Automation is not the problem. It is the limit.
Most factories already operate on automated systems, yet downtime, waste, and quality issues persist.
Machines follow rules. They do not learn from failure or adapt to change. That gap is becoming expensive.
This is where AI quietly changes industrial automation, not by replacing machines, but by making them smarter.
AI helps systems predict failures, spot defects, and optimize processes in real time.
This guide explains how AI works in industrial automation, where it delivers real impact, and how manufacturers use it to move from reactive operations to intelligent, data-driven production.
What is AI in Industrial Automation
Industrial automation was designed around fixed logic and predictable workflows.
That model works in stable environments, but struggles when production conditions change, data volumes increase, or failures appear without warning.
Modern factories generate constant machine and sensor data, yet traditional systems cannot interpret patterns or improve decisions on their own.
This limitation is where AI becomes relevant.
AI in industrial automation refers to the use of machine learning, computer vision, and data-driven models to help automation systems learn from operational data and improve performance over time.
Instead of executing only predefined instructions, AI systems analyze historical and real-time data to predict issues, optimize processes, and support better operational decisions.
Difference Between Rule-Based Automation and AI-Driven Automation
This shift enables advanced AI applications in industrial automation, such as predictive maintenance, intelligent quality inspection, and process optimization.
Why is AI Becoming Essential in Industrial Automation Today
Traditional automation still powers most industrial operations. It also explains why improvement often stalls after a point.
Production variability, tighter margins, and rising downtime costs expose the limits of fixed logic systems.
These constraints are pushing manufacturers toward AI-driven systems.
Why Traditional Automation is Hitting Limits
Rule-based automation operates on predefined conditions.
It performs well in predictable environments but fails when processes change or unexpected situations arise.
Common limitations include:
- No ability to learn from historical data
- Reactive maintenance and delayed fault detection
- Manual updates are required for every process change.
- Limited insight into future performance risks
How AI Changes What Automation Can Deliver
AI introduces continuous learning and data-driven decision-making into automation systems.
This expands what automation can realistically achieve.
Key improvements enabled by AI include:
- Early detection of failures before downtime occurs
- Adaptive process optimization based on real-time data
- Intelligent quality inspection that improves accuracy over time
- Better use of existing machine and sensor data
- Consistent performance across variable operating conditions
These capabilities power advanced AI applications in industrial automation and drive the measurable impact of AI integration in industrial automation.
For manufacturers, this translates into the practical benefits of AI in industrial automation, such as higher reliability, improved efficiency, and stronger operational control.
How Does AI Integrate With Existing Industrial Automation Systems
After understanding why AI has become essential, the next concern is practical adoption.
Most manufacturers already run complex automation environments built over years.
Any new technology must work within these systems, not disrupt them.
AI adoption succeeds only when it fits into existing operational and control layers.
Can AI Work With PLC, SCADA, and MES Systems?
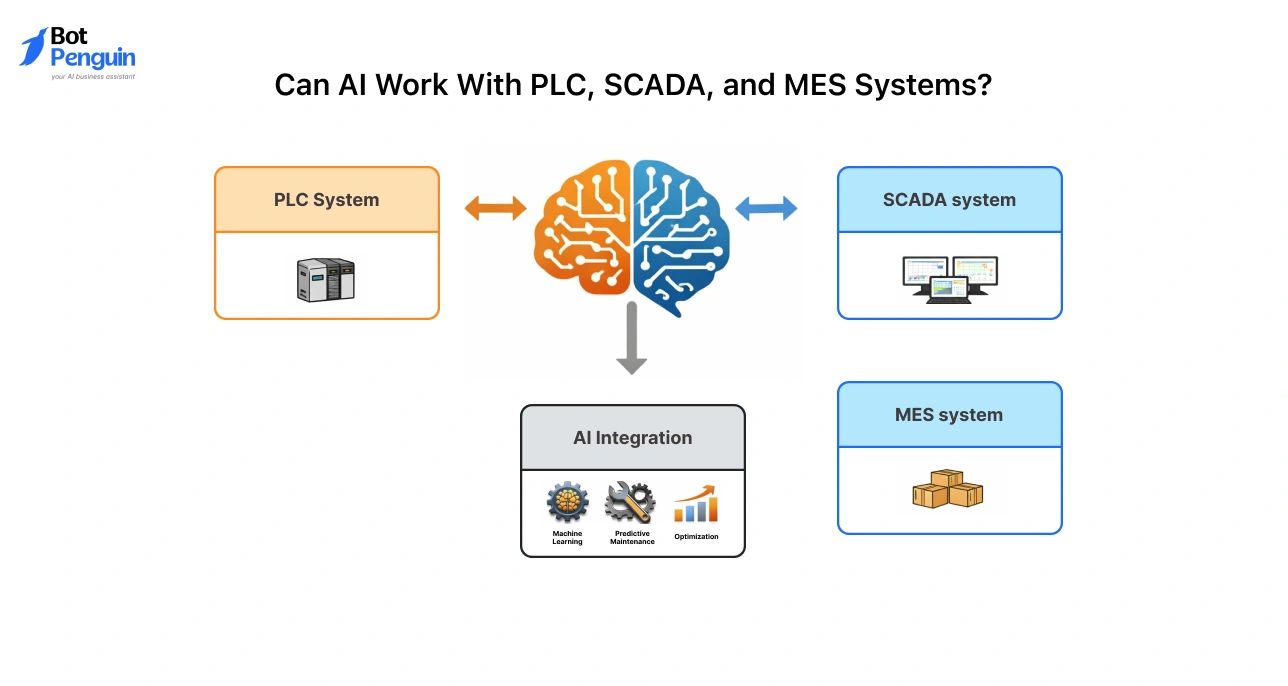
Yes. AI integrates with existing automation by operating above the control layer.
PLC systems continue handling real-time control. SCADA systems still manage monitoring and supervision.
MES platforms remain responsible for production planning and execution.
AI consumes data from these systems rather than replacing them.
It analyzes machine signals, process parameters, and historical logs to generate predictions and recommendations.
Outputs from AI are then fed back to operators or automation systems for action. This approach preserves system stability while expanding intelligence.
Does AI Require Replacing Existing Automation Infrastructure
No. AI in industrial automation is typically added as an intelligence layer. Existing machines, sensors, and control logic remain intact.
Practical integration follows a clear pattern:
- Data is collected from PLC, SCADA, and MES systems
- AI models analyze trends and patterns outside the control loop
- Insights support maintenance, quality, and process decisions
This model explains the impact of AI integration in industrial automation without introducing operational risk and supports scalable AI applications in industrial automation that deliver measurable benefits of AI in industrial automation.
What Are the Key AI Applications in Industrial Automation
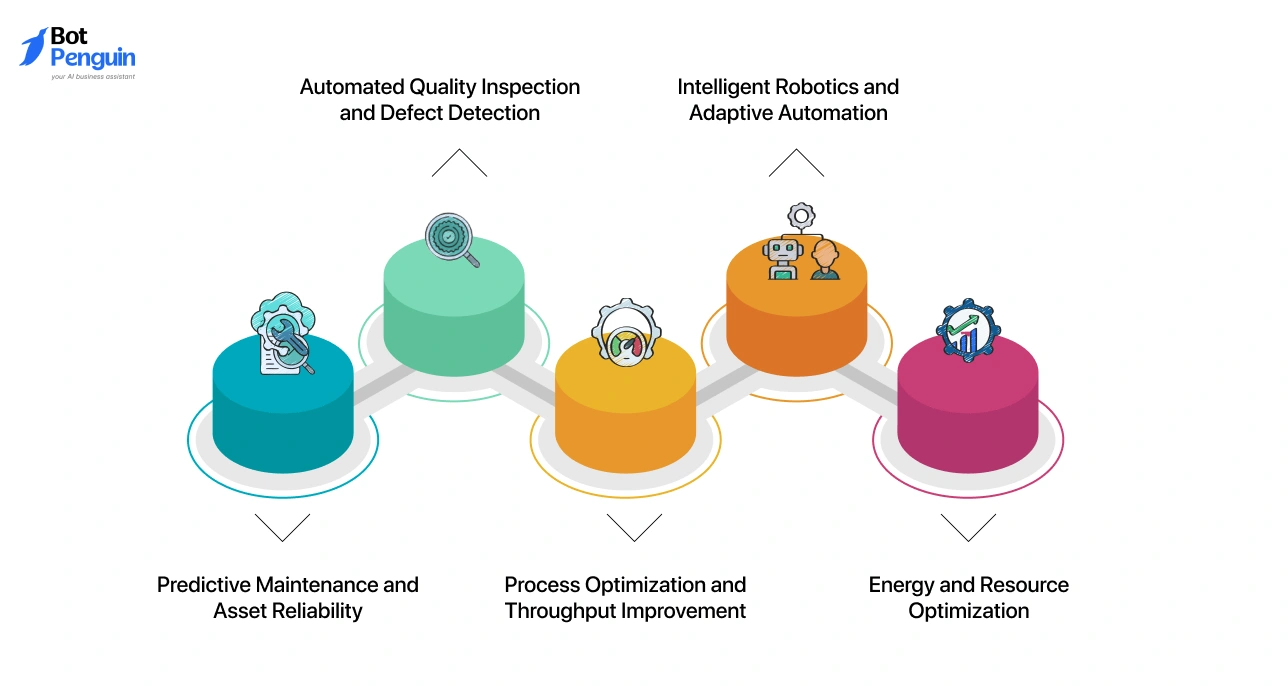
Once AI is integrated into existing automation environments, its value concentrates around a few high-impact operational areas.
These are not exploratory use cases. They address long-standing limitations of rule-driven systems and deliver measurable operational gains.
The most important AI applications in industrial automation focus on reliability, quality, throughput, and efficiency.
Predictive Maintenance and Asset Reliability
Predictive maintenance is one of the most widely adopted applications of AI in industrial settings.
AI models analyze machine signals such as vibration, temperature, and pressure alongside historical maintenance data.
Instead of reacting after failures occur, systems identify early degradation patterns.
This reduces unplanned downtime, extends asset life, and lowers maintenance costs.
Automated Quality Inspection and Defect Detection
Quality inspection benefits significantly from AI-based computer vision.
These systems inspect products continuously and detect defects that fixed-rule inspection often misses.
As more data is collected, detection accuracy improves. This leads to lower scrap rates, fewer recalls, and more consistent output.
Process Optimization and Throughput Improvement
AI improves process performance by analyzing interactions across machines and production stages.
It identifies optimal operating conditions based on real-time and historical data.
This reduces variation, stabilizes output, and improves overall equipment effectiveness without altering control logic.
Intelligent Robotics and Adaptive Automation
AI adds perception and decision capability to industrial robots.
Robots can adjust movements, recognize objects, and respond to variability without frequent reprogramming.
This increases flexibility in assembly, handling, and packaging operations where conditions change regularly.
Energy and Resource Optimization
AI models analyze energy usage across equipment and production cycles.
They identify inefficiencies and recommend adjustments that reduce waste while maintaining output.
This supports cost control and sustainability objectives.
Together, these applications define the practical impact of AI integration in industrial automation.
For manufacturers, the benefits of AI in industrial automation appear as improved reliability, higher productivity, and better use of existing automation investments.
What Are the Benefits of AI in Industrial Automation?
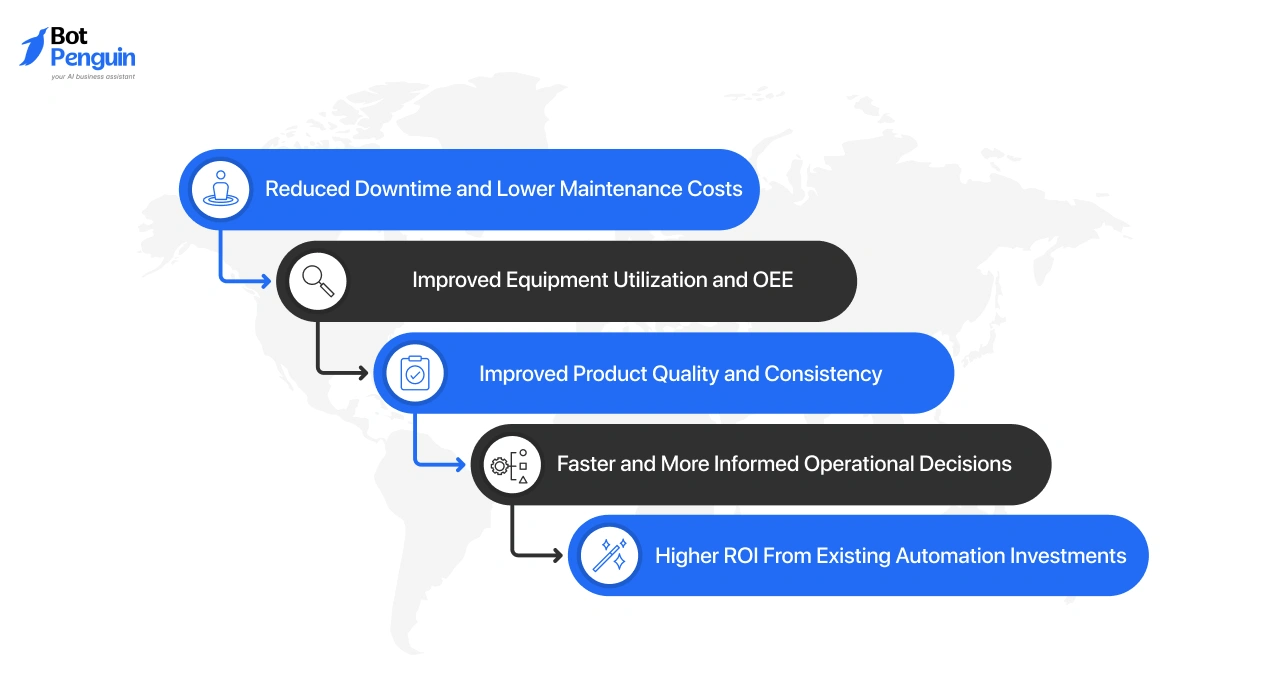
Once AI is applied to real operational use cases, its value becomes measurable.
Manufacturers adopt AI only when it improves performance indicators that matter on the factory floor.
The benefits of AI in industrial automation are closely tied to uptime, efficiency, quality, and financial returns from existing systems.
Reduced Downtime and Lower Maintenance Costs
AI enables early detection of equipment degradation by analyzing machine signals and historical performance data.
Maintenance shifts from reactive to planned interventions. This reduces unplanned downtime, lowers emergency repair costs, and improves asset reliability.
Improved Equipment Utilization and OEE
By monitoring performance trends across machines and shifts, AI identifies inefficiencies that are difficult to detect manually.
Operators gain insights into underperforming assets and process bottlenecks.
This leads to better utilization rates and improved overall equipment effectiveness.
Improved Product Quality and Consistency
AI-based inspection and process monitoring systems detect deviations early in production.
Quality issues are addressed before they spread across batches.
Continuous learning allows systems to maintain consistent output even as operating conditions change.
Faster and More Informed Operational Decisions
AI processes operational data in near real time and highlights issues that require attention.
Teams no longer depend solely on delayed reports or manual analysis. Faster access to insights improves response time and operational control.
Higher ROI From Existing Automation Investments
AI in industrial automation builds on current machines, sensors, and control systems.
Instead of replacing infrastructure, manufacturers extract more value from what they already own.
This strengthens the impact of AI integration in industrial automation and delivers sustained performance gains.
What is the Impact of AI in Industrial Automation Across Industries
The impact of AI integration in industrial automation becomes clearer when examined across industry-specific operating environments.
While production models and risk profiles differ, AI consistently improves predictability, operational control, and decision accuracy.
These gains come from earlier detection of issues, better process visibility, and reduced reliance on manual intervention.
Automotive and Discrete Manufacturing
Automotive and discrete manufacturing operations involve complex assembly lines and frequent product variation.
AI improves performance across both equipment reliability and quality control.
Key impacts include:
- Reduced unplanned downtime through predictive maintenance
- Early detection of wear and failure patterns
- Fewer line-wide stoppages and cascading delays
- Improved quality inspection at production speed
- Detection of micro-defects not visible to rule-based systems
- Lower rework and warranty risk
- Better line balancing and throughput control
- Stabilized output during shift changes
- Faster ramp-up during new product introductions
Pharmaceutical and Regulated Manufacturing
In regulated environments, consistency and traceability are critical to operational success and compliance.
Key impacts include:
- Early detection of process drift
- Identification of parameter deviations before batch failure
- Reduced scrap and batch rejection
- Stronger compliance and audit readiness
- Improved traceability across process and quality data
- More reliable documentation without manual overhead
- Improved process stability
- Consistent outcomes across multiple production runs
- Better control over critical quality attributes
FMCG and High-Volume Production
FMCG manufacturers operate under demand volatility and frequent changeovers. AI helps stabilize performance while protecting margins.
Key impacts include:
- Improved yield and waste reduction
- Optimization of machine settings across product variants
- Lower losses during changeovers and ramp-ups
- More consistent production output
- Reduced variation across shifts and operating conditions
- Better throughput predictability
- Enhanced production planning support
- Analysis of historical demand and performance data
- More efficient resource allocation
Heavy Industry and Energy Operations
Heavy industry and energy operations depend on asset reliability, safety, and efficiency at scale.
Key impacts include:
- Improved equipment reliability and uptime
- Early fault detection for critical assets
- Reduced catastrophic failure risk
- Increased energy efficiency
- Identification of performance degradation and inefficiencies
- Lower operational energy costs
- Enhanced safety and risk management
- Continuous monitoring of operating conditions
- Faster response to abnormal behavior
Across industries, the impact of AI integration in industrial automation is defined by stronger operational visibility, reduced uncertainty, and improved control over complex systems.
Manufacturers achieve these outcomes without replacing existing infrastructure, making AI a practical and scalable extension of modern industrial automation.
What Challenges Do Companies Face When Adopting AI in Industrial Automation?
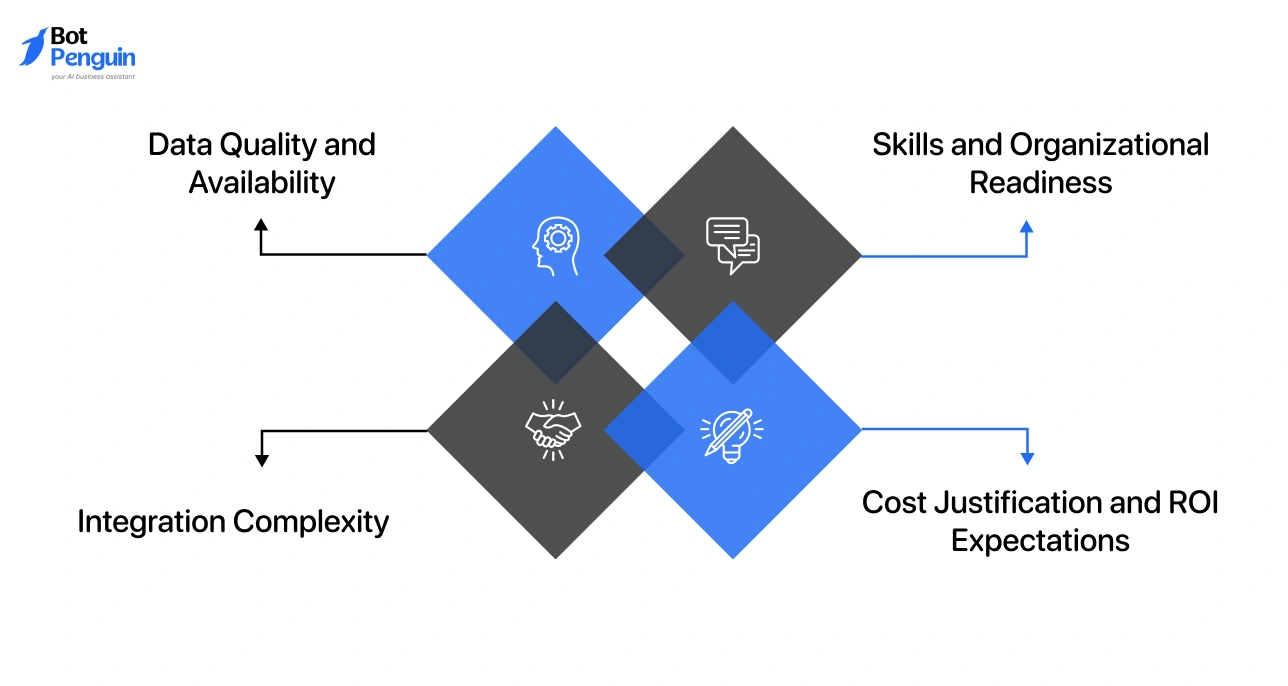
Despite clear benefits, AI adoption introduces challenges that must be addressed early.
These challenges are rarely technical alone. They often involve data readiness, organizational alignment, and implementation strategy.
Data Quality and Availability
AI systems depend on reliable operational data. Inconsistent sensor data, incomplete historical records, or poor data structure can limit model accuracy.
Data preparation is often the first major hurdle.
Skills and Organizational Readiness
Many teams lack experience working with AI-driven systems. Without proper training, insights may not be trusted or used effectively.
Change management is critical for adoption success.
Integration Complexity
While AI does not replace existing automation, integrating analytics layers with control systems requires careful planning.
Security, latency, and system stability must be maintained.
Cost Justification and ROI Expectations
AI initiatives often face scrutiny during budgeting and approval.
Without clear use case prioritization and measurable outcomes, projects can stall before delivering value.
Addressing these challenges early helps ensure that AI adoption delivers long-term operational gains rather than isolated experiments.
How Can Manufacturers Overcome AI Adoption Challenges
Overcoming AI adoption challenges requires discipline and control. Successful manufacturers avoid large-scale rollouts at the start.
Instead, they focus on reducing risk, validating value early, and scaling only after results are proven.
Start Small and Scale Safely
Beginning with focused use cases allows teams to test AI in real operating conditions without disrupting production.
Key practices include:
- Select one or two high-impact use cases with clear metrics
- Use existing machine and sensor data wherever possible
- Validate outcomes before expanding across assets or plants
- Build internal trust through visible early results
This approach creates a foundation for long-term AI adoption.
Reduce Risk During Implementation
Risk reduction depends on how AI is positioned within automation systems. AI should support decisions, not replace core control logic.
Effective risk controls include:
- Keep PLC and SCADA systems responsible for real-time control
- Use AI outputs as recommendations or alerts
- Define clear performance thresholds and escalation paths
- Maintain strong data governance and security controls
Turning AI Adoption Challenges Into Operational Outcomes
Most AI initiatives struggle after insights are generated. Predictions and recommendations often remain limited to dashboards, while real operational decisions continue to rely on manual coordination.
When AI outputs are not connected to daily workflows, adoption slows and trust declines.
Bridging the Gap Between Insight and Execution
This is where platforms like BotPenguin become relevant. Rather than acting as another isolated AI system, BotPenguin focuses on operational execution.
It functions as a connective layer that links AI-driven insights with the teams and systems responsible for action.
Enabling Structured and Controlled Automation
BotPenguin integrates with existing operational tools, CRMs, and internal workflows.
AI-generated alerts or recommendations can trigger defined actions such as team notifications, automated follow-ups, or controlled escalation to human operators.
This ensures decisions move forward quickly while maintaining oversight.
Supporting Trust and Measurable Outcomes
By reducing manual handoffs and standardizing response flows, BotPenguin helps address common adoption barriers, including slow response cycles and inconsistent execution.
The result is AI that operates within established processes and delivers consistent, measurable outcomes across industrial environments.
Final Thoughts
AI is no longer an experimental layer in industrial automation. It is becoming a practical requirement for manufacturers dealing with variability, cost pressure, and performance limits.
The real shift is not replacing existing systems, but enhancing them with intelligence that can learn, predict, and support better decisions.
When applied with the right use cases, integration approach, and governance, AI delivers measurable improvements in reliability, efficiency, and control. Success depends on moving beyond isolated insights and embedding AI into operational workflows where actions actually happen.
Manufacturers that treat AI as an operational capability rather than a technology upgrade are better positioned to achieve consistent results and long-term competitive advantage.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What Makes AI in Industrial Automation Different From Traditional Analytics Tools
AI in industrial automation learns continuously from operational data, while traditional analytics rely on static reports and require manual interpretation.
What is the Long-Term Impact of AI Integration in Industrial Automation?
The impact of AI integration in industrial automation includes higher operational resilience, faster adaptation to change, and stronger alignment between production and business outcomes.
Which AI Applications in Industrial Automation Are Easiest to Scale
AI applications in industrial automation that use centralized data and standardized workflows are easier to scale across multiple plants.
What Are the Less Obvious Benefits of AI in Industrial Automation?
Benefits of AI in industrial automation include consistent decision-making, reduced reliance on individual expertise, and improved operational predictability.
How Does BotPenguin Support AI in Industrial Automation Without Replacing Existing Systems?
BotPenguin connects AI insights to operational workflows, enabling alerts, follow-ups, and controlled human escalation within existing tools, without replacing automation infrastructure.