What is Selling in Marketing?
In marketing, selling is a vital process that is responsible for promoting and selling products or services, including market research and advertising.
It's a discipline that distinctively tries to convert leads to customers by explicitly demonstrating value to them and persuading them to make a purchase.
The Concept of Selling
Selling is essentially communicating the value of a product or service in a way that a potential customer realizes they don't just want the product but need it.
It involves tactics and strategies aimed at convincing the customer to make a buying decision in favor of the product or service.
Types of Selling
Different scenarios and markets often require unique selling approaches:
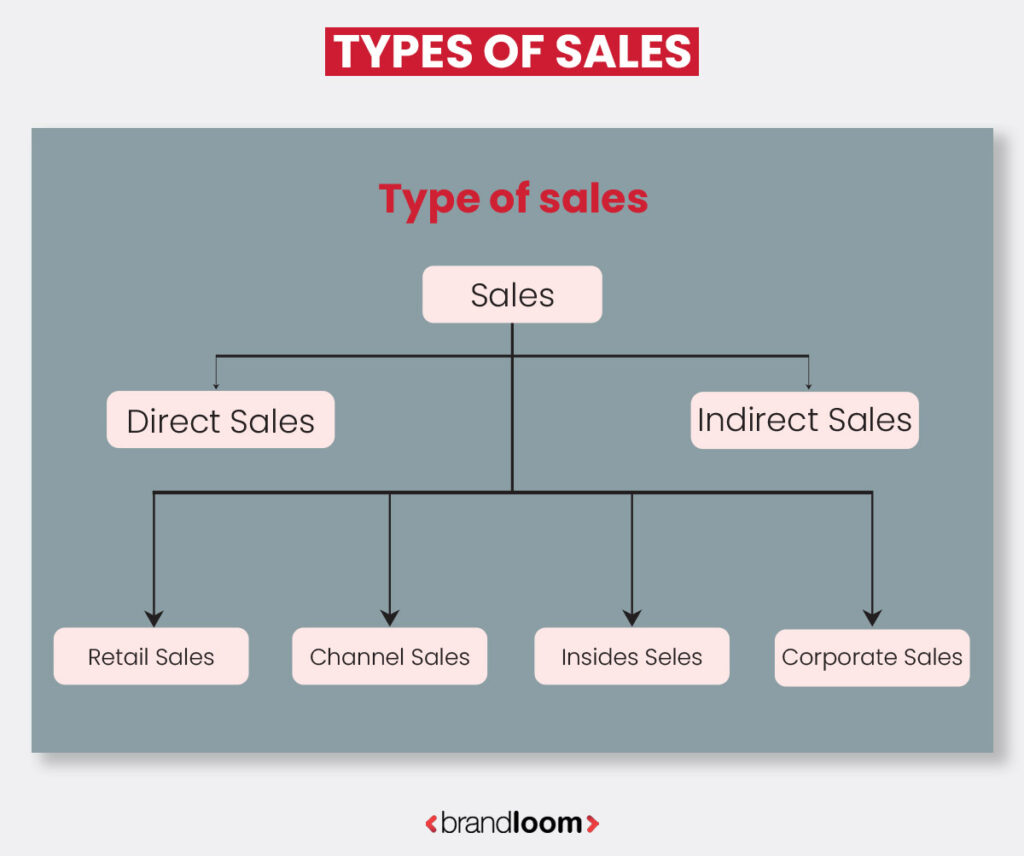
- Direct Selling: The process of selling products directly to consumers without the need for intermediaries.
- Telemarketing: Selling products over the telephone or through video conferencing calls.
- Retail Selling: Selling products in small quantities directly to consumers, usually in a specific physical location like a storefront.
- Industrial Selling: The process of selling products or services to other businesses.
- Online Selling: Selling goods or services over the internet, typically through eCommerce websites.
Importance of Selling
Selling is a key component of a business's revenue-generating process. It impacts the success of a product or service in the following ways:
- Acquiring Customers: An effective selling strategy can attract new customers, which directly increases sales volumes and revenue.
- Building Relationships: Selling is not a one-time transaction—it's about cultivating long-term relationships with customers, instilling in them trust and loyalty.
- Market Positioning: Good selling techniques help in positioning the product favorably in the minds of customers, ultimately improving the product's market position.
Effective Selling Techniques

Several effective selling techniques can increase the chances of a successful sale:
- Listening: Understanding the needs, problems, and desires of potential customers through active listening.
- Communicating Value: Clearly explaining the benefits and value of the product to the customer.
- Selling Solutions, Not Just Products: Positioning the product or service as a solution to the customer's problem.
- Follow-ups: Regularly following up on leads and inquiries can help close sales.
Challenges in Selling
Despite its undeniable importance, the selling process in marketing often comes with its share of challenges:
- Customer Hesitation: Overcoming customer apprehension and doubt can be a struggle, particularly for high-cost items or new products.
- Building Trust: Establishing credibility and trust, especially in a new market, is often a major hurdle.
- Competition: Intense market competition can complicate selling efforts, as businesses need to constantly differentiate themselves from their competitors.
Who is Involved in Selling
Selling in a business setting typically involves several key players, each with distinct roles and responsibilities.
- Sales Representatives: Sales representatives are on the front line in the selling process. Their main duties include presenting and selling products to potential clients, carrying out market research, and maintaining customer relationships.
- Sales Managers: Sales managers oversee the sales team. They develop sales plans, manage budgets, set sales goals, analyze sales data, and train and motivate their team.
- Marketing Team: The marketing team is essential in the selling process, though they might not be directly involved in sales transactions.
Marketing professionals develop strategies to attract potential customers, create compelling advertising campaigns, and work on improving product visibility.
- Customers: Customers are the end recipients in the selling process. They can be individuals (B2C) or businesses (B2B) and their needs and wants are the central focus of any selling effort.
- Customer Service and Support: This team plays a crucial role in addressing queries and issues, resolving complaints, and ensuring a smooth post-purchase experience, thus fostering customer loyalty and retention.
When Selling Takes Place
The selling process is a continuous effort that unfolds across multiple stages of a buyer's journey.
Pre-sales Stage
The pre-sales stage involves attracting potential customers through marketing and promotional strategies. It includes understanding customer needs, market research, and lead generation.
Sales Stage
The sales stage is where the actual selling happens. It involves presenting the product to the customer, overcoming objections, and closing the sale.
Post-sales Stage
The post-sales stage involves ensuring customer satisfaction after the purchase. This can include customer service, follow-ups, and building customer relationships for repeat business and referrals.
Where Selling Happens
The arena where selling occurs varies depending on the type of selling involved.
Brick-and-mortar Retail Stores
Traditional selling takes place in physical retail stores, where the customer can directly interact with the product before making a purchase.
Online Platforms
With the advent of eCommerce, selling has found a major platform online. Companies can sell their products and services directly from their websites or through eCommerce platforms.
Direct Selling
Direct selling typically happens at the customer's location—whether a home or a business. This includes door-to-door selling or network marketing.
Tradeshow or Exhibitions
These events provide an opportunity for businesses to directly showcase and sell their products to a large, industry-specific audience.
Telemarketing
Telemarketing involves selling products over the phone. It allows businesses to reach a vast number of potential customers without any geographic restrictions.
Why Selling is Important
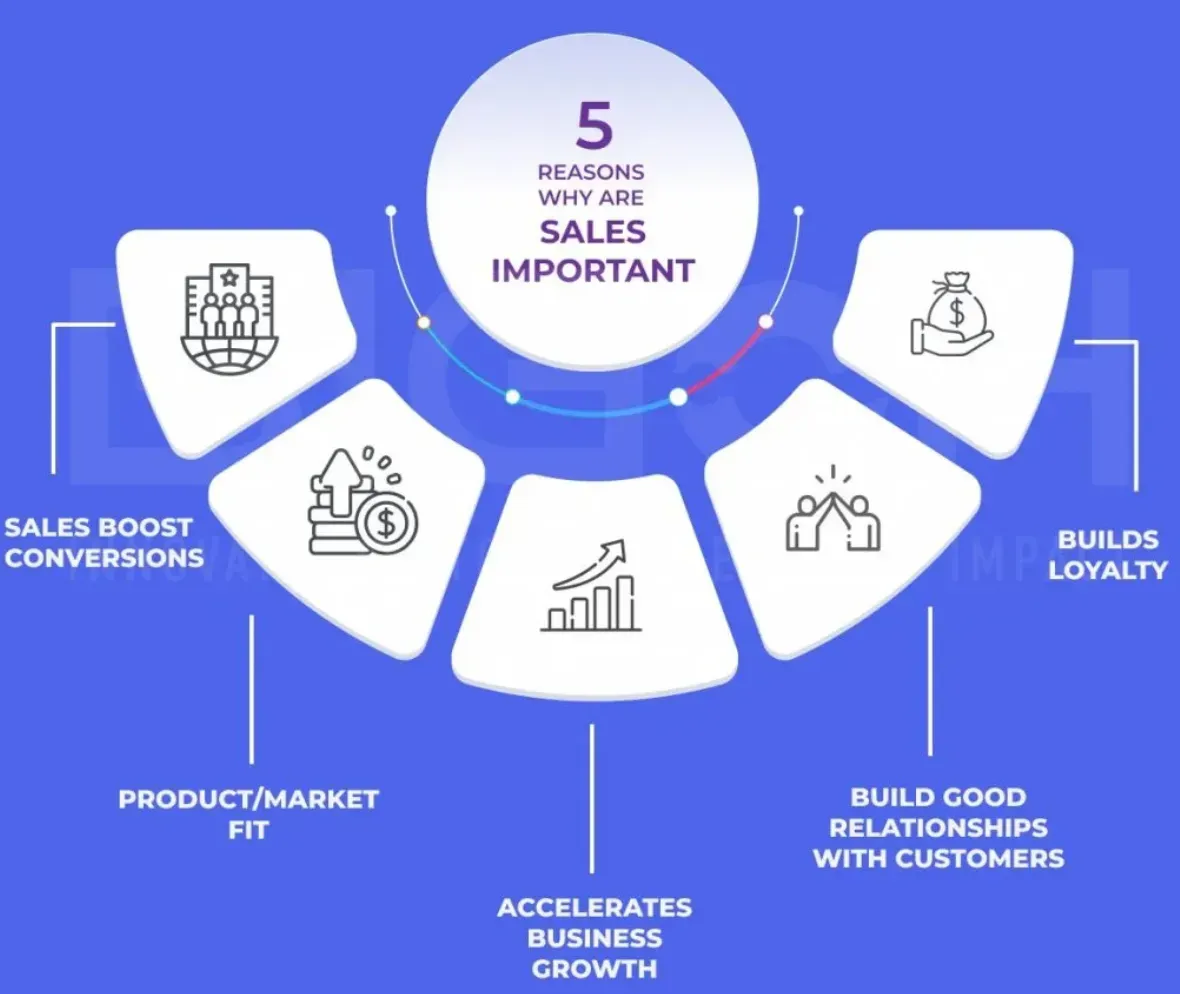
Selling plays a vital role in the lifeblood of any business:
- Revenue Generation: At its most basic, selling is important because it directly leads to revenue generation. No selling means no income for the business.
- Customer Acquisition: Selling allows businesses to attract new customers. A business's growth and survival hinge greatly on its capacity to consistently acquire new customers.
- Relationship Building: Selling fosters relationships with customers. These relationships influence future sales and can lead to customer loyalty and ongoing business.
- Feedback Loop: Selling provides an opportunity to gather customer feedback. This feedback can influence product development and improvements, thereby shaping the business's future direction.
- Market Expansion: Effective selling can help businesses expand their market presence. By selling in different markets or to new consumer segments, businesses can diversify their revenue streams and lower risk.
How to Sell in Marketing
Successfully selling a product or service involves a blend of strategies and tactics.
- Understand Your Customer: The first step to successful selling is understanding your customer's needs and wants. This understanding allows you to position your product as a solution for the customer.
- Deliver a Clear Value Proposition: Make sure the customer clearly understands the value of the product. Highlight its benefits, and emphasize how it offers a solution to their problem.
- Master the Art of Persuasion: Empathize with the customer, build trust, and skillfully guide the conversation towards why your product is the best choice.
- Provide Exceptional Customer Service: Providing excellent customer service—before, during, and after the sales process—helps to foster customer satisfaction and loyalty.
- Be Persistent: Persist in your selling efforts, even overcoming objections and turning rejections into learning opportunities.
Best Practices in Selling
To achieve success in selling, it's essential to adopt several best practices that ultimately enhance the customer experience and improve sales performance.
Prioritize the Customer
- Always put the customer's needs and interests first.
- Approach sales conversations with a problem-solving mindset.
- Offer genuine value and benefits that address customer pain points.
Develop Strong Relationships
- Focus on building long-term relationships with customers rather than just closing deals.
- Address customer concerns promptly and maintain open lines of communication.
- Strive for customer satisfaction and loyalty, as this can lead to repeat business and referrals.
Create a Sales Strategy
- Set clear and achievable sales targets.
- Develop a plan for reaching and engaging with target customers.
- Determine appropriate tactics and channels for reaching and influencing prospective customers.
Communicate Effectively
- Master the art of active listening to understand and empathize with the customer.
- Tailor your language, tone, and approach to each customer, based on their needs and preferences.
- Clearly articulate the value and benefits of your product or service to make a compelling case.
Leverage Technology
- Employ CRM tools and other sales technology to automate, streamline, and improve the sales process.
- Analyze customer data and insights to make informed decisions and personalize the sales approach.
- Utilize technology to optimize lead generation, tracking, and follow-up efforts.
Challenges in Selling
Selling is not without challenges. Some common obstacles faced by businesses attempting to sell their products or services include:
Intense Competition
- Differentiating your offerings from those of competitors can be difficult, especially in saturated markets.
- Developing strategies to stand out and convince customers to choose your products or services over others requires creativity and persistence.
Building Customer Trust
- Establishing credibility and trust with potential customers is crucial but can be challenging, particularly when entering new markets or niches.
- Handling skepticism and negative perceptions requires effective communication and transparency.
Scaling the Sales Process
- As a business grows, maintaining the same level of personal touch and quality customer service can be a major challenge.
- Adjusting sales strategies to account for organizational changes, including personnel and resources, can be difficult.
Keeping Up with Innovations
- Adapting to new technologies, industry trends, and changing customer preferences is essential to remain competitive.
- Continuously updating sales tactics, and tools, and offering adjustments to reflect evolving market conditions.
Navigating Regulatory Compliance
- Complying with applicable regulations in areas such as customer engagement, product claims, and data protection can be complex.
- Understanding and adhering to the legal and regulatory framework is crucial to avoid potential penalties and harm to the company's reputation.
Examples of Successful Selling
To illustrate these best practices and challenges, here are two examples of successful selling.
Apple
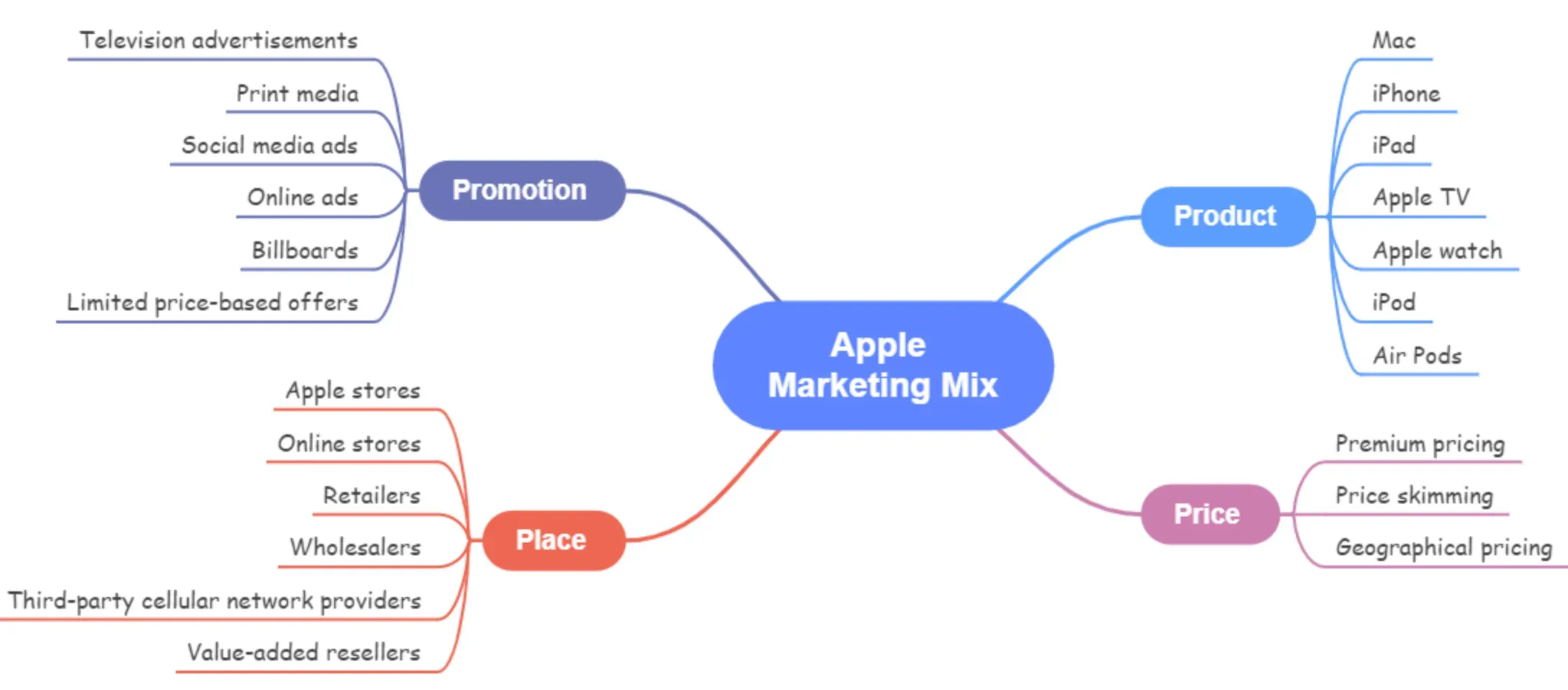
Apple is known for creating high-quality, innovative products and positioning them as premium, must-have items. The company's selling success is attributed to:
- Prioritizing Customer Experience: Apple products are designed with user experience in mind, consistently delivering value to customers.
- Strong Branding: Apple has built a strong brand, based on innovation, quality, and customer trust. This has translated into customer loyalty and repeat purchases.
- Retail Experience: Apple retail stores provide an interactive space for customers to explore and experience the products, creating a unique and memorable buying process.
Challenges Apple has faced:
- Intense Competition: Apple faces significant competition from other tech giants like Samsung and Google. To stay ahead, the company must constantly innovate and differentiate.
- Maintaining Customer Trust: Apple has faced customer concerns related to data privacy or pricing. As a result, transparent communications and responsive customer service are crucial.
Amazon

Amazon is a prime example of effective online selling. Its success is showcased in the following ways:
- Customer-Centric Approach: Amazon prioritizes customer satisfaction, with a vast selection, competitive pricing, and excellent customer service.
- Efficient Delivery System: Amazon ensures fast and efficient delivery services, impressing customers with speedy shipping and straightforward return policies.
- Personalized Experiences: Amazon uses advanced algorithms to offer personalized recommendations based on individual customer preferences, significantly enhancing the shopping experience.
Challenges Amazon has faced:
- Scaling Customer Service: With Amazon's ever-expanding product offerings, providing consistent and personalized customer service requires continuous investment in resources and technology.
- Regulatory Compliance: As Amazon deals with customer data and international transactions, the company must abide by strict compliance regulations and data protection laws.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is the difference between selling and marketing?
Selling focuses on promoting and closing sales for products or services, while marketing covers a broader spectrum of positioning, promotion, and understanding of customer needs and preferences.
How do sales funnels enhance selling strategy?
Sales funnels map the customer journey from awareness to conversion, helping businesses understand their potential customers and design targeted, strategic selling techniques for better results.
What role do CRM tools play in selling?
Customer Relationship Management (CRM) tools streamline and optimize the sales processes by managing leads, customer interactions and data, helping sales teams make informed decisions and close deals.
What is cross-selling in marketing?
Cross-selling involves recommending complementary products or services to customers based on their purchase history or preferences, increasing revenue and enhancing customer experiences.
Why is competitive analysis important in selling?
Understanding your competition helps you differentiate your offering, identify shortcomings, and develop unique selling points, enabling more effective selling strategies and higher conversion rates.

