What is the Waterfall Methodology?
Waterfall Methodology is a project management approach where tasks are completed in a specified sequential order.
The process initiates at the topmost phase, eventually cascading downward to the final stage, akin to water cascading down a waterfall.
Origin and Overview
This methodology finds its roots in the manufacturing and construction industries—sectors that often have fixed and physical outcomes.
Dr. Winston Royce brought this methodology to the world of software development in 1970.
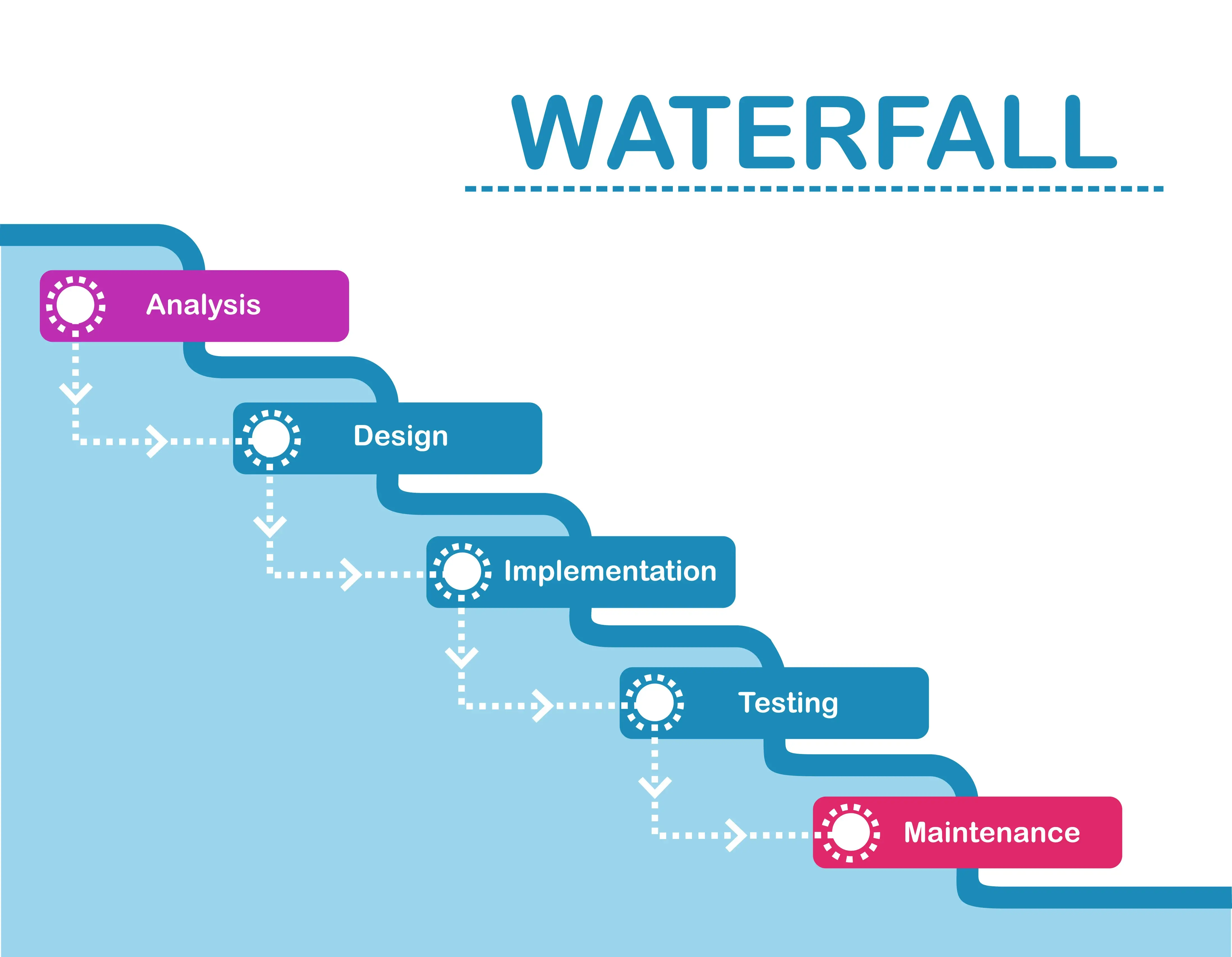
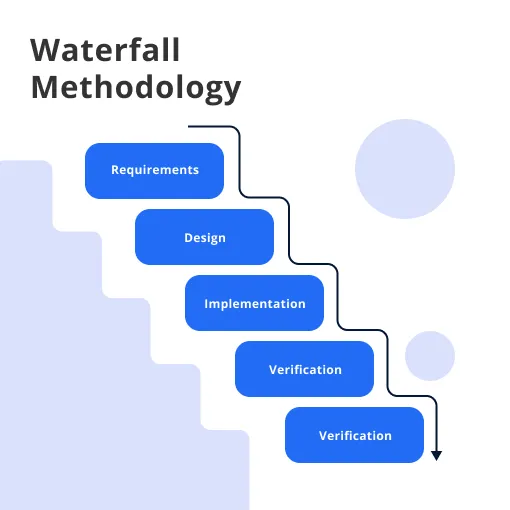
Stages of Waterfall Model
Typically, the Waterfall Methodology includes six key phases: Requirements, Design, Implementation, Verification, Deployment, and Maintenance.
Every phase depends on the deliverables of the former stage and correlates with the next one.
Key Characteristics
The process is systematic, easy to manage, and simple to understand, which enables clear objectives and timelines.
However, the methodology’s lack of flexibility can lead to difficulties in adjusting requirements or solutions during the process.
Applications of Waterfall Methodology
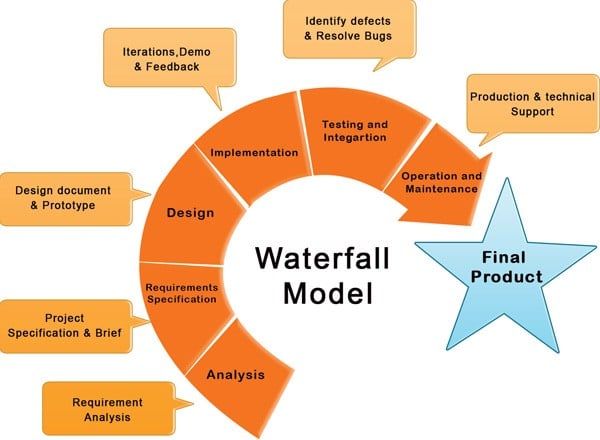
In software development, Waterfall is commonly used for straightforward projects where the requirements are clear and unlikely to change.
- Large-Scale Projects: Large-scale and complex projects that require substantial planning, time, and resources are often managed under the Waterfall methodology.
- System/Infrastructure Projects: This method is beneficial for system or infrastructure projects where a substantial amount of testing needs to be done before moving on to the next step.
- Hardware Development: In hardware development, requirements are typically well-defined and unchanging, necessitating the rigidity and sequence embedded in the Waterfall model.
Strengths of Waterfall Methodology
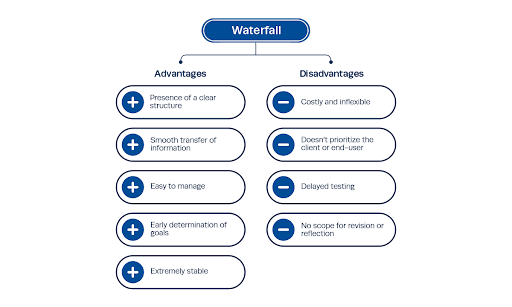
Before the actual development begins, extensive planning and design preparation in the Waterfall methodology can lead to a more efficient process.
- Clear Objectives and Deadlines: With the Waterfall model, managers and teams possess a clear understanding of the project's objectives and deadlines, which can lead to better utilization of resources.
- Documentation: Waterfall projects are often well-documented since all the functional specifications and designs are established and recorded in the early stages.
- Ease of Management: With its simple, linear approach, managing Waterfall projects is often straightforward, giving managers clear oversight of progress and potential bottlenecks.
Downsides of Waterfall Methodology
One of the most prominent drawbacks of the Waterfall model is its lack of flexibility. Changes cannot be easily accommodated once the project is underway.
- Increased Risk and Uncertainty: Waterfall projects often carry more risk and uncertainty, as any significant error found late in the cycle may require revisiting previous steps in the cascade.
- Delayed Testing: Since testing only occurs after the development phase, any bugs or issues would not be discovered until late into the project. This can inflate overall costs and delay the project timeline.
- Limited Customer Engagement: Customer engagement is generally isolated to the initial stages, leading to possible dissatisfaction if the project outcome does not meet their evolving needs or expectations.
Comparing Waterfall Methodology
Here’s a detailed comparison of the Waterfall model with other methods we use:
Waterfall vs Agile
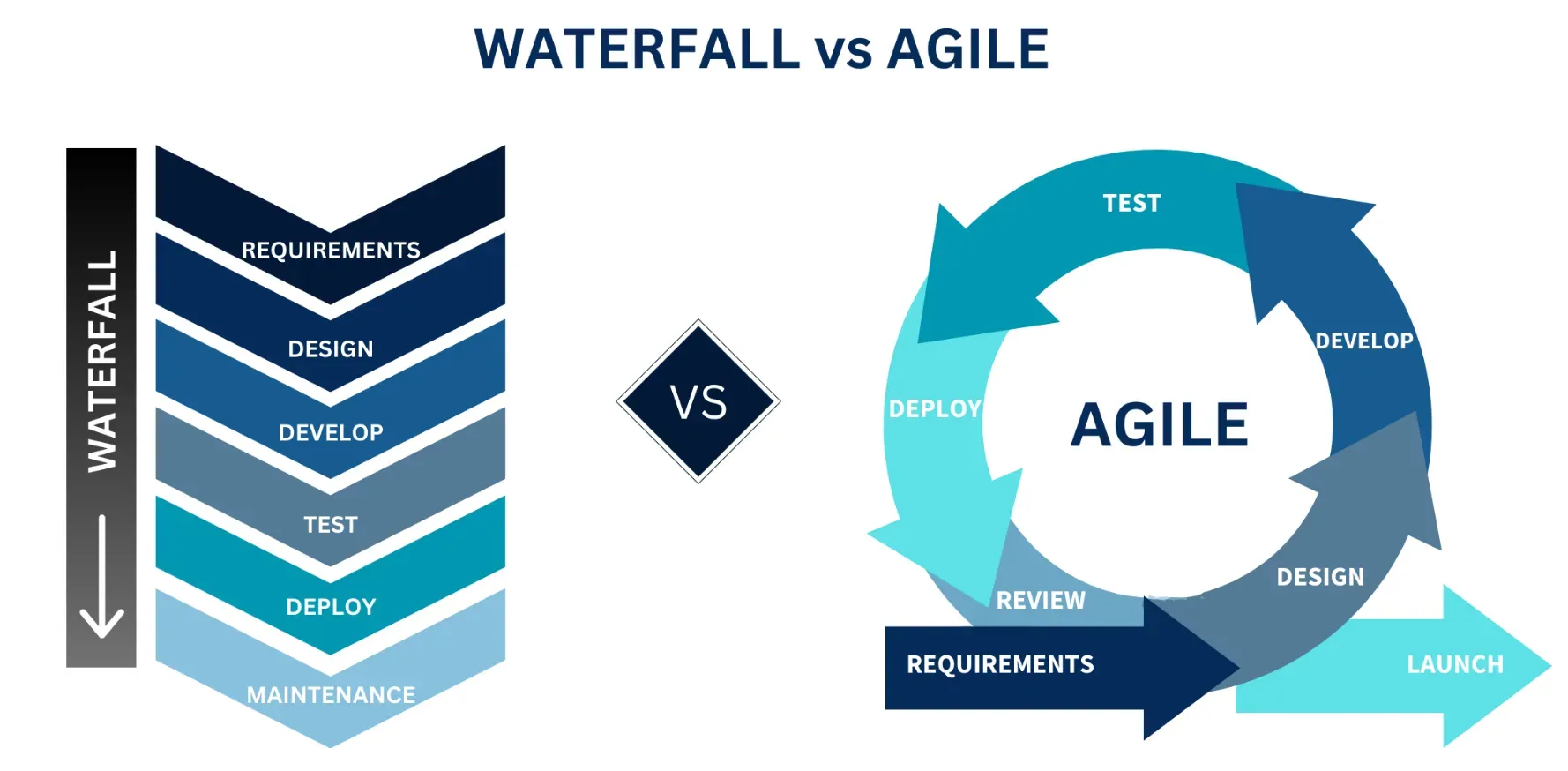
Compared to Agile, a more iterative and collaborative approach, the waterfall is more rigid and sequence-focused.
Whereas Agile advocates for flexibility and customer interaction throughout the process, Waterfall spends more time upfront with comprehensive planning before moving forward.
Waterfall vs Scrum
Scrum is a subtype of Agile characterized by short iterations called sprints.
Unlike the deploy-once approach of Waterfall, Scrum continuously delivers smaller components of the project, allowing for adaptability and regular feedback.
Waterfall vs Lean
Lean focuses on removing any waste in the development process, emphasizing speedy delivery. Unlike Waterfall, Lean allows for simultaneous progress in different project stages.
Waterfall vs Kanban
Kanban uses visual management to allow teams to progress with flexibility, which contrasts with Waterfall's strict phase-by-phase progression.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Can the Waterfall Methodology handle complex projects?
Yes, the Waterfall Methodology can handle complex projects as long as the requirements are well-defined and the project team follows a structured approach to each phase.
Is client involvement important in the Waterfall Methodology?
Client involvement is limited in the Waterfall Methodology. The focus is more on delivering a final product based on predetermined requirements rather than constant collaboration with the client.
How does the Waterfall Methodology ensure quality in software development?
The Waterfall Methodology emphasizes careful planning, detailed documentation, and consecutive execution of each phase, ensuring a systematic approach that enhances the quality of the final product.
Can the Waterfall Methodology be combined with Agile practices?
Yes, it is possible to combine Waterfall and Agile practices, creating a hybrid approach that incorporates the structure of Waterfall while allowing for some flexibility and iterative development.
Is the Waterfall Methodology suitable for all types of projects?
While the Waterfall Methodology can be applied to various projects, it is most suitable for projects with well-structured and defined requirements, where changes during development are minimal or undesirable.