Many Android users notice their messages changing format without warning, creating confusion about why some chats behave differently.
Features appear inconsistently, media quality varies, and certain threads shift into an RCS message, prompting users to search for clarity.
These differences raise questions about reliability, compatibility, and whether RCS is suitable for everyday communication. For businesses, the impact is more significant because message delivery must remain consistent across all customers.
This blog explains RCS in simple terms, outlines its behaviour, highlights its limitations, and compares it with other messaging systems. It also presents stable alternatives for users and organisations that need predictable communication.
What is RCS Messaging?
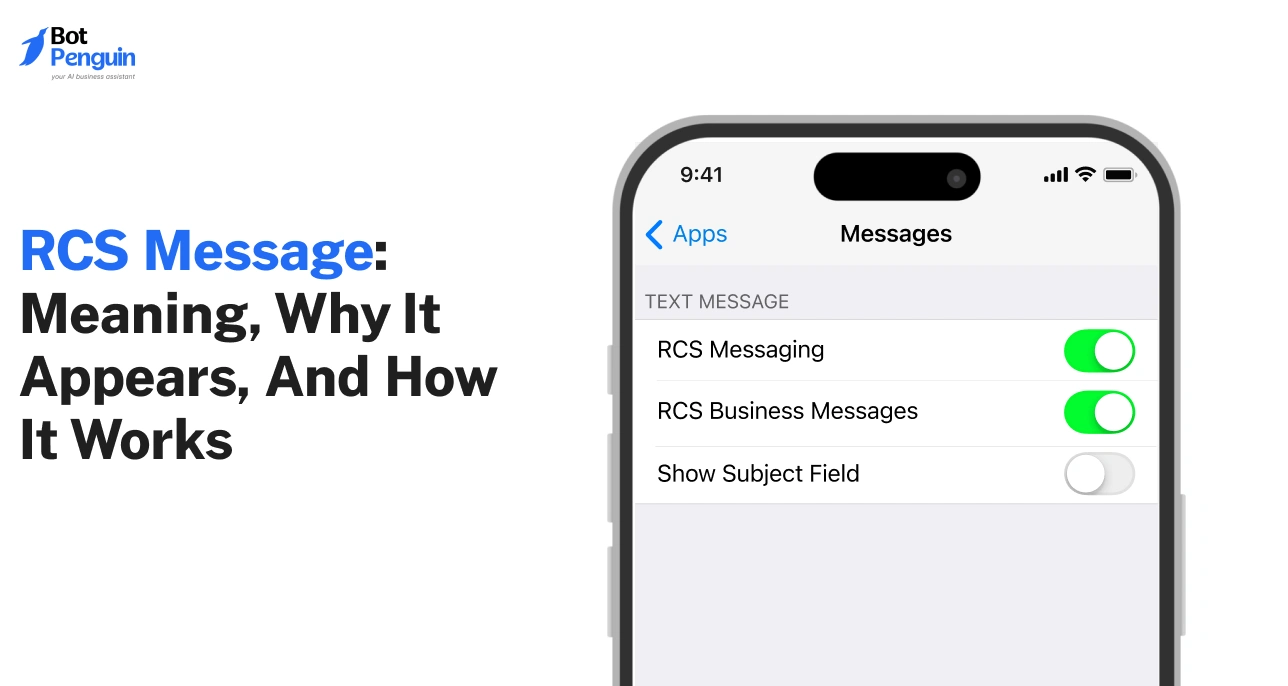
RCS is the upgraded messaging format used by Android devices when enhanced communication features are available between two contacts.
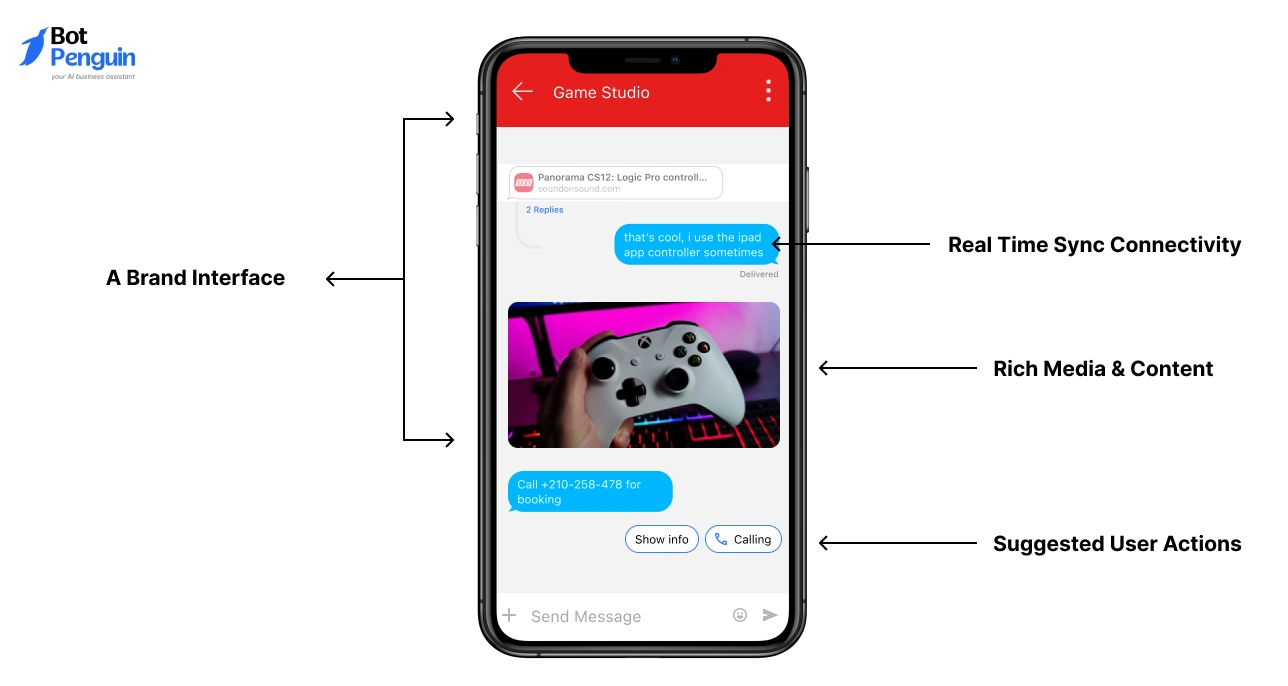
It moves regular SMS into a richer environment that supports improved media handling, delivery status, and advanced chat functions.
Users typically notice this shift when a thread displays an RCS message, especially after capability updates inside the messaging app.
The format activates automatically, which is why behaviour can vary from one contact to another.
Why RCS Looks Like a Chat App Inside Text Messages?
RCS adopts features commonly seen in modern chat applications. These include high-quality image sharing, typing indicators, and improved message control.
After a Google Messages RCS chat update, the app may begin presenting these elements inside the same interface used for SMS. As a result, a regular conversation may start showing richer media and real time activity indicators.
This change can make the thread resemble an internet-based chat, which is why some users search text message RCS meaning when they notice new behaviours in familiar conversations.
Who Controls RCS: Google or Carriers?
RCS operates through joint support from Google and participating carriers. Google manages the platform inside its messaging app, while carriers handle delivery capabilities on the network side.
This shared responsibility explains why RCS messaging works smoothly in some regions and inconsistently in others.
If either component lacks full support, the device returns to SMS as the fallback format. This is also why one contact may trigger RCS features while another remains limited to basic texting.
This overview clarifies how RCS works in real settings and why message behaviour changes across contacts. With this base established, the next section examines the specific features offered by RCS and how they influence everyday communication.
Features of RCS Messaging
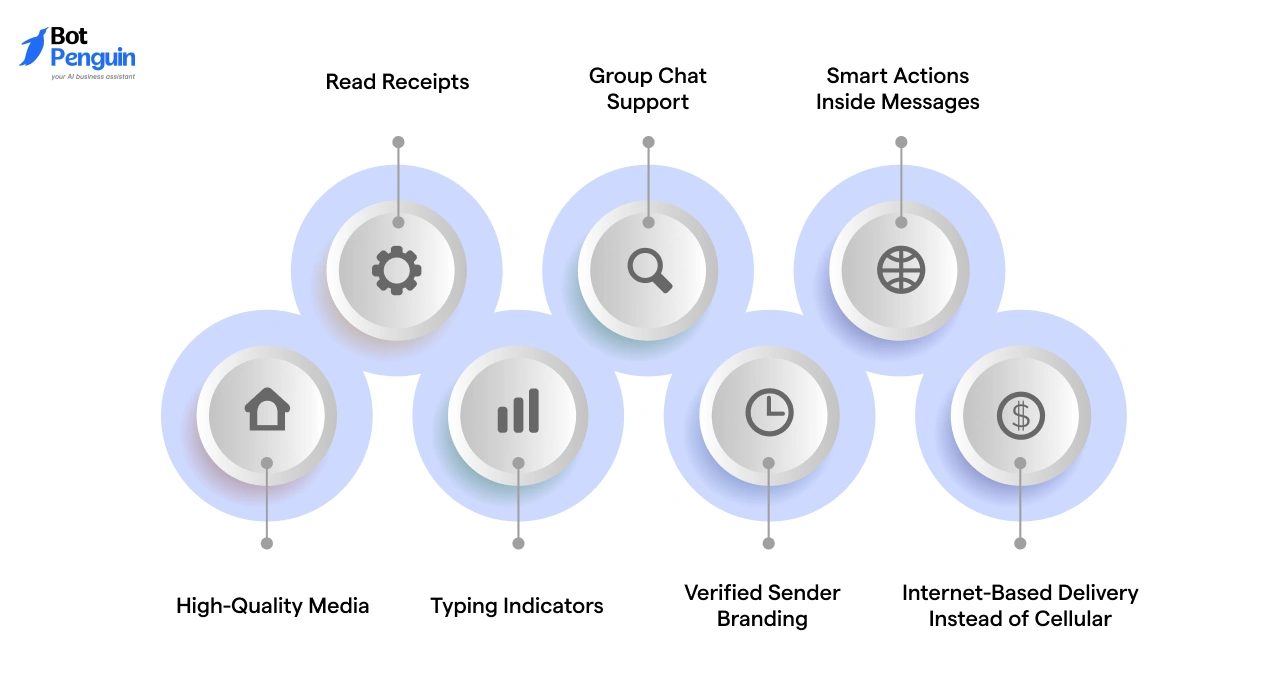
RCS introduces an upgraded structure for messaging that enhances how information is shared between supported devices.
Users often notice these capabilities when a conversation shifts to an RCS message, especially after capability updates or compatibility detection.
Each feature influences how messages are delivered, displayed, and managed across different contacts. The points below explain these capabilities with clarity and practical relevance.
High-Quality Media
RCS supports larger and clearer images, videos, and documents. Files retain their resolution because they are delivered through data rather than compressed cellular channels.
This allows users to share presentations, travel photos, or product images without losing clarity.
Read Receipts
RCS confirms when a message is opened. This is particularly useful for coordinating tasks, sending time-sensitive information, or verifying whether a recipient has viewed a critical update.
The status is precise because it relies on app-level acknowledgements instead of network assumptions.
Typing Indicators
The system displays when the other person is composing a reply. This reduces uncertainty in active conversations and helps users manage response timing in collaborative communication.
It functions consistently across supported devices and mirrors the behaviour of modern chat platforms.
Group Chat Support
RCS improves group communication by enabling higher quality media exchange, stable message delivery, and synchronized thread updates.
Group members can share files, coordinate decisions, and track responses without the fragmentation often seen in SMS based group chats.
Verified Sender Branding
Businesses can send messages with verified identity markers. This differentiates legitimate communication from unsolicited or potentially fraudulent sources.
It increases trust in service notifications, appointment reminders, or transactional updates and improves visibility for recognized organisations.
Smart Actions Inside Messages
RCS can include interactive elements such as quick reply buttons, event confirmations, or link actions that launch directly from the chat window.
These functions reduce manual steps and help users complete actions efficiently, such as confirming deliveries or accessing service portals.
Internet-Based Delivery Instead of Cellular
RCS uses data or Wi Fi for message transmission, which supports larger payloads and faster delivery when the network is stable.
This also explains why some users encounter differences in message behaviour and search what does text message RCS mean when the delivery method shifts between data and fallback SMS.
These capabilities show how RCS expands the range of what messaging can handle and why conversations may behave differently across contacts.
With the functional aspects clarified, the next section outlines the benefits these features provide for everyday communication.
Benefits of RCS Messaging for Users
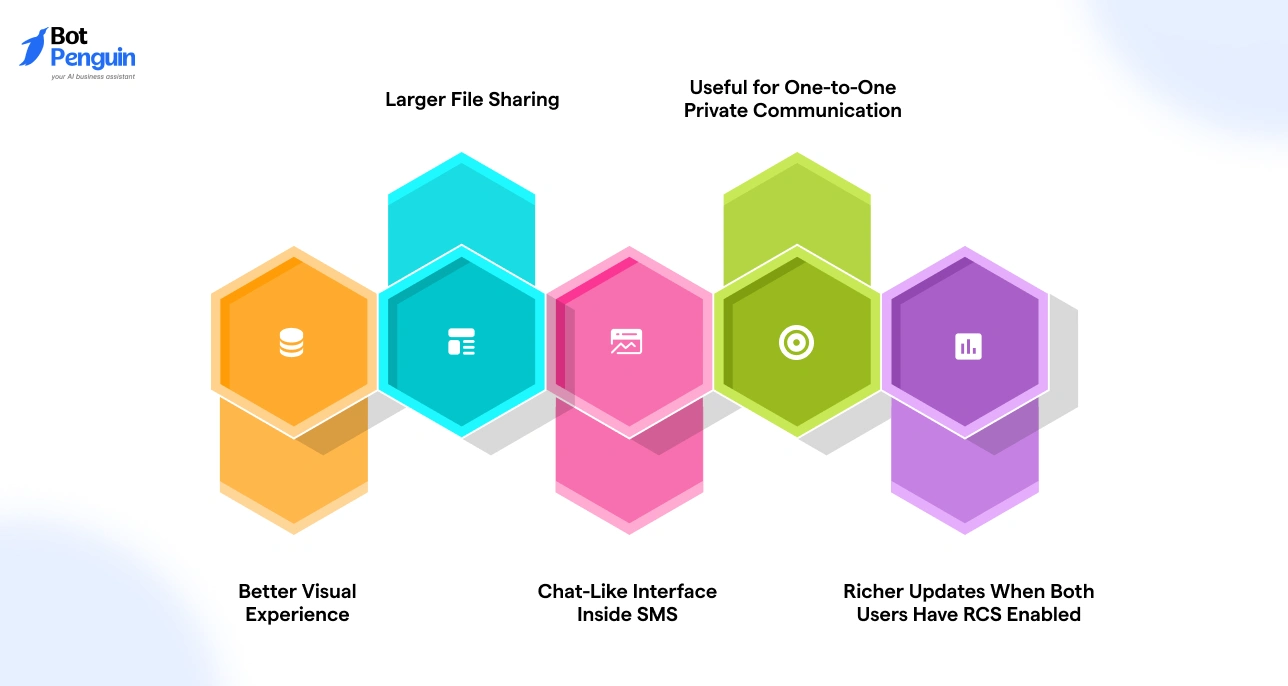
The features described earlier translate into practical advantages for daily communication, especially when both devices support the enhanced format.
Users often notice these improvements when a conversation displays an RCS messaging label after capability updates.
Each benefit reflects how RCS changes message handling, visual clarity, and interaction quality across supported contacts.
Better Visual Experience
Images and videos retain their clarity because RCS delivers media using data instead of the compression used by older formats.
This helps users share detailed visuals such as documents, product images, and travel photos without distortion.
Larger File Sharing
RCS supports higher file size limits, allowing users to send presentations, reports, or extended videos that SMS cannot transmit.
This is particularly useful for work related exchanges that require complete and readable files.
Chat-Like Interface Inside SMS
Typing indicators, read acknowledgements, and improved delivery insights make conversations feel more responsive.
These changes often appear after the messaging app updates its capabilities, which can cause users to wonder why the conversation format has shifted and why certain features activate only in specific threads.
Useful for One-to-One Private Communication
RCS works well when both users have compatible devices and stable connectivity.
It supports faster exchanges and real-time activity awareness, which improves coordination between individuals sharing regular updates.
Richer Updates When Both Users Have RCS Enabled
Delivery reports, media handling, and message timing work more efficiently when both devices support the enhanced protocol.
This creates a consistent experience for detailed conversations where accuracy and clarity matter.
These benefits highlight why RCS can enhance personal communication under the right conditions.
The next section expands on these advantages by comparing RCS with SMS, MMS, and other messaging formats to illustrate how each option performs in different scenarios.
RCS vs Other Messaging Formats
RCS offers enhanced capabilities, but users continue to compare it with other messaging formats that serve different technical roles.
These comparisons become more visible when a thread shifts into an RCS messaging mode, especially after device or app updates.
Each messaging method handles media, delivery, and interaction differently, which influences how users and businesses select the most suitable option for their communication environment.
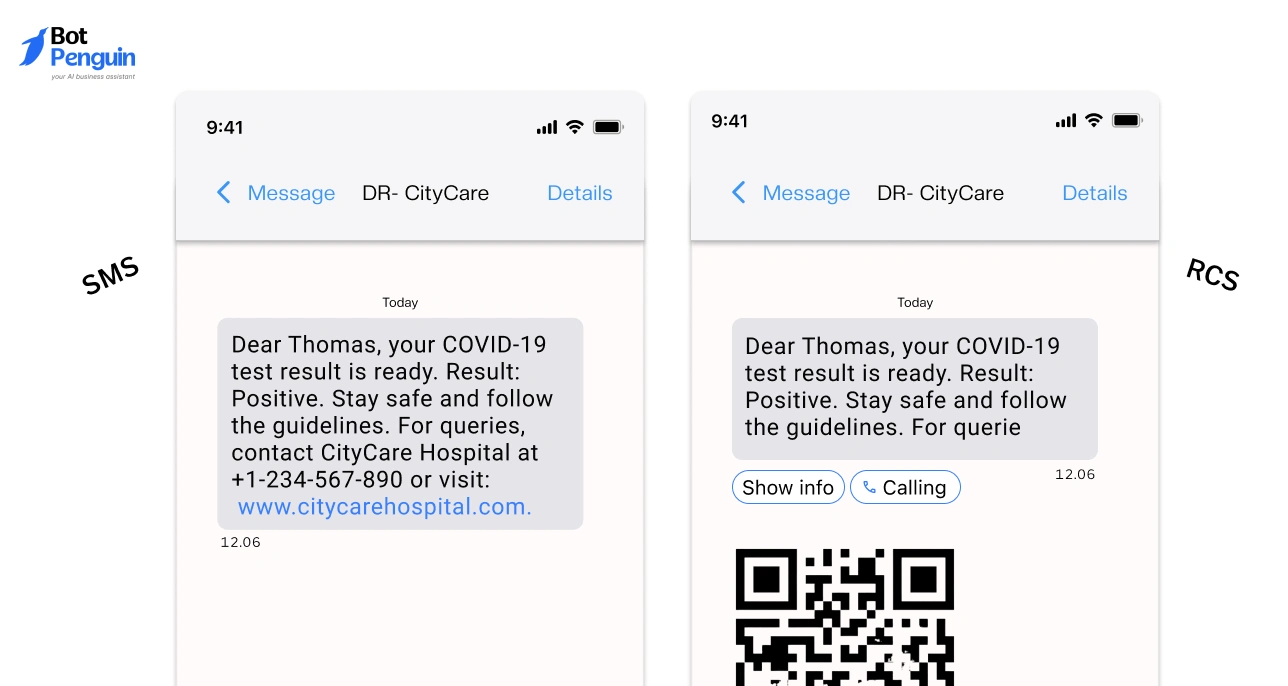
RCS vs SMS
SMS functions on every device without dependency on app versions or network configuration. RCS adds higher-quality media handling, message activity indicators, and improved delivery control.
SMS remains more predictable because it operates uniformly across all devices, whereas RCS depends heavily on contact-level compatibility.
RCS vs MMS
MMS compresses images and restricts file size, limiting the clarity of shared media. RCS removes these constraints by using data for delivery, allowing users to send large videos, detailed images, and full-sized documents.
This makes RCS a clear upgrade for users who frequently exchange media.
RCS vs RBM
RBM builds on RCS capabilities to support business communication. It enables verified identities, structured responses, suggested actions, and interactive templates designed for service updates and promotional workflows.
RCS focuses on user messaging, while RBM introduces advanced tools suitable for enterprise communication at scale.
RCS vs OTT Apps Like WhatsApp, Instagram, and Messenger
OTT applications operate independently of carrier infrastructure and provide consistent performance across devices. They support encryption, large file transfers, and real time conversation features.
Users may switch to OTT platforms when RCS capability varies across contacts, especially when a text message RCS appears for one user but not another due to device or network limitations.
RCS vs iMessage
iMessage delivers rich communication features for Apple devices, including high-quality media, delivery insights, and message sync across Apple hardware. RCS aims to offer comparable features on Android devices, but the two systems do not interoperate.
This creates a split environment where compatibility depends entirely on the recipient’s device ecosystem.
RCS vs AI Chatbot Messaging
AI chatbot messaging supports automation, workflow management, customer support, sales routing, and CRM connectivity. These capabilities extend far beyond device-based messaging.
RCS does not automate replies or perform system-level tasks, which limits its effectiveness for businesses that require structured and consistent communication.
Which Option is More Reliable Today
SMS remains universally accessible, OTT platforms provide strong consistency and feature coverage, and RBM supports advanced business interactions.
RCS performs well when the device and carrier support align. AI platforms deliver the highest reliability for organisations that depend on automation, system integration, and controlled communication flows.
These comparisons highlight where RCS fits in the broader messaging landscape and where alternative formats provide greater efficiency or reliability.
With this understanding in place, the next section explains why Google continues to promote RCS as the successor to traditional SMS.
Color Code Meanings
- Green: Strong performance. Reliable across most scenarios.
- Yellow: Moderate or conditional performance. Works in some scenarios, not all.
- Red: Weak or missing capability. Major limitations.
This structured comparison highlights where each messaging format delivers value and where limitations appear in real communication environments.
It clarifies why some users shift between RCS messaging and other platforms depending on device support and communication needs.
With this foundation in place, the following section explains why Google continues promoting the RCS format as the successor to SMS despite its dependency on compatibility.
Why Google Replaces SMS With RCS
The comparison of messaging formats highlights why RCS gained attention as a modern replacement for SMS. Google views the traditional system as limited for today’s communication standards.
These limitations become more visible when a user receives an RCS message and notices richer media, activity status, or improved delivery insights that SMS cannot provide.
The following points outline the strategic reasons behind Google’s support for RCS.
Modernizing Text Messaging
SMS lacks features that users expect from current communication platforms. Messaging today involves high-quality media, delivery context, and real-time interaction.
RCS introduces these capabilities in a structured way within the default messaging app. This aligns with user expectations without requiring a separate service.
Matching iMessage Experience for Android
iMessage provides enriched communication across Apple devices. Google aims to match this functionality for Android users, so both major ecosystems offer similar communication standards.
RCS adds typing indicators, read acknowledgements, and better media output, reducing the gap experienced by users when comparing native messaging systems.
Improving Media Quality and Engagement
Image and video sharing over SMS or MMS results in compression and limited file size. RCS uses data-based delivery, which maintains clarity and supports larger files.
This improves personal messaging, group interaction, and information sharing without relying on third-party apps.
Google’s Push for a Universal Chat Standard
Google promotes RCS to unify messaging across Android devices and carriers. A universal standard reduces fragmentation and improves delivery consistency.
This becomes important after a Google Messages RCS chat update, which activates new capabilities for supported users. The goal is a modern, cohesive messaging experience that does not depend on multiple incompatible systems.
These factors illustrate Google’s long-term objective for RCS and the role it plays in improving native messaging.
With this strategic direction defined, the following section explains when RCS should be used and where it may not deliver consistent results across different communication scenarios.
When You Should Use RCS and When You Should Not
RCS behaviour varies across devices and networks, so users often evaluate when the enhanced format improves communication and when it introduces inconsistency.
These decisions become more relevant when a thread switches into an RCS message, creating noticeable differences in delivery and media handling.
When You Should Use RCS
- When both users have compatible Android devices
- When the network connection is stable and supports data-based delivery
- When sharing high-quality images, videos, or documents
- When private conversations benefit from typing indicators and delivery insights
- When communicating one-to-one in an environment where both devices are updated
- When group chats involve only users who support the enhanced format
When You Should Not Use RCS
- When communicating with iPhone users or a mixed device ecosystem
- When message delivery must remain consistent across all contacts
- When conversations occur in areas with weak data connectivity
- When traveling or roaming across regions with limited RCS support
- When communication requires automation, logs, or workflow control for business use
- When app versions vary and cause fallback to SMS or format switching
These pointers outline the practical scenarios that determine whether RCS improves messaging or introduces variability.
The next section covers common technical issues users encounter and explains why RCS behaves unpredictably in certain environments.
Most Common RCS Problems and Why They Happen
RCS depends on device capability, carrier support, app configuration, and network stability. Because these elements vary across users, many conversations behave differently, even within the same messaging app.
These issues become more visible when a thread switches into an RCS messaging format and features do not activate consistently across contacts. The following points explain why the most frequently reported RCS problems occur.
RCS Stuck on Connecting
This happens when the device cannot authenticate with the RCS server. Common reasons include unstable data networks, incomplete carrier support in that region, or outdated configuration files inside the messaging app.
The device attempts connection repeatedly, which keeps the status locked.
RCS Messages are Not Delivering
RCS delivery requires both devices to support the protocol at the same time. If the recipient device temporarily loses RCS capability, the message may fail instead of falling back smoothly to SMS.
This explains why users receiving a text message RCS from some contacts see different delivery outcomes.
RCS is Only Working With Some Contacts
RCS works only when both users meet all requirements, including compatible devices, carrier support, updated software, and active chat features.
If any element is missing, the conversation automatically returns to SMS. This shift often feels unexplained to users because it happens silently in the background.
RCS is Breaking After the Phone Update
System updates may replace network libraries, reset carrier settings, or modify app permissions.
When this happens, the RCS registration token becomes invalid and the phone must re authenticate. Until that process completes, messages may revert to SMS.
RCS is Failing After the SIM Change
RCS ties registration to both device and phone number. A SIM change forces the system to verify identity again.
If the carrier does not respond quickly, RCS will remain inactive until registration is completed successfully.
RCS is Not Working With iPhones
Apple does not support RCS. Any conversation involving an iPhone falls back to SMS because the two ecosystems do not share a unified protocol.
This is why RCS features disappear immediately when a contact uses iOS.
RCS is Turning on Automatically
After a Google Messages RCS chat update, the app may re enable chat features if it detects capability on both sides. Google designs the system to activate the enhanced format automatically when supported.
This leads to unexpected changes such as a thread switching to an RCS message without user input.
These issues occur because RCS relies on multiple systems working together, which introduces variability across devices and networks.
The next section explains how businesses address these limitations by using stable communication platforms that operate independently of carrier based protocols.
Better Alternative to RCS Messaging for Businesses
The challenges described earlier show that RCS depends heavily on device capability, network stability, and carrier participation.
These conditions make it difficult for organisations to rely on RCS for customer engagement, especially when a conversation unexpectedly switches into an RCS message and behaviour varies across users.
Businesses require consistent delivery, automation, and integration, which RCS cannot provide. BotPenguin addresses these gaps by offering a controlled and reliable communication environment across multiple channels.
BotPenguin Works Across WhatsApp, Instagram, Facebook, and Web
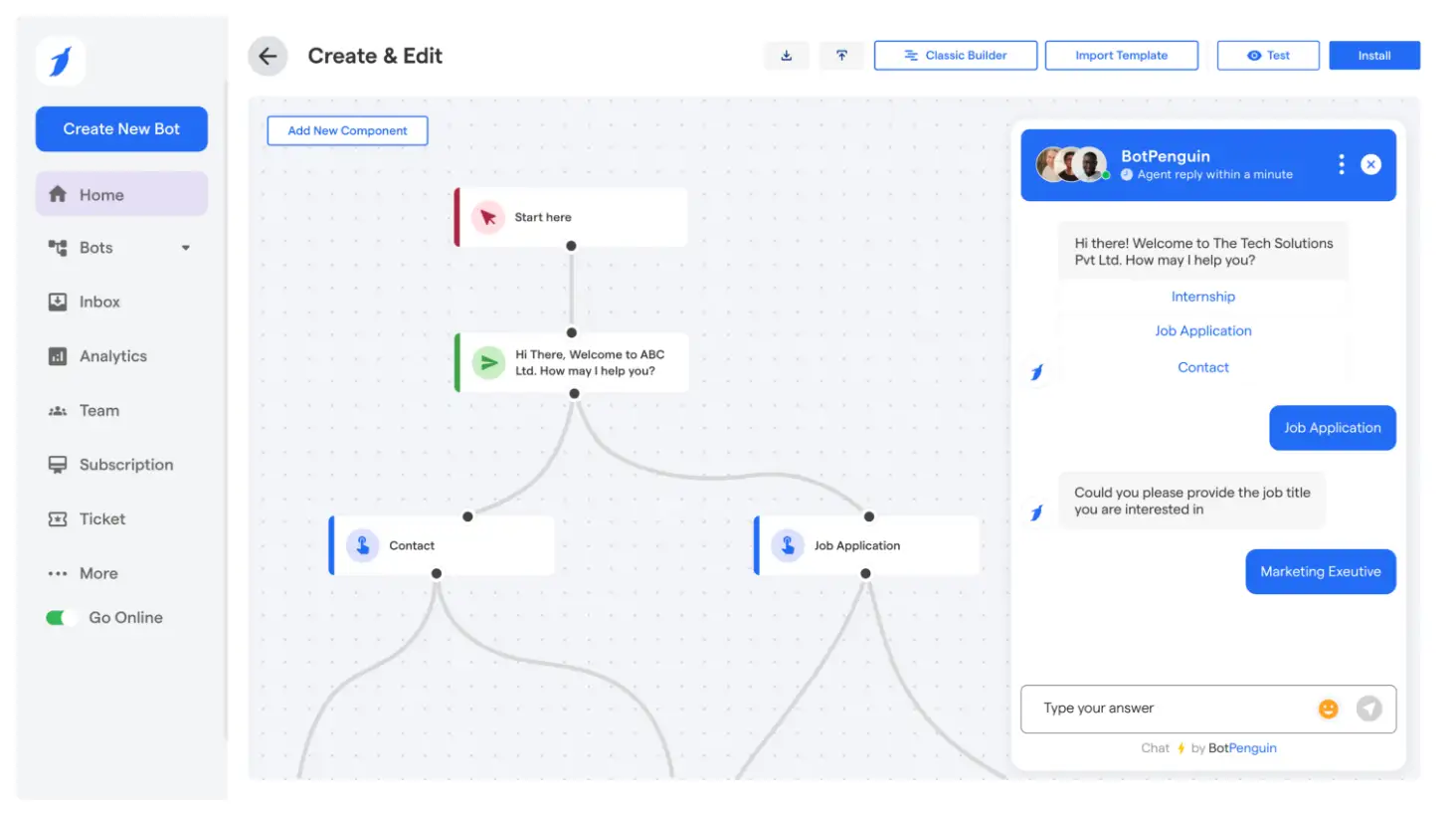
BotPenguin allows businesses to manage customer conversations across major platforms without the compatibility issues that affect RCS.
Messages behave consistently, whether the user is on mobile or web, and delivery remains stable across all devices.
AI Replies for Instant Customer Handling
The platform uses AI to understand customer intent and respond instantly. This reduces wait times and eliminates the need for agents to handle repetitive queries.
It also ensures that communication remains responsive during peak hours.
CRM Sync and Customer Profiles
BotPenguin integrates with CRM systems to maintain a complete communication history for every customer.
This enables teams to view past interactions, preferences, and issue patterns in one place. RCS cannot provide similar data-level insights because it functions entirely at the device level.
Automated Support and Lead Routing
Workflows can assign conversations to the right agent based on topic, language, or customer type.
Automated routing ensures that leads move through the correct process without manual intervention. This is essential for high-volume environments where response accuracy matters.
Reliable Delivery for All Messages
BotPenguin uses stable APIs that do not depend on device compatibility or carrier support.
This ensures that promotional messages, reminders, and support replies reach the user without interruptions or format changes. Businesses avoid the uncertainty that occurs when a text message RCS triggers inconsistent delivery paths.
Multi-Agent Inbox and Ticketing
Teams can collaborate in a shared inbox that assigns tickets, tracks progress, and logs activity.
This structure helps organisations resolve customer issues efficiently while maintaining accountability across support teams.
Perfect for Support Sales Reminders and Notifications
The platform handles transactional alerts, order updates, lead communication, and engagement workflows with predictable performance.
These requirements cannot be fulfilled reliably through RCS due to its lack of automation and inconsistent activation across users.
BotPenguin offers a controlled and dependable communication system that removes the variability seen in RCS.
This foundation prepares the discussion for the concluding section, which outlines how businesses can transition to a more stable messaging structure while supporting long term communication needs.
Conclusion
RCS improves personal communication with richer media and modern chat features, but its behaviour changes across devices, networks, and app versions.
These inconsistencies become noticeable when a thread shifts into an RCS message, making it unreliable for business communication that depends on accuracy and predictable delivery.
Organisations require a stable system that supports automation, multi-channel handling, and consistent workflows.
BotPenguin provides this structure by offering reliable messaging across major platforms, along with AI-driven responses, CRM sync, and controlled routing.
It is the practical upgrade for teams that need dependable communication without the limitations that affect device-based formats like RCS.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is Text Message RCS Meaning in Android Phones
Text message RCS meaning refers to enhanced messaging features that activate when both devices support RCS.
It enables better media, typing status, and delivery insights compared to SMS, but only works when compatibility conditions match.
What Does Text Message RCS Mean When it Appears in a Chat
It means the conversation is using RCS instead of SMS. The phone detected support on both sides and activated richer messaging features.
If compatibility changes, the chat may switch back to standard SMS.
Why am I Receiving an RCS Text Message From Only Some Contacts
An RCS text message appears only when both users have compatible devices, updated apps, and stable data availability.
If any requirement is not met, the thread reverts to SMS, creating different behaviour across contacts.
What Does RCS Message Mean When it Shows Up Automatically
It means the messaging app detected RCS capability after an update or network change and enabled it without manual activation.
This often occurs after a Google Messages configuration refresh or capability check.
Why Does My Phone Show What is Text Message RCS During Setup
This appears when the device is registering RCS features for the first time.
The system checks compatibility with your carrier and app version before enabling enhanced messaging like higher media quality and activity indicators.
Can BotPenguin Automate the Workflows That RCS Messaging Cannot Handle
Yes. BotPenguin supports automation, CRM sync, ticketing, reminders, and AI-driven replies.
These capabilities are not possible within RCS because it lacks system integration and workflow features.