Most businesses don’t need to build software to make money from it.
They already recommend tools, platforms, and systems to clients every day. The only thing missing is ownership of that revenue. Instead of building products from scratch, many service-led businesses are quietly turning recommendations into repeat income.
This shift is changing how agencies, consultants, and IT firms grow. Selling outcomes matters more than selling hours. Software simply becomes part of the solution, not the product itself.
This guide explains how that model works in practice. You’ll learn how businesses approach it, where the income comes from, and what it realistically takes to make it work.
What is a SaaS Reseller
A SaaS reseller is a business or individual that sells software built by another company instead of creating their own product.
Rather than developing technology from scratch, the focus stays on distribution, relationships, and problem-solving. The reseller introduces the software to the right customers, explains how it fits their needs, and often supports onboarding or ongoing use.
Simply put, the software company owns the product, while the reseller drives adoption and revenue. This model allows service-led businesses to generate recurring income without moving away from what they already do best.
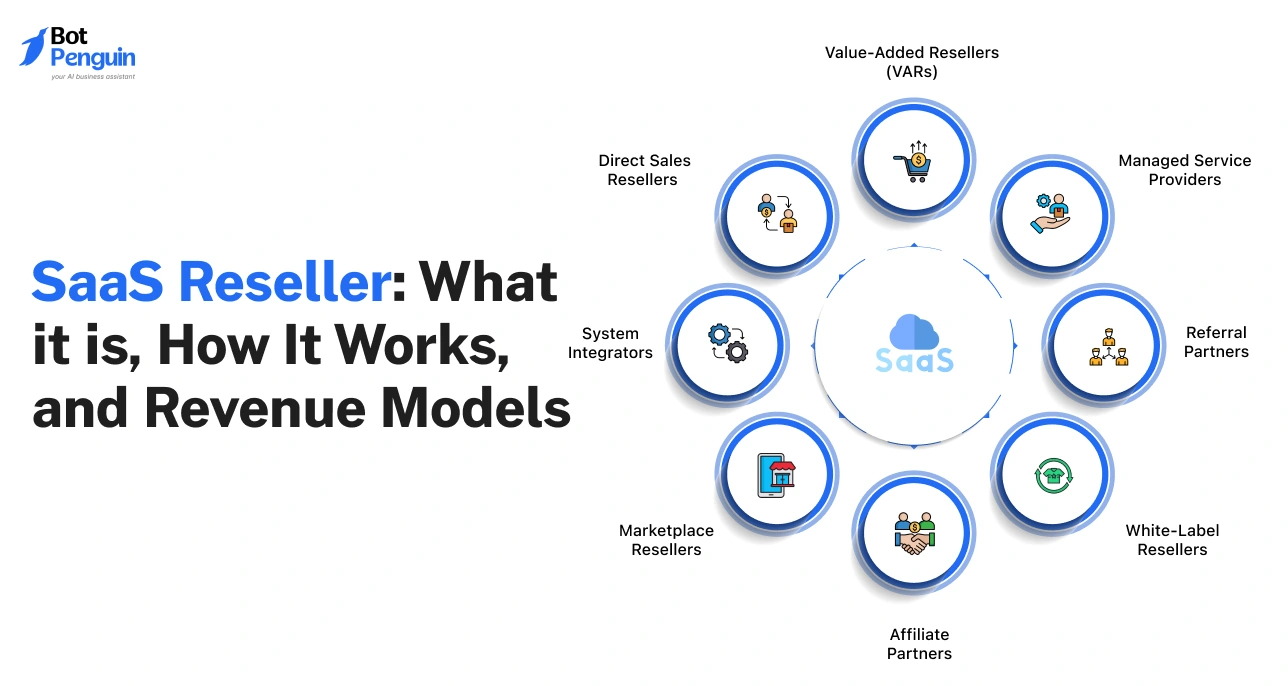
Types of SaaS Resellers and Reseller SaaS Business Models
SaaS resellers operate under different business models depending on how deeply they are involved in sales, delivery, and customer management.
The structure a reseller chooses affects revenue control, operational effort, and long-term scalability. Understanding these models helps businesses choose an approach that aligns with their skills, resources, and growth goals.
Below are the three most common operating models used in reseller SaaS businesses.
Commission-Based SaaS Resellers in Reseller Programs
This model focuses primarily on sales and referrals. The reseller acts as a distribution partner while the software vendor handles most operational responsibilities.
How this model works
- The reseller promotes the software to potential customers
- The vendor manages pricing, billing, and product support
- The reseller earns a commission per sale or subscription
Best suited for
- Freelancers and solo consultants
- Agencies testing reseller programs
- Businesses with strong sales reach but limited support capacity
Key considerations
- Lower operational effort
- Limited control over pricing and renewals
- Revenue depends on the commission structure
Value Added SaaS Resellers in Software Reselling
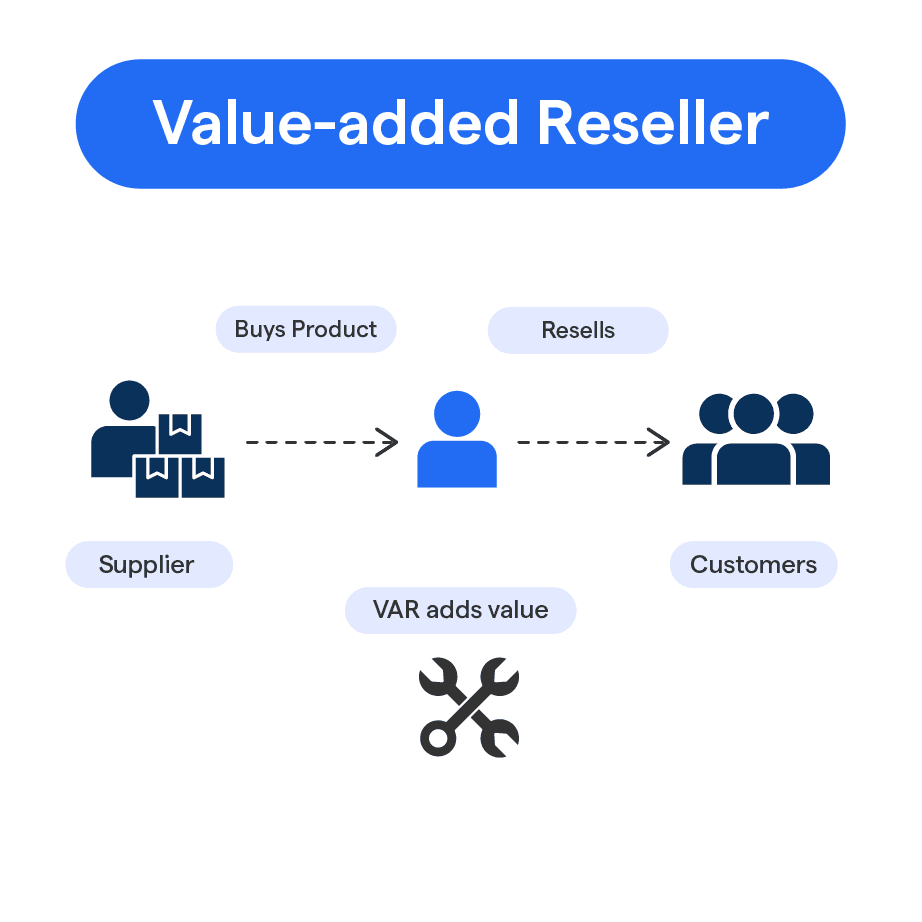
Value-added resellers combine software access with professional services. The software becomes part of a broader solution rather than a standalone product.
How this model works
- The reseller sells the software along with services such as setup or customization.
- Customers rely on the reseller for onboarding and optimization
- Services generate additional recurring or one-time revenue
Best suited for
- Digital marketing agencies
- CRM and automation consultants
- Service businesses offering implementation support
Key considerations
- Higher margins due to service bundling
- Stronger customer relationships
- Requires deeper product understanding
Managed Service Providers as SaaS Resellers
This model involves full ownership of software delivery and ongoing management. The reseller acts as a long-term operational partner for the customer.
How this model works
- The reseller sells and manages the software continuously
- Ongoing support, monitoring, and updates are included
- Clients usually sign longer-term service contracts
Best suited for
- IT service providers
- Operations-focused firms
- Businesses managing multiple tools for clients
Key considerations
- Highest responsibility and accountability
- Strong retention and predictable revenue
- Requires mature support processes
Comparison of SaaS Reseller Business Models
There is no single best model. Businesses that want speed and simplicity often start with commission-based reseller programs.
Those aiming for higher margins and stronger client retention usually move toward value-added or managed service models as their capabilities mature.
How SaaS Resellers Make Money Through SaaS Reseller Programs
Revenue is the main reason businesses explore reseller SaaS models. Unlike one-time service work, software reselling introduces predictable income streams that compound over time.
The exact earning structure depends on how the reseller program is designed and how much responsibility the reseller takes on after the sale. Most models combine recurring income with optional service-based revenue, which creates flexibility and scale.
Below are the primary ways SaaS resellers generate revenue in practice.
Revenue Share and Commission Models in SaaS Reseller Programs
This is the foundation of most reseller programs. The reseller earns a percentage of the revenue generated from customers they bring in.
Typical commission ranges
- Entry-level programs usually offer 15 to 25 percent revenue share
- Mature or performance-based programs may go up to 40 percent
- Some programs increase commissions based on volume or retention
What impacts margins
- Pricing control retained by the vendor
- Length of customer subscription
- Renewal ownership and churn rates
- Whether commissions are lifetime-based or time-limited
This model suits businesses focused on sales and distribution. Revenue scales with volume, but control over pricing and long-term margins is limited.
Subscription Income When You Resell SaaS Software
Subscription-based income is where software reselling becomes predictable. Customers pay monthly or yearly, and the reseller earns a recurring portion of that payment.
How recurring revenue works
- Each active customer contributes revenue every billing cycle
- Income grows cumulatively as more customers are added
- Renewals often require less effort than new sales
Why this matters
- Cash flow becomes more stable
- Business valuation improves due to recurring income
- Sales effort compounds instead of resetting every month
Resellers who focus on long-term customer retention benefit the most from this structure.
Service Fees, Upsells, and Software Reselling Add-Ons
Many resellers increase earnings by adding services around the software. This is common in value-added and managed service models.
Common service revenue streams
- Set up and onboarding fees for initial configuration
- Customization charges for workflows or integrations
- Ongoing management and optimization retainers
Why services increase profitability
- Services are priced independently of the software
- Margins are higher than commissions alone
- Customer dependency and retention improve
Revenue Model Comparison
The most sustainable reseller businesses do not rely on a single income stream. Combining subscription revenue with clearly defined services creates stronger margins, better customer retention, and long-term business stability.
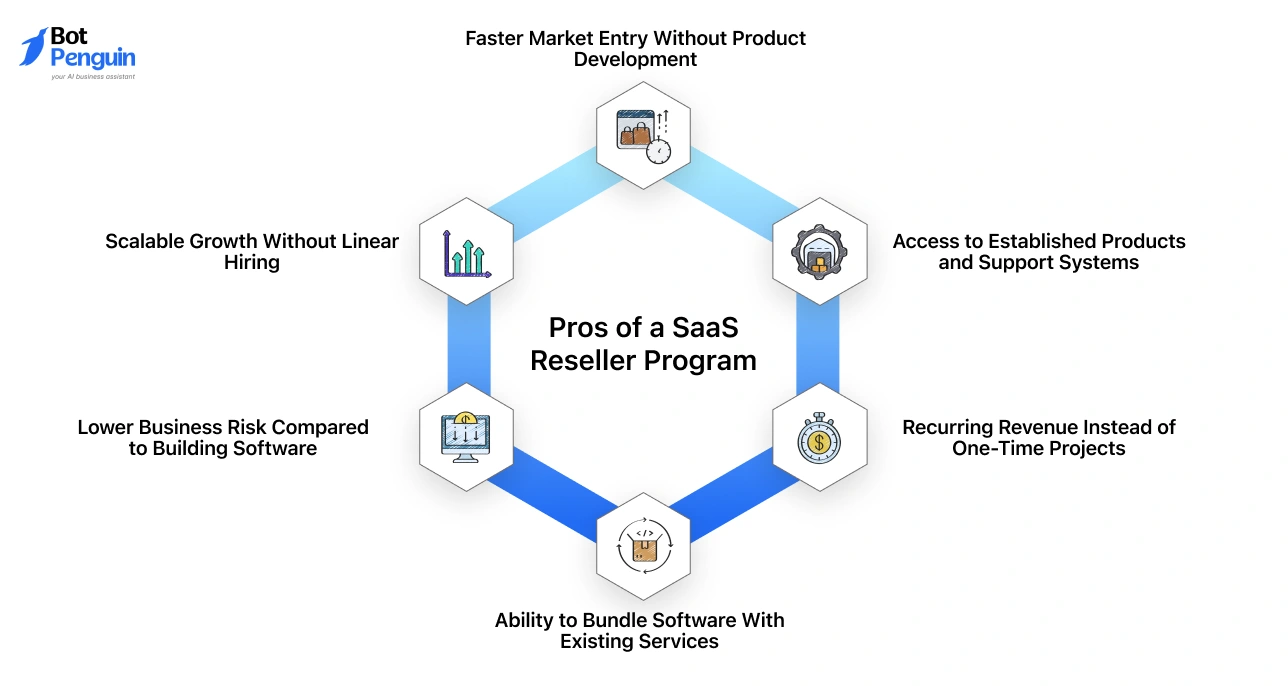
Pros of a SaaS Reseller Program
After understanding how revenue is generated, it is important to evaluate why many businesses choose this model in the first place. The benefits are not theoretical.
There are operational and financial advantages that appeal to agencies, consultants, and service-focused firms looking for stable growth. When executed correctly, this approach complements existing services rather than replacing them.
Below are the primary advantages that drive the adoption of reseller SaaS models.
Faster Market Entry Without Product Development
Building software requires time, capital, and ongoing maintenance. As a reseller, you bypass product development entirely. The software already exists, is tested in the market, and continues to improve without your involvement.
This allows businesses to enter the software space quickly while staying focused on sales, delivery, and customer outcomes.
Recurring Revenue Instead of One-Time Projects
Traditional service work ends when the project is delivered. Software reselling introduces recurring income through subscriptions and renewals.
Each customer contributes revenue over time, which improves cash flow stability and reduces pressure to constantly acquire new clients.
Ability to Bundle Software With Existing Services
Reselling software works best when combined with services. Agencies and consultants can package tools with implementation, support, or optimization.
This strengthens client relationships and increases the overall value of each engagement without significantly increasing delivery complexity.
Lower Business Risk Compared to Building Software
Product businesses carry long-term risk related to adoption, maintenance, and competition. Resellers avoid these risks because the vendor remains responsible for product development, security, and updates.
Your role stays focused on distribution and customer success rather than engineering decisions.
Scalable Growth Without Linear Hiring
Software-based revenue does not scale the same way services do. One product can be sold to many customers without proportional increases in headcount.
This makes it easier to grow revenue without expanding teams at the same rate, especially when supported by strong reseller programs and clear processes.
Access to Established Products and Support Systems
Most reseller programs provide sales resources, documentation, and onboarding support. This reduces the learning curve and improves sales effectiveness.
Instead of starting from zero, resellers build on proven platforms and existing market demand.
Becoming a reseller is most effective for businesses that already manage client relationships and want predictable revenue. The model rewards consistency, retention, and operational discipline rather than product invention.
Cons of SaaS Reseller Programs
Along with clear advantages, reseller programs also introduce constraints that businesses must account for before committing. These challenges are operational and commercial in nature.
Ignoring them often leads to margin pressure, support overload, or dependency risks. Understanding these limitations early helps set realistic expectations and choose the right program structure.
Below are the key challenges commonly faced by SaaS resellers.
Limited Control Over Pricing and Product Decisions
In most reseller programs, pricing and product direction remain with the software provider. This limits how much flexibility you have when responding to customer demands.
Changes in pricing or features can directly affect your customers, even when those decisions are outside your control.
Dependency on the Software Provider
Resellers rely on the vendor for platform stability, updates, and long-term viability. Any disruption on the vendor side can impact your reputation and customer relationships.
This dependency makes partner evaluation and platform reliability critical for long-term success.
Margin Constraints in Commission Focused Models
Commission-based reseller SaaS models often come with fixed earning limits. Margins may be reduced by discounts, plan changes, or capped revenue shares.
Without service-based add-ons, scaling revenue can become volume-dependent rather than value-driven.
Increased Customer Support Responsibility
Even when vendors offer technical support, customers usually contact the reseller first. This increases operational load around onboarding, issue resolution, and communication.
Without clearly defined boundaries, support efforts can grow faster than revenue.
Retention Risks Beyond Direct Control
Recurring revenue depends on renewals, but resellers may not control all factors influencing retention. Product usage challenges, missing features, or roadmap changes can affect renewal decisions.
Strong onboarding and ongoing engagement become essential to reduce churn risk.
Reseller programs work best for businesses that plan for constraints, not just benefits. Clear service scope, strong vendor selection, and realistic margin expectations are key to building a stable and sustainable reseller business.
What to Do Before You Start Reselling SaaS Software
Preparation determines whether reselling becomes a stable revenue stream or a short-lived experiment. Many failures happen before the first sale due to poor category selection, weak partner fit, or unclear terms.
This section highlights the core checks that should be completed before committing time, effort, or capital.
Choose the Right SaaS Category Based on Industry Fit
Select software that aligns with industries you already understand.
Key considerations:
- Existing client relationships
- Familiar buying behavior
- Clear understanding of industry workflows
Better industry fit reduces sales resistance and onboarding effort.
Validate Problem Relevance Before Selecting a Product
Resell software that solves frequent and important problems.
Focus on:
- Daily operational challenges
- Revenue or efficiency impact
- Problems customers already pay to solve
Low-priority tools are harder to sell and retain.
Evaluate SaaS Reseller Programs and Partner Structures Carefully
Saas Reseller programs vary widely in flexibility and control.
Check for:
- Clear commission structure
- Renewal ownership clarity
- Pricing control boundaries
- Access to sales and training resources
Programs with vague terms create long-term friction.
Review Support and Responsibility Boundaries Early
Clarify who handles what after the sale.
Confirm responsibility for:
- Onboarding support
- Technical issue handling
- Customer escalations
Undefined boundaries lead to support overload.
Understand Ownership Terms in SaaS Reseller Agreements
Ownership affects long-term account value.
Review terms related to:
- Customer relationship control
- Branding permissions
- Access to customer data
Limited ownership restricts upsell and retention efforts.
Assess Exit Clauses and Long-Term Flexibility
Exit terms matter even if termination is unlikely.
Verify:
- Notice period requirements
- Commission eligibility after exit
- Data access after the partnership ends
Clear exit terms protect future revenue and clients.
Reseller success starts with preparation. Clear category focus, strong partner alignment, and well-understood agreements reduce operational risk and support sustainable growth.
Skills and Infrastructure Required for SaaS Resellers
Reselling software is not passive income. It requires clear skills and basic systems to operate efficiently.
This section helps businesses self-assess readiness before scaling sales or onboarding customers. Gaps here often explain stalled growth or high churn.
Sales and Marketing Skills for SaaS Resellers
Selling software differs from selling services. Buyers expect clarity, proof, and repeatable value.
Key capabilities include:
- Explaining outcomes instead of features
- Handling objections related to pricing and commitment
- Communicating long-term value and renewals
Clear positioning improves close rates and retention
CRM, Tools, and Reseller Software Requirements
Managing customers at scale requires visibility and structure.
Core needs include:
- Tracking leads and active accounts
- Monitoring subscription status and renewals
- Managing communication history and follow-ups
Without basic systems, growth becomes difficult to sustain.
Support Readiness for SaaS Partner Programs
Customers expect guidance even when the vendor provides technical support.
Support readiness includes:
- Structured onboarding process
- Clear escalation paths
- Defined response expectations
Strong onboarding reduces churn and lowers ongoing support load.
Execution depends on discipline more than speed. Starting with existing clients, building service-led packages, and ensuring sales and support readiness creates a solid base for long-term reseller growth.
How to Become a SaaS Reseller
After understanding execution, skills, and readiness, the final consideration is platform fit. A reseller model only works when the underlying software supports sales, delivery, and long-term customer management.
BotPenguin is positioned to support reseller businesses that want predictable revenue without taking on product complexity. Its structure aligns well with how service-led businesses operate and scale.
Using BotPenguin as a Reseller SaaS Platform
BotPenguin offers both reseller and white label options designed for businesses that want control without development responsibility.
Key support areas include:
- White label setup with custom branding and pricing control ✅
- Reseller program access with a clear revenue-sharing structure ✅
- Central dashboard to manage customers, subscriptions, and usage ✅
- Built in support and documentation to reduce onboarding effort ✅
This allows resellers to focus on selling and client success rather than platform maintenance.
Why BotPenguin Fits Digital Marketing Reseller Programs
Digital marketing and automation-focused businesses benefit from platforms that integrate easily into existing workflows.
BotPenguin supports this through:
- Automation use cases across lead capture, customer support, and engagement ✅
- Integrations with CRM, ecommerce, and communication tools ✅
- Ability to scale across multiple clients without operational overhead ✅
For agencies, the software becomes part of a broader solution rather than a standalone product.
Best SaaS Partner Programs
The best SaaS partner programs offer more than commissions. They provide control over branding, pricing, customer ownership, and long-term revenue potential.
1. White Label Program
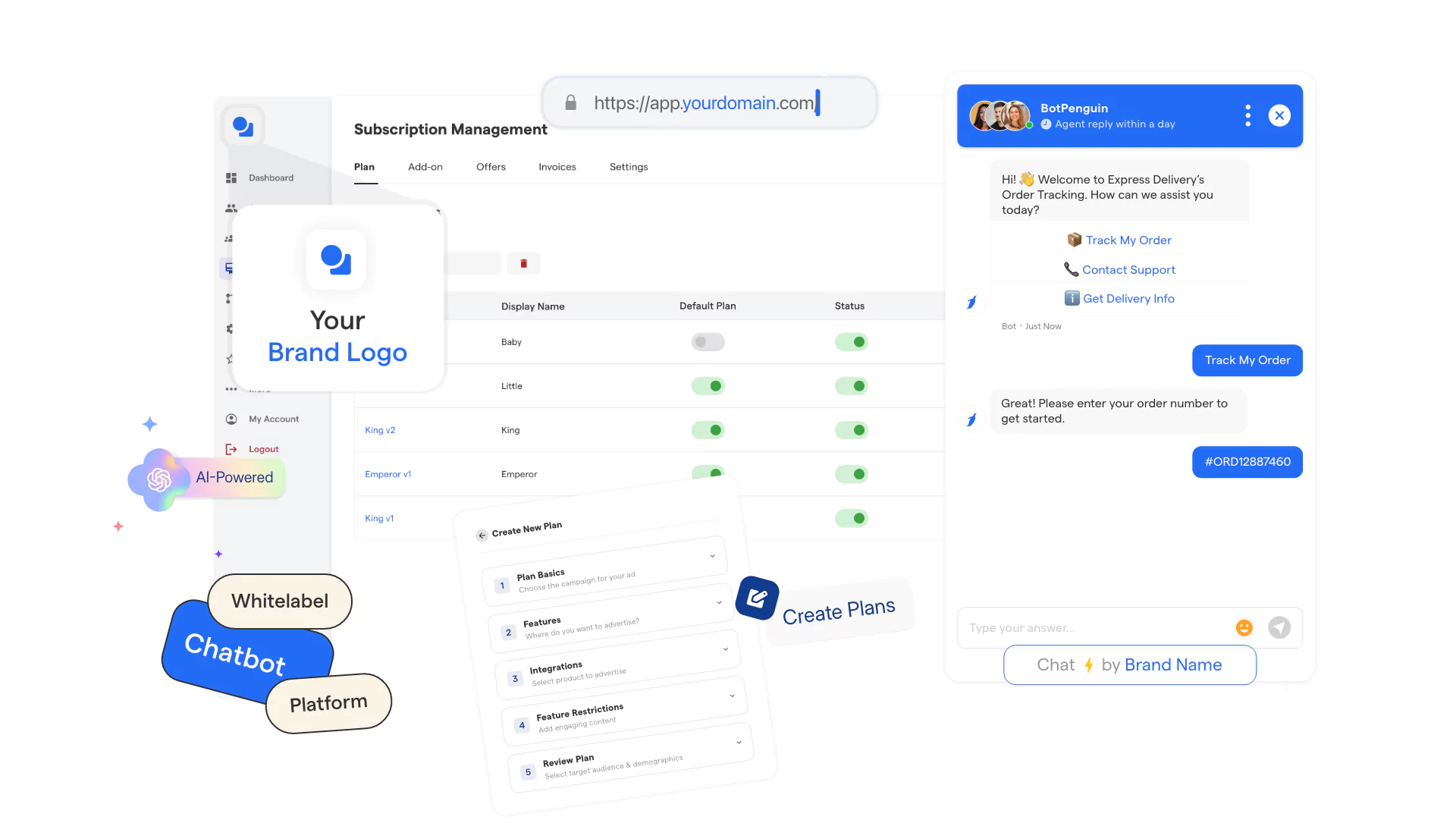
White Label Program option is built for businesses that want to sell software as their own product, not as a referral. You operate under your own brand. Your customers never see the underlying platform.
What this looks like in practice
- Your logo, domain, and pricing are used everywhere ✅
- You decide how plans are structured and positioned ✅
- Clients sign up, pay, and renew with your business ✅
- Software becomes part of your core offering ✅
Where value is created
- Recurring revenue stays fully within your business.
- Services such as onboarding, automation, and support can be packaged together.
- Long-term client relationships are owned and retained.
- Expansion happens through upgrades and additional use cases.
Who this fits
- Agencies selling outcomes, not tools
- Consultants productizing their services
- Businesses building predictable subscription income.
This path suits teams ready to treat software as a revenue engine, not an add-on.
2. Reseller Program

Reseller program option is designed for selling without operational ownership. You focus on distribution. The platform handles delivery.
What this looks like in practice
- Software is sold under the vendor brand.
- Pricing and billing are managed by the platform.
- You earn a recurring share from every active customer.
- Sales effort ends once the account is active.
Where value is created
- Fast monetization of existing networks ✅
- No infrastructure or branding setup required ✅
- Lower operational load after conversion ✅
- Clear earnings tied to customer retention ✅
Who this fits
- Freelancers and solo operators
- Sales-driven teams testing software resale
- Service providers are adding software without a process change.
This path works for businesses that want revenue participation without running a software operation.
Choosing from the best SaaS partner programs comes down to ownership, flexibility, and how well the platform supports long-term customer relationships.
Take the First Step Toward SaaS Reselling
Reselling software is no longer limited to large partners or technical firms. Agencies, consultants, and service providers already influence the tools their clients use. The difference now is the ability to own that revenue instead of passing it on.
The opportunity is not in experimentation. It is in choosing a platform that fits your services, supports long-term customers, and allows you to operate with clarity.
Partner structure, control, and support matter as much as the product itself.
Platforms like BotPenguin are built for this model. They support both reseller and white label approaches, allowing businesses to scale recurring revenue without taking on product complexity.
With the right setup and focus on outcomes, SaaS reselling can become a stable and scalable part of your business.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
How is a Software Reseller Different From a SaaS Reseller?
A software reseller may sell licenses or one-time products, while a SaaS reseller focuses on subscriptions, renewals, and ongoing customer relationships tied to recurring revenue.
What Role Does Reseller Software Play in Scaling a Reseller Business?
Reseller software helps track customers, subscriptions, renewals, and commissions, reducing manual work and enabling resellers to manage growth without increasing operational complexity.
Are the Best SaaS Partner Programs Suitable for Small Agencies?
Yes. Many of the best SaaS partner programs are designed for small teams, offering low entry barriers, predefined processes, and support systems that reduce risk during early adoption.
When Should Businesses Work With SaaS Business Brokers?
SaaS business brokers are useful when entering regulated markets, negotiating complex contracts, or accessing enterprise-focused partner programs that are difficult to approach directly.
Can Software Reselling Work Without Long-Term Contracts?
Yes. Some software reselling models rely on month-to-month subscriptions, but retention depends on ongoing value delivery rather than contractual lock-in.