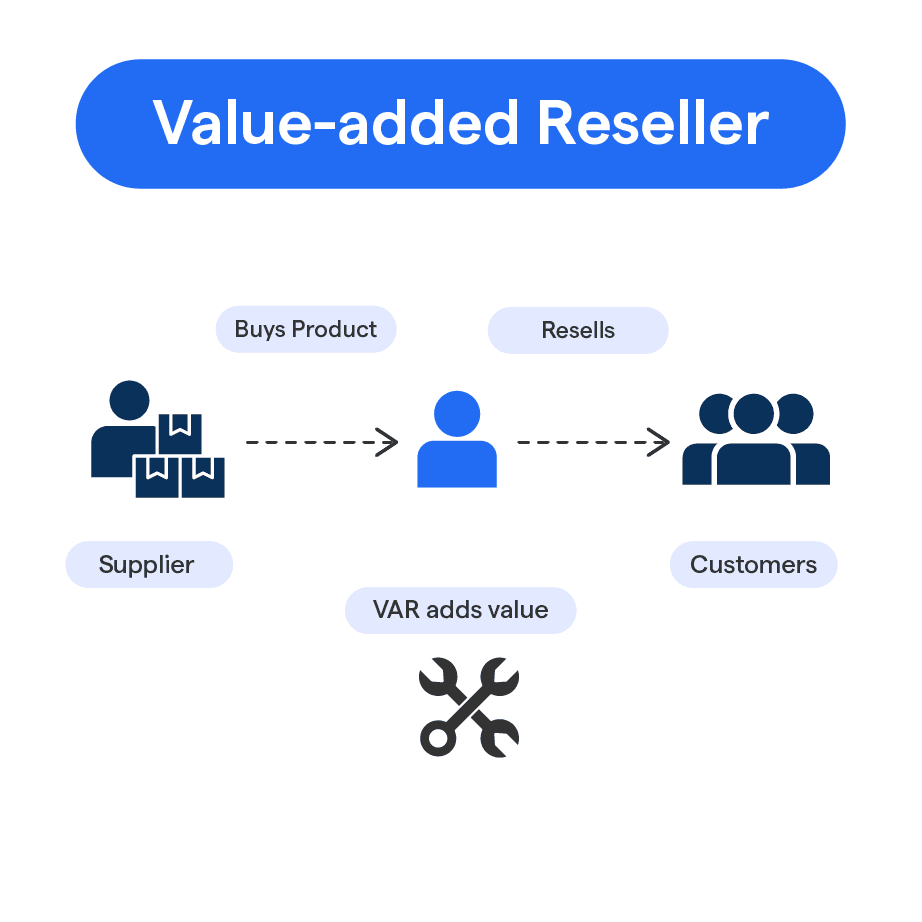
What is a Value-Added Reseller?
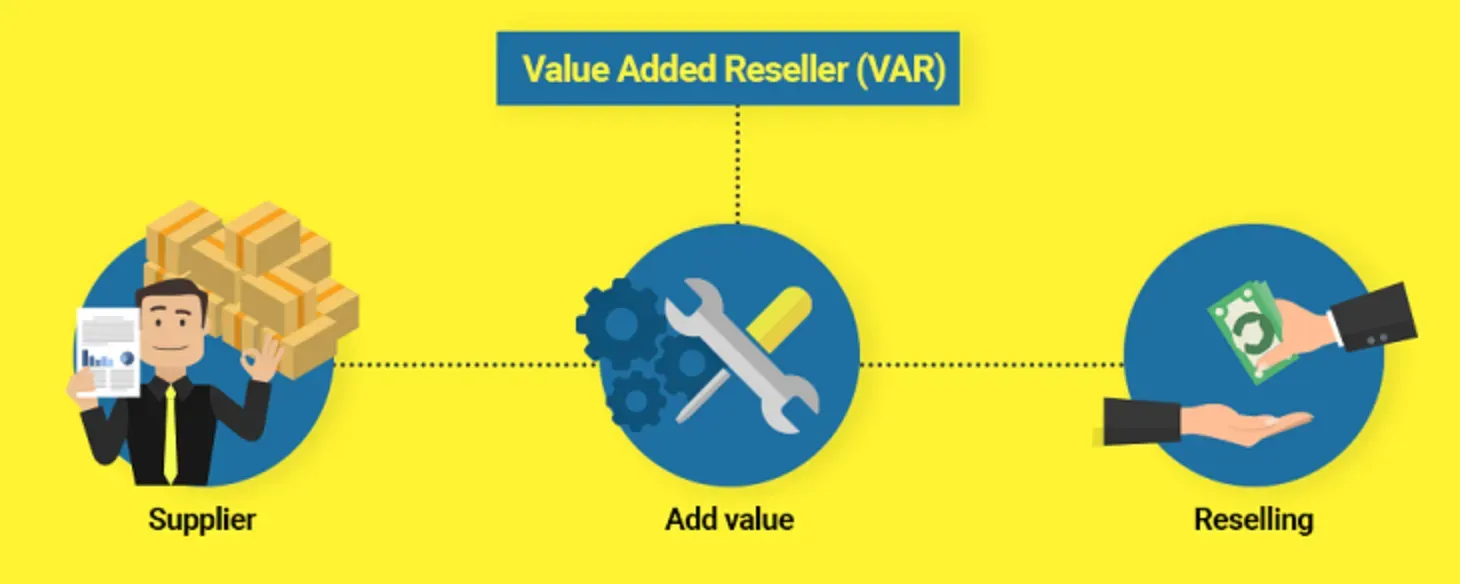
Often known by the acronym VAR, a Value-Added Reseller is a company that procures products, especially software and hardware, from a provider, enhances them by adding customized features or services, and then resells the enriched package as an end-to-end solution.
How does a VAR Work?
A VAR buys a product or a suite of products, customizes it by blending additional features, services, or integrations, and re-offers the value-added package to customers. The added value justifies a higher selling price and can be more appealing to customers seeking comprehensive solutions.
Importance of a Value-Added Reseller
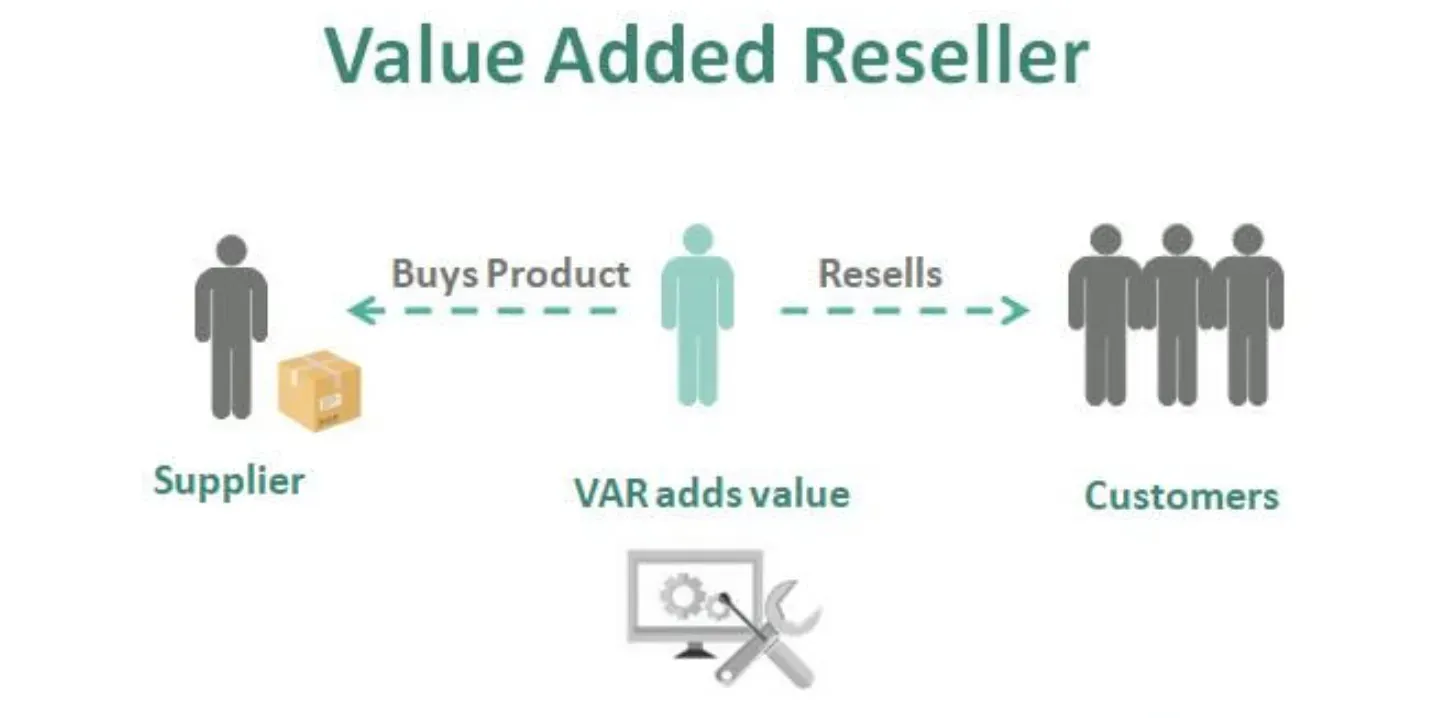
To understand why VARs matter, let's explore their relevance and benefits.
Value-Added Offerings
The added value offered by a VAR brings a personalized touch. They take the generic product and modify it to better suit the specific needs of a customer. This customization allows businesses to purchase a solution that's a closer fit to their requirements.
Filling Market Gaps
VARs fill gaps in the market by catering to niche demands that manufacturers are unable to fulfill on a mass scale. They, therefore, extend the original manufacturer's reach to clients that they might otherwise miss.
VAR Revenue Generation
Getting a grip on how a VAR generates its income will provide insight into its business model.
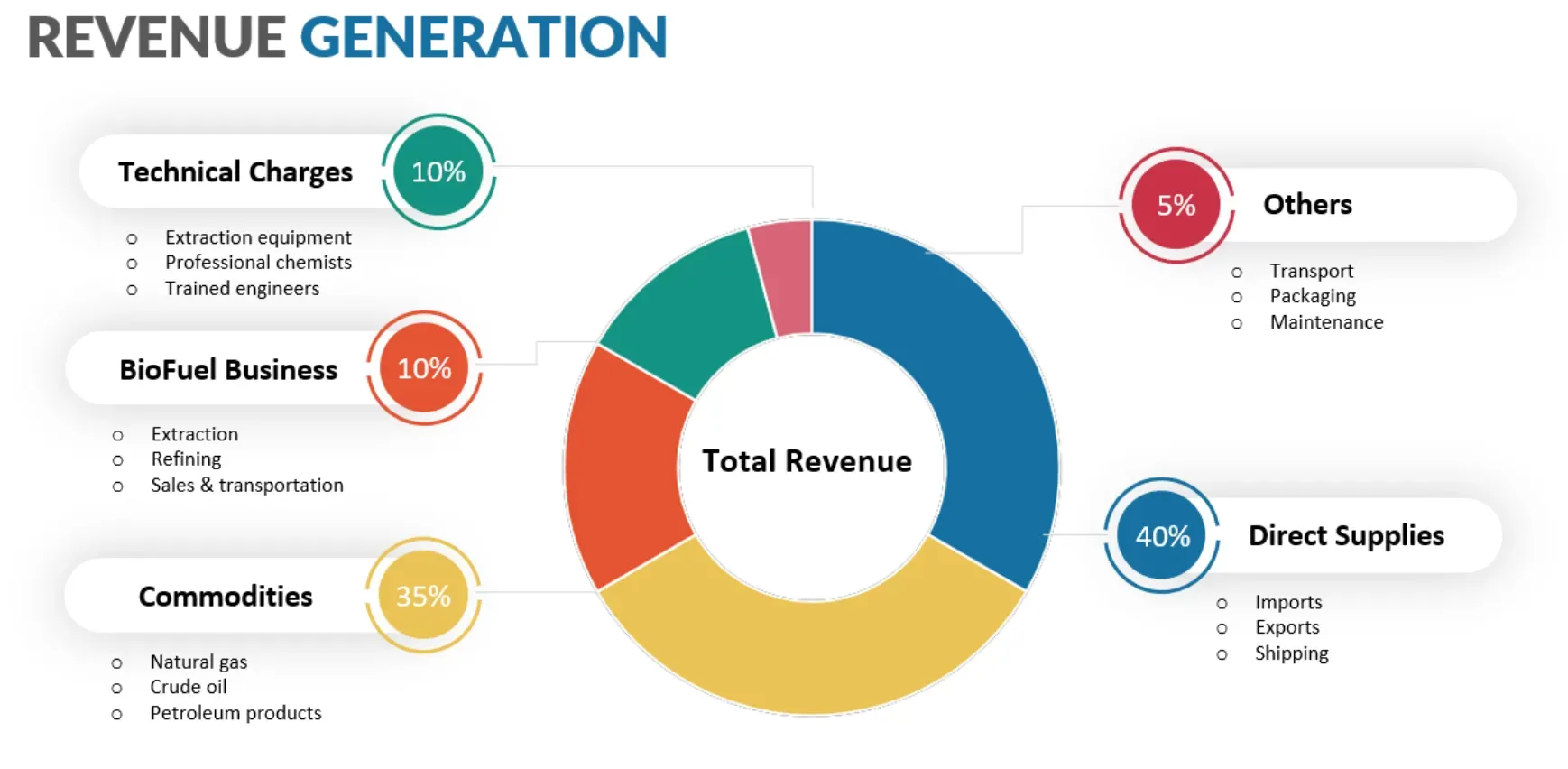
Sale of Products and Services
Although they revamp the original product, the sale of this product, now augmented with additional features or services, is the primary revenue source for VARs. This business model is what classifies them as resellers.
Ongoing Support and Maintenance
Apart from product sales, VARs often provide ongoing support and maintenance to customers - another significant revenue source. The proactive assistance offered helps build long-lasting customer relationships, leading to continuous revenue streams.
Different Types of Value-Added Resellers
There are different types of VARs tailored to various sectors. Let's look into a few.
Software VARs
Software VARs specialize in acquiring software products from developers before customizing and combining them with other software, peripherals, and even hardware to form a complete solution that appeals to a targeted customer base.
Hardware VARs
Hardware VARs typically work with computer hardware like servers, storage systems, or networking equipment. They can offer tailored hardware systems with industry-specific software applications, turning them into fully customized solutions for businesses in specific sectors.
Relationships in the VAR Ecosystem
The VAR ecosystem involves multiple parties, each playing a critical role.

VARs and Original Equipment Manufacturers (OEMs)
The relationship between VARs and OEMs is symbiotic. VARs boost the sales of OEMs by reaching segments the OEM may not directly target. Meanwhile, the VAR relies on the OEMs' products as the primary ingredient in their value-added package.
VARs and Their Customers
Customer relationships hallmark the VAR business model. VARs work closely with customers to create tailored solutions. Their success hinges on how well they cater to their customers' requirements and provide appropriate post-sales support.
Understanding the VAR Agreement
Participation in the VAR world is guided by specific agreements.
VAR and OEM Agreement
A VAR agreement between a VAR and OEM outlines important aspects like the product's pricing and minimum order quantity, payment terms, delivery details, and after-sales support. These agreements are legally binding and stipulate the responsibilities of both parties.
End-User Licensing Agreement (EULA)
In the world of software VARs, an End-User Licensing Agreement (EULA) governs the consumer’s rights regarding the use of the software. This EULA is typically inclusive of the additional features or services that the VAR adds.
Challenges Faced by a VAR
While it all might seem rosy, being a VAR comes with its share of challenges.
Stiff Competition
The VAR market is becoming increasingly competitive. To stay ahead, VARs need to consistently create tailored solutions with significant value-adds to stand out in the crowded marketplace.
Technical Complexity
As tech evolves at a lightning pace, VARs need to keep up with the latest technologies to incorporate them into their offerings. Balancing this need with running the business can be a tough juggle.
Future of Value-Added Resellers

The future of the VAR industry is dynamic and riding on the wave of tech advancements.
Technology Advancements
VARs are gearing up to incorporate technology advancements like AI and machine learning into their offerings. They're also moving towards cloud-based solutions, harnessing the power of cloud computing to elevate their services.
Expansion into Consultancy Services
Many VARs are expanding their offerings and stepping into consultancy roles. They're not only providing customized solutions but also advising clients on the most suitable tech solutions for their needs.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is a value added reseller?
A value-added reseller (VAR) is a company or business that purchases products or services from a manufacturer or vendor and enhances their value by adding additional features, services, or customization before reselling them to end customers. VARs play a role in distributing and supporting technology products and solutions.
What is the role of a value-added reseller (VAR) in the supply chain?
VARs act as intermediaries between manufacturers and end customers, adding value to products or services through customization, integration, training, and support before offering them to customers.
How do VARs generate revenue?
VARs generate revenue through product sales, value-added services, maintenance contracts, consulting fees, and training programs.
What are the benefits of partnering with a VAR?
Partnering with a VAR provides cost savings, access to expertise, enhanced customer experience, increased efficiency, and flexibility and scalability in meeting specific business needs.
How should businesses choose the right VAR partner?
Businesses should consider factors like industry expertise, product knowledge, track record, market reach, and cultural alignment when selecting a VAR partner.
How can businesses foster a successful VAR partnership?
Building strong relationships, maintaining open communication, and setting clear expectations are key to a successful VAR partnership. Regular collaboration, joint marketing efforts, and continuous evaluation of performance metrics are also important.