What is Weak AI?
Weak AI, also known as Narrow AI, is a sub-field of Artificial Intelligence (AI) that is focused on building intelligent machines that can perform specific tasks.
It is designed to solve a specific problem or perform a particular task, such as playing a game, recognizing images, responding to voice commands, or translating languages.
Applications of Weak AI
Weak AI is used in a variety of applications, including virtual assistants, chatbots, image and object recognition, and sentiment analysis.
It is used to automate routine tasks, make predictions based on data, and provide solutions for complex problems.
Weak AI vs Strong AI
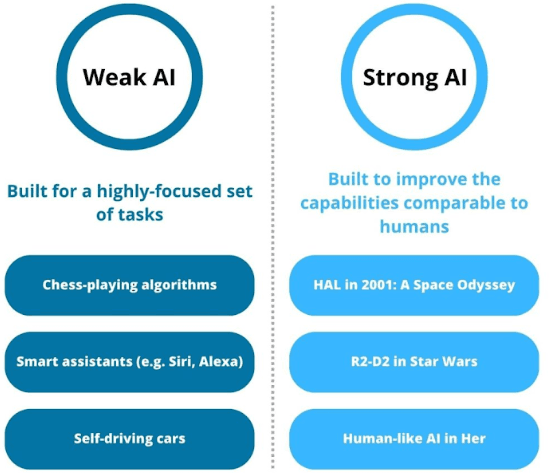
Unlike Strong AI, which is capable of performing any intellectual task that a human could do, Weak AI is designed to perform narrow, specific tasks.
While Weak AI can be highly efficient and accurate in carrying out specific tasks, it does not possess general intelligence or consciousness.
Why is Weak AI important?
Weak AI has become increasingly important in the technology industry because of its ability to automate routine tasks, process large amounts of data, and provide intelligent solutions to complex problems.
Advantages of Weak AI
Some advantages of Weak AI include:
- Increased efficiency and accuracy in performing specific tasks.
- Can be used to automate routine and repetitive tasks, freeing up time for more complex work.
- Can process large amounts of data and provide insights for decision-making.
- Can help to improve customer service by providing 24/7 assistance through chatbots and virtual assistants.
Who is Using Weak AI?
Many industries are currently using Weak AI to solve specific problems or improve their operations.
Industries currently using Weak AI
Some industries that are currently using Weak AI include:
- Healthcare: Using sentiment analysis to monitor patient feedback and providing virtual assistants to answer common health questions.
- Retail: Using chatbots to assist customers with order tracking and product recommendations.
- Finance: Using machine learning algorithms to detect fraud and automate routine financial tasks.
- Manufacturing: Using robotic process automation to automate assembly lines and reduce errors.
When is Weak AI useful?
Weak AI is useful in a variety of scenarios, from automating routine tasks to providing intelligent solutions to complex problems.
Scenarios where Weak AI is useful
Weak AI is useful in scenarios such as:
- Routine and repetitive tasks.
- Data processing and analysis.
- Customer service and support.
- Image and object recognition.
- Language translation and voice recognition.
Limitations of Weak AI
There are also limitations to Weak AI, such as:
- Limited in the types of tasks it can perform.
- Vulnerable to bias and faulty algorithms.
- Not capable of general intelligence or creativity.
- May require constant updates and maintenance.
How Does Weak AI Work?
Weak AI works through a combination of machine learning algorithms, natural language processing, and expert systems.
Machine Learning Algorithms
Machine learning algorithms enable Weak AI to learn from data and improve its performance over time.
By analyzing patterns and making predictions based on that data, Weak AI can provide intelligent solutions to specific tasks.
Natural Language Processing
Natural language processing allows Weak AI to understand human language and respond appropriately.
By using algorithms to analyze language patterns, Weak AI can recognize speech, translate languages, and respond to voice commands.
Expert Systems
Expert systems are a type of Weak AI that use rules and logic to solve specific problems.
By incorporating human expertise and knowledge into algorithms, expert systems can provide intelligent solutions to complex problems.
Types of Weak AI
There are several different types of Weak AI, each designed to perform specific tasks.
Virtual Assistants
Virtual assistants, such as Siri and Alexa, are designed to understand voice commands and respond to questions. They can provide information, set reminders, and perform simple tasks.
Chatbots
Chatbots are used in customer service and support to answer common questions and automate routine tasks. They are designed to simulate conversation and provide solutions to problems.
Image and Object Recognition
Image and object recognition is used to identify and classify images. It is used in applications such as facial recognition, self-driving cars, and security systems.
Sentiment Analysis
Sentiment analysis is used to analyze customer feedback and track brand reputation. It can be used to identify customer sentiment and provide solutions to improve customer satisfaction.
Key Players in Weak AI
Several companies are currently developing Weak AI solutions and contributing to advancements in the field.
Companies that are developing Weak AI
Some notable companies developing Weak AI include:
- IBM Watson
- Google AI
- Amazon Web Services (AWS)
- Microsoft AI
Future of Weak AI
The future of Weak AI is expected to be marked by continued advancements and growth.
Current Trends in Weak AI
Some current trends in Weak AI include:
- Increased focus on explainable AI to increase transparency and reduce bias.
- Growing use of AI in healthcare and medicine.
- Improved Natural Language Processing capabilities.
Predictions on the future of Weak AI
Some predictions for the future of Weak AI include:
- Increased use of AI to automate routine tasks and improve efficiency.
- Enhanced accuracy in image and object recognition.
- Continued development of machine learning algorithms.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is Weak AI?
Weak AI refers to artificial intelligence systems that are designed to perform specific tasks, such as playing chess or recognizing speech, but they do not possess human-like intelligence.
What is Strong AI?
Strong AI, also known as Artificial General Intelligence (AGI), refers to AI systems with human-like intelligence.
These systems possess the ability to understand, learn, and apply knowledge across diverse domains, enabling them to autonomously perform tasks and solve problems in a wide range of contexts.
How is Weak AI different from Strong AI?
While Weak AI focuses on narrow tasks, Strong AI aims to develop human-level intelligence. Weak AI applications excel at specific tasks, whereas Strong AI works towards mimicking human reasoning and problem-solving abilities.
What are some examples of Weak AI?
Some popular examples of Weak AI include virtual assistants like Siri and Alexa, spam filters, recommendation systems, and image recognition software.
Can Weak AI learn and improve over time?
Yes, Weak AI can learn and improve through machine learning techniques. By analyzing data and adjusting its algorithms, Weak AI systems can enhance their accuracy and performance.
Is Weak AI a threat to humanity?
Unlike Strong AI, Weak AI does not possess general intelligence, so the risk of it becoming a threat is quite low. Its purpose is to assist and augment human capabilities, rather than replace humans altogether.