What is Symbolic Interactionism?
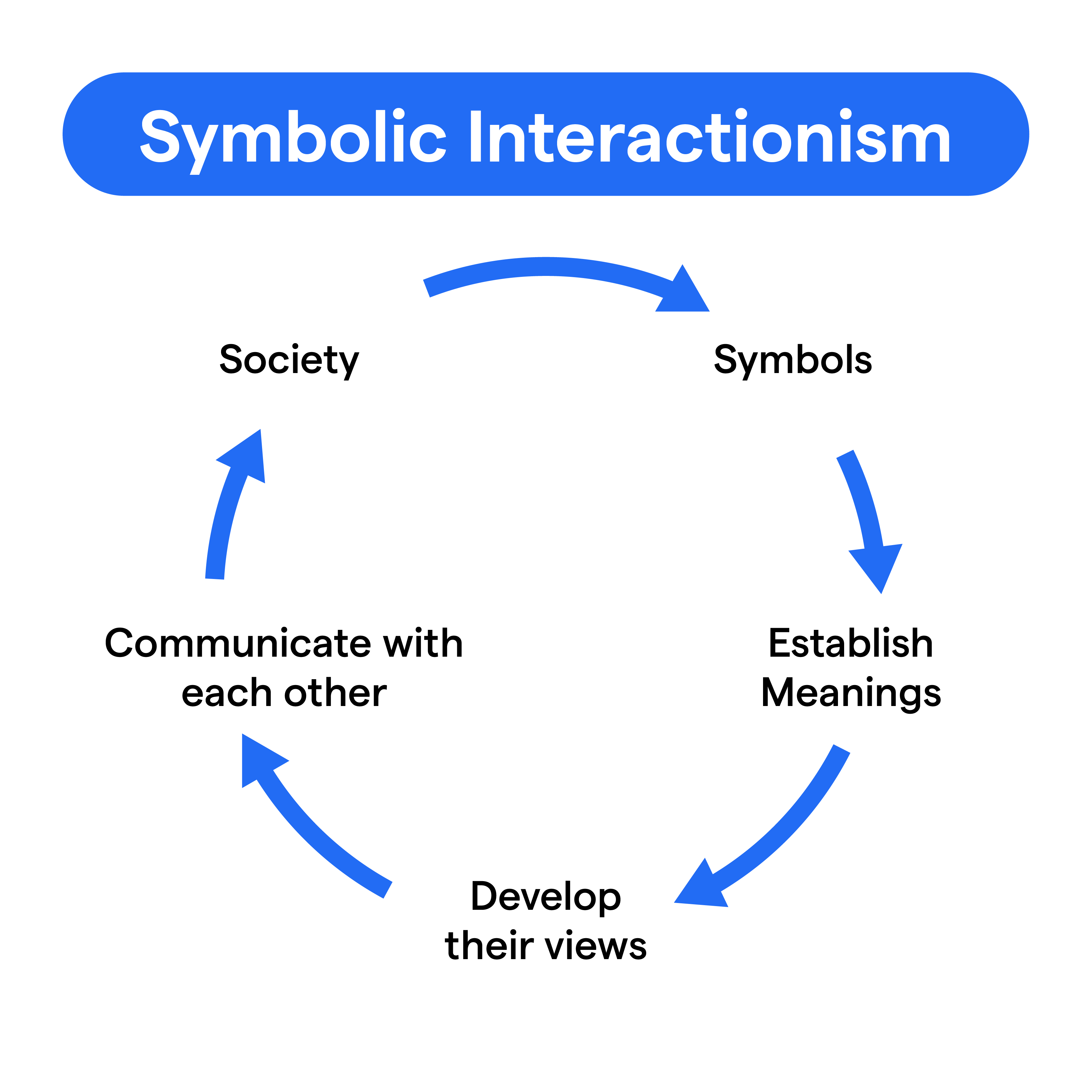
Symbolic Interactionism is a theoretical framework that conceptualizes society as a network of interpersonal relationships formed through communication and interpretation of symbols.
Key Components
Symbols and meanings are at the heart of Symbolic Interactionism psychology. It places importance on how individuals interpret and attach meanings to these symbols and base their behaviors upon them.
Founding Figures
George Herbert Mead and Herbert Blumer, among a few others, were instrumental in the development and propagation of Symbolic Interactionism.
Basic Assumptions
Symbolic Interactionism psychology assumes that individuals act based on the meanings they associate with people and things around them.
These meanings originate from social interactions, and these meanings are modified through an interpretive process
Conceptual Understanding
Symbolic Interactionism psychology proposes that individuals construct their realities through symbolic interactions within the society, and these interaction patterns shape the society as a whole.
Why is Symbolic Interactionism Important?
Symbolic Interactionism provides an insightful lens into the intricate dynamics of society and human behavior.
- Role in Sociological Understanding: Symbolic interactionism perspective is known to offer a unique perspective on how society is shaped by individual interactions and the interpretation of symbols.
- In Research and Analysis: Symbolic interactionism perspective is used in sociological research and analysis. Thus providing detailed insights into social behavior and societal structures.
- In Understanding Human Behavior: Symbolic interactionism perspective sheds light on human behavior by highlighting how subjective meanings and interpretations guide actions.
- Unveiling Micro-level Interactions: Symbolic interactionism psychology emphasizes the importance of micro-level interactions in the formation and progression of bigger societal structures.
- Highlighting Social Change: Symbolic interactionism perspective provides a framework to analyze social change that emerges from shifts in symbolic interactions and interpretations.
When is Symbolic Interactionism Used?

Symbolic Interactionism offers a valuable tool to analyze social behavior, interactions, and structures across varied contexts.
Sociological Research
Symbolic interactionism psychology is used when conducting sociological research that seeks to understand social behaviors, interactions, and societal structures from the perspective of individuals involved.
Data Interpretation

In qualitative research, Symbolic interactionism perspective assists in interpreting data by focusing on the meanings that individuals attach to their actions and the symbols around them.
Therapeutic Interventions
Counselors and therapists use Symbolic interactionism psychology to understand the subjective experiences of individuals and the meanings they attach to key symbols in their life.
Policy Making
Symbolic interactionism perspective can guide policy making by unpacking how cumulative symbolic interactions contribute to macro-level societal phenomena.
Education and Learning
In education, Symbolic interactionism perspective is used to understand the classroom dynamics, teacher-student interactions, and the overall learning process.
Where is Symbolic Interactionism Applied?
There are many symbolic interactionism examples present in various fields owing to its focus on individual experiences and interactive dynamics.
- Sociological Analysis: One of the Symbolic interactionism examples is sociological analysis. It is predominantly applied in sociology to understand societal structures, norms, and behaviors.
- Mental Health: Symbolic interactionism examples show a pivotal role in therapeutic interventions and mental health support, providing insights into patients' subjective experiences.
- Social and Public Policy: In social and public policies, symbolic interactionism examples are in the formulation of an understanding of society's intricate dynamics and interactions.
- Business and Marketing: Symbolic interactionism examples contribute to the realm of business and marketing, throwing light on consumer behavior and branding strategies.
- Education: Symbolic interactionism examples in education shows the framework to interpret classroom dynamics, pedagogical practices, and the learning process.
How Does Symbolic Interactionism Work?
Symbolic Interactionism operates on the conviction that individuals, through their interpretations and symbol-based interactions, play an active role in constructing their social realities.
- Interpretation: The first step involves individuals interpreting the symbols around them based on their experiences and societal orientations.
- Meaning: Through the interpretative process, meaning is attached to these symbols which then guide the individual's behavior and actions.
- Interactions: These meanings form the basis of interpersonal interactions and communications, further reinforcing or modifying the symbols and associated meanings.
- Social Construction: This constant interplay of symbols, meanings and interactions leads to the construction of social realities and societal structures.
- Constant Change: Symbolic Interactionism assumes a dynamic social reality, susceptible to change with the shifting patterns of symbolic interactions and meanings.
Cognitive and Sociological Aspects
The understanding of Symbolic interactionism perspective includes cognitive and sociological elements, grounding it in both individual and societal contexts.
- Cognitive Processes Involved: Symbolic Interactionism involves cognitive processes such as perception, interpretation and memory.
- Societal Influence: The societal structure and norms significantly influence individuals' perceptions and interpretations of symbols.
- Individual Impact on Society: Individuals, through their behavior based on symbolic interpretations, impact and shape the societal structure.
- Role of Language: Language, as a system of symbols, plays a key role in communication and social interaction in Symbolic Interactionism.
- Importance of Context: Context plays a cardinal role in the interpretation of symbols and meanings in Symbolic Interactionism, contributing to the diversity of social behavior and structures.
Role of Symbolic Interactionism in Qualitative Research
Symbolic interactionism psychology forms a robust base for qualitative research, fostering an in-depth exploration of social phenomena.
Guiding Framework
Symbolic interactionism psychology serves as a guiding framework in qualitative research, shaping the research questions, design, data collection and analysis processes.
Focus on Meanings
Symbolic interactionism allows researchers to delve deep into the meanings individuals attach to their behaviors, interactions and environments.
Understanding Context
Symbolic Interactionism emphasizes the role of context in shaping individuals' interpretations and interactions, thus enriching data analysis in qualitative research.
Exploration of Social Phenomena
Symbolic interactionism fosters a holistic understanding of social phenomena by enabling an exploration of individual experiences and micro-level interactions that contribute to the larger societal structures.
Challenge of Subjectivity
While Symbolic Interactionism enriches qualitative research, the interpretive, subjective nature of meanings can pose challenges in terms of validity and bias control in research.
Recent Developments and Future Trends
The field of Symbolic Interactionism continues to evolve with fresh research insights and methodological advancements.
Integration with Other Theories
Recent trends show the integration of Symbolic Interactionism with other sociological theories to garner a more multi-dimensional understanding of social phenomena.
Advancements in Research Methodology
Methodological advancements, such as digital ethnography or online observations, are being incorporated in Symbolic Interactionism research.
Diverse Applications
Symbolic Interactionism is being applied in new areas, including digital communications, online communities, environmental studies, and health research.
Addressing Global Issues
Symbolic Interactionism is being utilized to understand and address pressing global issues like climate change, social inequality and healthcare disparities.
Inclusion and Diversity
An increased focus on understanding and representing diverse experiences and identities is shaping future trends in Symbolic Interactionism research.
Best Practices in Symbolic Interactionism Research
To effectively use Symbolic Interactionism in research, the following best practices are crucial:
Clear Conceptualization
- Define the research problem, questions and objectives within the framework of Symbolic Interactionism.
- Ensure the research design and methods used are aligned with the theoretical framework.
Deeper Engagement
- Build rapport and trust with participants to encourage open and honest sharing of experiences and meanings.
- Use methods like in-depth interviews, immersive observations, and participatory approaches to explore participants' symbolic worlds.
Contextual Understanding
- Recognize the broader social, economic, cultural, and historical context of participants' lives to better understand their interpretations.
- Include this contextual understanding in data analysis to reveal how it shapes symbolic meanings and interactions.
Reflective Analysis
- Approach data analysis with a reflective mindset, being open to questioning, revisiting, and reinterpreting meanings and patterns.
- Use a combination of inductive and deductive data analysis techniques to enhance the rigor and comprehensiveness.
Ethical Research
- Adhere to ethical guidelines throughout the research process, safeguarding participants' privacy, confidentiality, and informed consent.
- Be sensitive to the power dynamics and vulnerability of participants, ensuring respectful and responsible engagement.
Challenges in Symbolic Interactionism Research
Applying Symbolic Interactionism in research can entail some challenges that demand adept management:
Subjective Bias
- Controlling researchers' subjective bias is challenging due to the interpretative nature of Symbolic Interactionism.
- Maintaining reflexivity and implementing strategies like peer debriefing and member checks can help address this issue.
Lack of Universality
- The context-specific nature of meanings and interpretations in Symbolic Interactionism limits the universality and transferability of research findings.
- Employing techniques like thick description and purposive sampling can enhance the transferability of research outcomes.
Complex Analysis
- Qualitative data analysis within the framework of Symbolic Interactionism involves intricate interpretations of meanings and symbols.
- Researchers need to be vigilant and thorough in their analyses, ensuring the results accurately represent participants' perspectives.
Ethical Concerns
- Navigating ethical issues in the exploration of personal and sensitive areas of participants' lives can be challenging.
- Adhering to professional codes of ethics, obtaining consent, and constantly monitoring potential ethical dilemmas are essential.
Time and Resources
- Symbolic Interactionism-based research can be resource-intensive and time-consuming because of the depth and detail of data collection and analysis.
- Researchers must carefully plan their research timeline and budget to accommodate these demands.
Examples of Symbolic Interactionism in Research
Below are three illustrative Symbolic interactionism examples of research studies conducted using the Symbolic Interactionism framework:
Understanding Stigma Associated with Mental Illness
The first Symbolic interactionism examples is understanding stigma associated with mental illness.
- Objective: To explore the experiences of individuals living with mental illness and understand the meanings they ascribe to the stigma surrounding mental illness.
- Methods: In-depth interviews, participant observations, and document analysis of online forums and support groups were employed to gather rich data on individuals' experiences, interactions, and interpretations.
- Outcome: The study revealed the complex and varied ways individuals interpret and navigate the stigma associated with mental illness, resulting in different patterns of interaction, disclosure, and help-seeking behavior.
Examining the Role of Social Media in the Construction of Identity
Below are three illustrative Symbolic interactionism examples of research studies conducted using the Symbolic Interactionism framework
- Objective: To investigate how young adults construct and negotiate their identities using social media platforms as a site for symbolic interaction.
- Methods: Virtual ethnography, content analysis of social media posts, and focus group discussions were utilized to uncover the meanings, symbols, and interactions enacted on social media.
- Outcome: The study showcased the importance of social media as a space for identity formation and expression, highlighting the influence of digital platforms on individual and social behavior.
Teacher-Student Interactions in the Classroom
Last, symbolic interactionism examples is to showcase the teacher student interactions in the classroom.
- Objective: To explore the meanings and dynamics of teacher-student interactions in the classroom and their implications for the learning process.
- Methods: Classroom observations, semi-structured interviews with teachers and students, and analysis of learning materials were used to capture the nuances of symbolic interactions within the educational setting.
- Outcome: The study found that teacher-student interactions shaped by expectations, power dynamics, and symbols significantly impact the learning environment and the educational outcomes achieved.
Symbolic Interactionism, as a potent theoretical framework, demands meticulous attention to detail and precision in research practices.
By recognizing and addressing the associated challenges and harnessing the best practices, researchers can unlock the immense potential this perspective offers.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
How does Symbolic Interactionism impact individual behavior?
Symbolic Interactionism posits that individuals develop behaviors based on the symbols or signals they decode from their interactions with others. In a sense, our actions are a continuous response to the interpreted symbols from our social environment.
Can you give an example of Symbolic Interactionism?
Take a wedding ring, for example. In most societies, it symbolizes marital status. When people see a wedding ring, they interpret the wearer as being married and adjust their behavior or interaction towards them accordingly.
What role does Symbolic Interactionism Play in Society?
It plays a key role in maintaining societal order. Through shared symbols and meanings, members of a society learn to interpret symbols correctly, ensuring smooth social interactions and mutual understanding.
Who are the Key Theorists behind Symbolic Interactionism?
Symbolic Interactionism's foundational pillars were set by George Herbert Mead and Charles Horton Cooley. However, Herbert Blumer, a student of Mead's, is credited with coining the term 'Symbolic Interactionism'.
How does Symbolic Interactionism Relate to Socialization?
Symbolic Interactionism is foundational to socialization. Through it, individuals learn societal norms, behaviors, and roles by deciphering symbols received during interactions, helping them smoothly integrate into society.