What is Biometric Recognition?
Biometric recognition is the process of using biological and behavioral traits to automatically identify individuals.
These traits include physical characteristics such as fingerprints, faces, and irises, as well as behavioral characteristics such as voice and typing rhythm.
Biometric systems work by enrolling an individual's traits, storing them in a database, and comparing them to new data to verify or identify the person.
Examples of Biometric Recognition in Use
Biometric recognition technology is widely used across various industries and applications.
Examples include facial recognition in public safety, fingerprint recognition for smartphone authentication, and voice recognition for online banking.
How Does Biometric Recognition Work?
There are different steps that need to be followed for Biometric Recognition to work. To help you understand, we have listed the process below -
Step 1
Enrollment
The first step in biometric recognition is enrollment. During this process, the individual's biometric traits, such as fingerprints or facial features, are captured and converted into digital format.
The resulting data is stored in a database, forming a template against which future biometric data will be compared for identification.
Step 2
Storage
In the next step, the digital template is securely stored in a database for later use.
The data can be encrypted or hashed to ensure that it cannot be decoded by unauthorized users.
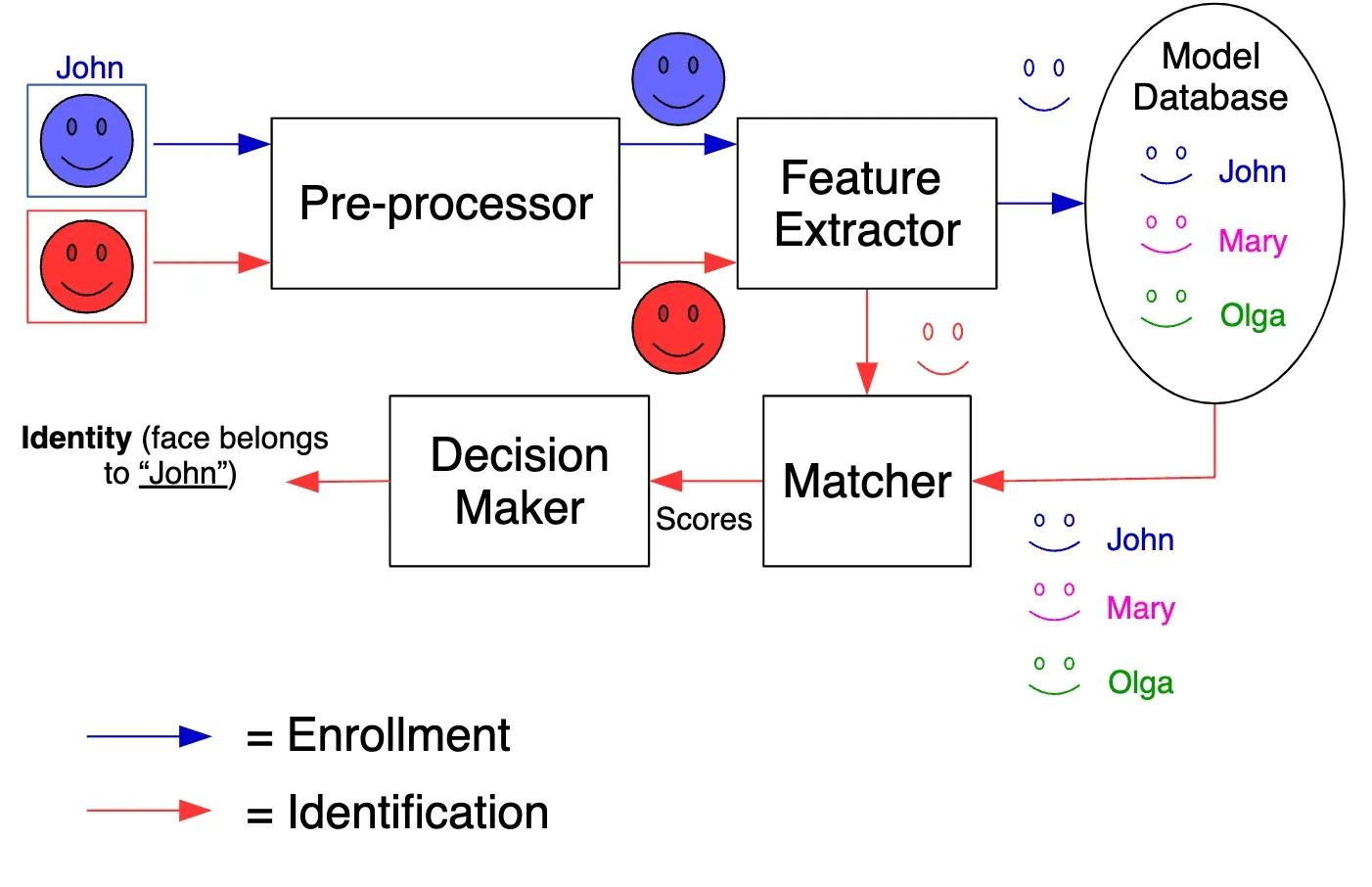
Step 3
Comparison
The comparison stage involves capturing the individual's biometric data again and comparing it with the stored template.
The system uses complex algorithms to process the data to determine whether a match is found.
For example, in a facial recognition system, the system will analyze the features of the captured image to determine whether they match the features in the stored database.
Step 4
Decision
After the comparison process is complete, the system will decide based on the match or non-match.
If the biometric data matches the stored template, the system will allow access or verify the individual's identity.
If there is no match, the system will deny access or reject the identification attempt.
Step 5
Feedback
Finally, the system will provide feedback to the user based on the decision. If access is granted, the user can proceed with the operation.
If access is denied, the system will usually provide a reason for the failure, such as an invalid biometric trait or an unrecognized individual.
Goals of Biometric Recognition for Authentication
The primary goals of biometric recognition for authentication are verification and identification.
Verification is the process of confirming an individual's identity, while identification is the process of determining who a person is when their identity is unknown.
Biometric recognition allows for real-time matching of biometric data with detected images or data to ensure accurate and efficient identification and authentication.
Biometric Recognition Characteristics
Biometric recognition can be classified into two categories: physiological biometrics and behavioral biometrics.
Physiological biometrics include sight, sound, smell, taste, and touch.
Behavioral biometrics, on the other hand, include gait, walking rhythm, writing style, and typing speed. Biometric characteristics must be reliable, unique, and convenient to use to be effective.
Types of Biometric Recognition Devices
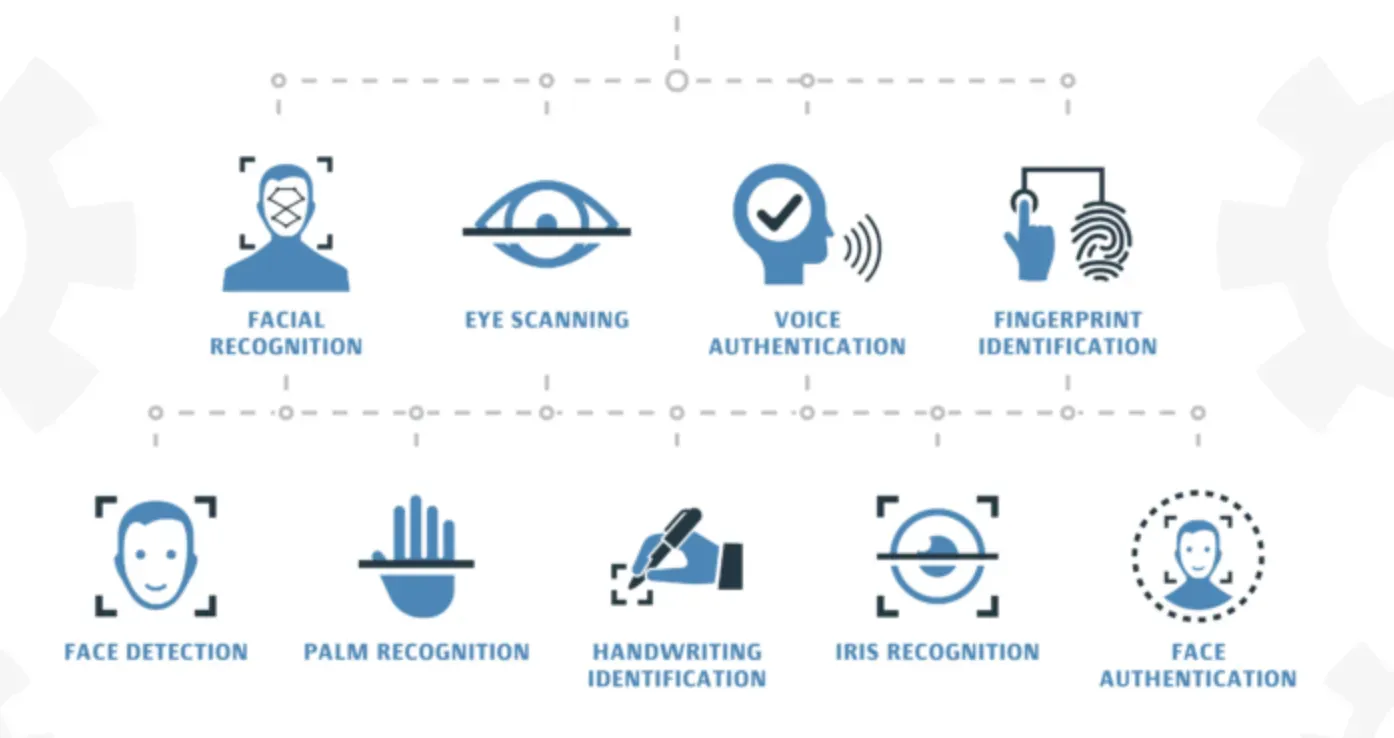
Different types of biometric recognition devices are available to capture various types of biometric data.
Fingerprint scanners
These devices capture fingerprints to authenticate users based on their unique patterns of ridges and valleys.
Facial recognition devices
These devices analyze facial features such as the distance between eyes, the nose's length, and the face's contours.
Iris recognition devices
These devices use pattern recognition to analyze the unique features of an individual's iris.
Voice recognition devices
These devices analyze elements of an individual's voice, such as tone, pitch, and rhythm, to authenticate users.
Hand geometry scanners
These devices analyze metrics such as the length and width of fingers, the distance between knuckles, and the thickness of the hand to authenticate users.
Each biometric recognition device has its own unique advantages and drawbacks, and the best device for a given situation will depend on factors such as security needs, the environment, and the user population.
Importance of Biometric Recognition

The importance of biometric recognition includes enhanced security, increased profitability, easy user operation, and high efficiency.
Enhanced Security
Biometric recognition provides enhanced security compared to traditional authentication methods such as passwords or PINs.
Biometric traits are unique to each individual and difficult to replicate, making it difficult for unauthorized users to access protected areas or information.
Increased Profitability
Biometric recognition can result in increased profitability for businesses. Authentication processes can be streamlined, reducing the need for passwords or tokens.
In addition to this, automated biometric recognition makes it easier to manage user identity, reducing administrative overhead.
Easy User Operation
Biometric recognition is easy for users. There is no need to remember or enter complex passwords or codes.
Users simply provide their biometric traits, and the system will authenticate them quickly and accurately.
High Efficiency
Biometric recognition provides a high level of efficiency in various settings, such as identity verification, security, and time management.
In mass screening, biometric recognition can identify people rapidly, reducing waiting times and increasing throughput for organizations dealing with access control, tickets, or visas.
Reliable Verification and Identification
Biometric recognition offers a reliable way to verify and identify individuals. The traits used for biometric recognition are unique to each individual and cannot be lost or misplaced.
Verification and identification processes involving biometrics are more robust against fraud and error, ultimately leading to more secure transactions.
Challenges and Concerns with Biometric Recognition
Privacy and security concerns are the primary challenges associated with biometric recognition technology.
Here are some challenges and concerns with biometric recognition:
Privacy Concerns
Collecting and storing sensitive biometric data raises privacy concerns, as there is a risk of unauthorized access or misuse of this personal information.
Security Concerns
Securing biometric data from unauthorized access or theft is crucial. Additionally, there is a risk of biometric data being spoofed or manipulated, leading to fraudulent transactions or unauthorized access.
Technical Challenges
Various factors, such as lighting and environmental factors, can impact the accuracy of biometric recognition systems.
Additionally, interoperability challenges may arise when integrating or deploying biometric recognition systems across different platforms or devices.
Regulatory Compliance
Different countries have varying legal and ethical frameworks governing the use of biometric recognition technology.
Organizations must comply with relevant regulations to protect user privacy and mitigate legal risks.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Can biometric recognition be used for mobile devices?
Yes, biometric recognition is increasingly being used for mobile devices to provide secure and convenient authentication methods, such as facial recognition and fingerprint scanning.
What are some potential drawbacks of using biometric recognition technology?
Potential drawbacks of biometric recognition include data privacy concerns, the possibility of false positives and negatives, and cost and the complexity of implementation.
What happens if my biometric data is compromised?
If your biometric data is compromised, it could be used to impersonate you in fraudulent transactions. Steps should be taken to alert relevant parties and prevent unauthorized access or use.
Can biometric recognition systems be upgraded or modified over time?
Yes, biometric recognition systems can be updated to improve accuracy and security. However, care should be taken to ensure upgrades do not introduce new vulnerabilities or risks.
What are some emerging biometric technologies to watch for in the future?
Emerging biometric technologies to watch for in the future include vein recognition, gait recognition, and brainwave recognition.