What are the 5 V's of Big Data?
In the world of data, the 5 V's of Big Data are like a compass guiding us through the vast sea of information.
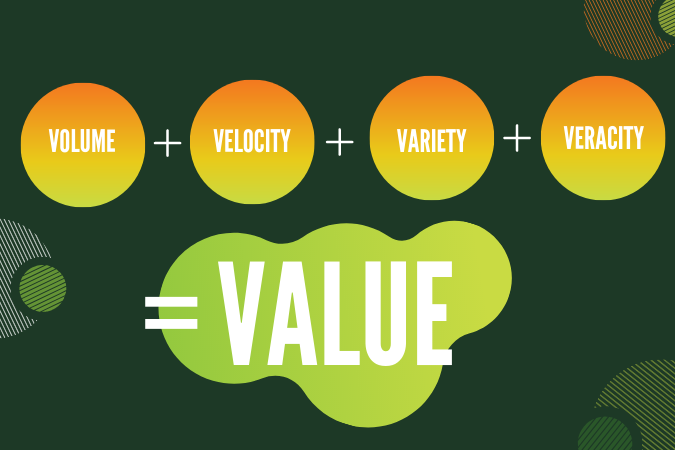
They help us understand the nature and challenges of dealing with enormous amounts of data. These V's—Volume, Velocity, Variety, Veracity, and Value—act as pillars supporting the data analysis structure.
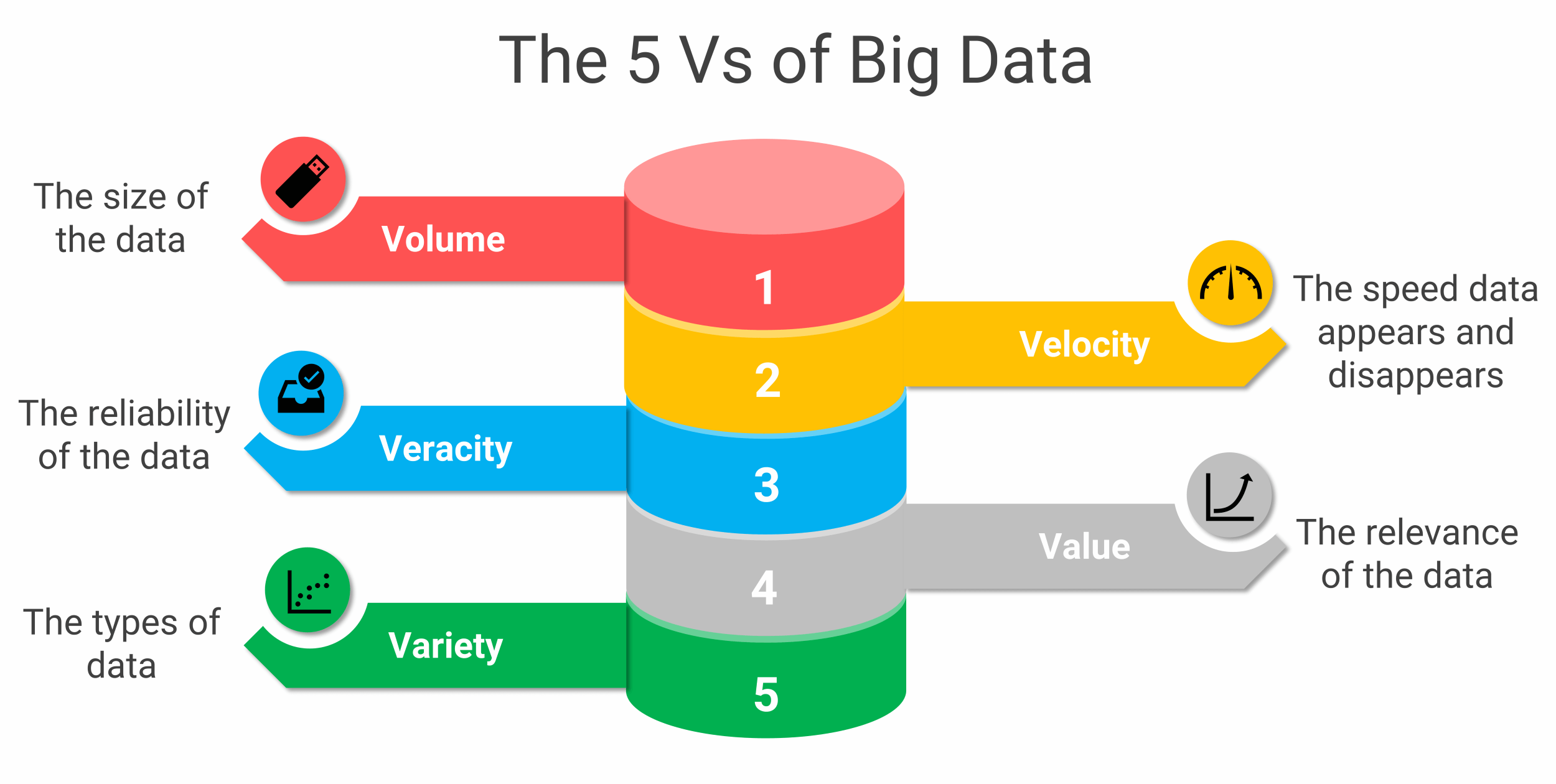
Volume
- Definition: Volume in big data, one of the five characteristics, denotes the vast amount of data generated, collected, and processed.
- Examples: Consider the massive amount of data generated daily from social media posts, online transactions, IoT devices, and sensor networks.
- Scale: The volume of data is enormous, measured in terabytes, petabytes, or even exabytes.
- Growth: Data volume continuously expands due to increasing digitalization and connected devices.
- Implications: Handling large data volumes poses several challenges and opportunities in data management, analytics, and storage.
- Technological Solutions: Organizations use scalable storage solutions, distributed computing frameworks, and cloud platforms to manage and process massive data volumes efficiently.
Velocity
- Definition: Velocity in big data is the rapid generation, processing, and analysis of data, emphasizing its speed within the system. It is one of the key aspects of the 5 V's of Big Data.
- Real-Time Processing: Velocity is crucial for applications requiring immediate insights and actions based on incoming data streams.
- Examples: Think of stock market trading, where decisions need to be made in milliseconds based on real-time market data.
- Streaming Data: Velocity is evident in streaming platforms like social media feeds, IoT devices, and online gaming.
- Challenges: High-velocity data requires efficient processing to derive timely insights and maintain responsiveness.
Variety
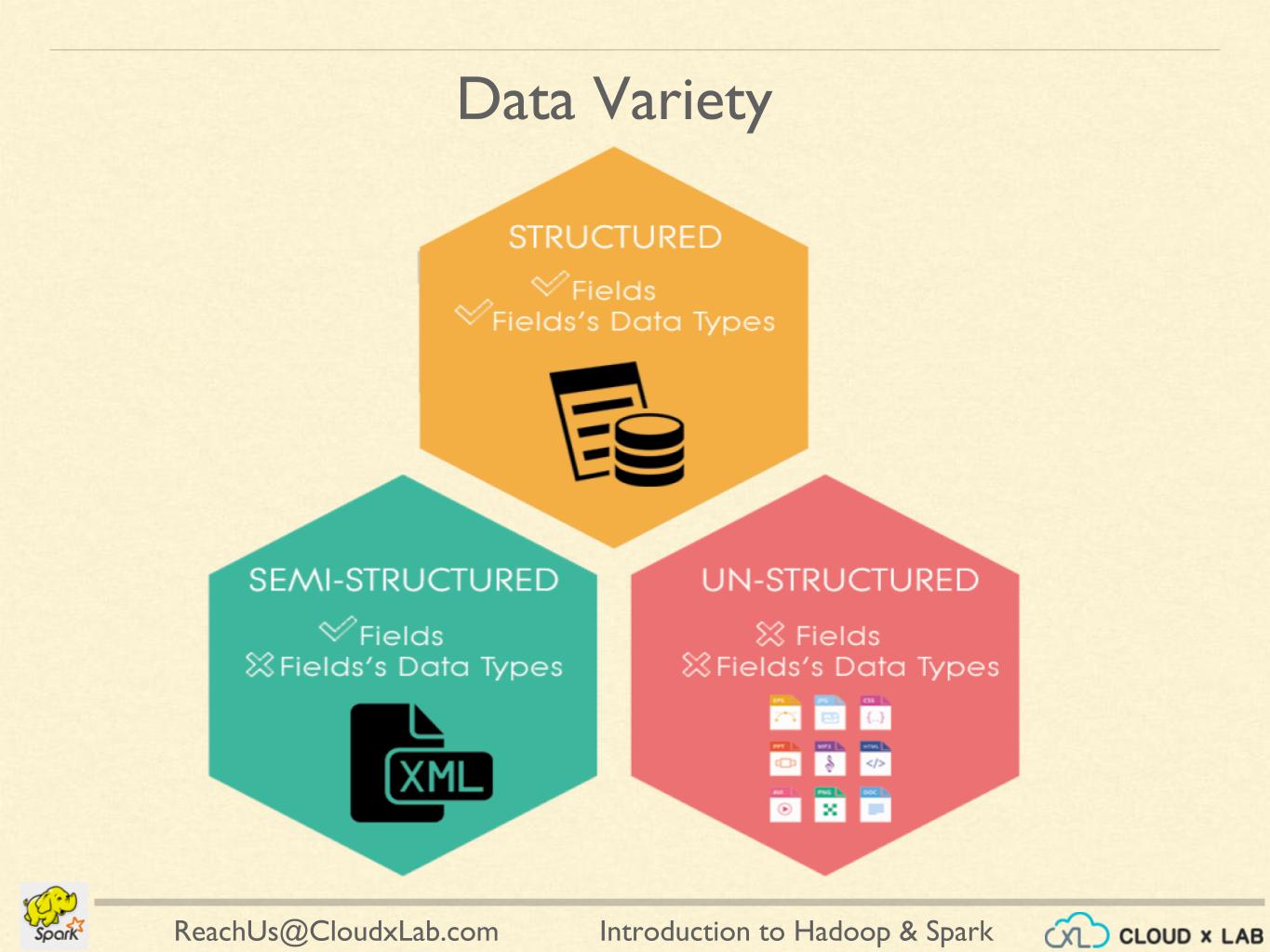
Definition: Variety in big data refers to the different types and formats of data organizations encounter. It encompasses structured, semi-structured, and unstructured data.
Types of Data Variety
- Structured Data: Data organized into predefined formats (e.g., relational databases).
- Semi-Structured Data: Data that does not fit into a rigid structure but has some organization (e.g., JSON, XML).
- Unstructured Data: Data with no predefined format or organization (e.g., text documents, images, videos, social media posts).
Implications for Data Integration and Analytics
- Integration Challenges: Variety complicates data integration efforts, as different data types require diverse processing methods.
- Analytical Opportunities: Embracing data variety enables organizations to gain deeper insights by analyzing diverse data sources.
- Tools and Techniques: Data integration platforms and ETL (Extract, Transform, Load) processes are used to harmonize disparate data types for analytics.
Veracity
Definition: Veracity in big data refers to the reliability and accuracy of the data. It's about ensuring that the data used for analysis is trustworthy and free from errors or biases.
Significance of Data Quality
- Reliable Insights: High-quality data leads to more reliable and actionable insights
. - Trustworthiness: Data quality builds trust among stakeholders and decision-makers.
- Cost Reduction: Poor data quality can lead to costly errors and inefficiencies.
Techniques for Ensuring Data Accuracy and Reliability
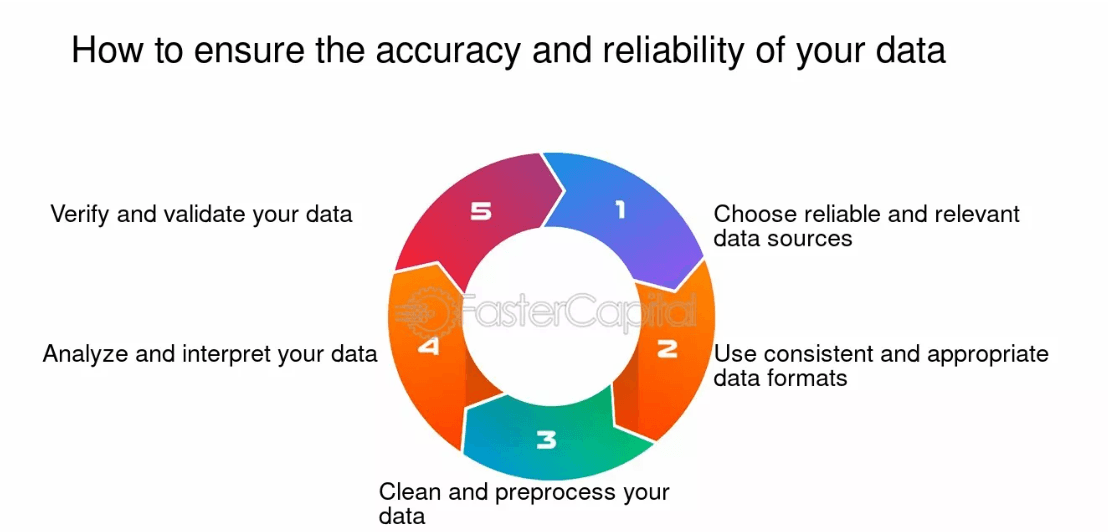
- Data Validation: Rules and checks ensure data meets standards, maintaining accuracy and reliability within predefined parameters.
- Data Cleansing: Eliminating duplicates, outliers, and inaccuracies enhances data quality, ensuring reliability and accuracy.
- Metadata Management: Maintaining metadata tracks data lineage, quality, and context, crucial for ensuring data accuracy and reliability.
- Machine Learning: Algorithms identify and correct data anomalies, improving accuracy and reliability through automated pattern recognition.
- Data Governance: Policies and procedures ensure data quality management and accountability, crucial for maintaining accuracy and reliability.
Value
- Data Analytics: Leveraging advanced analytics techniques (e.g., machine learning, predictive analytics) to extract insights from large datasets.
- Identifying Patterns: Analyzing data to identify trends, correlations, and patterns that can inform strategic decisions.
- Personalization: Using data to personalize customer experiences, optimize marketing campaigns, and tailor product offerings.
- Operational Optimization: Applying data-driven insights to optimize processes, improve supply chain management, and enhance operational efficiency.
- Innovation and Strategy: Using data to drive innovation, identify new business opportunities, and stay competitive in the market.
Who Benefits from Understanding the 5 V's of Big Data
Understanding the 5 V's of Big Data isn't just important for tech companies—it's revolutionizing industries across the board.
Let's explore how different sectors benefit:
Healthcare
Healthcare providers use big data to improve patient outcomes, personalize treatments, and optimize resource allocation.
Retail
Retailers leverage big data for customer analytics, supply chain optimization, and targeted marketing campaigns.
Finance
Financial institutions use big data for fraud detection, risk assessment, algorithmic trading, and customer insights.
Manufacturing
Manufacturers utilize big data for predictive maintenance, quality control, and process optimization.
Transportation
Transportation companies use big data for route optimization, fleet management, and demand forecasting.
Telecommunications
Telecom companies leverage big data for network optimization, customer churn prediction, and personalized services.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What are the 5 V's of Big Data?
The 5 V's of big data include volume, velocity, variety, veracity, and value, which describe the characteristics of big data, encompassing its scale, speed, diversity, quality, and potential business impact.
Why is Volume important in big data?
Volume refers to the vast amount of data generated. Managing and analyzing large volumes enable organizations to derive valuable insights and make data-driven decisions.
How does Velocity impact big data analytics?
Velocity relates to the speed at which data is generated and processed. Real-time processing of high-velocity data allows for immediate insights and timely actions.
What is the significance of Variety in big data?
Variety refers to the different types and sources of data. Handling diverse data types (structured, semi-structured, unstructured) is crucial for comprehensive analytics and insights.
Why is Veracity in big data essential for analytics?
Veracity ensures data quality and reliability. High veracity data leads to accurate insights, enhancing decision-making and trust in data-driven strategies.
How can organizations derive Value from big data?
Deriving value from big data involves analyzing data to uncover actionable insights that drive business growth, innovation, and competitive advantage.
