What is the Bullwhip Effect?
Let’s begin with knowing about the Bullwhip effect.
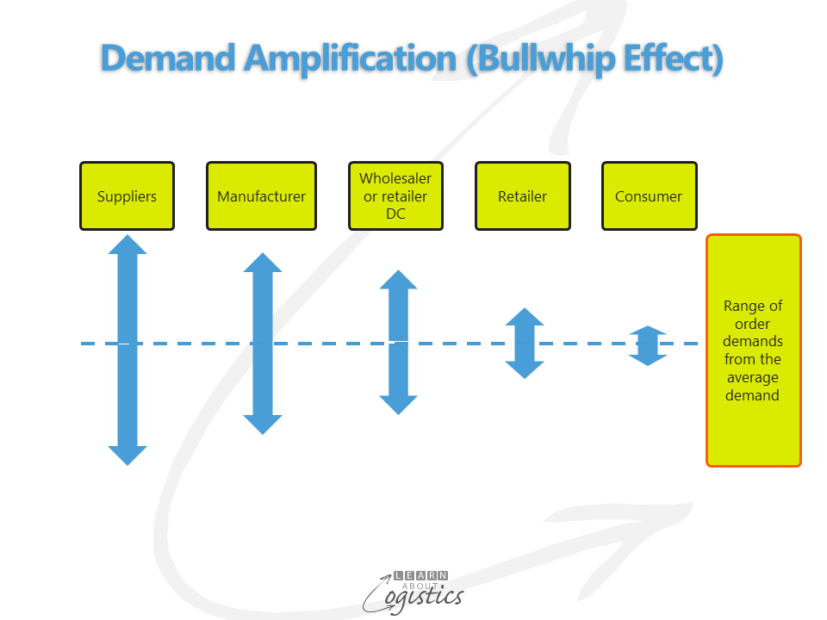
Understanding Demand Distortion
At its heart, the Bullwhip Effect distorts demand visibility throughout the supply chain. When customer demand changes, businesses adjust their inventory levels. But due to miscommunication or misinterpretation of data, each supply chain member amplifies these adjustments. The result? Wildly swinging inventory levels that don’t match the actual consumer demand.
Why Does the Bullwhip Effect Happen?
The root cause is misunderstanding demand. Companies often interpret sales data as direct reflections of consumer need, missing the nuances of market behavior. This misunderstanding leads to overreaction in ordering practices, amplifying minor demand changes up the supply chain.
A Visual Explanation: The Demand Amplification Chain
Imagine a child’s whisper game, where a message gets distorted with each whisper. Similarly, as demand forecasts pass from retailers to manufacturers, small changes escalate into significant variances—think of an order for 100 units turning into a request for 1000 units due to overcompensation at every stage.
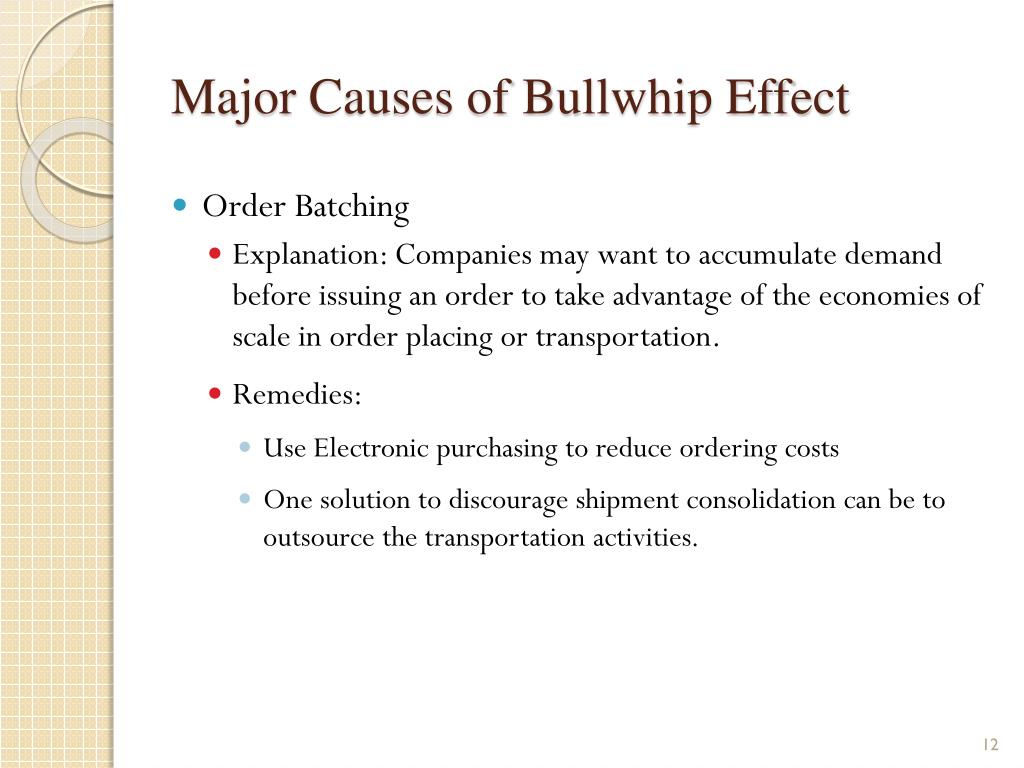
Causes of the Bullwhip Effect
The causes of the Bullwhip effect are the following:
Ordering in Uncertain Environments (Demand Fluctuations):In unpredictable markets, businesses often order more than needed to safeguard against shortages, inadvertently causing wider swings in inventory and demand forecasts.
Ordering in Batches (Quantity Discounts):Seeking to lower costs, companies buy in bulk. This practice can lead to excess inventory and periods of high demand, suddenly followed by none, as companies wait to order until the next discount.
The Fear of Stockouts (Shortage Gaming):Businesses hoard inventory fearing future shortages, leading to artificial demand spikes and subsequent inventory gluts when all companies in the chain do the same.
Information Asymmetry (Lack of Visibility):When companies don’t share demand and inventory data, it creates a gap that each player fills with guesswork, exacerbating the bullwhip effect.
Ordering Lead Times and Inaccurate Forecasts:Long lead times and forecasting errors introduce more opportunities for the bullwhip effect as companies compensate by ordering more or less than needed.
Impacts of the Bullwhip Effect
The impacts of the Bullwhip effect are the following:
Increased Inventory Costs (Storage, Obsolescence):Holding excess inventory ties up capital in warehouses, increasing storage costs and risk of obsolescence.
Reduced Product Availability (Stockouts):Ironically, the bullwhip effect can lead to stockouts, as distorted demand forecasts result in inadequate restocking.
Inefficient Production Planning (Excess or Insufficient Output):Manufacturers swing between overproduction and underproduction, straining resources and sometimes missing market opportunities.
Price Fluctuations (Discounts and Price Wars):Companies might slash prices to offload excess inventory, sparking price wars and harming industry profitability.
Wasted Resources (Transportation, Labor):The inefficient use of transportation and labor not only increases costs but also has a negative environmental impact.
Mitigating the Bullwhip Effect
Here is how to mitigate the Bullwhip effect:
Collaborative Forecasting (Sharing Demand Data): Companies along the supply chain should share sales, inventory, and forecast data to align demand predictions and reduce discrepancies.
Vendor Managed Inventory (VMI) - How it Works: With VMI, suppliers take charge of managing inventory levels for the buyer, ensuring the stock matches actual sales data closely.
Continuous Replenishment Programs (CRP) - Just-in-Time Approach:CRP systems automate replenishment based on actual sales and inventory data, minimizing the need for large safety stocks.
Improved Information Sharing (Transparency) - Benefits and Challenges:Though sharing detailed operational data opens opportunities for efficiency, it requires trust and technology that some businesses lack.
Beyond the Basics
In this section, you'll find beyond the basic information about the Bullwhip effect.
The Forrester Effect (Another Name for the Bullwhip Effect?): Some circles refer to the bullwhip effect as the Forrester Effect, highlighting its systemic nature in information flow across parties.
The Bullwhip Effect in Different Industries (Retail, Manufacturing):Every sector, from retail to manufacturing, experiences the bullwhip effect, affecting how companies manage inventory and production.
The Impact of Technology on the Bullwhip Effect (Benefits and Drawbacks):While technology offers solutions for better demand prediction and inventory management, it requires investment and can initially disrupt existing processes.
Real-World Examples of the Bullwhip Effect (Case Studies):Studying instances where companies either succumbed to or overcame the bullwhip effect provides valuable lessons in supply chain management.
The Bullwhip Effect and the Global Supply Chain:In an interconnected world, the bullwhip effect can have global ramifications, making international coordination crucial for mitigation.
Conclusion
Understanding and addressing the bullwhip effect is crucial for efficient supply chain management, cost control, and meeting customer demand accurately.Employing strategies like collaborative forecasting, VMI, CRP, and fostering transparency can significantly reduce the bullwhip effect's impact. Thus leading to a more responsive and efficient supply chain.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is the bullwhip effect also known as?
The bullwhip effect is also known as the Forrester Effect, highlighting its influence on information distortion across supply chains.
Is the bullwhip effect positive or negative?
The bullwhip effect is generally negative, leading to inefficiencies and misalignments in supply chain operations and inventory management.
Where does the bullwhip effect have its greatest impact?
The bullwhip effect hits hardest in sectors like retail and manufacturing, where demand forecast accuracy is crucial for inventory management.
What are the effects of the bullwhip effect?
It causes inventory swings, increased costs, inefficiency in production planning, stockouts, price fluctuations, and wasted resources, all impacting the bottom line.