Introduction
Generative AI is revolutionizing industries across the globe, offering new levels of efficiency, creativity, and personalization.
In fact, according to a report by PwC, generative AI could contribute up to $15.7 trillion to the global economy by 2030—a figure that highlights just how transformative this technology is.
From healthcare and finance to retail and entertainment, its applications reshape how businesses operate and interact with customers.
Whether it's creating personalized content, optimizing operations, or improving decision-making, Generative AI is helping companies stay ahead in a highly competitive landscape.
As industries continue to embrace AI-driven innovation, the full potential of Generative AI is just beginning to unfold.
This blog explores how Generative AI is making waves across sectors and the exciting possibilities it holds for the future. Continue reading to know more about the generative AI examples that is transforming the industries.
What is Generative AI?
Generative AI refers to a class of artificial intelligence models designed to generate new content, data, or solutions based on patterns learned from existing data.

Unlike traditional AI, which is primarily focused on recognizing patterns and making predictions, Generative AI goes a step further by creating new and original outputs—be it text, images, music, videos, or even complex designs.
At its core, Generative AI relies on deep learning models, particularly generative adversarial networks (GANs) and transformers, which are trained on large datasets to understand the structure and intricacies of that data.
Once trained, these models can produce new content that mirrors the style, structure, and characteristics of the input data, but with unique elements.
Why is Generative AI Important?
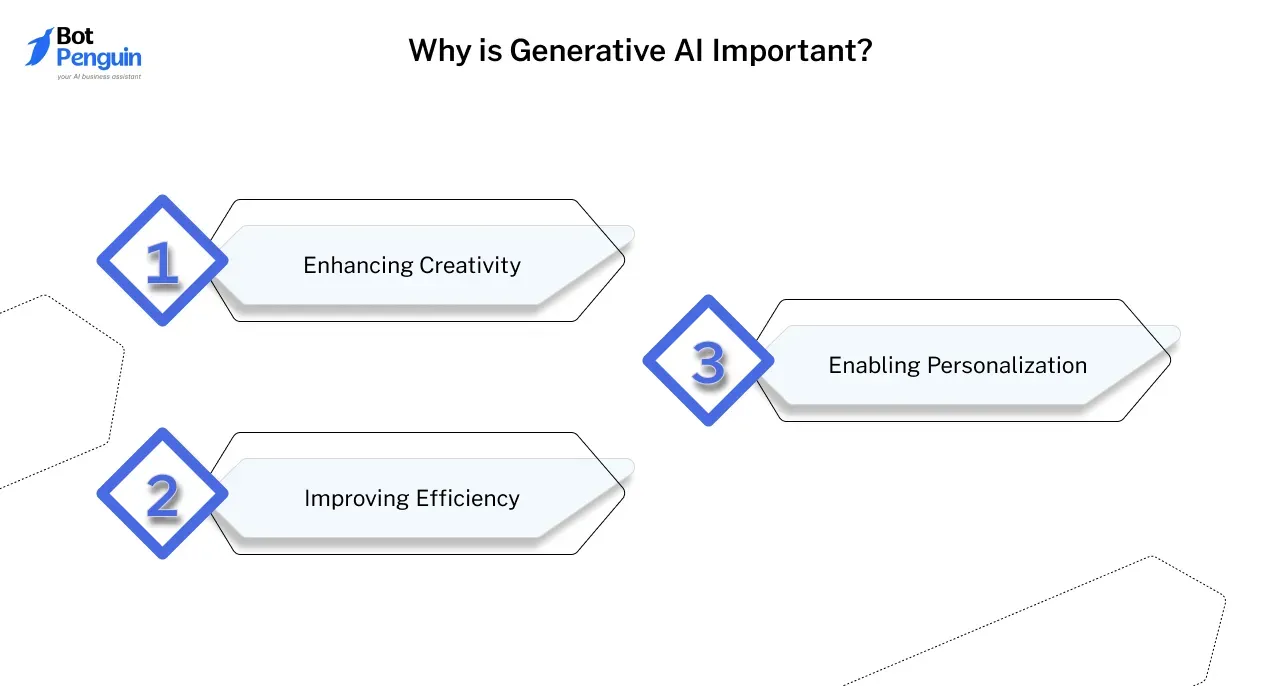
Generative AI holds transformative potential across multiple industries by:
- Enhancing Creativity: It unlocks new possibilities for artists, designers, and creators by providing tools that assist with the generation of novel and high-quality content.
- Improving Efficiency: In fields like healthcare and manufacturing, it can automate complex processes like drug discovery and product design, saving time and resources.
- Enabling Personalization: By generating custom content, AI can create personalized experiences for users, improving engagement and satisfaction in areas like retail, gaming, and media.
Advantages of Generative AI Examples
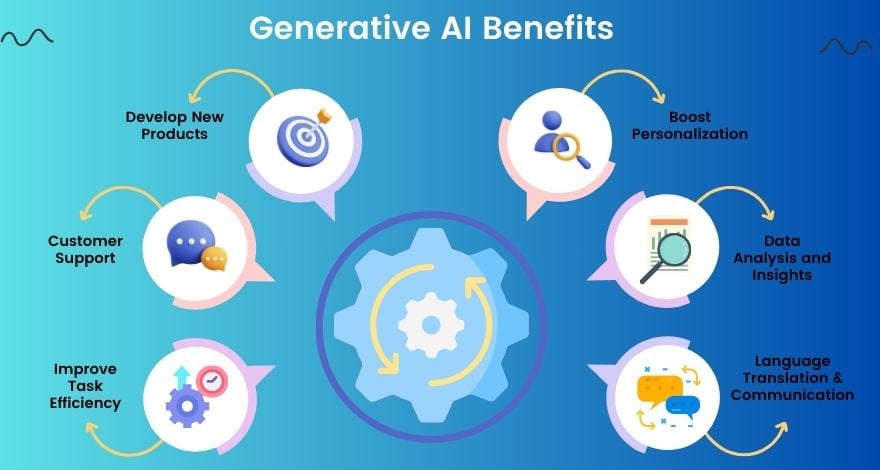
Generative AI is revolutionizing industries across the globe, introducing innovations that were once unimaginable.
From streamlining processes to unlocking new creative possibilities, Generative AI is reshaping the future of business operations.
Whether it's accelerating drug discovery, enhancing marketing efforts, or improving product design, this technology is proving indispensable.
In this section, we’ll explore the key advantages of Generative AI and how it’s impacting various industries in real-world scenarios.
Accelerated Innovation
Generative AI is driving innovation at an unprecedented pace. It enables rapid prototyping, allowing businesses to test ideas and solutions quickly without the need for costly physical prototypes.
For example, in the manufacturing industry, generative design algorithms optimize product designs, reducing material waste and enhancing performance.
A notable example is Tesla, which uses Generative AI to design complex automotive parts. This approach has reduced testing time significantly, helping Tesla bring new products to market faster than ever before.
Cost Efficiency
One of the most compelling advantages of Generative AI is its ability to reduce costs by automating tasks traditionally performed by humans.
In the healthcare sector, AI-driven drug discovery has made significant strides, allowing pharmaceutical companies to identify potential drug compounds much faster and at a lower cost.
Companies like Insilico Medicine use Generative AI to simulate molecular interactions, significantly cutting down research time and costs. By reducing the reliance on costly lab experiments, Generative AI can save millions in R&D expenses, ultimately improving the bottom line for businesses.
Personalization
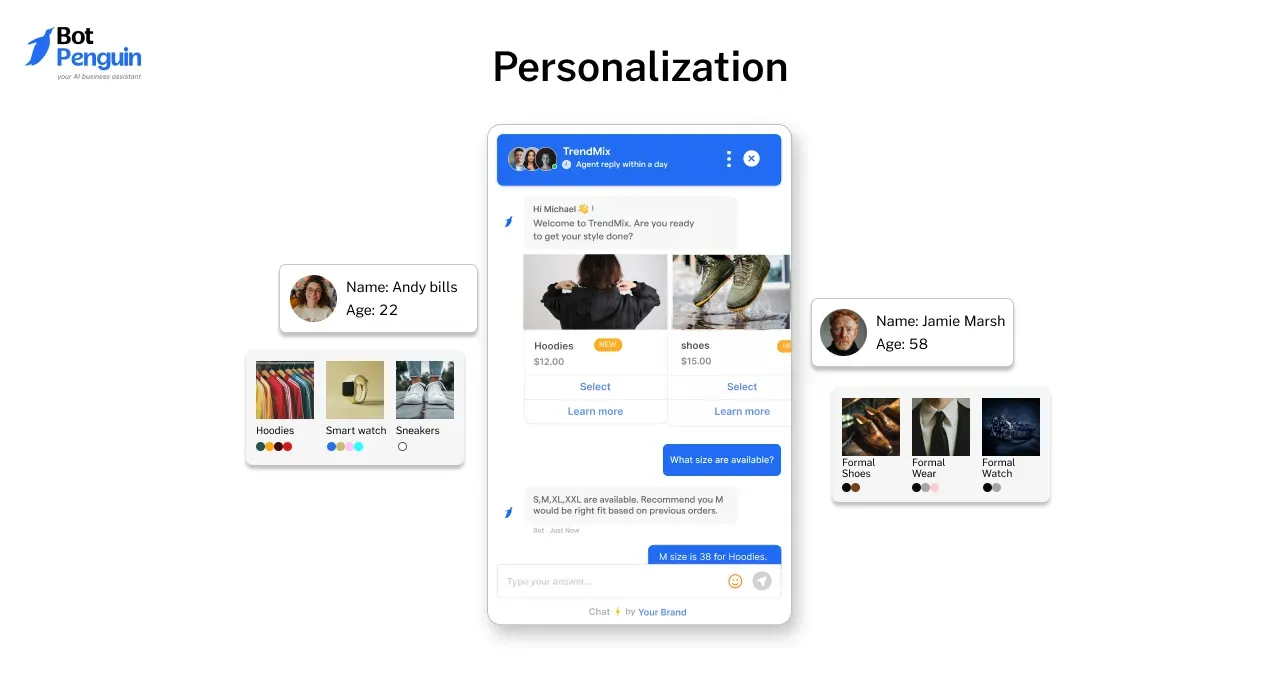
Personalization is at the heart of Generative AI. The ability to create tailored experiences is transforming industries like retail and marketing.
Online retailers like Amazon use Generative AI to analyze customer behavior and generate personalized product recommendations, which leads to higher conversion rates and improved customer satisfaction.
In the fashion industry, AI tools generate outfit recommendations based on individual preferences, body types, and even current trends, making the shopping experience more engaging and increasing sales.
Enhanced Creativity
Generative AI is also pushing the boundaries of creativity. It’s not just about creating functional products; it’s about creating something unique and innovative.
In the media and entertainment industries, Generative AI tools are helping artists and creators produce music, artwork, and even scripts.
For instance, OpenAI’s GPT models can generate original scripts and dialogues, which writers can use as inspiration or even directly in production. AI-generated music is also being utilized in commercial projects, saving both time and resources while pushing the limits of creative expression.
Improved Decision-Making
In industries like finance, Generative AI is transforming decision-making processes by providing data-driven insights. AI models can predict market trends with remarkable accuracy, allowing investors to make more informed decisions.
For example, BlackRock, a global investment firm, uses Generative AI to analyze massive datasets and generate insights for better portfolio management.
These AI-generated insights help investors predict market behavior and identify profitable trading strategies, ultimately improving decision-making and reducing risks.
Real-World Generative AI Use cases Across Industries
Generative AI is playing a pivotal role in transforming industries by enabling innovation, improving efficiency, and enhancing personalization.
Below are some real-world applications that highlight its impact across various sectors:
1. Healthcare and Life Sciences
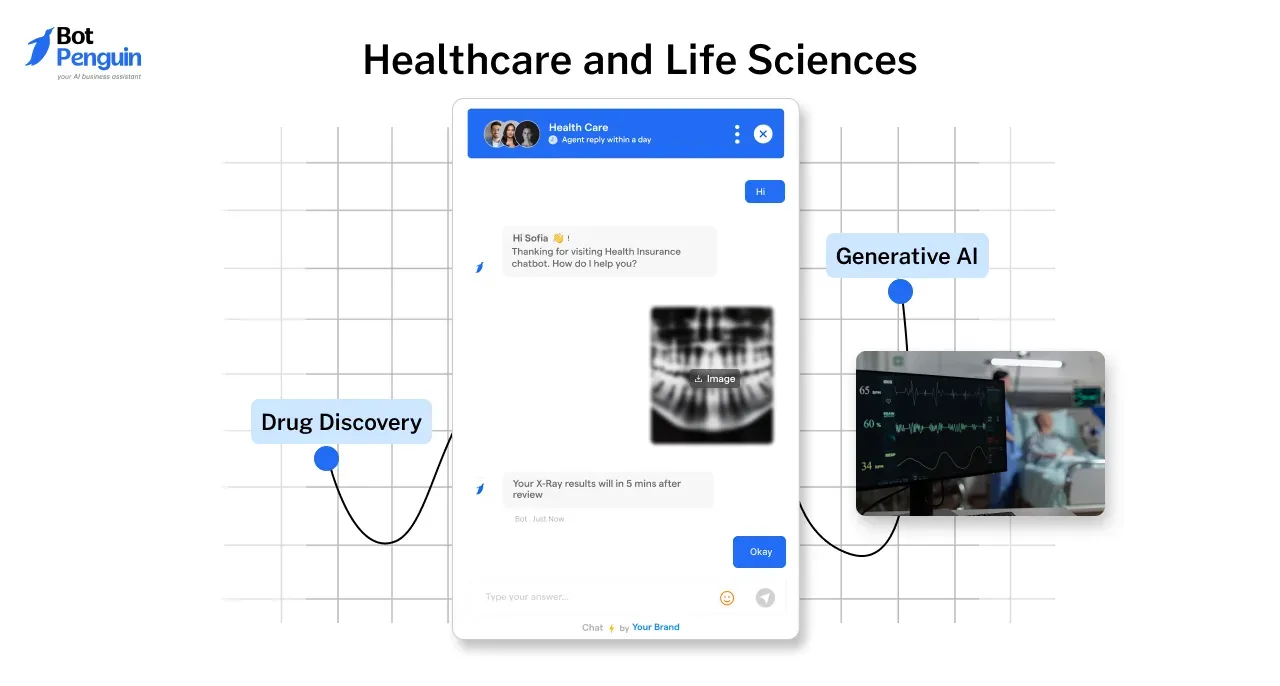
Following are some Generative AI usecases in healthcare:
Drug Discovery and Development:
Companies like Insilico Medicine and Atomwise are harnessing generative AI to revolutionize drug discovery.
By simulating molecular interactions and predicting how different molecules will behave, AI can significantly speed up the identification of potential drug candidates.
For instance, Insilico Medicine recently used AI to design a new drug for idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis, which would traditionally take years of lab research to develop.
By utilizing generative algorithms, these companies reduce the timeline from years to mere months, thus accelerating the delivery of life-saving drugs.
Medical Imaging:
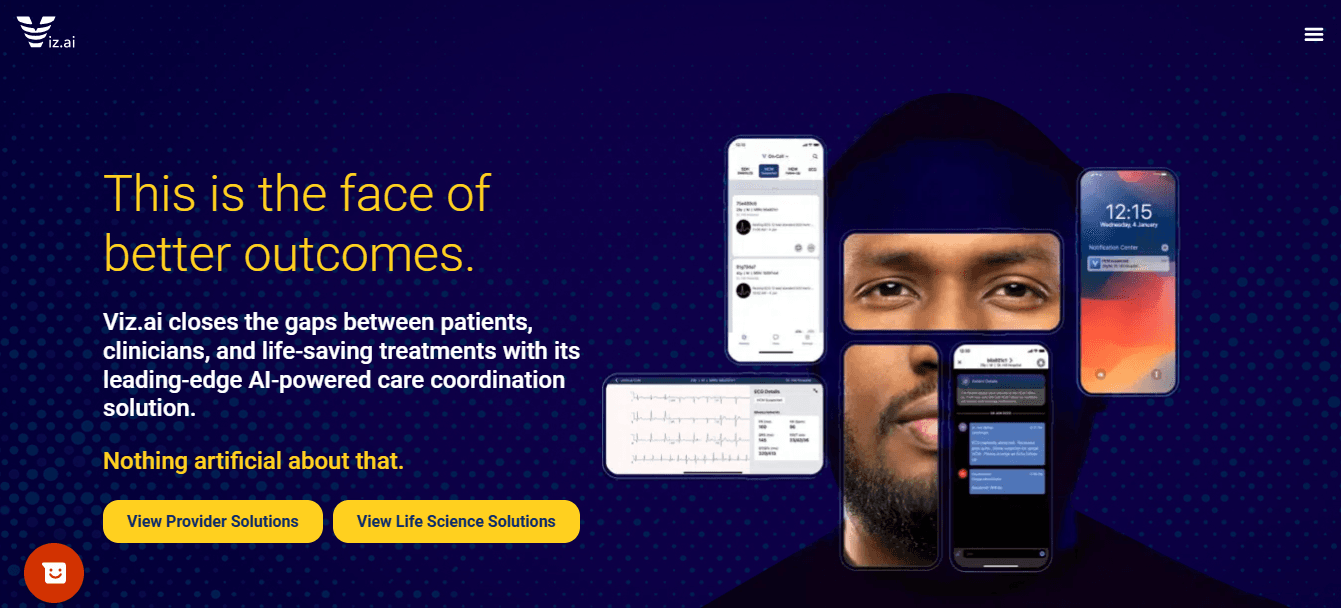
Generative AI tools such as Viz.ai are enhancing medical imaging by assisting radiologists in detecting anomalies such as strokes in real-time.
These AI-driven systems can analyze scans with far greater speed and precision than human doctors, enabling faster diagnoses and improving treatment outcomes.
For example, Viz.ai has been shown to reduce stroke diagnosis times by up to 50%, ensuring that patients receive timely interventions that could significantly improve their prognosis.
Personalized Treatment Plans:
Generative AI is transforming personalized medicine by designing treatment plans tailored to an individual’s unique genetic profile.
AI algorithms analyze patient data to create customized regimens, such as specific chemotherapy treatments, which are more effective and have fewer side effects.
For instance, Tempus, a leader in precision medicine, generative AI uses to design personalized cancer therapies based on patients' genetic data, improving survival rates and minimizing adverse effects.
2. Creative and Entertainment

Following are some Generative AI usecases in entertainment:
Content Creation:
Generative AI tools like OpenAI’s DALL·E and Adobe Firefly are streamlining the content creation process. These tools allow artists, designers, and writers to quickly generate high-quality visuals, music, and even written articles.
For example, DALL·E enables users to create detailed and original images from text prompts, making it a powerful tool for digital artists and marketers.
Adobe Firefly, on the other hand, uses AI to help designers create unique visuals and designs efficiently, offering faster turnaround times and more creative possibilities.
Gaming:
In the gaming industry, generative AI is enabling the creation of dynamic, interactive environments.
For example, No Man’s Sky, a popular game developed by Hello Games, uses AI algorithms to generate vast, procedurally created worlds, ensuring that each player’s experience is unique.
These AI-generated game environments provide endless exploration opportunities, with different planets, landscapes, and ecosystems created in real-time as players explore the universe.
Deepfake Technology:
Although controversial, deepfake technology, driven by generative AI, is being used in film production to recreate actors or swap faces seamlessly.
For example, Lucasfilm used deepfake technology to recreate a young Carrie Fisher in Star Wars: Rogue One, and James Dean was digitally resurrected for the movie Finding Jack.
While deepfake technology has ethical concerns, its potential for revolutionizing the entertainment industry in recreating deceased actors or even enhancing visual storytelling is significant.
3. Manufacturing and Design
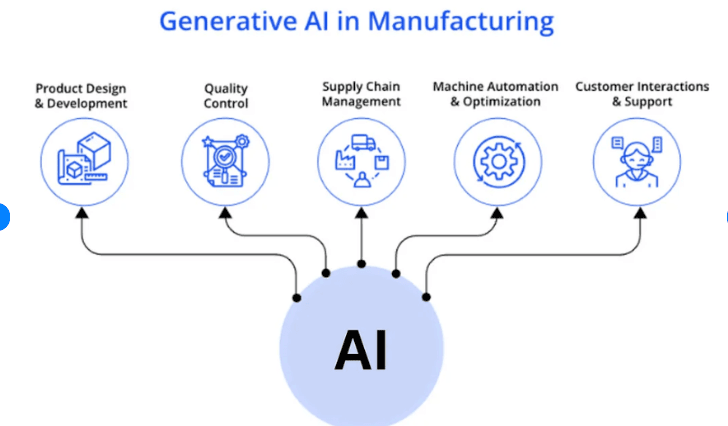
Following are some Generative AI uses in manufacturing:
Generative Design:
Companies like Siemens and Autodesk are pioneering the use of generative design to optimize product creation.
By using AI to simulate thousands of design alternatives, these companies can produce lighter, more efficient, and durable products while minimizing waste.
For example, Airbus used generative design in the creation of an aircraft cabin partition, resulting in a part that was 45% lighter yet just as strong, showcasing how AI can drastically reduce material usage and production costs.
Predictive Maintenance:
Generative AI models are also being employed to predict when machinery will fail, thus preventing costly downtime.
By analyzing sensor data from factory equipment, AI can identify patterns that suggest an impending malfunction.
General Electric (GE) uses AI-driven predictive maintenance systems to monitor its turbines and predict when maintenance is required, reducing unplanned shutdowns and extending the lifespan of their equipment.
Suggested Reading:
How to use Generative AI for Lead Generation?
Supply Chain Optimization:
Generative AI is transforming supply chain management by simulating various logistics scenarios to optimize routes and schedules.
For example, Amazon uses AI to predict demand and adjust shipping logistics in real-time, ensuring faster deliveries and reduced operational costs.
These AI systems analyze factors such as traffic, weather, and inventory to select the most efficient delivery routes, benefiting both the company and its customers.
4. Finance
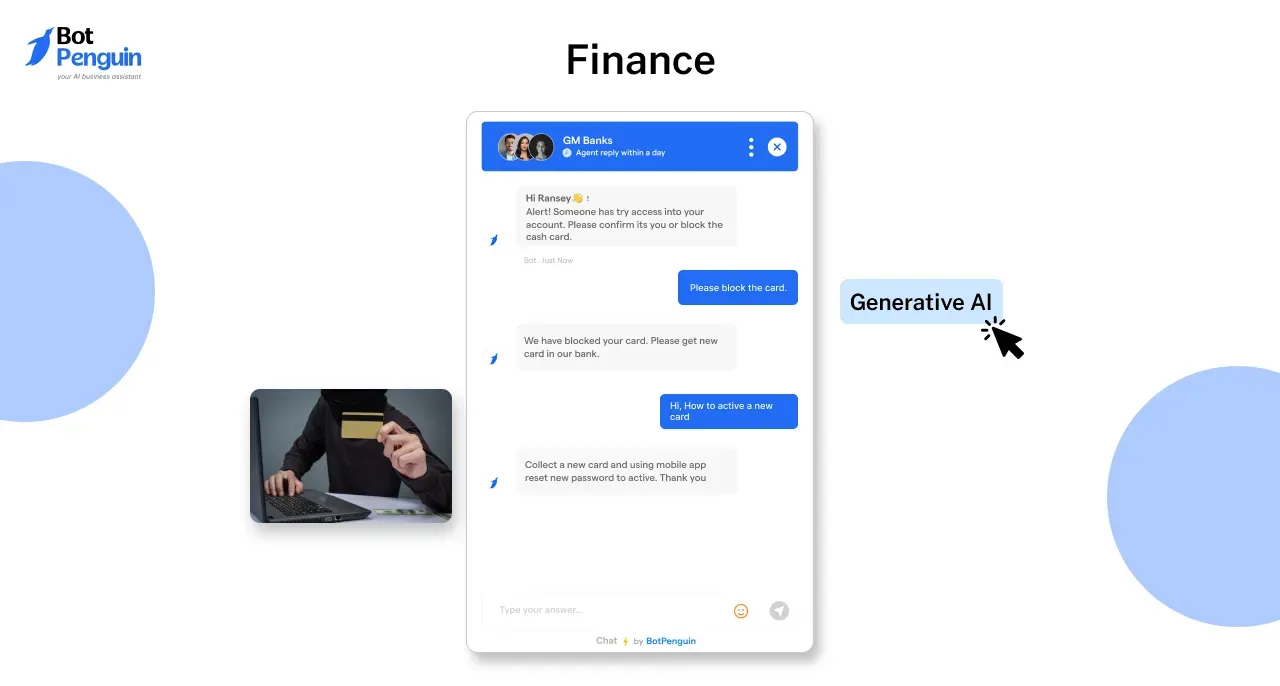
Following are some Generative AI uses in finance:
Fraud Detection:
Financial institutions like JPMorgan Chase are using generative AI to generate synthetic transaction data and identify patterns that might indicate fraudulent activity.
By simulating different fraudulent scenarios, these AI systems can detect anomalies in real-time, preventing financial losses before they occur.
This technology has helped the banking industry reduce fraud and improve security for customers, offering a more reliable service.
Algorithmic Trading:
Generative AI models are also used to develop trading strategies in real-time. For example, Two Sigma and other hedge funds use AI to generate algorithmic trading strategies that can predict market movements and react faster than human traders.
These AI systems analyze vast amounts of market data, enabling them to make real-time decisions that maximize profits and reduce risks.
Customer Service Automation:
In customer service, AI-powered chatbots like those used by Bank of America or Wells Fargo provide real-time support to customers.
These generative AI chatbots can handle a variety of tasks, from answering account-related questions to assisting with transactions, reducing wait times and improving customer satisfaction.
5. Retail and E-commerce

Following are some Generative AI examples in retail industry:
Personalized Recommendations:
E-commerce giants like Amazon and Shopify leverage AI to create personalized shopping experiences.
By analyzing customer data such as browsing behavior, purchase history, and preferences, these AI models can recommend products tailored to each individual, improving sales and customer satisfaction.
For example, Amazon’s recommendation engine drives a significant portion of its sales by suggesting products to customers based on their previous interactions.
Suggested Reading:
How Chatbots Powered by Generative AI are Transforming Interactions
Dynamic Pricing:
Generative AI is being used to adjust prices dynamically based on customer behavior, competitor pricing, and market trends.
Uber and Airbnb use AI to modify prices in real-time, ensuring competitive pricing that maximizes revenue. This pricing model is particularly effective in industries where demand fluctuates rapidly.
Virtual Try-Ons:
Retailers like Warby Parker and L'Oreal are using generative AI to offer virtual try-ons, allowing customers to visualize how products will look on them before making a purchase.
This reduces uncertainty for buyers, leading to higher conversion rates and lower return rates. For example, Warby Parker’s virtual try-on feature uses AI to superimpose glasses onto the customer's face in real-time through their smartphone camera.
6. Education
_1711949110.webp)
Following are some Generative AI usecases in Education sector:
Personalized Learning:
Generative AI is being used to create adaptive learning paths for students. For example, Khan Academy employs AI to provide tailored lessons, quizzes, and feedback based on students' strengths and weaknesses.
To maintain content authenticity and ensure that AI generated materials align with academic integrity, educators often rely on tools like an AI detector to verify originality and human input.
This personalized approach allows students to learn at their own pace and ensures that no one is left behind.
Content Creation:
Educational institutions are utilizing generative AI to automate the creation of quizzes, flashcards, and even textbooks.
For example, OpenAI’s GPT-3 is being used to generate interactive learning materials, reducing the workload on educators and improving engagement with students.
Virtual Tutors:
AI-powered virtual tutors are becoming more common in educational apps. Duolingo, a popular language-learning platform, uses generative AI to offer customized lessons, real-time feedback, and practice exercises tailored to individual learners, enhancing the learning experience.
7. Customer Service
Following are some Generative AI examples uses in customer services:
AI Chatbots and Virtual Assistants:
Tools like BotPenguin and Zendesk AI are transforming customer support by providing 24/7 automated assistance.
These AI chatbots can answer inquiries, resolve issues, and provide personalized support across various channels. For instance, BotPenguin helps businesses streamline customer interactions, improving response times and reducing operational costs.
Multilingual Support:
Generative AI is enabling businesses to provide multilingual customer support. By leveraging AI models such as Google Translate or DeepL, companies can communicate with customers in multiple languages, enhancing the global customer experience.
This is particularly useful for businesses that operate internationally and need to cater to diverse customer bases.
Challenges Associated with Generative AI Uses

While Generative AI has made remarkable strides in a variety of industries, it also presents several challenges that need to be addressed in order to maximize its potential.
From ethical concerns to technical limitations, the hurdles associated with Generative AI are significant, but not insurmountable. Here's a detailed look at some of the key challenges, along with real-world examples:
1. Bias and Fairness
One of the most pressing challenges with Generative AI is its tendency to reflect and amplify biases present in the data it’s trained on.
Since these AI models learn from vast datasets, they often inherit the societal, racial, gender, and cultural biases embedded in that data. This can lead to AI outputs that perpetuate stereotypes, discrimination, or unequal representation.
Real-World Example:
In 2020, researchers found that AI models used to generate images and videos often produced results that were racially biased.
For example, facial recognition systems trained predominantly on white datasets were less accurate at recognizing people of color, particularly women.
Similarly, text-generation models such as GPT-3 have been criticized for producing outputs that reinforce gender and racial stereotypes in their content.
Impact:
Bias in generative models can lead to unethical outcomes in industries like hiring, law enforcement, and healthcare, where biased data could perpetuate existing inequalities.
Potential Solution:
To combat this, developers are working on techniques like bias mitigation and fairness auditing during the training process to ensure that the AI outputs are diverse and equitable.
Additionally, diverse and inclusive datasets are being prioritized in training models.
Suggested Reading:
Role of Generative AI Development in Building Dynamic Chatbots
2. Intellectual Property (IP) Issues
Generative AI models can create content—like art, music, or writing—that is similar to or based on existing works. This raises concerns around ownership, copyright, and the potential for plagiarism.
Since the AI generates content based on patterns from pre-existing data, it can be challenging to determine whether the generated work belongs to the AI, the developer, or the original content creators.
Real-World Example:
In the music industry, AI models such as OpenAI’s Jukedeck and Amper Music can compose original music, but the use of AI in this creative space has led to debates over who owns the rights to AI-generated music.
In one case, a song composed by AI raised questions about whether the composer (the person who wrote the code) or the AI itself holds the copyright.
Impact:
Without clear guidelines on intellectual property, AI-generated works could be contested in courts, leading to potential legal battles and confusion over ownership.
This could particularly affect industries like art, music, and literature.
Potential Solution:
To address this, legal frameworks around AI-generated content are being explored to determine the rights of the AI, its creators, and the original content sources.
Creative commons licensing and the use of blockchain technology to track and assign ownership are also potential solutions.
The Future of Generative AI in Transforming Industries
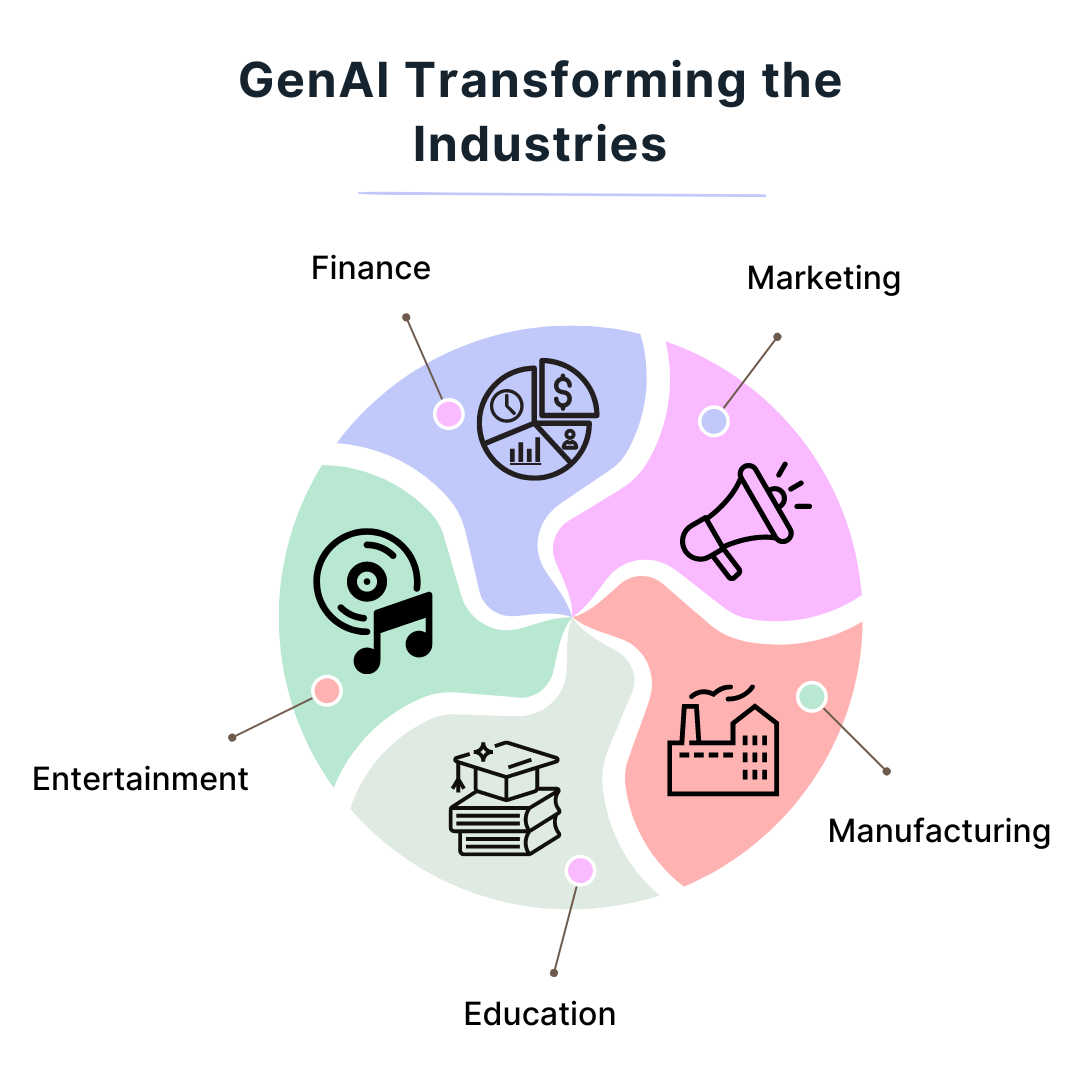
Generative AI is set to revolutionize multiple industries, offering automation, innovation, and enhanced productivity. Here's a brief look at its future impact:
- Healthcare: AI will accelerate drug discovery and personalize treatments by analyzing vast datasets, improving health outcomes and reducing costs.
For example, companies like Insilico Medicine are using AI to design new drugs faster.
- Retail: AI will enable personalized shopping experiences and optimize product development. Brands like Stitch Fix already use AI to suggest clothing designs and styles tailored to individual tastes.
- Finance: Generative AI will improve financial decision-making, forecasting, and risk management. AI platforms like AlphaSense help firms generate insights from financial data, improving market predictions.
- Entertainment: AI will transform content creation by generating personalized media, music, and interactive experiences.
OpenAI and Amper Music are leading the way in AI-generated music, while future applications could include AI-created films and video games.
- Manufacturing: AI will streamline design and production processes, optimizing efficiency and reducing waste.
Companies like Tesla and Airbus already use AI for component design, leading to more sustainable manufacturing.
- Education: Generative AI will personalize learning by tailoring lessons and feedback to individual students.
Platforms like Squirrel AI are already using AI for customized tutoring services.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Generative AI is reshaping industries by driving innovation, efficiency, and personalization across sectors. Its transformative power—from accelerating drug discovery in healthcare to enhancing content creation in the entertainment industry—demonstrates its vast potential.
As we’ve seen, businesses are already leveraging Generative AI to streamline operations, improve customer experiences, and unlock new levels of creativity. The real-world applications outlined in this blog are just the start of what this technology can achieve.
As Generative AI evolves, industries that embrace it will not only remain competitive but also lead the way in shaping the future of innovation.
By integrating Generative AI into their processes, businesses can propel themselves into a new era of productivity and growth, setting the stage for even greater advancements in the years to come. The future is bright for Generative AI, and its impact will only continue to expand.
With tools like BotPenguin, businesses can harness the power of AI to enhance customer support and drive efficiency, ensuring they stay ahead in this rapidly evolving landscape.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Which industries are most impacted by Generative AI?
Generative AI is transforming multiple industries, with significant impacts in healthcare, finance, retail, entertainment, and manufacturing.
By automating tasks, enhancing creativity, and optimizing processes, Generative AI is driving innovation and improving efficiency across these sectors.
How does Generative AI benefit the healthcare industry?
In healthcare, Generative AI accelerates drug discovery, improves medical imaging, and creates personalized treatment plans.
These applications reduce costs and timelines while improving patient outcomes, enabling quicker, more accurate diagnoses and better treatment options.
Can Generative AI improve financial services?
Yes, Generative AI enhances financial services by automating risk analysis, detecting fraud, offering personalized financial advice, and generating predictive models.
These capabilities lead to better decision-making, improved customer service, and a more efficient financial ecosystem.
How is Generative AI used in the retail industry?
In retail, Generative AI powers personalized marketing, dynamic pricing, and efficient inventory management.
By analyzing customer behavior, it generates content and recommendations tailored to individual preferences, enhancing the shopping experience and driving sales.
What are the ethical concerns surrounding Generative AI?
Ethical concerns with Generative AI include the misuse of deepfake technology, data privacy issues, and the spread of misinformation.
To address these, it’s essential to ensure transparency, fairness, and accountability in the development and deployment of Generative AI.