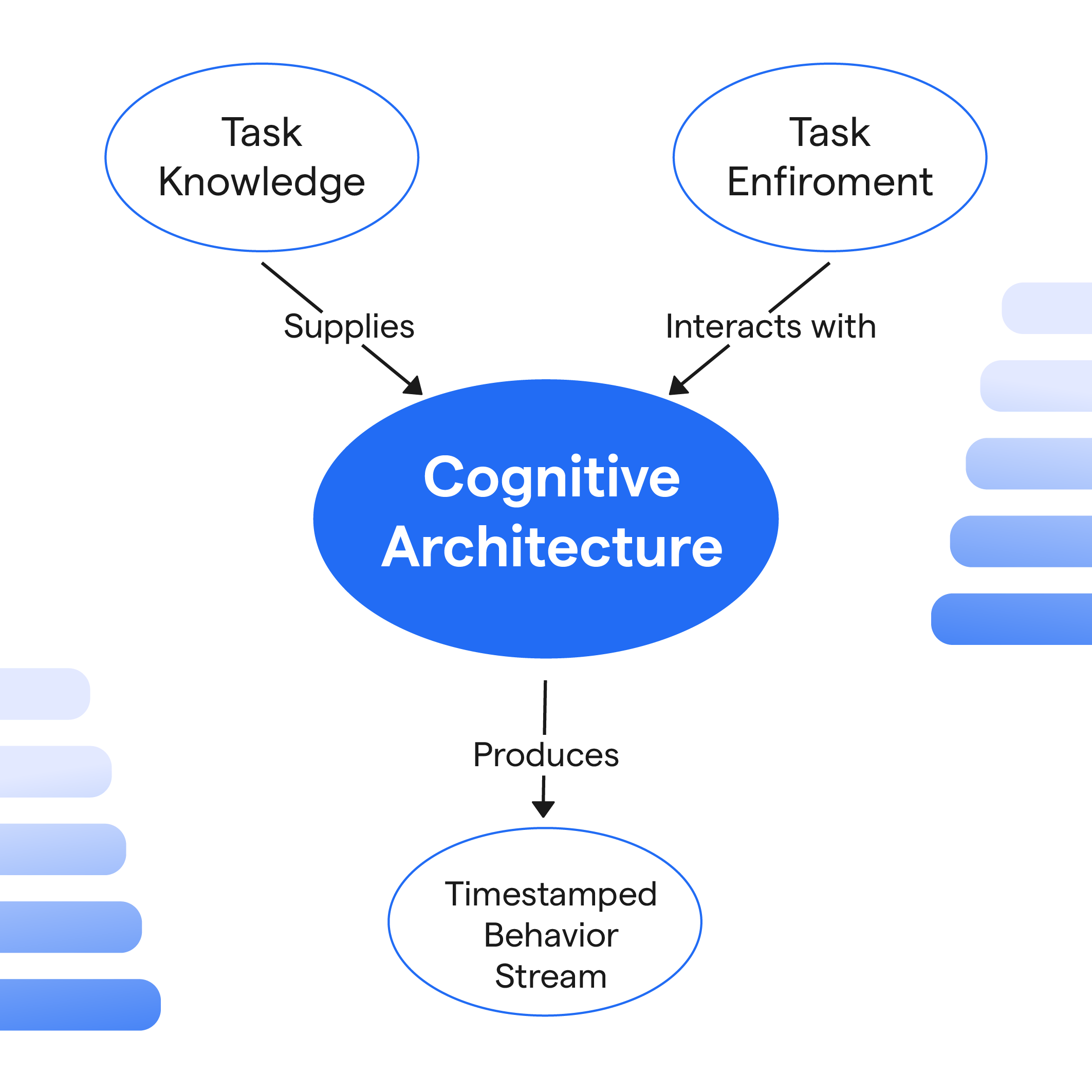
What is Cognitive Architecture?
Cognitive Architecture involves the underlying structure for cognition in humans and machines. With roots in psychology and computer science, it provides a systematic approach to understanding, predicting and imitating human cognitive abilities.
How is Cognitive Architecture Used?
Cognitive architecture is applied in creating intelligent agents, understanding human cognition, and developing artificially intelligent software.
Cognitive architecture helps design systems that mimic or simulate human cognitive processes. These systems have a wide range of applications, from AI-based interactions to autonomous tasks.
Several types of cognitive architectures exist, including rule-based, connectionist, hybrid, and integrative. Each type has a unique way of simulating human cognition.
Theories of Cognitive Architecture
Let's break down notable theories and models in cognitive architecture.
ACT-R Theory
Adaptive Control of Thought-Rational (ACT-R) Theory is a cognitive framework that simulates human tasks with a combination of procedural and declarative memory models.
SOAR Theory
SOAR (State, Operator, And Result) is another cognitive architecture model which emphasizes problem-solving and learning from experience.
EPIC Model
EPIC (Executive-Process/Interactive Control) Model focuses on information processing and how people multitask.
4CAPS Model
4CAPS (Four Core Aspects of Cognitive Processing) Model is a multi-agent theory that represents cognition as a distribute network of functionally specialized components.
Components of Cognitive Architecture
Understanding the individual components of cognitive architecture will shed light on the workings of the whole system.
Declarative Memory
Declarative memory stores factual information like concepts and events. It contains two subcomponents: semantic memory (knowledge about the world) and episodic memory (personal experiences).
Procedural Memory
Procedural memory holds information on how to perform certain tasks and procedures. This memory plays an essential role in rule-based cognitive architectures.
Perception Module
Perception module aids in input processing. It gathers sensory information and passes it to other components for further processing.
Action Module
Action Module is responsible for executing tasks and generating outputs. It translates cognitive processes into actions.
Cognitive Architecture and AI
Let's see how cognitive architecture blends with artificial intelligence to create intelligent agents.
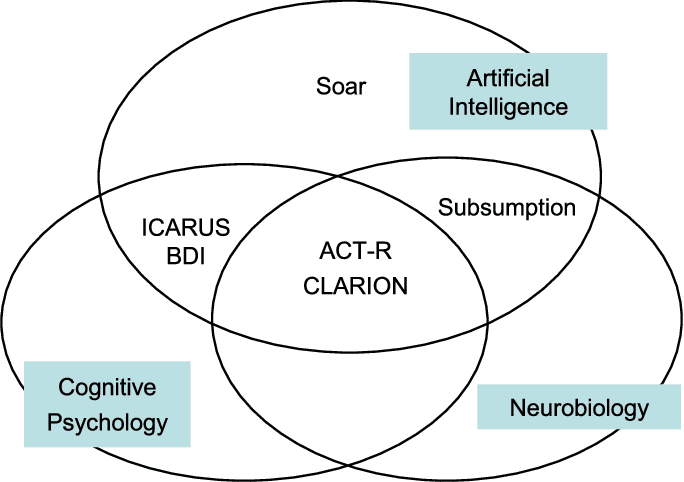
AI's Need for Cognitive Architecture
AI requires cognitive architecture to perform human-like cognitive tasks. The architecture enables AI with perception, reasoning, learning, and decision-making skills.
Cognitive Architectures in AI Models
Well-known AI models use cognitive architectures for problem-solving, decision-making, learning, and perception. Each model uses a somewhat different type of architecture suited to its specific purpose.
AI and Cognitive Architecture Research
Research in AI and cognitive architecture helps develop more robust, intuitive, and intelligent systems. It propels the field towards more advanced, human-like AI.
AI and Cognitive Architecture Applications
Applications of AI and cognitive architecture span various domains - healthcare, education, finance, and more. They facilitate intelligent decision-making, predictive modeling, and automated manual tasks.
Future of Cognitive Architecture
It's interesting to look at the potential future directions of cognitive architectures. Let's wrap up with some forward-looking thoughts.
Advanced Cognitive Architecture Models
Newer models with more advanced design principles are likely to emerge. These will offer a more accurate representation of human cognition.
Integration with Neuroscience
Cognitive architecture might see increased integration with neuroscience, increasing the potential for software that truly mimics the human brain.
Role in AI Advancements
As AI continues to evolve, cognitive architectures will play an even more crucial role in pushing the boundaries of what machines can do.
Ethical Considerations
Just as it's important to consider the potential advancements, it's also necessary to think about ethics to guide the use of advanced cognitive architectures and their applications.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What Does Human Cognitive Architecture Mean?
Human cognitive architecture is the arrangement and interrelation of cognitive processes residing within the human brain.
It involves coming to grips with how various cognitive happenings like sensory perception, the focus of attention, linguistic processing, memory applications, and several others are interwoven and function in tandem.
Can You Explain the Cognitive Process in Architecture?
When we speak of the cognitive process in architecture, we're referring to the mental involvements encountered in perceptually processing, comprehending, and generating architectural designs.
This includes several mental operations like spatial perception, creative problem-solving, memory recall, deciding amongst alternatives, and so on.
Can You Provide an Example of Cognitive Architecture?
To give you a concrete example of a cognitive architecture, consider the Soar architecture. Soar is a renowned cognitive architecture designed to simulate cognitive operations that closely resemble human cognitive processes.
This includes elements like sensory perception, the act of learning, focusing attention, and decision-making among others. Soar employs rule-based reasoning as its chosen method to emulate human intellect.
What are the Various Types of Cognitive Architecture?
Cognitive architecture can be classified into several categories, including symbolic models, connectionist models, and what we call hybrid models. Symbolic models make use of symbols and their logical relationships.
Contrastingly, connectionist models aim to simulate neurological neural networks. Lastly, hybrid models attempt to bring together the best features of both symbolic and connectionist constituents.
What Differentiates a Cognitive Architecture from a Cognitive Model?
It's important to distinguish a cognitive architecture from a cognitive model. A cognitive architecture pertains to the overarching, comprehensive framework or structure that underlines and explains the unified functioning of cognitive operations.
On a different note, a cognitive model is a distinct representation or method of implementation that resides within a cognitive architecture, specifically aimed at simulating particular cognitive processes like the application of memory or decision-making.