Introduction
In natural language processing (NLP), two names stand out: BERT and GPT. These powerful models have changed the way computers understand and generate human language. Let’s dive into what they are and why they matter and see the BERT vs GPT.
Overview of BERT
BERT also stands for Bidirectional Encoder Representations from Transformers, is a model developed by Google. It's known for understanding the context of a word in a sentence. Think of it as reading the entire sentence before deciding what a word means. This method is called "bidirectional" because BERT looks both ways—at the words before and after.
How BERT works?

Imagine you're reading a book. To understand a sentence, you need to see the words around it. BERT does the same. It reads the whole sentence to figure out each word's meaning. This helps it understand nuances and details.
Overview of GPT
GPT, developed by OpenAI, is another influential model in NLP. GPT stands for Generative Pre-trained Transformer. Unlike BERT , which focuses on understanding, GPT is all about generating text. It can write essays, stories, and even code.
How GPT works?
Picture a storyteller who knows a lot about many topics. GPT reads tons of text and learns patterns. Then, when given a prompt, it can continue the story or create a new one. It’s pre-trained on a huge amount of text, which makes it smart about language.
Key differences: BERT vs GPT
In this section, you will find the difference between BERT and GPT.
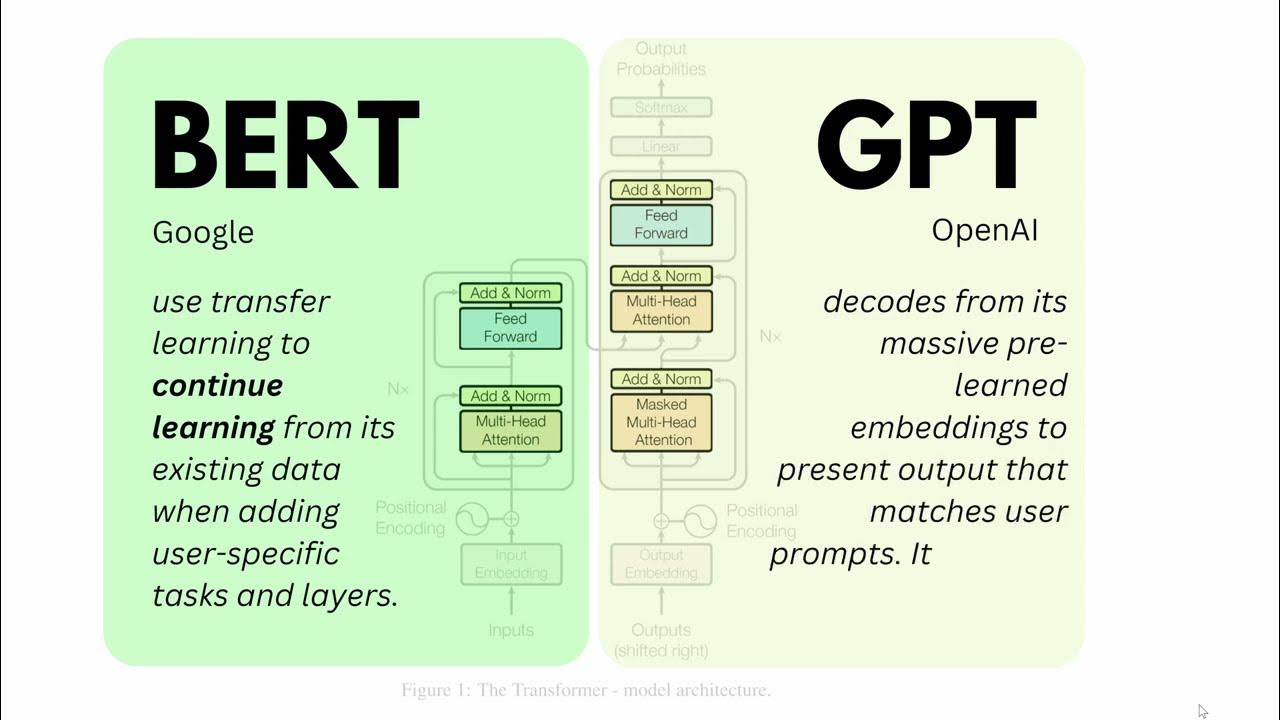
Architectural Differences
The architectural differences of BERT vs GPT are:
- BERT :
- BERT is bidirectional so it can read text in both directions, considering the context from all sides.
- Understands the full meaning of a word by looking at the words before and after it.
- GPT:
- GPT is autoregressive as it can read text one word at a time, in one direction.
- Predicts the next word based on the previous words.
Bidirectional vs Autoregressive
The bidirectional and autoregressive differences of BERT vs GPT are:
- BERT :
- Look at the entire sentence at once.
- This bidirectional approach helps understand the context better.
- GPT:
- Focuses on one word at a time, moving forward.
- This autoregressive method is great for generating text.
Contextual Embeddings
The contextual embeddings differences of BERT vs GPT are:
- BERT :
- Creates embeddings based on both the left and right context of a word.
- This results in a deeper understanding of the text.
- GPT:
- Generates embeddings using only the left context.
- This is effective for text generation but less so for understanding complex contexts.
Suggested Reading: GPT-3
Training Objectives
The training objectives differences of BERT vs GPT are:
- BERT :
- Uses masked language modeling.
- Randomly masks words in a sentence and trains the model to predict them.
- Helps understand the entire context.
- GPT:
- Uses next word prediction.
- Trains the model to predict the next word in a sentence.
- Focuses on the flow of text generation.
Use Cases and Strengths
The differences of use cases and strengths of BERT vs GPT are:
- BERT :
- Best for tasks where understanding the full context is crucial.
- Great for search engines, virtual assistants, and customer support.
- GPT:
- ChatGPT is best for tasks where generating coherent and contextually relevant text is important.
- Excellent for content creation, writing assistance, and creative writing.
Understanding vs. Generation
The understanding and generation differences of BERT vs GPT are:
- BERT :
- BERT is understanding as it excels at tasks that require comprehension.
- Ideal for question answering, text classification, and language understanding.
- GPT:
- GPT, like ChatGPT, is the generation as it excels at tasks that require creating text.
- Perfect for writing articles, stories, and generating conversational responses.
When to choose BERT over GPT
If you’re still confused between BERT vs GPT, then see the following:
Use BERT for these tasks
Here are the following reasons for you to use BERT :
- Question Answering: BERT can find specific answers within a text. It’s good for tasks like extracting information from articles or documents.
- Sentiment Analysis: If you need to understand emotions or opinions in text, BERT is your go-to. It captures the nuances of language, making it ideal for analyzing customer reviews or social media posts.
- Named Entity Recognition (NER): BERT is great at identifying names of people, places, dates, and other entities in text. Use it for organizing and categorizing information.
- Part-of-Speech Tagging: For tasks where you need to know the function of each word (like verbs, nouns, adjectives), BERT performs well.
- Text Classification: BERT is effective for classifying text into categories. This includes spam detection, topic labeling, and content filtering.
Use GPT for These Tasks
Here are the following reasons for you to use GPT:
- Text Generation: GPT like ChatGPT can write essays, stories, and even code. It’s perfect for creating content where fluent and coherent text is needed.
- Conversational Agents: For building chatbots or virtual assistants, GPT’s ability to generate natural responses makes it ideal.
- Translation: ChatGPT can translate text between languages, though it may not always capture the nuances as precisely as specialized translation models.
- Summarization: Need a summary of a long article? GPT can condense information while maintaining the core ideas.
- Creative Writing: For tasks that require creativity, like writing poems or brainstorming ideas, GPT shines.
Frequently Asked Questions(FAQs)
What are the key differences between BERT and GPT?
BERT excels at understanding context and language nuances, which is ideal for tasks like question-answering. GPT, on the other hand, is better at generating human-like text, useful for creating new content.
When should I use BERT instead of GPT?
Use BERT when you need deep language understanding or contextual analysis, particularly for tasks like sentiment analysis, language translation, or filling in missing text.
Can BERT generate text like GPT?
While BERT can generate text to some extent, it's primarily designed for understanding context. GPT, however, is specifically optimized for generating coherent and sophisticated text sequences.
Is GPT or BERT better for chatbots?
GPT is often preferred for chatbots due to its superior ability to generate conversational and contextually appropriate responses, making interactions more natural.
How do BERT and GPT handle language understanding differently?
BERT analyzes text in both directions (bidirectionally) to understand context, while GPT processes text sequentially, focusing on generating text based on the input it's given, making them suitable for different types of language tasks.
Which is more efficient for search engines between BERT and GPT?
BERT is generally more efficient for improving search engine results due to its ability to understand the context of search queries better, enhancing the relevance of the results.
