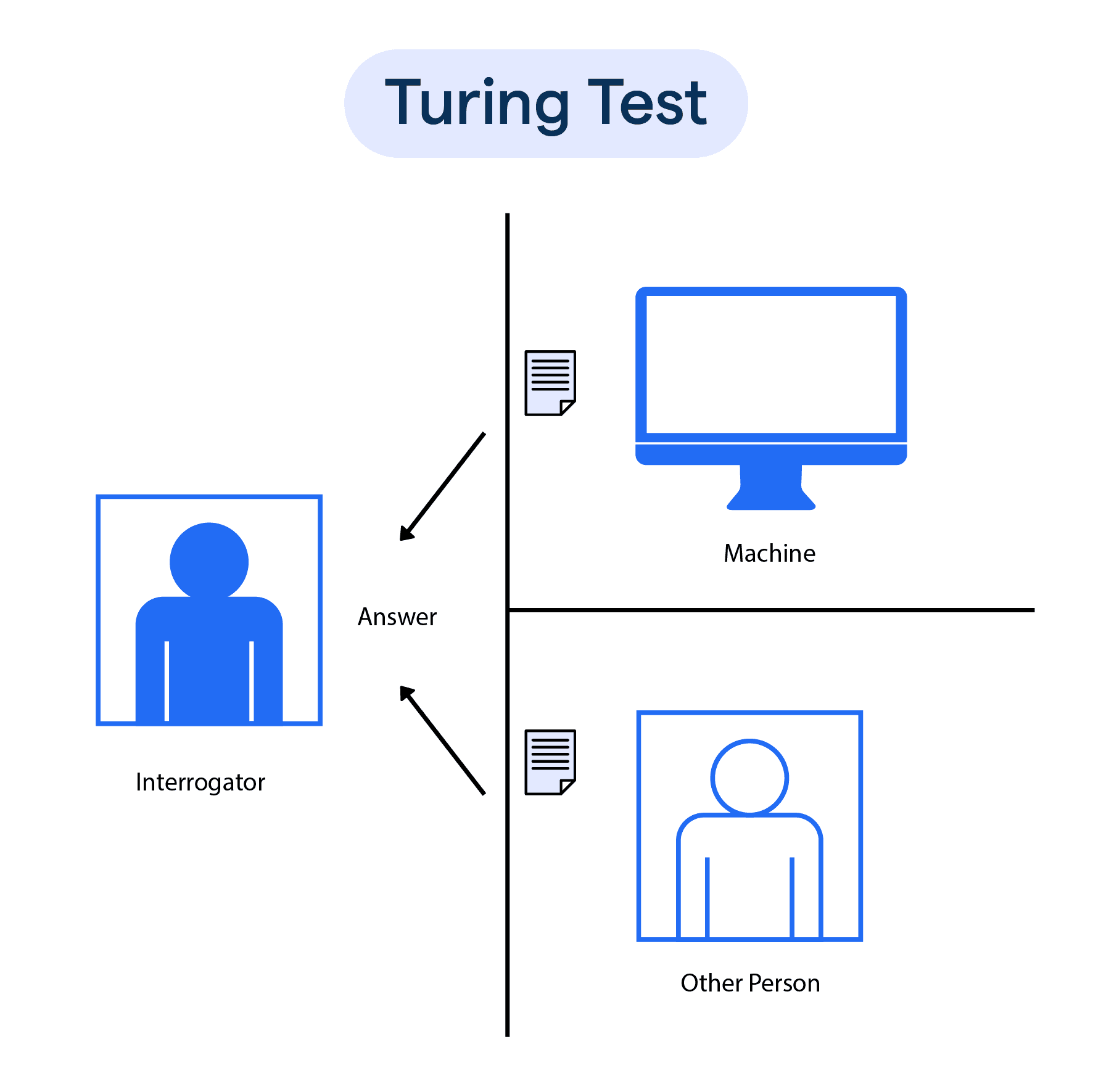
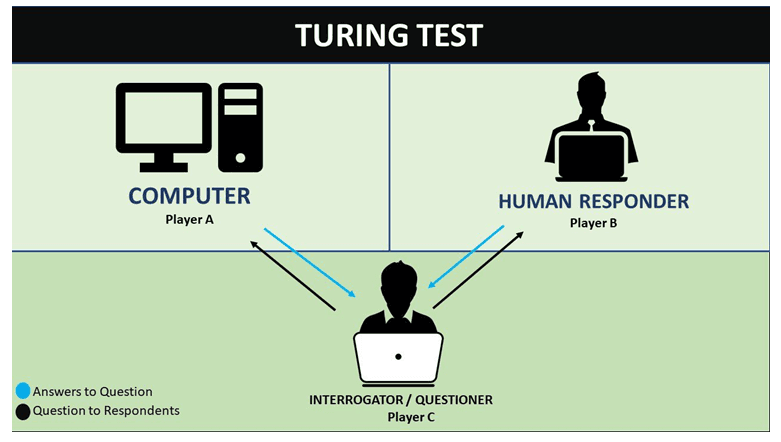
What is Turing Test?
The Turing Test, proposed by Alan Turing in 1950, is a method used to determine a machine's ability to exhibit intelligent behavior equivalent to, or indistinguishable from, human behavior.
In this test, a human evaluator communicates with a machine and another human.
If the evaluator cannot reliably determine which participant is the machine, then the machine is said to have passed the test, showcasing "human-like" intelligence.
Why Do We Need the Turing Test?
In this section, we will delve deeper into the purpose and significance of this test, and what it means for the future of AI.
Gauge Human-Like AI Performance
A primary function of the Turing Test is to measure an AI's ability to produce responses that are indistinguishable from those of a human.
This benchmark helps developers create AI systems that can effectively interact with people.
Promote Advancements in AI
Through the Turing Test, AI developers are encouraged to push the boundaries of the technology.
The competition drives innovation as they strive to create AI (artificial intelligence) that can pass the test and exhibit human-like intelligence.
Gather Insights on AI Progression
The Turing Test offers a method to track and evaluate AI's progress over time.
As developers refine their AI systems, the results of the Turing Test reveal the overall direction and milestones achieved in AI research and development.
Establish AI Credibility
By demonstrating an AI system's ability to pass the Turing Test, developers can help establish its credibility.
Achieving the human-like language recognition benchmark adds a level of trust and builds confidence in the AI system's capabilities.
Fuel Conversations on AI Ethics
As AI technologies continue to advance, questions related to AI ethics and their implications on human lives become more critical.
The Turing Test opens up conversations around the responsible development and deployment of AI systems, and their integration into society.
The Turing Test: How it Works
The Turing Test follows a specific methodology to assess a machine's intelligence. Let us walk you through the process step by step.
Step 1
The Test Setup
The test requires a human judge, a machine, and another human (known as the control).
The judge interacts with both the machine and the human control through a computer interface without knowing which is which.
Step 2
Communication
During the test, the judge engages in a conversation with both the machine and the human control, posing questions and conducting a dialogue.
The judge's main aim is to determine which is the machine and which is the human.
Step 3
The Evaluation
After the conversation, the judge provides their assessment and determines whether they could distinguish the machine from the human.
If the machine successfully convinces the judge that it is the human, it is considered to have passed the Turing Test.
Where Do We Use the Turing Test?
In this section, we will explore the various domains and industries where this test is applied, ranging from chatbots and virtual assistants to cybersecurity and ethical considerations surrounding AI.
Assessing AI Chatbots
Chatbots, now more than ever, need to effectively understand and respond to human input. The Turing Test can evaluate a chatbot's ability to mimic human conversation convincingly.
Evaluating Language Processing Software
Language processing applications, such as translation services, voice recognition, and transcription software, can employ the Turing Test.
It evaluates how accurately such applications understand, interpret, and mimic human language.
Testing Video Game AI
Video game developers use the Turing Test to gauge if the AI-controlled characters can simulate human-like behavior convincingly enough to provide a realistic gaming experience for players.
Screening Automation Tools
In automation, the Turing Test can help optimize tools that engage with humans.
Whether it's in customer service, tech support, or even sales, the test can help these tools interact more human-like and provide a better user experience.
Research and Development
In AI research and development, the Turing Test is a benchmark.
It pushes the boundaries of what AI can achieve, stimulating innovation and helping researchers track progress in achieving human-like AI.
The Controversies Surrounding the Turing Test
Despite its importance in the field, the Turing Test continues to be a topic of discussion and scrutiny for researchers and intellectuals alike.
In this section, we will delve into the critiques and debates surrounding the test.
Validity and Reliability
Some experts argue that the Turing Test does not truly measure machine intelligence, as it focuses more on the ability to deceive rather than actual understanding or consciousness.
They question whether passing the test equates to genuine intelligence.
Counterarguments
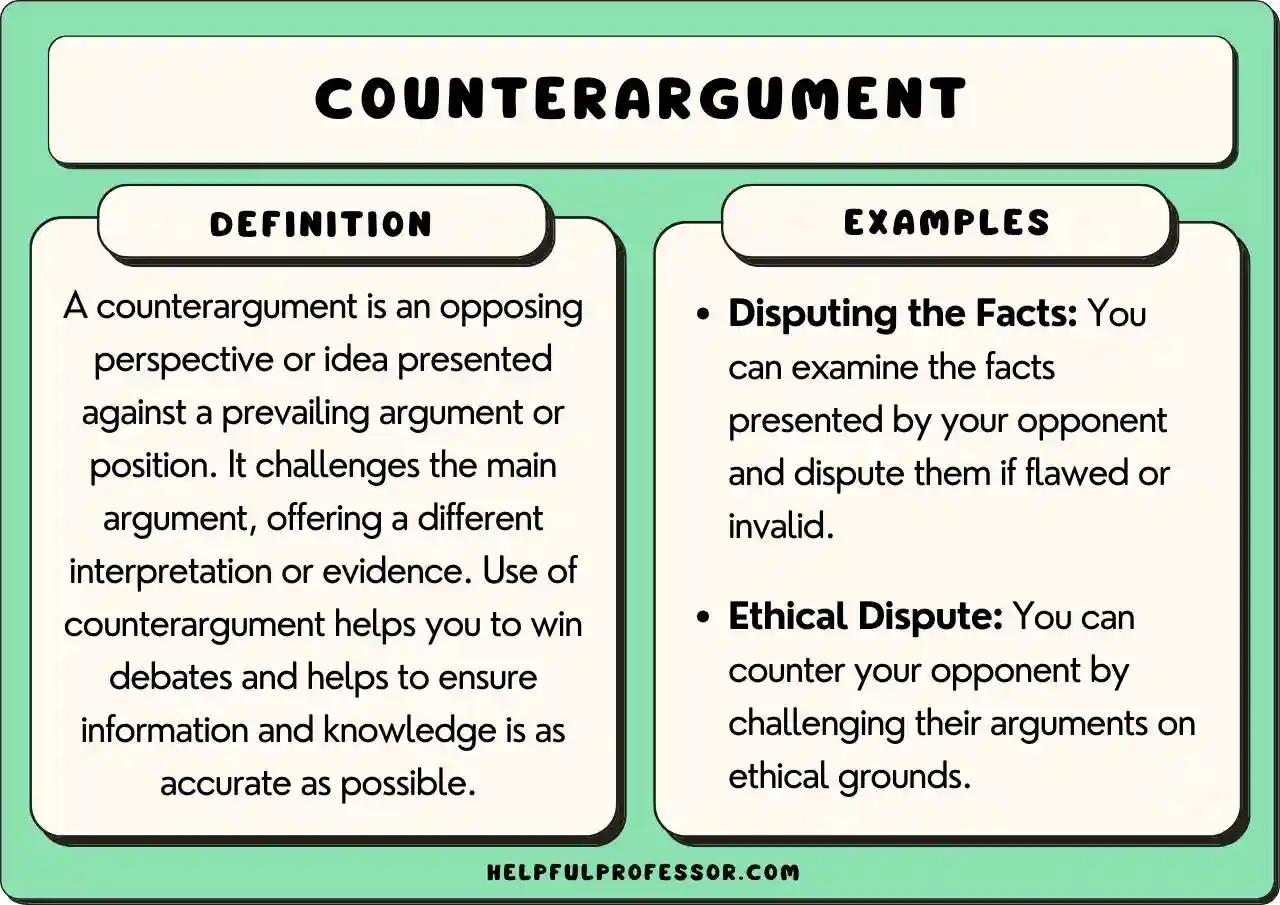
Supporters of the Turing Test defend its relevance, asserting that the ability to convincingly simulate human intelligence is an essential aspect of machine intelligence.
They argue that if a machine can effectively imitate human behavior, it demonstrates a level of understanding and intelligence.
The Turing Test and the Philosophy of Mind
The Turing Test has implications beyond artificial intelligence. It also intersects with the field of philosophy of mind, exploring the nature of consciousness and intelligence.
Nature of Consciousness and Intelligence
The Turing Test encourages us to ponder the fundamental questions of what it means to be conscious and intelligent.
By examining a machine's ability to replicate human behavior, we gain insights into the elusive qualities that define consciousness and intelligence.
Implications of Passing the Test
If a machine were ever to pass the Turing Test convincingly, it would challenge our notions of what it means to be human.
It would raise profound ethical and philosophical questions about the nature of humanity and the boundaries between humans and machines.
Current Applications and Limitations of the Turing Test
In this section, we will explore the diverse ways in which the test is applied in modern contexts.
Alongside its applications, we also delve into the limitations of the test, acknowledging its inability to fully capture the intricacies of true intelligence and the ongoing challenges in designing an infallible AI assessment.
- Evaluating Chatbot Intelligence: The Turing Test is often applied to assess the conversational ability of chatbots, with varying success in replicating human-like interactions.
- Stimulating AI Development: The test has fueled advancements in artificial intelligence by encouraging researchers to build more sophisticated AI systems capable of human-like communication.
- Testing Natural Language Understanding: The Turing Test evaluates AI systems' ability to comprehend and generate contextually relevant responses in natural language.
- Encouraging Conversational AI Research: The Turing Test has inspired further research in conversational AI, leading to improved voice assistants and chatbot technologies.
- Assessing Human-Machine Interaction: The test provides insight into the effectiveness of human-machine interactions, helping researchers design better AI-driven communication tools.
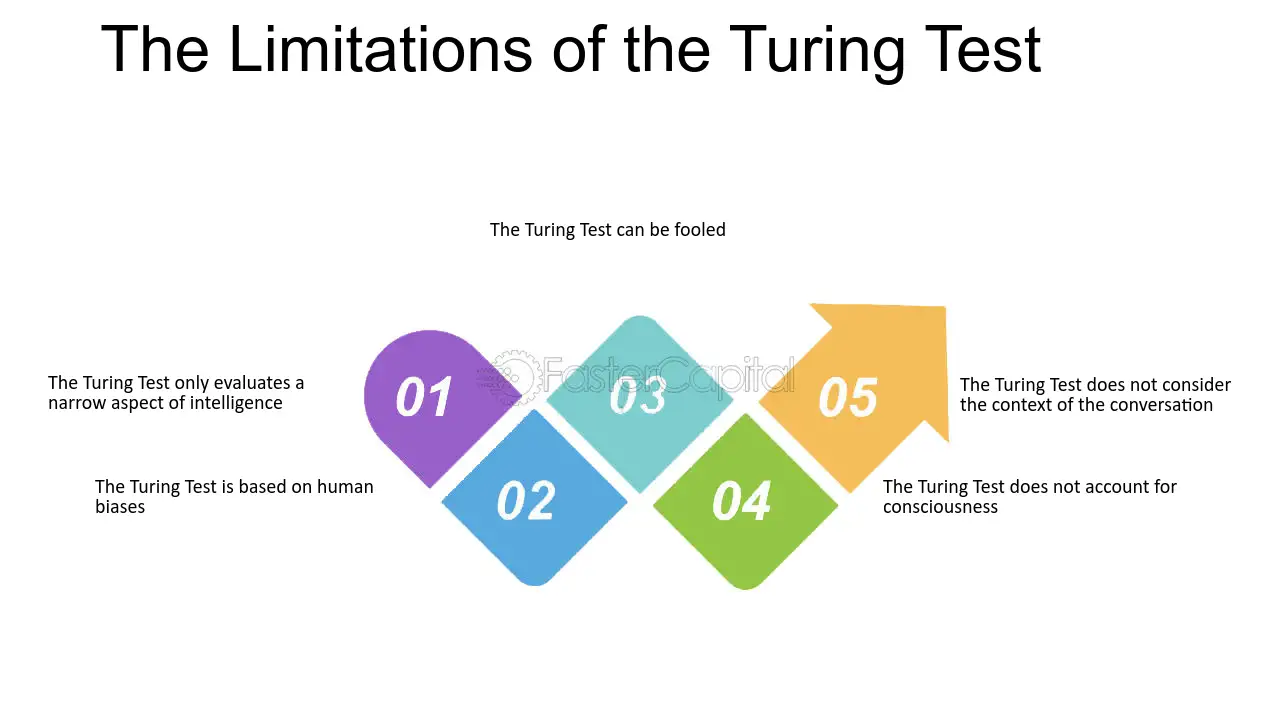
- Limited Measure of Intelligence: The Turing Test focuses on language capabilities, offering a limited perspective on overall machine intelligence in areas like problem-solving, learning, and reasoning.
- Susceptibility to Deception: The test can be manipulated, as some AI systems have passed it by using deception, without having truly human-like cognitive abilities.
- Lack of Standardized Criteria: The Turing Test lacks strict criteria for evaluating AI, leading to subjective judgments and ambiguity in interpreting test results.
- Emphasis on Imitation: The test emphasizes imitation rather than understanding, which may encourage AI development that prioritizes surface-level performance over deeper comprehension.
- Shift towards Alternative Methods: As the Turing Test's limitations become apparent, researchers are turning to alternative benchmark methods, such as the Winograd Schema Challenge or Hutter Prize, to evaluate AI capabilities more comprehensively.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is the Turing Test?
The Turing Test is an evaluation method created by Alan Turing to determine a machine's ability to exhibit human-like intelligence.
What is the purpose of the Turing Test?
The Turing Test aims to measure if a machine can replicate human intelligence and behavior to the point that it becomes indistinguishable from a human.
How does the Turing Test work?
During the Turing Test, an interrogator converses with a human and a machine through text-based interaction. If the interrogator can't distinguish between the two, the machine passes the test.
Has any AI system passed the Turing Test?
Some AI systems have claimed to pass the Turing Test, but there's ongoing debate about the validity and significance of such claims.
Are there alternatives to the Turing Test?
Yes, alternatives like the Winograd Schema Challenge and the Hutter Prize focus on more specific aspects of artificial intelligence and natural language understanding.