What is Swarm Intelligence?
Swarm Intelligence (SI) is an innovative distributed intelligent paradigm for solving optimization problems that has been derived from the biological examples by the self-organized behaviors of swarms of organisms, such as ant colonies, bird flocking, animal herding, honeybees, bacterial infection and even human social behavior.
Inspiration
This concept derives its inspiration from nature, specifically biological systems. The cooperative behavior of individuals, while simple individually, results in highly complex behavior on a group scale.
This collective intelligence emerges from decentralized, local interactions between the individuals and the environment.
Emergence
Emergence is a critical concept in swarm intelligence. An emergent property is a property which a system has but its individual constituents do not.
Examples
Some examples of swarm intelligence include ant colonies, bird flocking, animal herding, bacterial growth, and fish schooling.
SI systems are typically made up of a population of simple agents interacting locally with one another and with their environment.
Applications
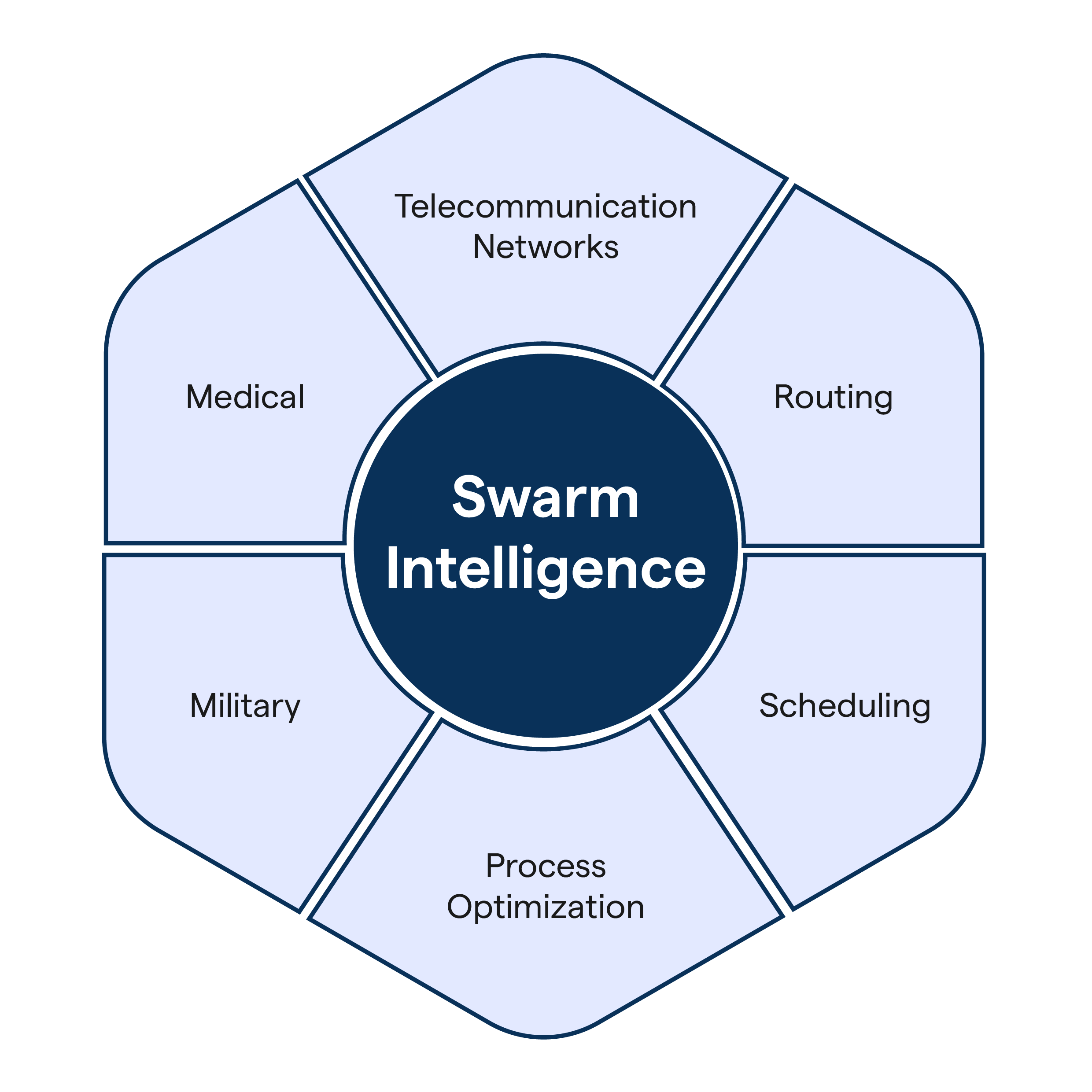
Swarm Intelligence has found applications in various domains, including artificial intelligence, computer science, robotics, data analysis, networking, and operational research.
Why is Swarm Intelligence Important?
Now that we know what Swarm Intelligence is, let's discuss why it's such a big deal:
- Flexibility: One of the key reasons why swarm intelligence is crucial lies in its flexibility - the individual agents in a system can adjust their behaviors in response to changing circumstances.
- Robustness: Swarm systems have a great degree of robustness. Even if a part of the system fails or is damaged, the collective can still fulfill its purpose. This is due to the decentralized nature of swarm systems.
- Scalability: Swarm Intelligence systems are highly scalable. The performance can be maintained by simply adding more agents.
- Complexity Reduction: Swarm intelligence helps in solving complex issues by breaking them down into manageable tasks that can be solved by simple agents.
- Real-Time Solutions: SI can be efficiently used to solve real-time problems due to its inherent parallelism and decentralized control.
Who Uses Swarm Intelligence?
Now let's talk about who actually uses Swarm Intelligence and how.
- Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning: Swarm intelligence is used in AI and machine learning to carry out tasks like clustering, routing, and scheduling.
- Robotics: In the field of robotics, swarm intelligence helps design control and coordination algorithms for groups of robots, known as swarm robotics.
- Network Systems: Network systems also rely on swarm intelligence for tasks such as routing, task allocation, load balancing, and security.
- Biological Research: SI models are used in biological research to understand and predict the behavior of swarms in nature.
- Operations Research: Swarm Intelligence is used in operational research for problem-solving and decision-making.
When is Swarm Intelligence used?
Understanding when Swarm Intelligence can be utilized:
- Optimization Problems: It is used when finding solutions to optimization problems that are otherwise difficult to crack with traditional methods.
- Dynamic Environments: It proves invaluable in dynamic environments that require adaptive and flexible solutions due to constantly changing conditions.
- Large Scale Problems: It's deployed when there is a need to solve large-scale problems with a high degree of complexity.
- Real-Time Applications: Swarm Intelligence can be called into action when real-time responses are required in complex scenarios.
- Unpredictable Scenarios: In unpredictable or unknown scenarios, SI can be used due to its inherent robustness and adaptability.
How is Swarm Intelligence applied?
A closer look at how Swarm Intelligence is applied in various fields:
Ant Colony Optimization
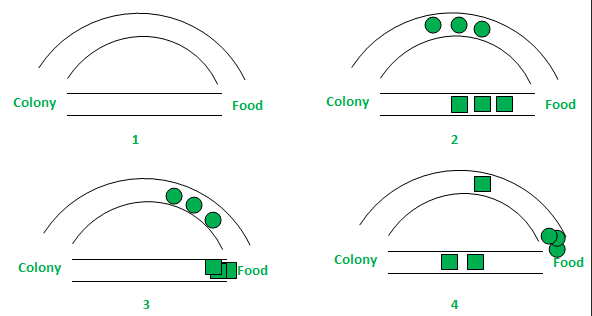
ACO uses models of ant behavior to solve problems. Ants communicate with each other using pheromones, forming a path that the other ants follow. This principle is applied to solve complex problems.
Particle Swarm Optimization
PSOs represent a problem in a multidimensional space and the solutions are candidate solutions. The particles' movement is determined by the best location they have found.
Stigmergy Collaboration
Stigmergy collaboration is when agents communicate indirectly through changes in their environment. This concept is widely used in collaborative projects, such as Wikipedia, where the content is built upon collaboration.
Bee Algorithm
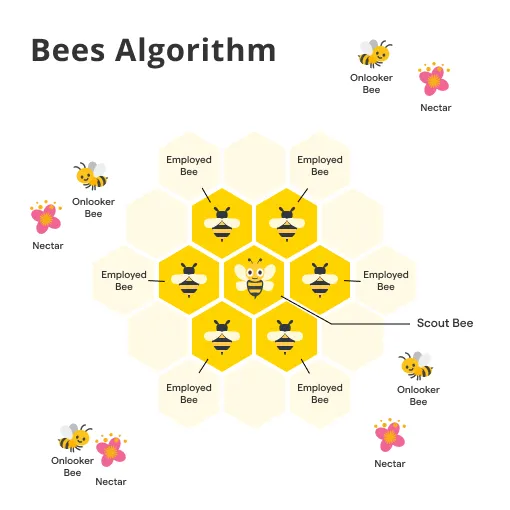
Inspired by the food foraging behavior of honey bees, this algorithm is used to search for and exploit valuable sources of information.
Swarm Robotics
Swarm robotics applies the concepts of swarm intelligence to the design of multi-robot systems.
Best Practices for Applying Swarm Intelligence
To ensure the effective implementation of SI, let's dig deeper into some critical best practices:
Achieving a Balance between Exploration and Exploitation
In swarm intelligence algorithms, a balance between exploration (searching for new potential solutions in the problem space) and exploitation (utilizing and refining already identified high-quality solutions) is vital.
Striking this balance is essential to ensure the algorithm can both locate diverse potential solutions and adequately refine these candidates.
Selecting Suitable Problems for Swarm Intelligence
Not all problems are suitable for swarm intelligence. It's important to evaluate the nature, complexity, and resources available for a problem before deciding to apply SI.
Problems with a high degree of non-linearity, multimodality, and dynamic characteristics are often excellent candidates for SI-based solutions.
Avoiding Premature Convergence
Premature convergence is a common issue in SI algorithms. This happens when all agents in the algorithm converge on a single solution too quickly and, as a result, the algorithm loses its diversity and gets stuck in local optima.
Various strategies can be implemented to counteract premature convergence, such as introducing diversity preservation techniques or altering the balance of exploration and exploitation over time.
Ensuring Adequate Problem Representation
The way a problem is represented can significantly impact the success of swarm intelligence algorithms.
Using an appropriate and high-quality representation ensures that problem specifics are captured correctly and adjustments can be feasibly translated into the solution format.
Ensuring Diversity within the Swarm
Just like biological swarms, maintaining diversity within the artificial swarm is crucial. It promotes robustness against perturbations and prevents the convergence to suboptimal solutions.
Diversity can be promoted through different means, such as using diverse initialization strategies and implementing reproduction methods that encourage diversity.
Challenges with Swarm Intelligence
Now, let's explore the challenges one could face while implementing Swarm Intelligence:
Complex System Design
The agents in swarm intelligence are ideally simple, but the design of a system capable of extracting collective intelligence is complex.
The challenge lies in configuring rules and parameters accurately to compel coordinated behavior that produces meaningful results.
Scaling Challenges
Swarm Intelligence systems are theoretically highly scalable, but practical implementation can present challenges.
As the swarm grows, the interactions may become too complex to manage or might result in a scenario where too many agents are doing the same thing, undermining the system's efficiency.
Predicting Outcomes
Derived from emergence, swarm outputs can be unpredictable due to the complexity of interactions between individual agents.
This means controlling the exact behaviors and outcomes of swarm systems can be challenging.
Hardware Limitations in Swarm Robotics
This refers to the limitations of the physical machine components in swarm robotics, such as sensors and actuators, that might interfere with the effective implementation of Swarm Intelligence.
Computing Resource Limitations
Some swarm intelligence implementations can require a significant amount of computational resources. This can be a challenge with large problem spaces or in systems where computational resources are limited.
Recent Trends in Swarm Intelligence
The final section delves into recent trends in Swarm Intelligence:
Evolution of Swarm Robotics
As robotics becomes more mainstream, expect to see more developments in swarm robotics with more complex and diverse robots being used in multiple industries.
Incorporation in IoT Systems
Internet of Things systems are beginning to incorporate swarm intelligence principles to enhance decision-making and network functionality.
Enhanced Algorithms
Researchers are developing improved algorithms designed to solve more complex problems.
Integration with other AI Techniques
Swarm Intelligence is being integrated with other AI techniques like Deep Learning for improved outcomes.
Advances in Biological Research
In the quest to better understand biological swarms like ant colonies or bird flocks, advances in SI modeling techniques are being made.
Going Beyond with Examples of Swarm Intelligence
Finally, let's delve deeper into some of the examples mentioned before to gain a better understanding:
Ant Colony Optimization
Ant Colony Optimization (ACO) solves optimization problems based on the food search behavior of ants. When foraging, ants lay down pheromone trails, creating a path that other ants then follow.
By mimicking this behavior, ACO allows the global optimal path to emerge over time through the collective behavior of relatively simple individual agents (the synthetic 'ants').
Particle Swarm Optimization
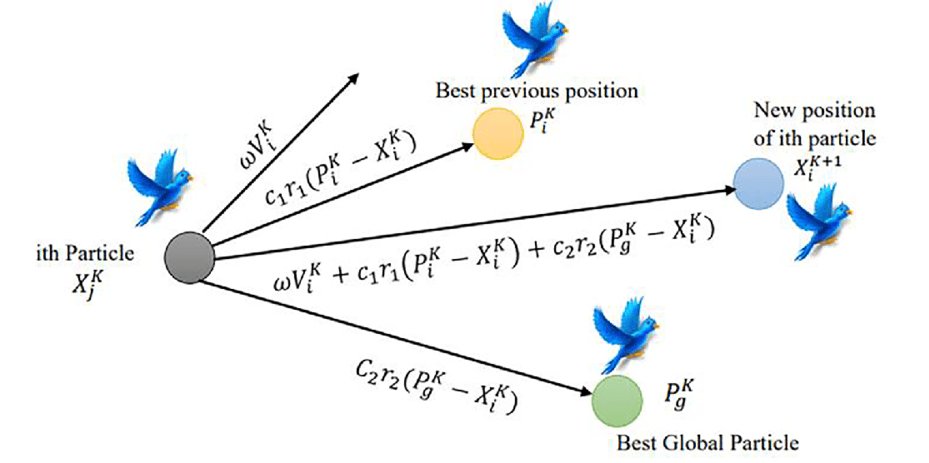
SParticle Swarm Optimization (PSO) is an SI algorithm used to solve optimization problems by iteratively trying to improve the candidate solution.
These candidate solutions, termed particles, fly through the problem space and are guided to the optimum solutions based on their own best experience and the best experience of their neighbors.
Stigmergy Collaboration
Whether it's termites building a complex mound or Wikipedia contributors building an article, stigmergy collaboration is a form of indirect coordination where agents adjust their behavior and actions based on signs or changes left in the environment.
Bee Algorithm
Inspired by the honey bees' nectar foraging behavior, the Bee Algorithm is used to multi-objective optimization. Scout bees are sent to random locations, and their discoveries guide the actions of the other bees.
This way, the algorithm ensures a good balance between exploration (search for new food sources) and exploitation (collecting nectar from known sources).
Swarm Robotics
Swarm robotics applies the principles of Swarm Intelligence to the design and operation of multi-robot systems.
The primary goal is to design a swarm where simple individual robots interact locally with one another and with their environment to provoke a global behavior capable of solving complex tasks.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
How does Swarm Intelligence mimic nature?
Swarm Intelligence is inspired by natural systems where collective behaviors emerge from simple individual actions—such as ants forming a colony, birds flocking, or bees swarming—making robust, scalable decisions.
What are common algorithms in Swarm Intelligence?
Particle Swarm Optimization (PSO) and Ant Colony Optimization (ACO) are commonly used Swarm Intelligence algorithms, inspired by social behavior of birds and ants respectively, for problem-solving and optimization tasks.
Can Swarm Intelligence be applied to robotics?
Yes, Swarm Intelligence is often applied in robotics, with swarm robots or 'swarms' performing tasks collaboratively, making the system robust against individual failures.
How does Swarm Intelligence aid in optimization?
Swarm Intelligence provides powerful solutions for optimization problems, often outperforming traditional methods. It leverages collective decision making, ensuring a near-optimal solution even in complex, dynamic environments.
Is Swarm Intelligence Relevant in Data Mining?
Swarm Intelligence is increasingly used in clustering, classification, and feature selection tasks in data mining, improving efficiency and quality of the results.