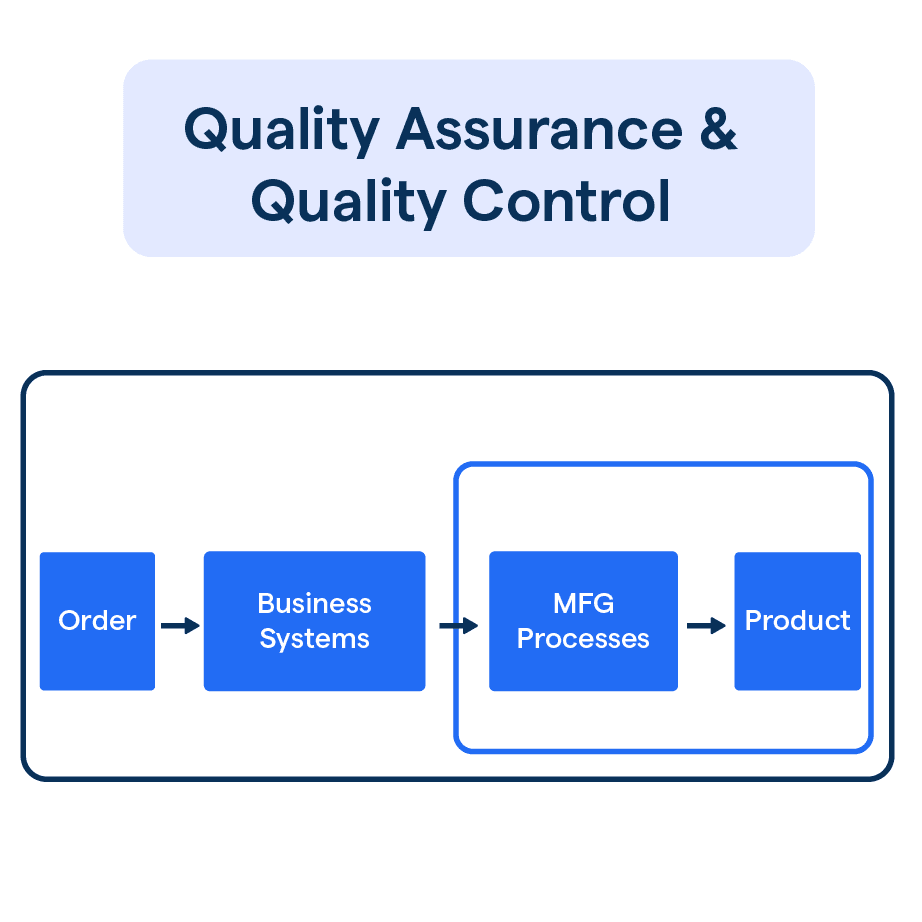
What are Quality Assurance and Quality Control?
Quality assurance (QA) focuses on preventing defects in a product or service by implementing best practices, methodologies, and standards during the development process.
Quality control (QC), on the other hand, involves identifying and correcting defects in the final output once it is produced, ensuring it meets predefined specifications.
Why are They Important?
Emphasis on QA and QC is crucial to ensure optimal product quality and functionality, enhancing customer satisfaction and minimizing the risk of product failure.
They collectively ensure that customer needs are met while reducing the overall cost incurred from undetected errors or defects.
Who Needs Quality Assurance and Quality Control?
Everyone invested in developing and delivering a product or service should be concerned with QA and QC. This includes companies developing software, manufacturers, food and beverage producers, and the service industry.
Stakeholders involved in these processes usually include project managers, developers, testers, and even customers.
Where are They Used?
QA procedures are applied throughout the entire product development cycle, from design inception to product deployment.
QC measures are implemented during the production, inspection, or testing stages to evaluate and rectify the end product's performance against predefined standards.
When to Implement Quality Assurance and Quality Control?
Quality assurance should be integrated from the outset of a project, with multiple checkpoints during the development cycle.
In contrast, quality control should be enforced near the completion of production or after the product has been developed, to detect defects before the final product reaches the end-user.
Key Activities of Quality Assurance and Quality Control
In this section, we'll delve into the primary activities involved in quality assurance and quality control.
Planning
Quality assurance begins with an effective plan that maps out the processes needed to reach quality objectives.
This includes defining the quality standards, developing procedures to meet those standards, and establishing metrics to measure effectiveness.
Process Development and Implementation
Achieving high quality requires well-defined and structured processes. These should include steps for inspection, documentation, auditing, and analyzing the outcomes.
Consistency is key in maintaining quality across all outputs.
Training and Education
Everyone involved in creating a product or delivering a service must be trained in relevant quality standards and processes.
This involves not only technical skills, but also an understanding of the overall quality objectives.
Inspection and Testing
This is the most recognizable part of quality control. Products or services are inspected or tested against specific standards.
Any deviations found are corrected or, if necessary, the product is rejected.
Documentation and Record Keeping
Accurate and comprehensive records are essential in quality control. These provide a reliable source of data for monitoring and analyzing process performance.
They can also be used to trace quality problems back to their source.
Continuous Improvement
Quality assurance and control doesn't stop once a product meets its quality standards.
The next step is to analyze the results, and use this information to improve processes and eliminate waste. This ensures the ongoing improvement of quality.
Embracing these key activities helps ensure that quality is ingrained in every aspect of your business.
It's not just about catching mistakes - it's about creating processes that minimize errors and maximize quality.
Benefits of Quality Assurance and Quality Control
Placing a premium on Quality Assurance aids in providing products or services with high-grade quality that align perfectly with customer requirements.
The result? Greater customer satisfaction, which seeds brand loyalty and encourages repeat patronage.
Boosted Efficiency
Quality Assurance props up efficient practices by spotting and eliminating inefficiencies. By doing this, it supports improved processes, minimizes waste, and fosters productivity levels.
Cost-Efficient Practices
Preventing errors and defects rather than merely reacting to them saves organizations' costs related to revisions, waste management, and handling customer dissatisfaction.
Thus, Quality Assurance ensures resources are strategically used and profit margins are benefited.
Adherence to Standards
Quality Assurance safeguards compliance with industry standards and regulations, helping organizations steer clear of legal penalties and prevent damage to their reputation.
On-going Enhancements
Quality Assurance is not a one-time event but an ongoing process aimed at identifying avenues for improvement. By helping organizations introduce necessary modifications, it facilitates continuous enhancement of service or product quality, supporting a competitive edge in the market.
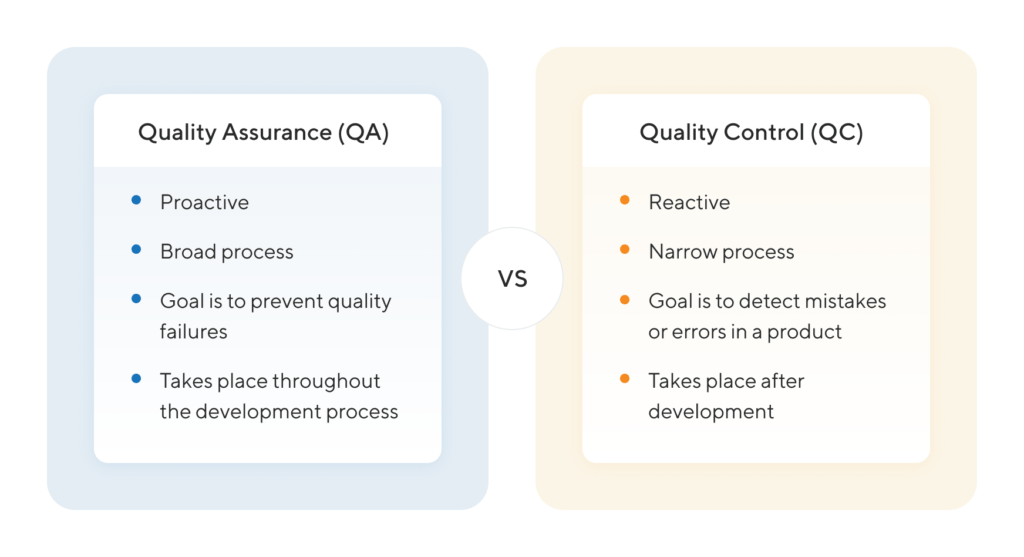
Differences between Quality Assurance and Quality Control
Quality Assurance (QA) is a process-oriented practice that focuses on preventing defects in a system or product. It's about implementing standards, guidelines and systematic activities even before work starts to ensure quality is built into the entire process.
Quality Control (QC) on the other hand, is product-oriented. It involves checking, testing, and reviewing the actual products or outputs to identify and correct defects. Unlike QA, QC is carried out after a product has been developed.
Purpose
QA's primary goal is to prevent defects before they happen. It anticipates and fixes potential issues within the system or process, thus enhancing the efficiency of production.
Meanwhile, QC aims to identify and rectify defects in the finished products, ensuring they meet the established quality standards.
Methodology
QA follows a proactive approach. It incorporates activities like auditing, process design, training, and development of policies and procedures to avoid any non-conformance.
QC employs a reactive approach, inspecting and testing the outputs to detect any defects and determine corrective actions to fix those problems. It follows procedures like inspections, examinations, and testing of materials or goods.
Responsibility
In an organization, QA is typically the responsibility of everyone involved in the development process. Each individual is accountable for adhering to the established policies and procedures to ensure quality.
In contrast, QC is generally designated to specific team members or a Quality Control department who check and test the final product for compliance with standards.
Outcome
QA aims to improve development and test processes so that defects do not arise when the product is being developed. It's more about building a quality system.
QC, however, ensures that the end product is error-free and provides a solution as per the customer’s expectation. It's about testing the quality of the product.
Tools & Techniques
QA uses methods like process auditing and methodologies like Six Sigma and Total Quality Management (TQM), among others.
Conversely, QC utilizes techniques such as visual inspection, statistical sampling, and lab testing to assess and improve the quality of the end product.
By understanding these differences, businesses can better implement both QA and QC practices effectively, ensuring top-notch quality in both their processes and end products.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Why is Quality Assurance Important?
QA is important because it ensures that the right processes and standards are followed to meet customer requirements.
It helps in preventing defects, reducing rework, and improving overall efficiency and effectiveness.
Why is Quality Control Important?
Quality Control is important because it ensures that the end products meet the specified quality standards.
It helps in identifying and correcting defects before the products are delivered to the customers.
What are the Roles and Responsibilities of Quality Assurance?
The roles and responsibilities of QA include defining quality standards, developing quality control processes, conducting audits, and ensuring compliance with regulations and standards.
What are the Roles and Responsibilities of Quality Control?
The roles and responsibilities of QC include inspecting and testing products or services, identifying defects or deviations, analyzing data, and implementing corrective actions.
How does Quality Assurance contribute to risk management?
Quality Assurance helps to identify and mitigate risks by implementing processes and procedures that prevent errors, defects, and discrepancies. It ensures that products or services are delivered with the required level of quality, reducing the likelihood of failures or adverse events.