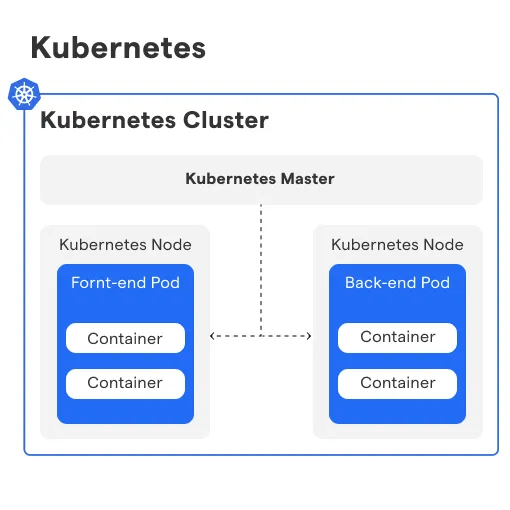
What is Kubernetes?
Kubernetes is a platform that manages containers —- self-contained software packages that include everything an application needs to run, making it easy to deploy and manage applications.
It can scale up web servers when there is high traffic and scale them down when the traffic is low.
Kubernetes features load-balancing capabilities to route traffic to web servers in operations.
It is a portable and extensible platform that empowers businesses to manage operational workloads and services more effectively.
Popular Use Cases of Containers
Containers have become a fundamental building block in Kubernetes, offering various use cases that empower organizations to deploy and manage applications efficiently.
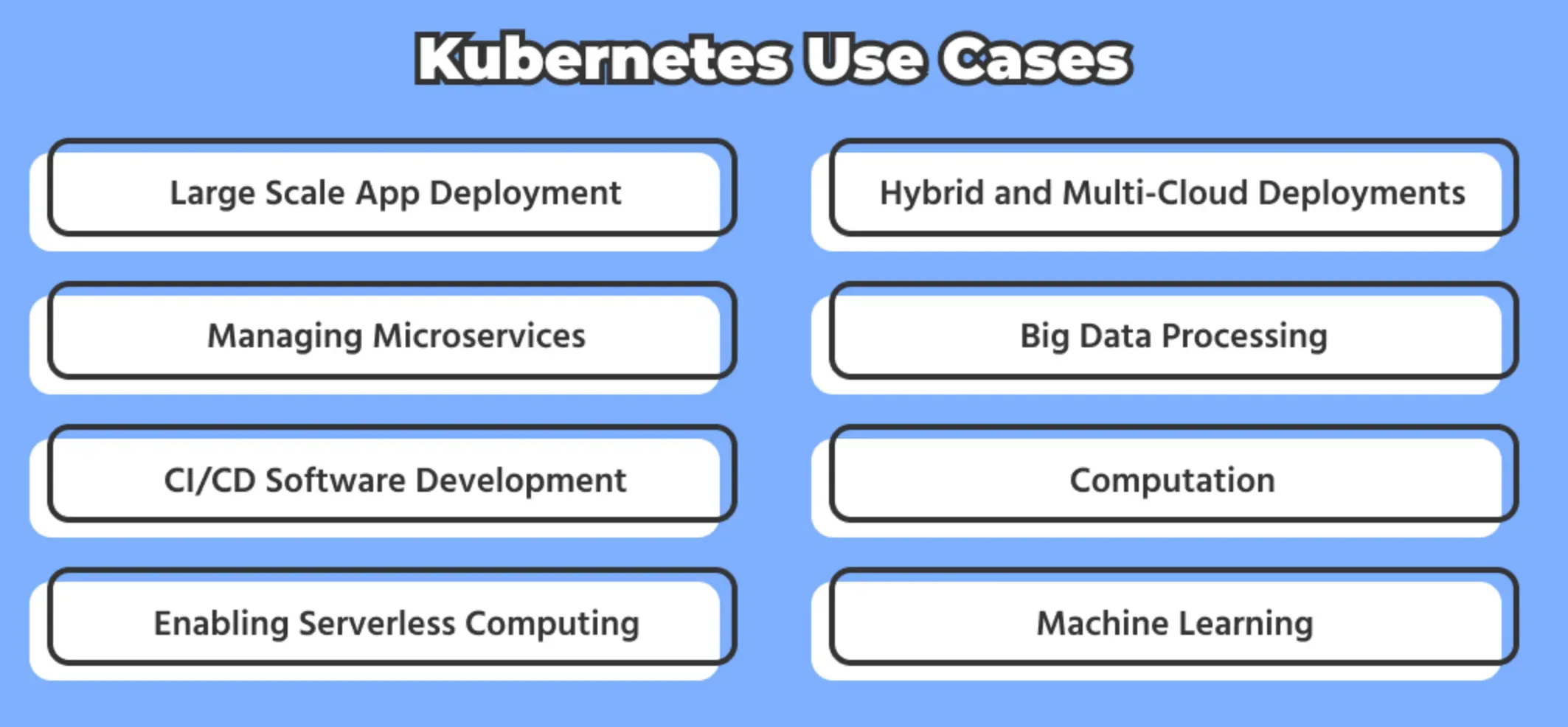
Here are five popular use cases of containers in Kubernetes:
Microservices Architecture
Containers enable the decomposition of complex applications into smaller, independent microservices. Kubernetes orchestrates these containers, making it easier to scale, update, and manage individual services.
Application Scaling
Kubernetes can automatically scale containers up or down based on resource demands, ensuring optimal performance. This elasticity is crucial for handling varying workloads efficiently.
Continuous Integration/Continuous Deployment (CI/CD)
Containers simplify the packaging and deployment of applications, allowing for consistent testing and deployment pipelines. Kubernetes automates rolling updates and rollbacks, ensuring seamless CI/CD processes.
Stateless Applications
Stateless applications, which don't rely on local storage, are well-suited for containers in Kubernetes. These containers can be easily replicated and replaced as needed.
Resource Isolation and Efficiency
Kubernetes provides fine-grained control over resource allocation, ensuring containers operate in isolation.
This isolation enhances security and resource efficiency, making it easier to optimize infrastructure utilization.
These use cases showcase how containers, when integrated with Kubernetes, offer a flexible and powerful platform for developing, deploying, and managing applications in today's dynamic IT landscape.
Containerization and Kubernetes go hand in hand, providing a robust foundation for modern application development and operations.
How does Kubernetes work?
Kubernetes orchestrates containerized applications, automating deployment, scaling, and management across clusters of servers. For a better understanding, below mentioned are the ways how Kubernetes works:
Cluster Management
Kubernetes is a cluster manager at its core. It manages a cluster of worker nodes that run containerized applications and services, making it easier to deploy, scale, and manage them.
Pod and Container Orchestration
Kubernetes uses pods as the smallest deployable units that can run one or more containers. It coordinates the creation, scheduling, scaling, and termination of these pods based on resource utilization and configuration requirements.
Service Discovery and Load Balancing
Kubernetes allows applications to be accessed via an abstract service that routes traffic to the appropriate pod(s) based on selectors and labels. It can also perform load balancing and automatically scale the service as per demand.
Storage Orchestration
Kubernetes supports various storage systems and provides a consistent API to manage them as storage objects. It can create and mount storage volumes on demand and provide persistent storage to stateful applications.
Resource Management and Monitoring
Kubernetes provides resource quotas and limits to prevent resource starvation and ensure fair sharing of resources among pods. It also supports various monitoring and logging tools to track the health and performance of the cluster and its components.
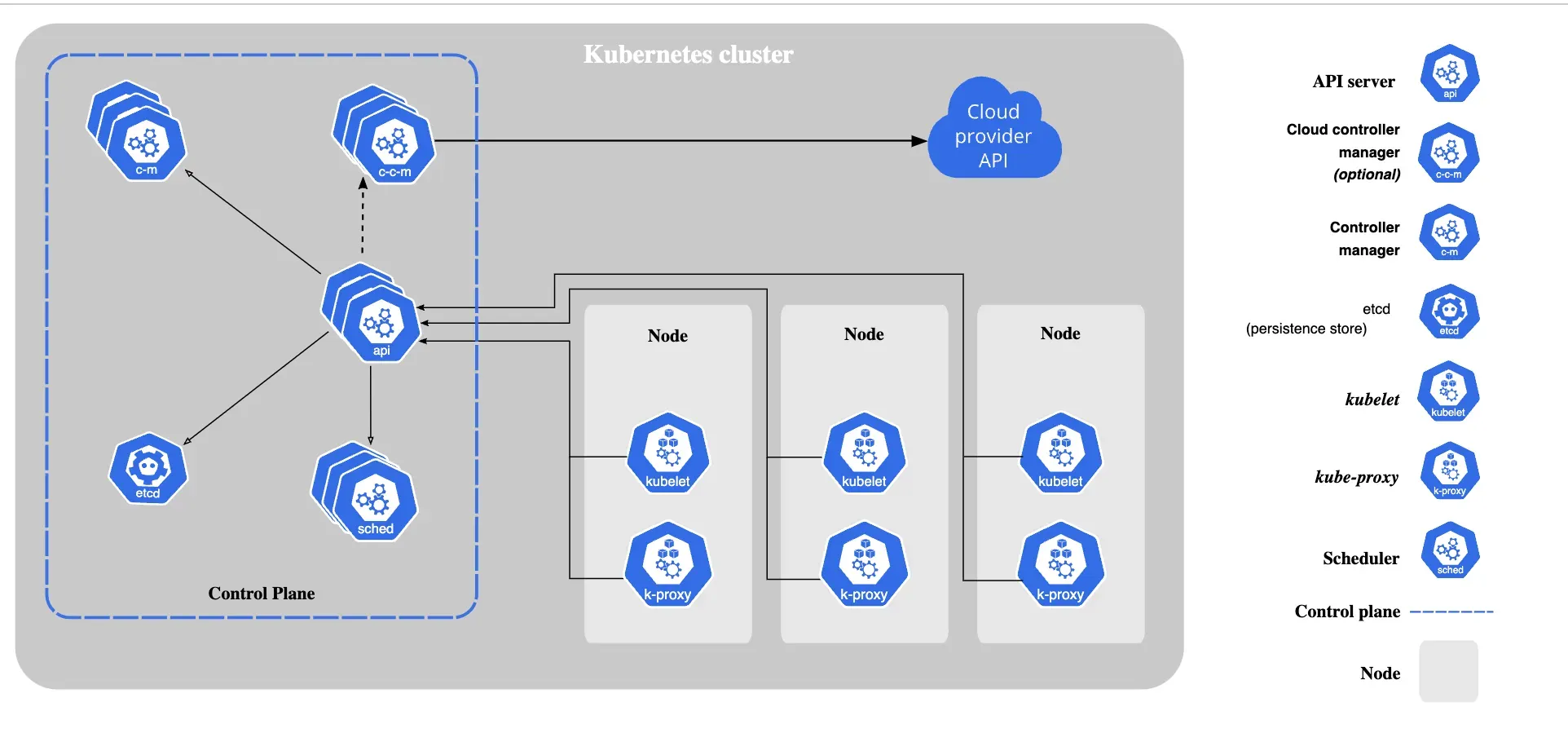
What are Kubernetes Components?
The Kubernetes control plane has five components of its own and worker nodes, while the individual worker nodes have three components of their own.
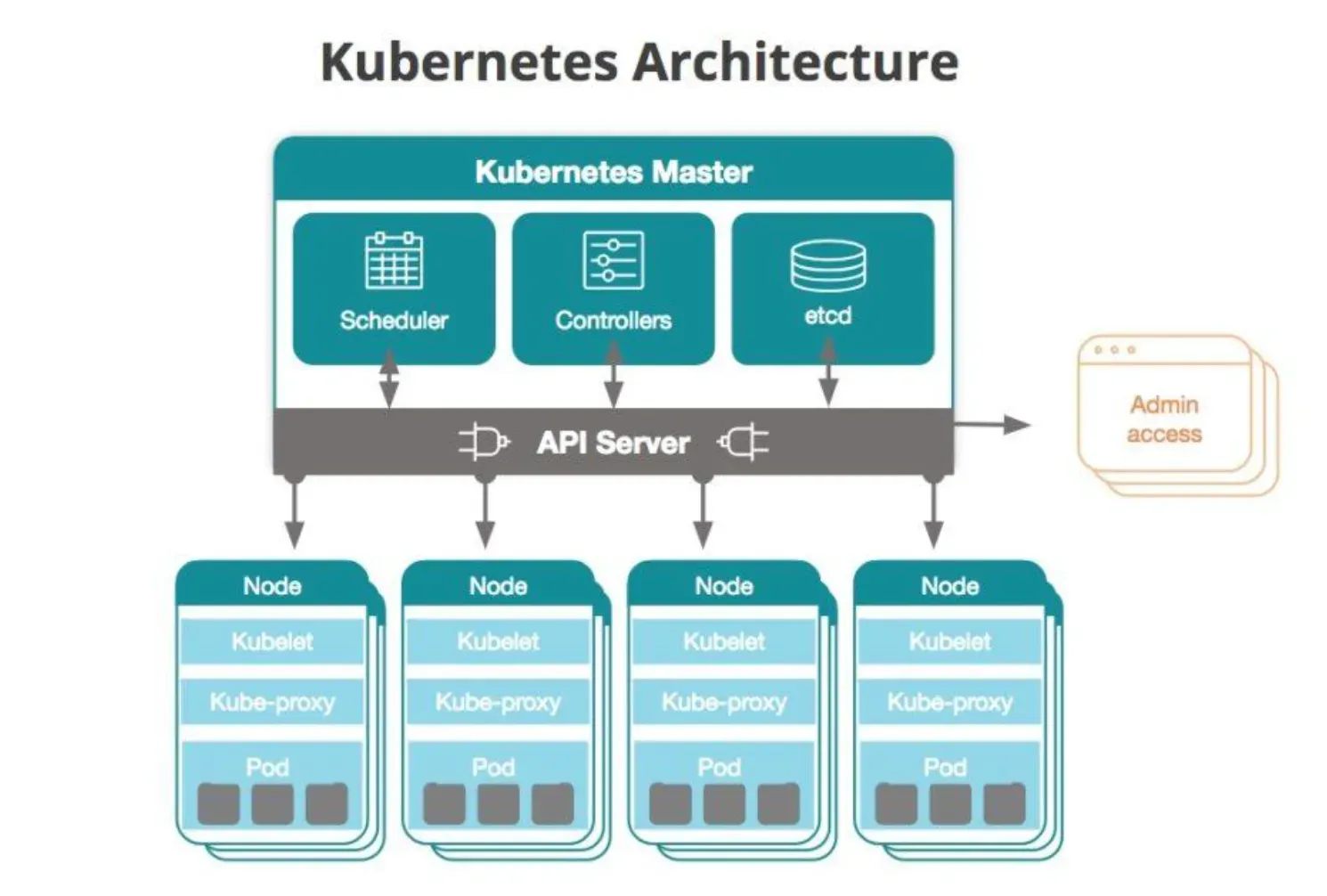
Components of the Control Plane
- The scheduler: It looks at resource capacity and makes sure that all the worker nodes are performing at optimal capacity.
- The API server: It exposes the Kubernetes API and is the front-end for the control plane.
- The controller manager: This looks after a range of controllers that respond to various events.
- Etcd: Kubernetes' backing store for all cluster data.
- The cloud controller manager: This links the cluster to the cloud provider's API and separates parts that work with the cloud from those only dealing with the cluster.
Components of Individual Nodes
- Kubelet: It runs on every node in a cluster. It ensures that the containers are running in a pod.
- The container runtime: This is responsible for actually running containers.
- Kube-proxy: It runs on all the nodes of a cluster. It implements a part of the Kubernetes Service concept and maintains network rules on your nodes, which permit network communication to your Pods from network sessions inside or outside your cluster.
What Deployment Options does Kubernetes offer?
Kubernetes offers four different deployment options based on your objectives and needs. These include:
- On-premise: It turns your data center into a Kubernetes cluster.
- Cloud: It deploys Kubernetes on the cloud and makes an infinite number of virtual machines.
- Hybrid: Uses virtual machines on a cloud in situations where in-house servers are at full capacity, distributing computing resources more effectively.
- Multi-cloud: Reduces risk and avoids vendor lock-in.
What is the Advantage of Kubernetes?
Kubernetes has numerous advantages that have been mentioned below, providing more clarity on how useful it is in managing containers.
Scalability
Kubernetes enables automatic scaling of applications horizontally and vertically, ensuring that the application can handle increased traffic or sudden spikes in usage.
It also allows you to easily add or remove nodes to cater to changing resource demands.
High availability
Kubernetes includes features such as replication and self-healing that ensure that an application is always available, even if one of the nodes or containers fails.
This guarantees minimal downtime and improved reliability.
Flexibility
Kubernetes can run on a variety of platforms and can manage both stateless and stateful applications, making it highly flexible and adaptable.
It also supports Hybrid and multi-cloud environments, which makes it easier to manage deployments across different platforms.
Resource efficiency
Kubernetes enables efficient use of computing resources by running multiple containers on a single node and scheduling them across multiple nodes in the cluster based on resource requirements.
This leads to more efficient use of resources and cost savings.
Community
Kubernetes is an open-source project with a large and vibrant community. This ensures that it is constantly improving, with new features and plugins being developed and shared.
This community makes it easier to find answers to problems and get support.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
How can I deploy an application in Kubernetes?
To deploy an application in Kubernetes, you need to create a deployment object that specifies the container image, replicas, and other configurations. You can use kubectl apply command to create and manage deployments.
What is a pod in Kubernetes?
A pod is the smallest deployable unit in Kubernetes. It can contain one or more containers and shares a network namespace and storage volumes. Pods are used for deploying and scaling applications.
How does Kubernetes ensure high availability?
Kubernetes ensures high availability using features such as replication controllers, self-healing, and automatic failover. It also supports rolling updates and can manage multiple replicas of a pod for redundancy.
Can Kubernetes run on multiple cloud platforms?
Yes, Kubernetes can run on multiple cloud platforms, including AWS, Azure, GCP, and IBM Cloud. It also supports hybrid and multi-cloud environments, making it easier to manage deployments across different platforms.
What is a service in Kubernetes?
A service in Kubernetes is an abstract endpoint that provides a stable IP address, hostname, and port number for pods running in the cluster. It enables communication between pods and outside the cluster and supports load balancing and scaling.