What is Cognitive Ability
Cognitive ability refers to the mental capabilities that allow us to think, learn, reason, and solve problems.
It's the brain's way of processing information and making decisions, which are essential cognitive skills for navigating the world around us.
Cognative ability is often considered synonymous with intelligence, but it encompasses a broader range of mental skills and processes.
Components of Cognitive Ability
Cognitive ability is made up of several key components, including:
Component | Description |
| Attention | The ability to focus on specific tasks or stimuli. |
| Memory | The capacity to store and recall information. |
| Language Skills | The ability to understand and apply language. |
| Problem-Solving | The ability to analyze situations and implement solutions. |
| Visual-Spatial Skills | The ability to interpret visual information. |
| Executive Function | Higher-order mental processes that regulate behavior. |
Why is Cognitive Ability Important?
Cognitive ability plays a crucial role in our daily lives, helping us to:
- Learn new information and cognitive skills
- Make decisions and solve problems
- Communicate effectively with others
- Navigate our physical environment
- Manage our emotions and impulses
Cognitive Ability and Success
Research has shown that cognitive ability is a strong predictor of success in various areas of life, including:
- Academic achievement
- Job performance
- Health and well-being
- Social relationships
Having strong cognitive agility can help us excel in our personal and professional lives, making it an essential aspect of human development.
Uses of Cognitive Functions
Cognitive functions play a significant role in various sectors of life.
In education, they're responsible for understanding, learning, and skills application. In a professional environment, cognitive skills help tackle complex tasks, solve problems, innovate and communicate effectively.
Cognitive function is also crucial in social interactions, playing a vital role in how we perceive situations and respond to them.
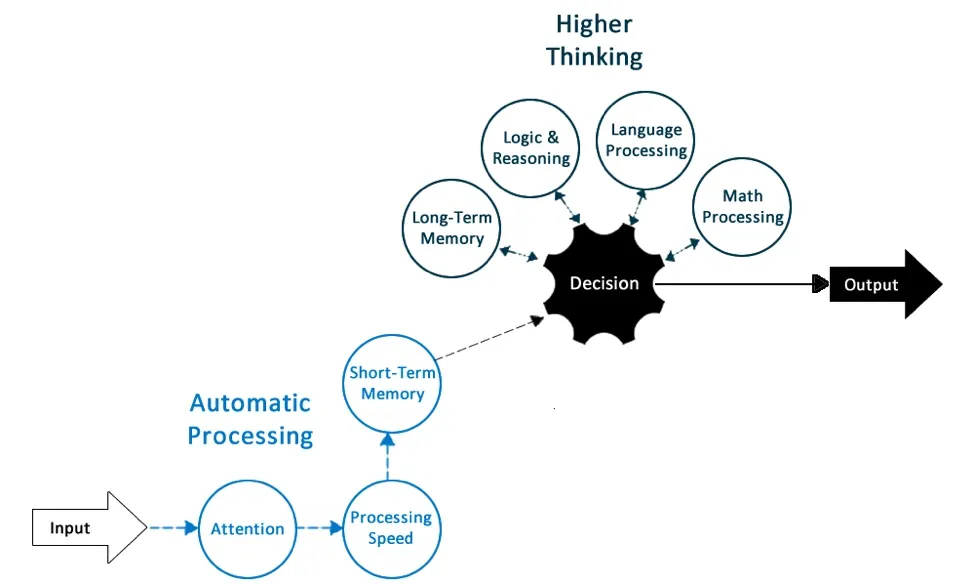
What is Cognitive Processes and What Skills are Involved
Cognitive capacity represents the total amount of information the brain is capable of retaining. This involves several processes and cognitive skills, such as attention, memory, language skills, problem-solving, and more.
Each plays a key role in how we interpret and interact with the world around us.
Cognitive capabilities ultimately influence our decision-making processes, creativity, problem-solving skills, and overall ability to accomplish tasks.
What is the Impact of Cognitive Functions
The cognitive ability definition extends to its impacts, which are experienced in every stage of life.
Cognative capabilities influence our learning proficiency, problem-solving, and decision-making skills, thus determining our academic and professional success.
Poor cognitive functions may hinder personal growth, whereas high cognitive function can present as giftedness.
What are the Types of Cognitive Ability
Fluid Intelligence
Fluid intelligence refers to our ability to reason, think abstractly, and solve problems in novel situations. It's the raw processing power of our brain that allows us to adapt and learn quickly.
Fluid intelligence is considered independent of prior knowledge, making it a measure of our innate cognitive potential.
Crystallized Intelligence
Crystallized intelligence is the knowledge and cognitive skills we acquire through experience and learning.
It represents our accumulated wisdom, including vocabulary, general knowledge, and problem-solving strategies.
Unlike fluid intelligence, crystallized intelligence tends to increase with age as we gain more experience and knowledge.
Processing Speed
Processing speed is the rate at which our brain can process and react to information.
It's an essential component of cognitive ability, as it affects our ability to perform tasks quickly and accurately. Processing speed can be influenced by factors such as age, health, and cognitive training.
Memory
Memory is the cognitive ability that allows us to store, retain, and retrieve information. There are several types of memory, including:
- Short-term memory: The temporary storage of information, lasting seconds to minutes.
- Working memory: The ability to hold and manipulate information in our mind while performing tasks.
- Long-term memory: The permanent storage of information, which can last for years or even a lifetime.
How to Measure Cognitive Ability
Intelligence Quotient (IQ) Tests
Intelligence quotient (IQ) tests are standardized assessments designed to measure cognitive ability.
They typically consist of a series of tasks that assess various aspects of cognitive functioning, such as verbal reasoning, mathematical cognitive skills, and visual-spatial abilities.
IQ tests provide a score that represents an individual's cognitive ability relative to others in their age group.
Standardized Cognitive Assessments
In addition to IQ tests, there are numerous standardized cognitive assessments that measure specific aspects of cognitive ability. Some common examples include:
- The Wechsler Intelligence Scale for Children (WISC) and the Wechsler Adult Intelligence Scale (WAIS), which assess a wide range of cognitive abilities.
- The Woodcock-Johnson Tests of Cognitive Abilities, which measure various aspects of cognitive functioning, including memory, processing speed, and reasoning.
- The Cognitive Abilities Test (CogAT), which assesses verbal, quantitative, and nonverbal reasoning skills.
Suggested Reading:
Cognitive Architecture: Key Concepts and Applications
Informal Assessments
Informal assessments of cognitive ability can include observations, interviews, and non-standardized tests.
These methods can provide valuable insights into an individual's cognitive strengths and weaknesses, but they may not offer the same level of reliability and validity as standardized assessments.
Factors Influencing Cognitive Ability
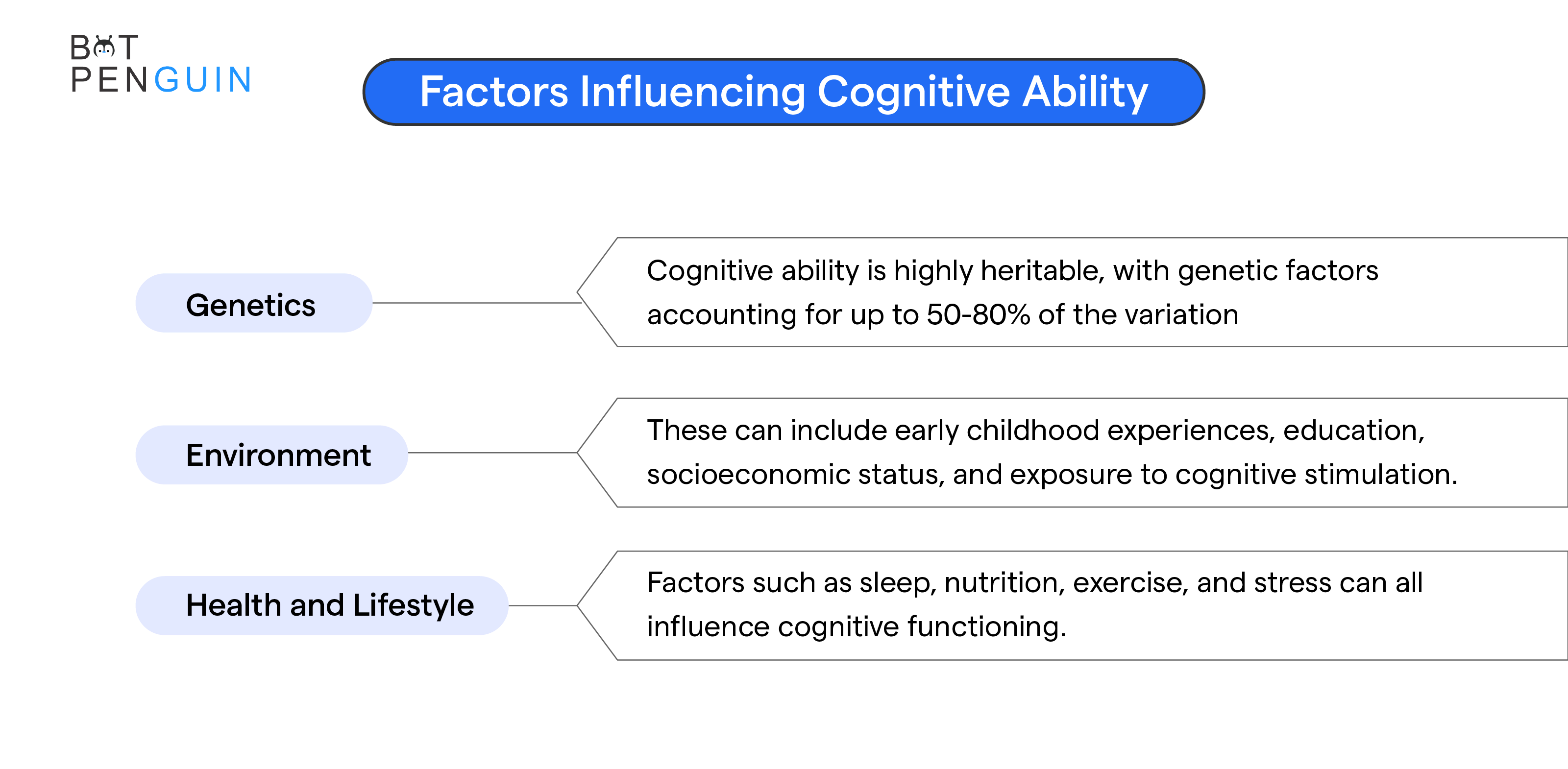
Genetics
Genetics plays a significant role in determining our cognitive abilities.
Studies of twins and families have shown that cognitive ability is highly heritable, with genetic factors accounting for up to 50-80% of the variation in cognitive ability between individuals.
Environment
Environmental factors also contribute to our cognitive abilities. These can include early childhood experiences, education, socioeconomic status, and exposure to cognitive stimulation.
A nurturing and stimulating environment can help to maximize an individual's cognitive potential.
Health and Lifestyle
Our overall health and lifestyle can impact our cognitive abilities. Factors such as sleep, nutrition, exercise, and stress can all influence cognitive functioning.
Maintaining a healthy lifestyle can help to support optimal cognitive performance.
How to Improve Cognitive Ability
Cognitive Training
Cognitive training involves engaging in activities and exercises designed to improve specific cognitive skills.
This can include puzzles, memory games, and other brain-boosting activities. Research has shown that cognitive training can lead to improvements in cognitive performance, particularly in the areas of memory and processing speed.
Physical Exercise
Regular physical exercise has been shown to have numerous benefits for cognitive health.
Aerobic exercise, in particular, has been linked to improvements in memory, attention, and executive functions. Exercise may also help to protect against age-related cognitive decline.
Nutrition and Supplements
A healthy diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean protein can support optimal cognitive functioning.
Some research suggests that certain nutrients and supplements, such as omega-3 fatty acids, antioxidants, and B vitamins, may also have cognitive benefits.
What Causes Cognitive Decline
Cognitive decline often occurs as a natural part of aging, but it can also be brought on by various factors such as stress, disease, lack of stimulation, or injury.
Chronic conditions like Alzheimer's and dementia, as well as lifestyle-related diseases like diabetes and heart disease, can all contribute to cognitive decline.
Lastly, external factors such as drug use, alcohol, and poor diet can further accelerate this process.
Cognitive Ability in Different Age Groups
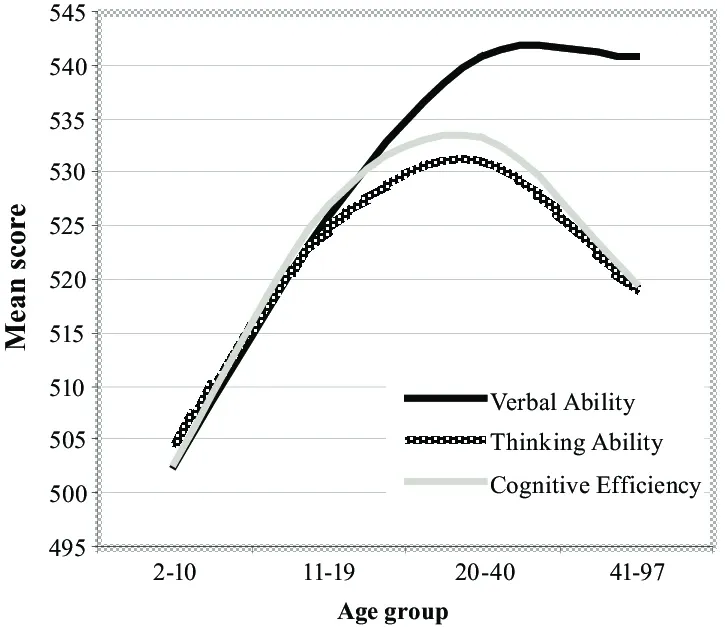
Cognitive Development in Children
Cognitive development refers to the process by which children acquire new cognitive abilities and skills.
This process is influenced by a combination of genetic and environmental factors, as well as the child's experiences and interactions with their environment.
Early childhood is a critical period for cognitive development, with rapid changes occurring in areas such as language, memory, and problem-solving.
What is Cognitive Aging and Decline
As we age, our cognitive abilities may decline, particularly in areas such as processing speed, memory, and executive functions.
However, not all individuals experience significant cognitive decline, and some aspects of cognitive ability, such as crystallized intelligence, may remain stable or even improve with age.
Engaging in mentally stimulating activities, maintaining a healthy lifestyle, and staying socially connected can all help to support cognitive health in older adults.
Cognitive Ability and Learning Disabilities
Common Learning Disabilities
Learning disabilities are neuro developmental disorders that affect an individual's ability to learn, process, and retain information. Some common learning disabilities include:
- Dyslexia: Difficulty with reading and language processing
- Dyscalculia: Difficulty with mathematical concepts and calculations
- Attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD): Difficulty with attention, impulse control, and executive functions
Strategies for Supporting Individuals with Learning Disabilities
Individuals with learning disabilities may require additional support and accommodations to help them succeed academically and in other areas of life.
Some strategies for supporting individuals with learning disabilities include:
- Providing extra time and support for learning tasks
- Using multisensory teaching methods
- Implementing individualized education plans (IEPs)
- Offering assistive technology and tools
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is cognitive ability and why is it important for businesses?
Cognitive ability refers to a person's mental capacity for learning, problem-solving, and critical thinking.
In a business context, it is crucial as it contributes to better decision-making, innovation, and overall productivity.
What is cognitive function?
Cognitive function refers to the mental processes involved in thinking, learning, remembering, and problem-solving.
It's essentially how your brain works to acquire and process information.
How can businesses assess cognitive ability during the hiring process?
Businesses can assess cognitive ability through various methods such as cognitive ability tests, problem-solving exercises, and structured interviews that evaluate a candidate's critical thinking, reasoning, and problem-solving cognitive skills.
How does cognitive ability impact employee performance and productivity?
Higher cognitive ability among employees is linked to improved performance and productivity.
It enables individuals to quickly learn new cognitive skills, adapt to changes, solve complex problems efficiently, and make sound decisions.
Can cognitive ability be developed or improved?
While cognitive ability is partly influenced by genetics, it can also be developed and improved through continuous learning, training, and engaging in activities that stimulate critical thinking, problem-solving, and decision-making.
What is cognitive functioning?
Cognitive functioning refers to the overall mental ability and performance of an individual across various cognitive domains.
It encompasses processes such as perception, memory, language, reasoning, and executive function.
Why is cognitive function important?
Cognitive function is integral to our daily activities. It allows us to process information, make decisions, solve problems, and interact effectively with our environment.
These cognitive capabilities are vital for performing everyday tasks and contribute to our overall quality of life.
What is the function of cognitive psychology?
Cognitive psychology explores how we process information. It studies how we think, perceive, remember, and learn.
The cognitive function definition in psychology underpins our understanding of human behavior and how processes like attention, memory, perception, problem-solving and language use function.
What is an example of a cognitive skill learning?
Problem-solving is a great example of cognitive skill learning. It involves several key cognitive processes, such as interpreting the problem, formulating strategies, and implementing solutions.
This process relies on various cognitive skills, including attention, working memory, and decision-making.