many are opportunities.
A website visitor asks about pricing. The assistant explains options, then asks a simple follow-up. Company size. Use case. Timeline.
These questions feel natural, not like a form.
BotPenguin captures this information and syncs it to connected systems in the background. Sales teams get clean leads without manual entry.
Conversations stay smooth.
This flow reflects how to use AI chatbot assistant to balance automation with human context.
Knowing When to Escalate to Humans
No assistant should handle everything. Some conversations need empathy, negotiation, or deeper investigation.
BotPenguin supports live chat handoff when the assistant detects uncertainty or when a user requests assistance.
The full conversation history moves with the handoff. The human does not start blind.
This avoids frustration. Users feel heard. Teams stay in control.
Applying use of chatbot assistant here keeps trust intact.
Over time, these daily interactions reveal what works and what needs adjustment. That feedback serves as the foundation for further improving the assistant.
Improving Chatbot Assistant Performance Over Time
Once the assistant starts handling daily conversations, small issues begin to surface. Some questions repeat. Some replies feel unclear. Others work perfectly.
This stage is not about fixing mistakes. It is about learning from real use.
A chatbot assistant improves through review and adjustment, not rework. BotPenguin makes this easier by giving teams visibility into conversations and simple ways to refine behavior.
The goal is steady improvement. Small changes. Clear gains.
Reviewing Conversations and Gaps
The fastest way to improve an assistant is to read what users actually say. BotPenguin stores conversation history so teams can review questions, responses, and outcomes.
For example, you might notice users asking the same follow-up after a pricing explanation. That is a gap.
Or you may see the assistant hesitating on a support edge case. That is a signal.
By reviewing these moments, you learn what information is missing or unclear.
You are not adding features. You are removing friction. This review cycle sits at the core of using a chatbot assistant that evolves with real usage.
Updating Prompts and Responses
Once gaps are clear, fixes are simple. You update instructions. You refine responses. You adjust tone.
In BotPenguin, this does not mean rebuilding the assistant. You edit prompts or training content directly. A minor change in instructions can improve dozens of future conversations.
For instance, adding one clarification to a refund response can eliminate repeated questions. Tweaking tone can make replies feel more human.
This ease of iteration supports AI chatbot assistant approaches that treat the assistant as a living system.
As improvements add up, patterns also reveal what beginners often get wrong. Those patterns are worth paying attention to next.
Common Mistakes Beginners Make
Most early mistakes are not technical. They come from rushing or trying to do too much at once.
A chatbot assistant is flexible, but it still needs structure. When results feel off, it is often because expectations were unrealistic or the user experience was ignored.
This section highlights common missteps without assigning blame, making them easier to avoid.
Fixing these does not require rebuilding. It usually takes one or two small changes.
Expecting the Assistant to Do Everything
One of the most common mistakes is trying to automate every conversation from day one. Support, sales, onboarding, follow-ups. All at once.
This usually leads to shallow answers and confused users. A better approach is to start with one job and expand slowly.
For example, begin with order tracking or demo requests. Let real usage show what to add next.
Even with powerful platforms, restraint matters. This mindset aligns with AI chatbot assistant practices that prioritize focus over coverage.
Ignoring User Experience
Another mistake is to focus only on accuracy and forget how replies feel.
Long messages, dense explanations, or formal language push users away.
If a reply looks hard to read on a phone, it probably is. Short sentences work better. Clear options help. A simple follow-up question often beats a long explanation.
Small adjustments can improve satisfaction quickly. Applying these chatbot assistant principles here keeps conversations natural.
Avoiding these mistakes makes one thing clearer. A chatbot assistant works best in the right situations, with the right expectations. Knowing when to use one comes next.
When a Chatbot Assistant is the Right Choice
By the time you reach this section, the decision is less about curiosity and more about clarity.
You now understand how a chatbot assistant is built, how it behaves, and how it improves. This section helps you pause and evaluate readiness, not features.
Use the points below as a checklist. If most of them apply, moving forward is a practical step, not an experiment.
This is where the "how to use chatbot assistant" guide becomes a real decision.
Signs You Are Ready to Use a Chatbot Assistant
- The same customer questions appear repeatedly across conversations.
- Your team already responds with similar answers most of the time.
- Response delays are starting to affect user experience or lead quality.
- Conversations increase during off-hours when no one is available.
- Manual handling feels repetitive rather than thoughtful.
- You can clearly define what the assistant should manage and what it should not.
- You are willing to review conversations and improve responses over time.
- You prefer gradual automation instead of replacing human interaction entirely.
- You want control and visibility, not a black-box system.
If these points resonate, a chatbot assistant is a good fit for your current stage.
Conclusion
Building a chatbot assistant is not about chasing automation. It is about removing friction where conversations repeat and time is wasted.
Throughout this guide, the focus remained on clarity, real-world usage, and small improvements informed by actual conversations.
This how to use chatbot assistant guide also showed that results come from defining roles, training with purpose, and refining behavior over time.
When done right, a chatbot assistant becomes a support system, not a shortcut.
If you are ready to apply these steps without complexity, BotPenguin offers a simple, structured way to get started and grow at your own pace.
So, build your chatbot assistant today!
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Can a chatbot assistant work alongside my existing support team?
Yes. A chatbot assistant is designed to reduce repetitive work, not replace humans. It handles common queries first and escalates complex cases, allowing teams to focus on conversations that need judgment or empathy.
How long does it usually take to set up a chatbot assistant with BotPenguin?
Most basic setups can be completed in a few hours. The initial build is fast. Refinement happens gradually as real conversations reveal what needs improvement.
How accurate is a chatbot assistant at answering user questions?
Accuracy depends on training quality. When trained on clear, updated FAQs and product content, a chatbot assistant delivers consistent answers and improves over time through iteration.
Is a chatbot assistant suitable for small businesses or only large teams?
It works well for both. Small teams benefit from time savings, while larger teams benefit from scale. The key factor is repeated conversations, not company size.
Can a chatbot assistant be used across multiple channels?
Yes. With BotPenguin, you can deploy a chatbot assistant to operate across websites and messaging apps, adapting responses to channel-specific user behavior.
How do I measure the success of my chatbot assistant?
Success is measured through response time, reduced manual workload, resolved conversations, and improved lead handling. These indicators show whether the assistant is delivering practical value.