Introduction
Customer opinions and reviews are vital to understanding how your products or services perform in the market. However, manually going through huge amounts of data to read and analyze every statement for positive or negative feedback about your products can be tedious and time-consuming.
This is where LLM sentiment analysis comes into the picture. The technology analyzes linguistic patterns to identify sentiment, helping you understand how users feel. By predicting user reactions, it enables you to craft messages that resonate and influence audiences effectively.
But it is not just for marketing. From improving mental health support to managing crises, LLM sentiment analysis has endless uses. Let us unpack its benefits and the surprising ways it is shaping our world.
What is Sentiment Analysis?
Sentiment analysis uses Natural Language Processing (NLP) to identify sentiments, opinions, and emotions in text, determining whether they are positive, negative, or neutral.
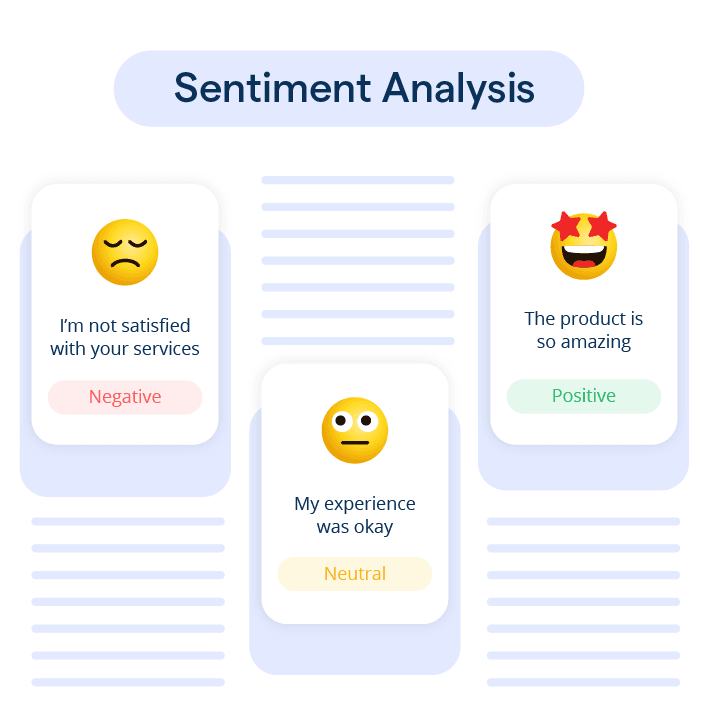
It can even recognize nuanced emotions like joy, sadness, or anger. The main objective of sentiment analysis is to employ computational methods to train the models that can automatically segregate the digital text, much like humans do.
How Does Sentiment Analysis Work with LLMs?
Understanding how LLM sentiment analysis works is crucial to grasp its transformative potential. By using advanced language models like GPT, BERT, and RoBERTa, it decodes emotions hidden in the text.
These models are designed to mimic human comprehension, turning unstructured data into actionable insights. Let us explore how these models work and how they determine the sentiment of any given text.
How do LLMs Analyze Sentiment?
LLMs use pre-trained models to detect sentiment. They are trained on vast amounts of data, which includes text from books, websites, and social media. This pre-training enables them to recognize patterns and relationships between words and phrases.
When using LLM for sentiment analysis, these pre-trained models are often "fine-tuned" with specific sentiment-labeled datasets. Fine-tuning helps LLMs adapt to specialized tasks, such as analyzing product reviews, social media posts, or customer feedback.
Once trained, they can identify emotional cues like positivity in "This is fantastic!" or negativity in "This is disappointing."
A Few Practical Examples of LLMs Detecting Sentiment
In customer service, LLM sentiment analysis can flag emails containing frustration or anger, enabling companies to prioritize responses.
For instance, a model might detect a neutral sentiment in "I need assistance with my account" but a negative tone in "I’m extremely unhappy with your service."
Another example is social media monitoring. A fine-tuned model might classify "Amazing concert last night!" as positive sentiment, while "The traffic was unbearable after the concert" would be negative.
Using LLM for sentiment analysis here provides insights into public perception and helps businesses respond appropriately.
Even in mental health applications, Large Language Models (LLMs) can gauge emotional states by analyzing user input, offering a supportive response to "I feel so overwhelmed."
Benefits of LLM Sentiment Analysis
The benefits of LLM sentiment analysis extend far beyond basic emotion detection. By using advanced language models, businesses and organizations can gain accurate, scalable, and efficient insights from massive volumes of text.
These capabilities make it a game-changer across industries. Here is a closer look at what makes this technology so impactful.
Accuracy and Nuance
LLM sentiment analysis excels in understanding the subtleties of human language. It can detect sarcasm, irony, and even context-dependent emotions, challenges that traditional methods often miss.
For instance, the phrase "Great, another delay" might be flagged as positive by older systems but is correctly identified as negative by LLMs.
By using LLM for sentiment analysis, businesses can analyze customer reviews or social media comments with greater precision. This ensures they accurately capture how users feel, helping them respond more effectively.
Scalability
Traditional sentiment analysis relied on rule-based systems and classical machine learning models. These methods often struggled with understanding context, sarcasm, and processing large-scale data efficiently.
In contrast, LLM sentiment analysis excels in scalability, handling vast amounts of text in real-time. Whether it is monitoring thousands of tweets during a product launch or analyzing global news articles, scalability is a key strength.
For example, companies can deploy LLM for sentiment analysis to analyze customer feedback across multiple regions instantly. This saves time and provides actionable insights faster than manual analysis ever could.
Versatility Across Industries
One of the biggest advantages of LLM sentiment analysis is its versatility. It works across industries such as marketing, healthcare, finance, and customer service. It is equally effective in multiple languages, making it invaluable for global businesses.
In healthcare, using LLM for sentiment analysis helps detect patient distress in online consultations. In finance, it identifies market sentiment from news or investor commentary. This adaptability makes it a universal tool for data-driven decision-making.
Automation and Efficiency
Manually analyzing emotions in the text is time-consuming and prone to error. LLM sentiment analysis automates this process, reducing the need for human intervention. Models fine-tuned for specific tasks can analyze data faster and with greater consistency.
For instance, companies can fine tune LLM for sentiment analysis to monitor customer feedback 24/7. This not only increases efficiency but also ensures timely responses to critical issues, such as a viral negative review.
With its accuracy, scalability, versatility, and automation, LLM sentiment analysis is transforming how businesses interpret emotions in text.
Whether improving customer engagement, monitoring brand reputation, or extracting market insights, the ability to fine tune LLM for sentiment analysis ensures more precise and meaningful results, making it an indispensable tool in today’s data-driven world.
Common Use Cases
LLM sentiment analysis is changing how organizations interpret emotions and opinions hidden in the text. Its ability to analyze large-scale data while capturing subtle nuances makes it invaluable across industries.
From customer service to market research, it enables businesses to extract actionable insights. Let us dive into the most impactful use cases where using LLM for sentiment analysis can drive meaningful results.
Customer Feedback Analysis
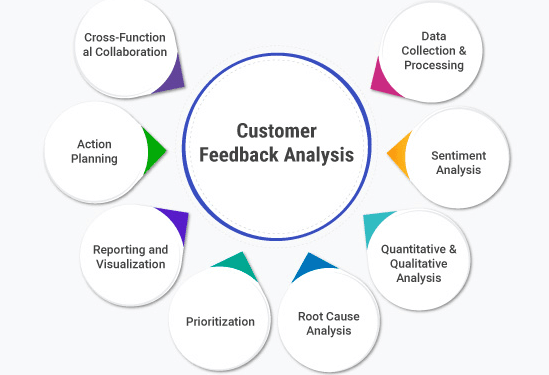
Understanding customer feedback is essential for improving products and services. LLM sentiment analysis processes large volumes of reviews, surveys, and complaints to extract sentiment trends and actionable insights.
Unlike older techniques such as rule-based systems and classical machine learning models that often struggle with context, sarcasm, and subtle emotional cues, LLMs can accurately interpret sentiment by recognizing complex language patterns and contextual subtleties.
For instance, an online retailer can use LLM for sentiment analysis to identify patterns in customer feedback. Reviews like "The product is great, but the delivery was late" are flagged as mixed sentiment, helping the company address delivery issues without assuming dissatisfaction with the product itself. Over time, this analysis helps improve customer satisfaction and loyalty.
Additionally, businesses can analyze survey responses across regions to understand localized sentiment differences. This allows them to fine-tune strategies to meet specific customer needs.
Social Media Monitoring
Social media platforms are goldmines of real-time consumer sentiment. Brands often rely on LLM sentiment analysis to monitor conversations, track campaigns, and gauge public opinion. LLMs can analyze social media posts, tweets, and comments, detecting both explicit and implicit emotions.
For example, during a product launch, a company might fine tune LLM for sentiment analysis to monitor hashtags and mentions.
Positive feedback like "This product is a game-changer!" can help amplify marketing efforts, while negative trends like "Terrible customer service today!" can alert teams to address issues promptly.
Moreover, LLMs can detect sarcasm or mixed opinions, such as "Another day, another glitch in this app, so innovative!" Traditional tools often misclassify such text, but LLMs provide more accurate interpretations, enabling brands to respond appropriately.
Chatbots and Customer Support
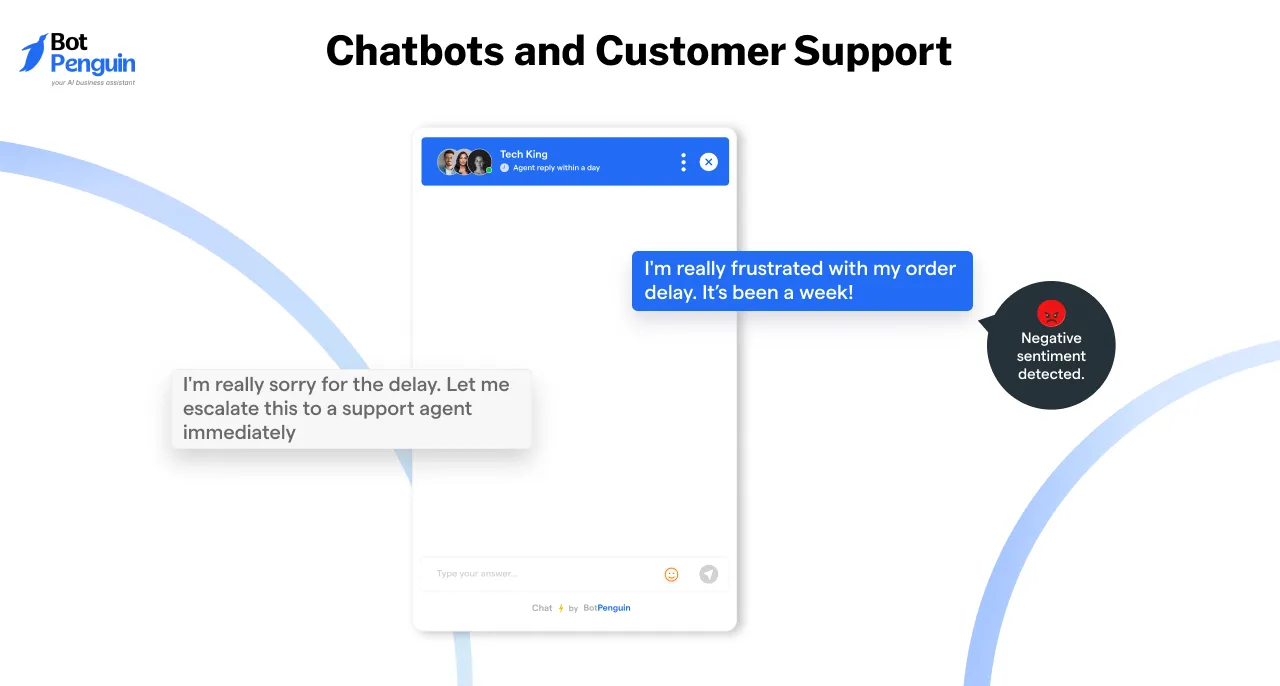
Chatbots and customer support systems are becoming smarter and more empathetic thanks to LLM sentiment analysis. By detecting a customer’s emotional tone, these systems can provide tailored responses, improving the overall user experience.
For example, if a customer messages a chatbot with frustration, such as "I’ve been trying to fix this issue for hours!" the system can escalate the query to a human agent or offer an immediate solution.
Using LLM for sentiment analysis, the bot adjusts its tone, responding empathetically rather than with generic replies.
This technology also helps prioritize critical issues. Sentiment-aware bots can flag negative or urgent messages, ensuring quick attention to dissatisfied customers while streamlining overall support operations.
Market Research
Market research requires a deep understanding of consumer preferences and trends. LLM sentiment analysis provides the scalability needed to process massive data from news articles, forums, and blogs. This allows organizations to identify emerging patterns and inform strategic decisions.
For instance, an automobile manufacturer might use LLM for sentiment analysis to analyze online discussions about electric vehicles.
Positive sentiment around affordability and sustainability could guide marketing campaigns, while negative comments about battery life might inform product development priorities.
Similarly, in retail, market researchers can track how customers feel about new fashion trends or seasonal products. This insight helps companies stay ahead of consumer demands, improving their market positioning.
Employee Feedback and Surveys
Organizations are increasingly turning to LLM sentiment analysis to evaluate employee feedback. By analyzing text from surveys, performance reviews, and internal communications, businesses gain a clearer understanding of workplace sentiment and morale.
For example, HR teams might fine tune LLM for sentiment analysis to assess responses to a new hybrid work policy. Comments like "I enjoy the flexibility but feel disconnected from the team" can reveal mixed sentiments, prompting the company to implement measures like team-building activities.
This use case is especially valuable for identifying patterns in anonymous feedback. By analyzing sentiment trends over time, businesses can proactively address issues before they escalate, fostering a healthier and more engaged workplace.
From customer insights to employee sentiment, fine-tuning LLM for sentiment analysis empowers businesses to make data-driven decisions with greater accuracy.
Whether enhancing customer service, tracking market trends, or optimizing internal feedback, this technology is revolutionizing how organizations understand emotions in text.
With AI-driven platforms like BotPenguin, businesses can seamlessly integrate sentiment-aware chatbots and AI agents to automate and improve interactions, ensuring smarter, more responsive engagement.
Comparing LLM Sentiment Analysis to Traditional Methods
LLM sentiment analysis has redefined how emotions and opinions in text are analyzed. But how does it stack up against traditional methods like rule-based systems or classical machine learning? Let us explore further.
Traditional methods, such as rule-based systems and classical machine learning, rely on pre-defined rules or manually engineered features. For instance, rule-based methods classify sentiment by matching specific keywords (e.g., "good" as positive, "bad" as negative).
Classical machine learning adds statistical models but still requires significant human effort to design features.
In contrast, LLM sentiment analysis uses pre-trained models like GPT and BERT that learn patterns from vast datasets.
These models don’t need explicit rules or extensive feature engineering. Instead, they understand context, sarcasm, and subtle emotions, challenges that traditional methods struggle to address.
How to Implement LLM Sentiment Analysis?
Implementing LLM sentiment analysis can seem complex, but with the right tools and steps, it is straightforward and rewarding.
Whether you are analyzing product reviews, social media comments, or survey responses, following a clear process ensures accurate and actionable insights. Here is how to get started.
Step 1
Choose the Right LLM Model
Start by selecting a Large Language Model (LLM) that suits your sentiment analysis needs. Options include:
- OpenAI’s GPT models (e.g., GPT-4)
- Meta’s Llama
- Open-source models like Mistral or Falcon
If your industry has specific language patterns, fine-tuning LLM sentiment analysis on domain-specific data will improve results.
Step 2
Collect and Prepare Data
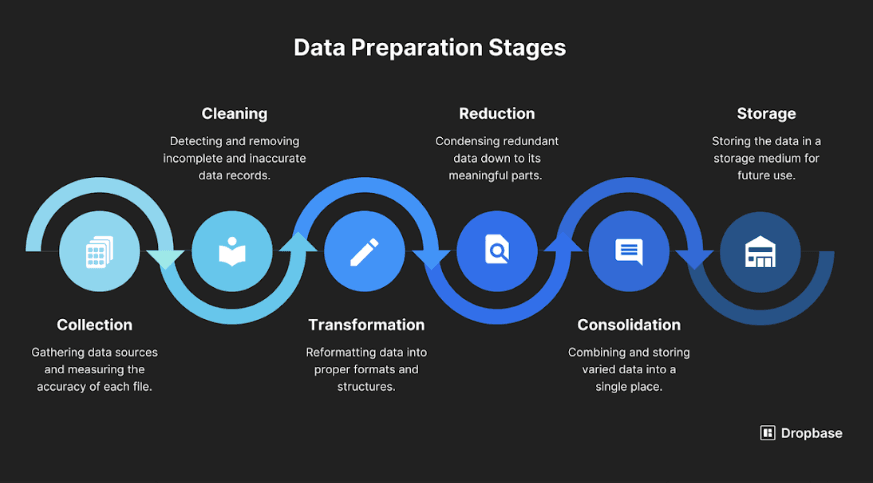
To train or fine-tune your LLM, gather a high-quality dataset containing labeled text samples with sentiment classifications (positive, negative, neutral). Reliable sources include:
- Customer reviews
- Social media comments
- Product feedback
- Support tickets
Clean the data by removing duplicates, noise, and irrelevant content to enhance model performance.
Step 3
Train or Fine-Tune the Model
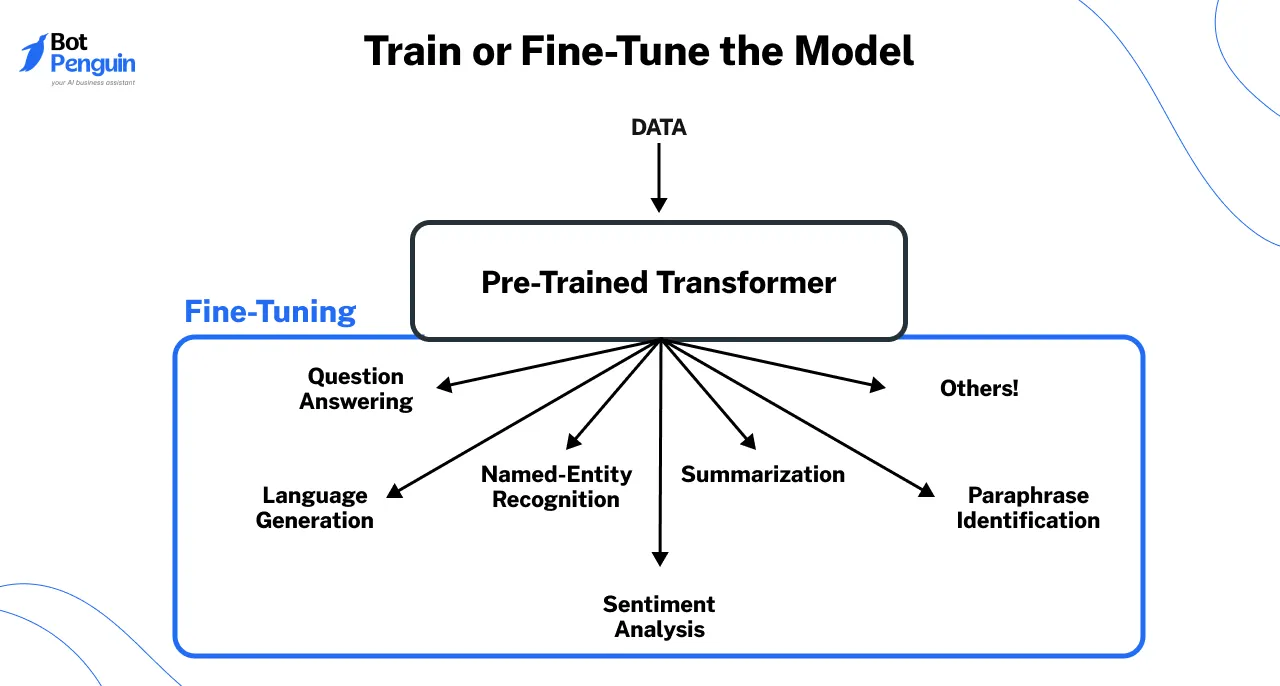
If a pre-trained LLM doesn’t meet your needs, fine-tuning LLM sentiment analysis can help. This involves:
- Training the model on industry-specific sentiment data
- Optimizing parameters to handle sarcasm, context shifts, and mixed emotions
- Validating performance using test datasets to prevent overfitting.
Fine-tuning ensures the model accurately interprets actual sentiment variations across different contexts.
Step 4
Implement Sentiment Classification
Once trained, the model must classify incoming text into sentiment categories. You can achieve this by:
- Using APIs (e.g., OpenAI, Hugging Face) for seamless integration into applications
- Deploying the model within your system to enable real-time sentiment classification
- Integrating it into chatbots, customer support tools, or market analytics platforms. For example, BotPenguin, an AI agent and chatbot maker, can utilize LLM sentiment analysis to detect customer emotions in real-time, allowing businesses to automate responses and improve engagement.
This enables businesses to extract insights quickly from large volumes of text.
Step 5
Evaluate Model Performance
To ensure accuracy, test your LLM sentiment analysis model using key evaluation metrics such as:
- Precision & Recall: Measures how well the model distinguishes between different sentiments
- F1 Score: Balances precision and recall for an overall performance assessment
- Confusion Matrix: Helps identify misclassified sentiments for further improvements
Regular evaluation helps fine-tune the model for consistent and reliable sentiment detection.
Step 6
Deploy and Automate Sentiment Analysis
After successful validation, integrate LLM sentiment analysis into your business workflows. This includes:
- Customer service: Detecting negative sentiment for quick issue resolution
- Brand monitoring: Analyzing social media trends and public opinion
- Market research: Tracking consumer sentiment on products and services
Platforms like BotPenguin allow businesses to build sentiment-aware chatbots that analyze emotions in real-time and enhance customer interactions.
Step 7
Continuously Improve the Model
Sentiment trends evolve, so regularly update and fine-tune LLM sentiment analysis models with new data. Implement human-in-the-loop feedback, where human reviewers validate and refine model predictions, ensuring they stay relevant and accurate over time.
By following these steps, businesses can harness LLM sentiment analysis to gain deeper insights, improve decision-making, and enhance user experiences.
Popular Tools and Platforms for LLM Sentiment Analysis
When implementing LLM sentiment analysis, several powerful tools and platforms can help streamline the process. Here are some popular options that are widely used for sentiment analysis tasks:
- Hugging Face: Hugging Face offers open-source libraries and APIs for deploying pre-trained LLMs. Its user-friendly interface makes fine-tuning accessible for beginners.
- OpenAI: OpenAI’s GPT models are robust and versatile, making them ideal for LLM sentiment analysis. Their API allows seamless integration into various applications.
- Google AI: Google’s BERT and related models provide excellent support for sentiment analysis tasks. Their ecosystem includes tools for training and deploying models efficiently.
These platforms offer powerful solutions for businesses and developers looking to integrate LLM sentiment analysis into their applications, enabling more accurate and efficient sentiment detection across various use cases.
Key Considerations for Successful LLM Sentiment Analysis Implementation
Implementing LLM sentiment analysis effectively requires careful planning and consideration of several factors. Let us look at a few of them below:
- Computational Power: Running LLMs requires significant computational resources. Ensure you have access to GPUs or cloud services that support heavy workloads. This is especially important for fine-tuning and real-time processing.
- Fine-Tuning for Specific Tasks: While pre-trained models are powerful, fine-tuning LLM for sentiment analysis can significantly improve accuracy. Use domain-specific datasets to teach the model the nuances of your industry.
- Data Quality and Annotation: High-quality training data is critical for success. Annotate text data carefully, ensuring labels reflect the true sentiment. Poorly labeled data can lead to inaccurate predictions and reduce the model’s reliability.
Taking these factors into account will help optimize the performance of your LLM sentiment analysis system, ensuring that it delivers reliable, actionable insights and effectively supports your organization's goals.
Challenges and Limitations of LLM Sentiment Analysis
While LLM sentiment analysis offers impressive capabilities, it is not without challenges.
These limitations can affect accuracy, cost, and usability, making it essential to address them during implementation. Let us examine the key obstacles and their implications.
Bias in Models
One significant issue with LLM sentiment analysis is bias in the training data. If the datasets used to train the models contain biases such as gender, racial, or cultural prejudices, the outputs may reflect those biases.
For example, a biased model might consistently associate certain words with negative sentiment based on skewed training data.
Organizations must carefully evaluate and mitigate these biases to ensure fair and accurate sentiment analysis, especially when using LLM for sentiment analysis in sensitive contexts like hiring or public opinion monitoring.
Resource Demands
LLMs require substantial computational power and storage, which can make LLM sentiment analysis costly. Running these models on local servers often demands high-end GPUs, while using cloud-based solutions incurs ongoing expenses.
Smaller organizations might struggle to allocate resources for fine-tuning LLM for sentiment analysis or maintaining large-scale deployments. Efficient resource management and cloud services can help mitigate this challenge.
Complexity in Fine-Tuning
Adapting pre-trained models to specific use cases often requires fine-tuning, which demands expertise and effort.
For instance, fine-tuning an LLM for a niche industry like healthcare requires annotated data and careful model adjustments. This process can be time-consuming and costly.
Interpretability Issues
LLMs are often seen as "black boxes," making it hard to explain their decisions. In LLM sentiment analysis, this lack of transparency can be problematic, especially in regulated industries where clear reasoning is required for decisions.
Despite these challenges, addressing them effectively can lead to more accurate, efficient, and fair LLM sentiment analysis solutions, ultimately unlocking the full potential of this powerful technology.
Future of LLM Sentiment Analysis
The future of LLM sentiment analysis is promising, with emerging trends and innovations shaping how we understand human emotions.
From integrating multiple data types to addressing ethical concerns, advancements in this field are set to redefine its applications.
Trends in AI and Sentiment Analysis

One of the biggest challenges in sentiment analysis has been detecting context-dependent emotions like sarcasm, irony, and mixed emotions within a single statement.
Future LLM for sentiment analysis will move beyond simple positive, neutral, and negative classifications to a more nuanced emotion detection system. Let us explore more:
- Context-Aware AI: Models will better understand long-form conversations, slang, and shifting sentiments within a discussion. This is crucial in industries like finance, healthcare, and customer service, where misinterpreted sentiment could lead to flawed decision-making.
- Emotional Intensity Recognition: Instead of just detecting whether a customer review is negative, future AI will deduce how negative it is, distinguishing between mild dissatisfaction and outright frustration.
- Industry-Specific Sentiment Tuning: Businesses will be able to finetune LLM for sentiment analysis in their specific domain. For example, healthcare AI could detect patient distress, while e-commerce models could focus on purchase intent and satisfaction levels.
Multimodal Sentiment Analysis

The next step for sentiment analysis is multimodal integration; analyzing text, audio, and video simultaneously. By combining text data with facial expressions, tone of voice, and gestures, AI can provide a deeper understanding of emotions.
For instance, using LLM for sentiment analysis alongside audio cues could help detect customer frustration in support calls, improving service responses. Let us explore further:
- Voice Sentiment Detection: AI will analyze voice modulations, pauses, and stress levels to detect emotions. Customer service bots, for instance, could pick up on frustration before a caller even states their complaint.
- Video & Facial Analysis: Future models will integrate facial recognition to assess emotions. This could revolutionize market research, education, and even mental health monitoring.
- Cross-Platform Emotion Tracking: Sentiment analysis will evolve beyond just social media and text-based interactions. AI will soon track emotions across video calls, podcasts, and live-streamed events.
Ethical Considerations and Responsible AI Development
As sentiment analysis grows, ethical concerns must be addressed. Ensuring unbiased models, protecting user privacy, and maintaining transparency are critical.
Developers must take responsibility when they fine tune LLM for sentiment analysis to avoid harmful applications, ensuring this technology benefits society. Let us explore more below:
- Bias Reduction in AI Models: Developers must ensure that sentiment analysis tools are trained on diverse datasets to prevent cultural, gender, and racial biases.
- Privacy and Data Protection: As companies collect and analyze emotional data, stronger privacy regulations will be necessary to protect users. Future LLM for sentiment analysis models will need built-in encryption and anonymization techniques to ensure user safety.
- Explainable AI (XAI) for Transparency: Organizations will demand more transparency in AI decision-making. Understanding how a model arrived at a sentiment score will be just as important as the score itself.
AI-Driven Sentiment Analysis for Hyper-Personalization
With advancements in intelligent data processing, sentiment analysis will become more proactive rather than reactive.
Businesses will be able to respond instantly to customer feedback, social media trends, and even stock market sentiment. Let us explore further:
- Automated Customer Interaction: AI-driven chatbots will recognize emotional cues and adjust their tone dynamically, improving customer satisfaction.
- Stock Market Sentiment Analysis: Financial institutions will use LLM sentiment analysis to track market sentiment from news, social media, and analyst reports, predicting fluctuations based on emotional trends.
- Personalized Content & Marketing: AI will tailor content based on emotional responses, ensuring marketing messages resonate better with target audiences.
As these advancements unfold, the future of LLM sentiment analysis holds immense potential to enhance emotional intelligence in AI, making it more accurate, inclusive, and responsible in its applications across diverse industries.
Conclusion
LLM sentiment analysis has redefined how businesses interact with data, making it easier to understand and act on emotions embedded in text. From improving customer experiences to refining internal processes, it is clear that this technology has become indispensable across industries.
However, implementing such solutions can feel overwhelming for businesses without technical expertise.
That is where accessible tools like BotPenguin can make a difference. As an AI agent and a no-code AI chatbot platform, BotPenguin helps businesses create sentiment-aware chatbots effortlessly.
These chatbots can enhance user interactions, understand emotions, and provide tailored responses, all without needing advanced coding skills.
BotPenguin bridges the gap, enabling businesses to harness the potential of AI-driven sentiment analysis seamlessly.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What types of data can LLM sentiment analysis process?
LLM sentiment analysis can process a wide variety of text data, including customer reviews, social media posts, emails, surveys, chat conversations, and product feedback.
It works across multiple languages and industries, making it versatile for many business applications.
How accurate is LLM sentiment analysis compared to traditional methods?
LLM sentiment analysis is much more accurate than traditional methods due to its ability to understand context, irony, sarcasm, and complex emotions.
Traditional models often misinterpret these subtleties, while LLMs provide a more nuanced and reliable analysis.
Can LLM sentiment analysis handle multilingual data?
Yes, LLM sentiment analysis can handle multilingual data. Many LLMs, including those developed by companies like OpenAI and Hugging Face, are trained on diverse datasets and can accurately analyze sentiment in different languages, making them ideal for global businesses.
How do LLM models detect sentiment in text?
These models work by processing the input text through complex algorithms that analyze word choice, sentence structure, and context.
They use large-scale training data to recognize patterns in how emotions are conveyed through text, such as positive, negative, or neutral sentiment.
How can I get started with LLM sentiment analysis for my business?
To get started with LLM sentiment analysis, businesses can either use pre-trained models available through platforms like OpenAI or Hugging Face or fine-tune these models using domain-specific data.
Integrating APIs or using tools like BotPenguin for chatbots can help businesses implement sentiment analysis in real-time customer interactions.