What is Query Language?
A query language is a specialized programming language designed to communicate with databases and manage data.
It enables users to fetch, manipulate, and analyze information stored in structured data formats, like relational databases.
One well-known example is SQL (Structured Query Language), used for querying relational databases.
For instance, SQL's "SELECT" statement retrieves specific data by specifying conditions, such as
SELECT first_name, last_name FROM employees WHERE salary > 50000;
Which fetches the first and last names of employees earning more than 50,000.
Query languages make interacting with databases user-friendly and efficient, catering to both technical and non-technical users.
Who Uses Query Language?
Query languages, especially SQL (Structured Query Language), are used by a broad spectrum of professionals. Database administrators utilize them for organizing, troubleshooting, and ensuring the smooth operation of databases.
Data analysts and Data scientists heavily rely on these languages to retrieve necessary data, perform analytics, and draw insight from data. Back-end developers use query languages to integrate database information into applications.
Even professions you might not readily associate with coding, like digital marketers and financial analysts, often use query languages to access and interpret data, leading to informed decision-making. Ultimately, anyone who interacts with data could benefit from learning a query language.
What Are the Benefits of Query Language?
In this section, we'll explore the benefits of query language in data management and its significant impact on the efficiency and effectiveness of various data tasks.
Efficient Data Retrieval
Query languages allow users to specify and extract the information they need from complex databases. This efficient retrieval of data helps in reducing the time spent on searching for and extracting relevant information, making the overall data management process smoother and more efficient.
Simplified Data Management
Query languages offer an easy-to-understand syntax for managing databases. With a uniform language, users can create, read, update, and delete data effortlessly, even with limited technical knowledge. This way, query languages simplify various aspects of data management and allow non-technical users to interact with databases.
Increased Productivity
The use of query languages accelerates data management operations by enabling automation and standardization. By automating repetitive tasks and adopting a standardized approach, users can reduce errors and save time on manual operations, thereby increasing overall productivity.
Enhanced Data Security
Query languages often include features to manage user access and permissions. By controlling access to specific data and resources, organizations can ensure data security and protect sensitive information from unauthorized users. In addition to security features, query languages also provide reliable data backup and recovery solutions, further safeguarding against potential data loss.
Better Decision-Making
With query languages, users can extract, analyze, and interpret information with more precision and accuracy, leading to better decision-making within the organization. Query languages facilitate advanced data analysis, like aggregation and filtering, to derive valuable insights from large datasets, empowering businesses to make data-driven decisions.
In summary, query languages are essential tools in data management, providing numerous benefits in data retrieval, simplification, productivity, security, and informed decision-making. Incorporating query languages into your data management workflows can greatly enhance the overall efficiency and effectiveness of your organization's data operations.
Types of Query Language
In this section, we'll be diving into the different types of query languages and their unique purposes and functionalities.
Structured Query Language (SQL)
Possibly the most well-known type of query language, SQL is used primarily for managing data stored in Relational Database Management Systems (RDBMS). It allows the user to create, read, update, and delete (CRUD) operations on data.
Data Manipulation Language (DML)
Closely related to SQL, DML falls within SQL's range. Examples include SQL commands such as 'SELECT', 'UPDATE', 'INSERT' and 'DELETE'. These commands help users manipulate data in the database.
Data Definition Language (DDL)
DDL is a subset of SQL used to define and manage database schemas and objects. This includes commands such as 'CREATE', 'ALTER', 'DROP', 'TRUNCATE', etc. which help in creating, modifying, or deleting structural elements of the database.
Data Control Language (DCL)
DCL is another subset of SQL, focusing on controlling access to data stored in a database. Commands like 'GRANT' and 'REVOKE' form part of DCL, allowing administrators to manage permissions on who can access and manipulate the data.
Query by Example (QBE)
An intuitive, visual way of querying databases, QBE uses a template approach rather than command-based instructions. It's user-friendly and particularly useful for users unfamiliar with traditional query language syntax.
In conclusion, understanding the various types of query languages is crucial as they serve as the interface between users and databases, enabling efficient data handling and manipulation. Each type of query language holds its unique benefits and is suitable for different aspects of data management.
Common Query Language Commands
Now, let's take a closer look at some of the common Query Language commands:
In this section, we will decode ten crucial SQL commands that form the basis of data interaction and manipulation within relational databases.
SQL SELECT Command
The SELECT command is used to fetch data from a database. You can use it to select various columns of data and return a result set.
SQL INSERT INTO Command
INSERT INTO allows you to add rows of data to a table. You specify the table and the value you wish to insert.
SQL UPDATE Command
The UPDATE command modifies existing records in a table. With it, you can change the values of certain columns in selected rows.
SQL DELETE Command
DELETE is utilized to remove rows from a table. Be cautious while using it, as the action is irreversible.
SQL CREATE DATABASE Command
CREATE DATABASE lets you create a new, empty database. It's an essential part of set up when starting a new project or application.
SQL CREATE TABLE Command
With the CREATE TABLE command, you can structure your database by creating new tables within it, specifying the column names and types.
SQL DROP Command
The DROP command removes an existing database or table. It's a destructive command and should be used with care.
SQL ALTER Command
ALTER allows you to add, delete/drop, or modify columns in an existing table. It also allows you to modify the data type of a column.
SQL WHERE Command
The WHERE clause filters the records and excludes the ones that do not meet the specified criteria. It's commonly used with SELECT, UPDATE, and DELETE commands.
SQL JOIN Command
JOIN lets you combine rows from two or more tables based on a related column. This can significantly enhance your data processing ability and give a more comprehensive view of your data.
How does Query Language Work?
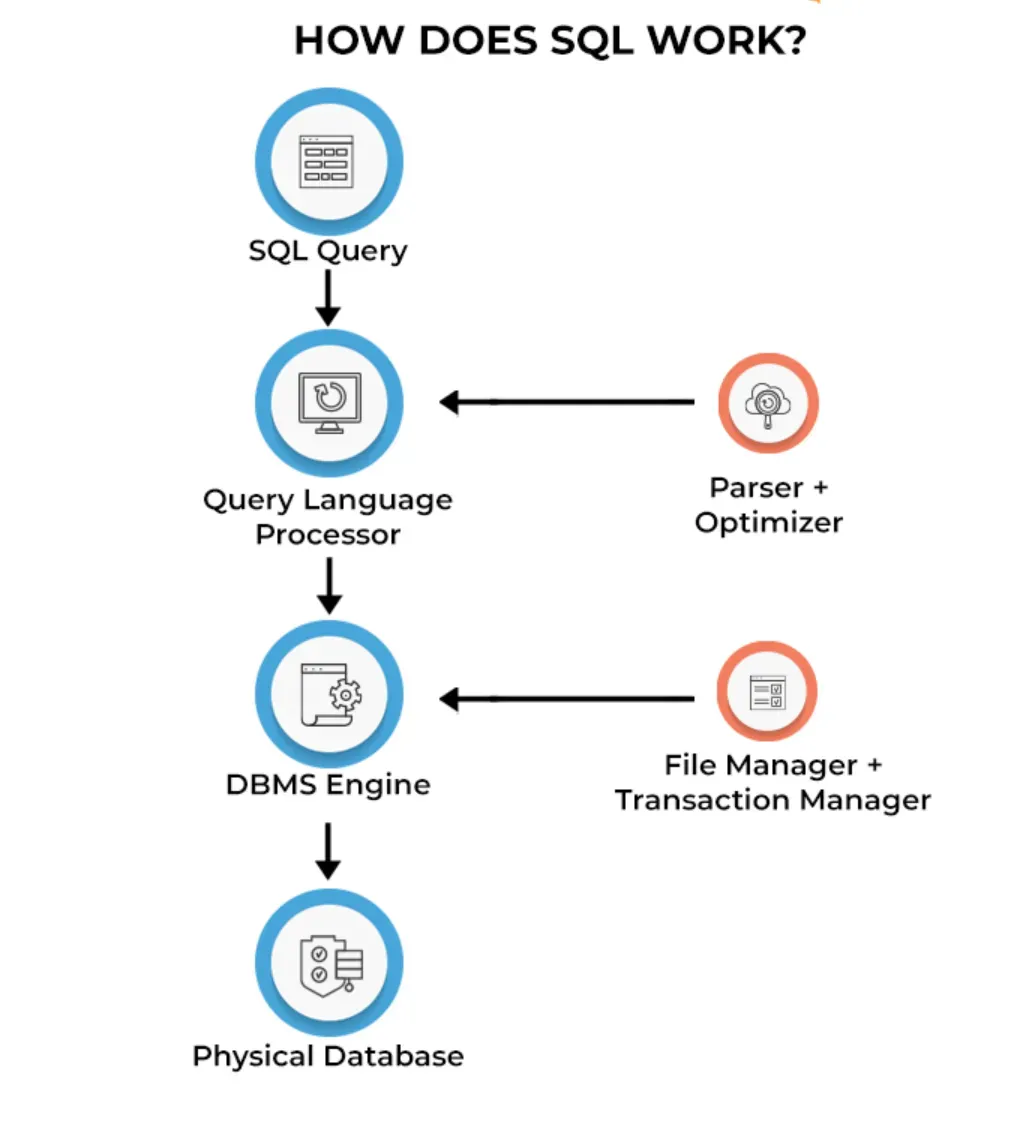
In this section, we'll explore the inner workings of a query language and how it interacts with databases to fetch, manage, and manipulate data effectively.
Establishing a Connection
Before a query language can interact with a database, it must first establish a connection.
This involves authenticating the user and ensuring they have the necessary permissions to access the desired data. Once the connection is secure, users can send queries to fetch or modify data.
Executing Prepared Statements
Query languages offer a feature called prepared statements to help enhance security and performance.
Prepared statements are predefined templates that can be reused with different sets of input values. These statements help prevent SQL injection attacks and optimize the query execution process by reducing the time needed to prepare and execute queries.
Interpreting Query Syntax
When a query is submitted, the query language's interpreter parses the statements, evaluates the syntax, and translates it into machine-readable instructions.
The interpreter ensures that the given syntax adheres to the rules and structure of the query language and processes any error messages or warnings that arise.
Processing and Optimizing Queries
To improve performance and efficiently access the data, query languages use a query optimizer. The optimizer analyzes the query and determines the best execution plan, considering factors like available indexes, table statistics, and join conditions.
By optimizing the query plan, the system can quickly and accurately retrieve the requested information from the database.
Returning Results
After executing the optimized query, the query language retrieves the requested data and formats it according to the user's specifications.
The results are then sent back to the user, allowing them to analyze, visualize, or further manipulate the data based on their needs.
Query languages play a vital role in managing and interacting with databases.
Their ability to establish connections, execute prepared statements, interpret syntax, process and optimize queries, and return results efficiently makes them indispensable tools in modern data management.
Best Practices for Query Language
In this section, we'll discuss the best practices for using query languages to efficiently manage and access data while maintaining performance and security.
Use Proper Indexing
Optimizing database indexing is crucial for query performance. Ensure you create indexes on commonly accessed columns, especially those used in WHERE and JOIN conditions. Keep in mind that while indexes improve query speed, they may also affect the performance of INSERT, UPDATE, and DELETE operations, so choose the right balance between querying and modifying data.
Write Maintainable and Readable Code
Adopting a consistent style for writing queries enhances the maintainability and readability of your code. Use meaningful and descriptive names for tables and columns, indent your code appropriately, and add comments to complex portions of your queries. Writing clear and well-structured code makes it easier for team members to understand and troubleshoot issues when needed.
Optimize Complex Queries
Identify and optimize complex or slow-performing queries to improve overall system performance. Use techniques like breaking down large queries into smaller, simpler parts, avoiding the use of subqueries when possible, and caching intermediate results. Use the query language's built-in tools, such as EXPLAIN or query profiling, to observe and analyze query execution plans.
Ensure Data Security
Apply data security best practices while using your query language. Use prepared statements to minimize the risk of SQL injection attacks, follow the principle of least privilege by granting necessary permissions only, and sanitize user inputs to further enhance data security. Regularly audit and review user access and permissions to maintain a secure query environment.
Test and Validate Queries
Before deploying your queries into production, test and validate them to ensure they produce the desired results. Use realistic sample data and environments to identify any potential errors or issues in query performance and functionality. Regularly monitoring query performance can help you identify and optimize potential bottlenecks proactively.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is a Query Language Used for?
Query languages are used for accessing, updating, or retrieving data stored within a database. They provide a means to manipulate and interact with data efficiently.
What Does SQL Stand for in Query Language?
SQL stands for Structured Query Language. It's a type of query language designed specifically for managing relational databases.
How Does a Data Definition Language (DDL) Differ From a Data Manipulation Language (DML)?
DDL involves commands that define or alter the structure of database objects, while DML involves commands that manipulate the data within these objects.
What is the Role of Data Control Language (DCL) in Query Language?
DCL is used for managing access to data in a database. It controls which users can retrieve or manipulate data by granting or revoking permissions.
What is Query by Example (QBE) in Query Language?
QBE is an intuitive query language that allows users to extract data from relational databases using visual templates, without needing to know command-based syntax.