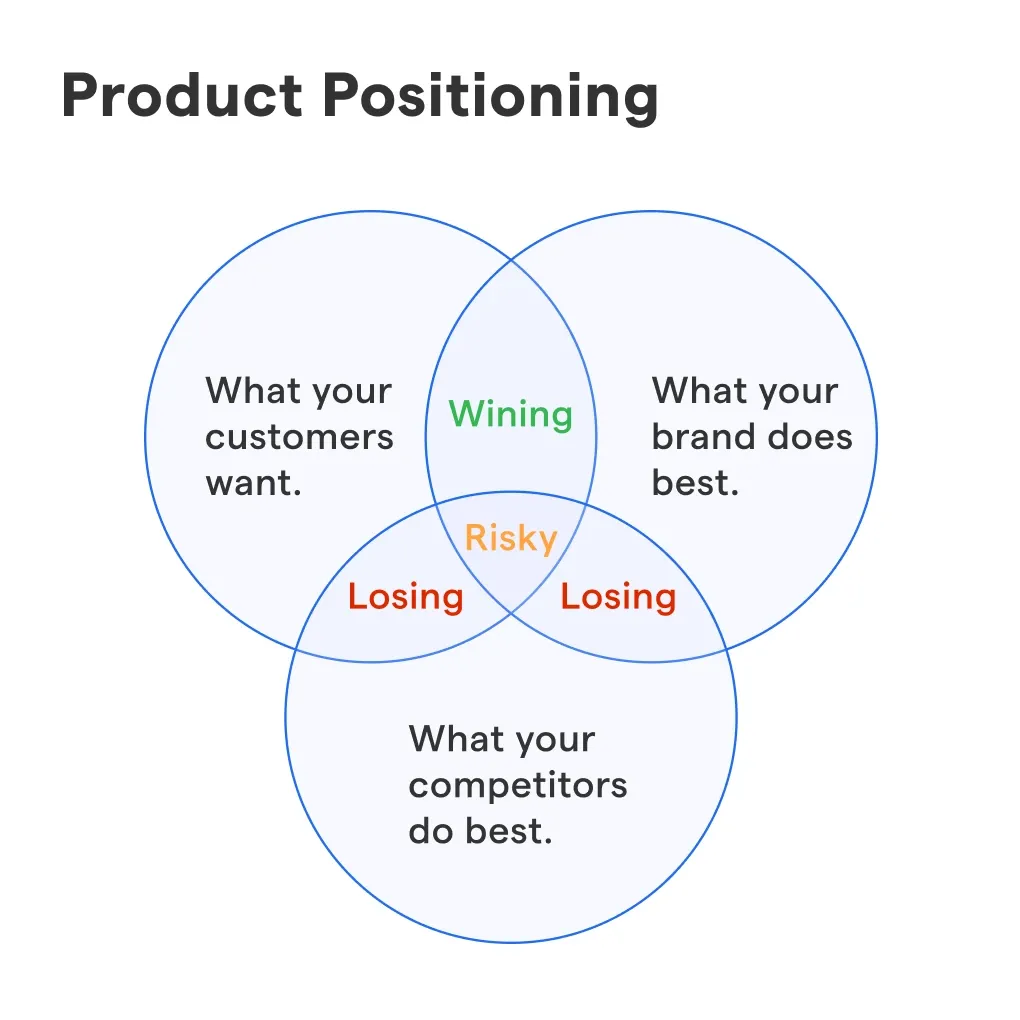
What is Product Positioning?
Product positioning refers to the marketing strategy for shaping customers' perceptions of a product or service relative to the competition.
Key Characteristics
Product positioning doesn't actually change the product—it changes how customers perceive it and where they see its place in the market.
Applications
This strategy is used in marketing campaigns, brand consulting, market research, and even product development stages.
Advantages
Product positioning enhances brand recognition, adds value to customers, and drives sales.
Limitations
Positioning wrongly can confuse customers and limit the product's appeal if not carefully executed.
Who Uses Product Positioning?
Here's a look at several types of professionals who regularly employ product positioning strategies.
Marketers
Marketers craft and execute strategies based on the product's positioning in the market.
Product Managers
Those managing products apply to position as they shape the product and its features.
Brand Strategists
These specialists use positioning to form a compelling brand narrative around products.
Sales Representatives
Sales representatives use product positioning when communicating the unique value of the product to potential customers.
Business Owners
Entrepreneurs and business owners craft product positioning as they build and scale their ventures.
Why is Product Positioning Used?
Product positioning is more than just a marketing buzzword—here's why it matters.
Standing Out in the Market
Positioning helps differentiate the product from competitors and makes it stand out in the crowd.
Driving Consumer Decisions
Well-executed positioning can influence consumers' purchasing decisions in favor of the product.
Guiding Marketing Strategy
It guides marketing and promotional campaigns, ensuring they align with the product's perceived position.
Defining Product Goals
Positioning helps in defining the goals for product development by aligning them with consumer expectations.
Ensuring Consistent Messaging
A well-defined product position ensures consistency in messaging across all marketing channels.
When is Product Positioning Used?
Knowing when to employ product positioning can make all the difference.
New Product Launches
Positioning is key when introducing a new product to the market.
Rebranding
A comprehensive rebrand often involves repositioning the product as well.
Entering New Markets
When a product is introduced to a new geographic or demographic market, its positioning may need to be adjusted.
Competitive Market
In a highly competitive market, effective product positioning can help a product stand out.
Product Updates
Significant changes or updates in the product may necessitate repositioning.
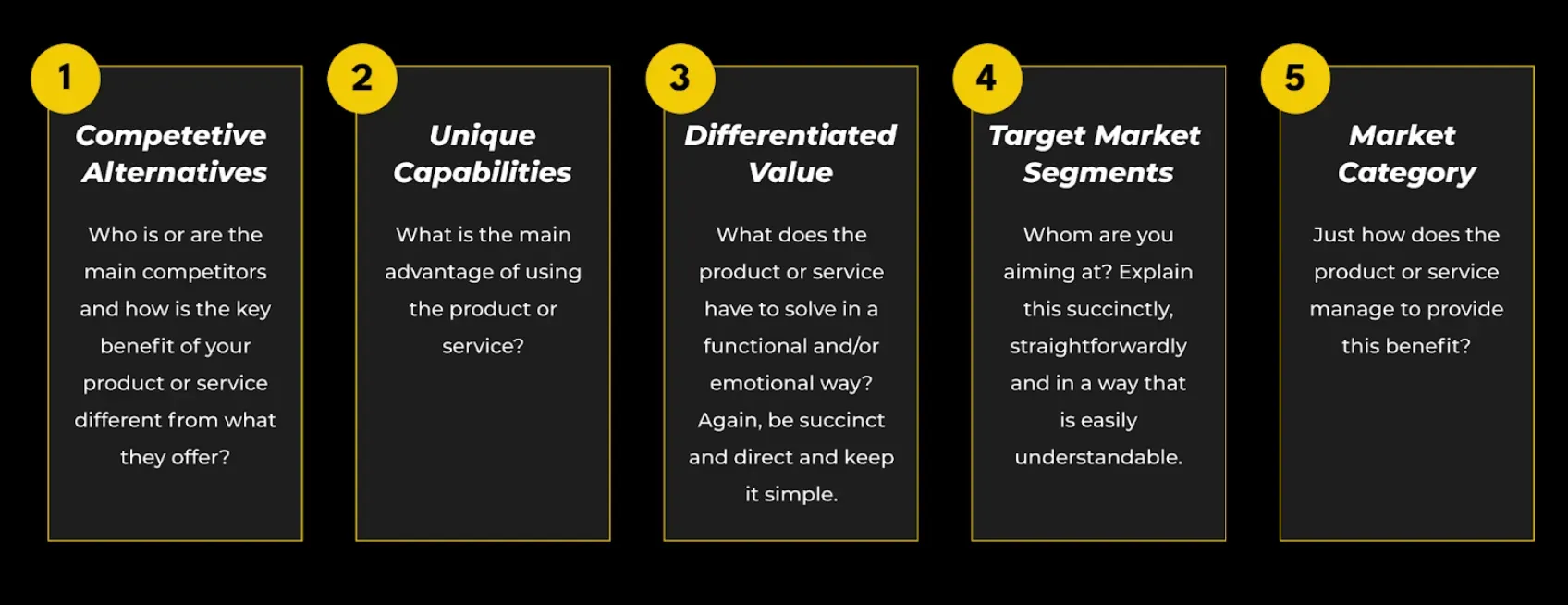
How is Product Positioning Implemented?
Now that we understand its importance, let's see how product positioning is done.
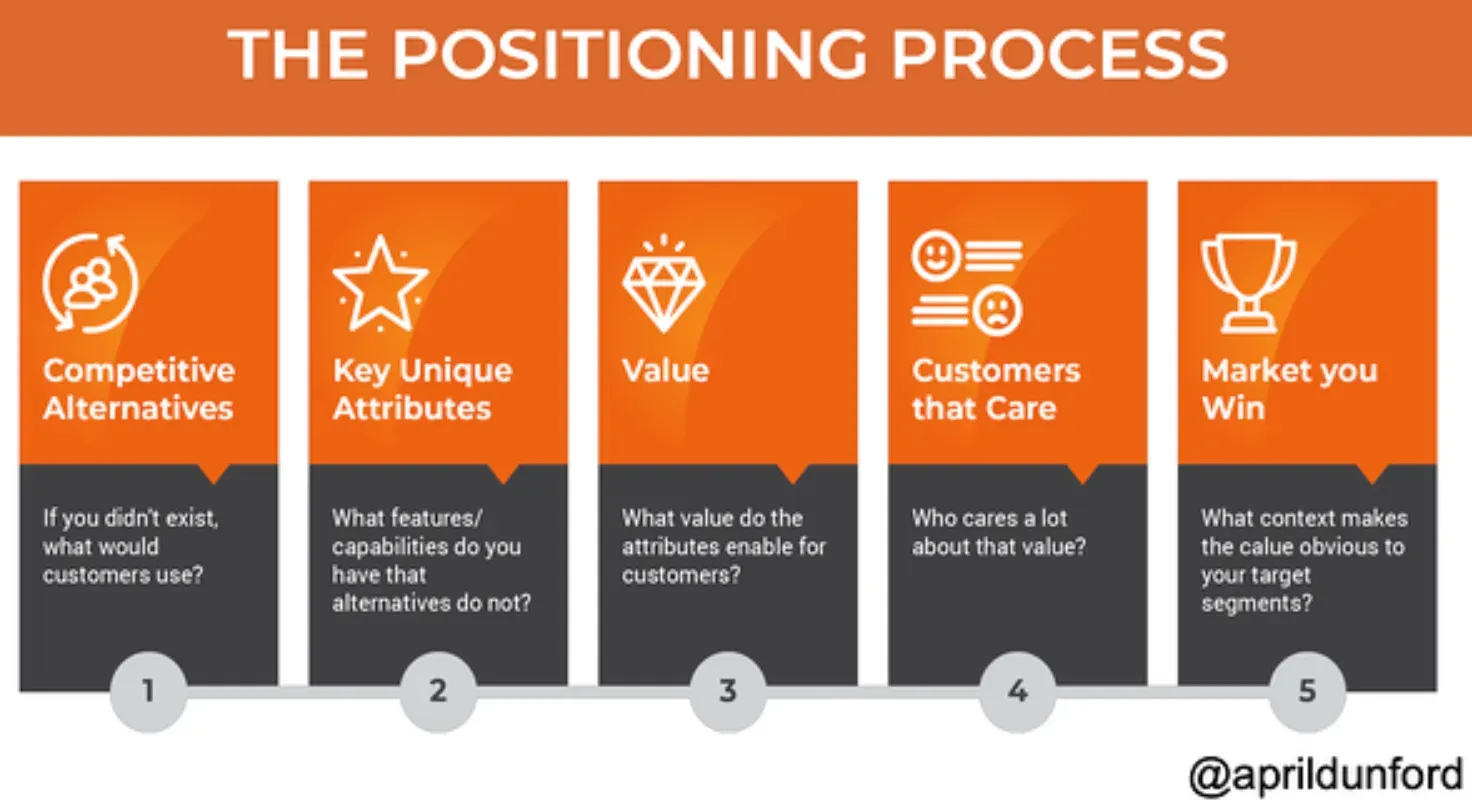
Identifying Unique Selling Proposition
This forms the crux of product positioning—the key features or benefits that set the product apart.
Defining Target Audience
Determining who the product's ideal users are is an essential step in positioning a product.
Analysing Competitors
Understanding the positioning of similar offerings in the market informs your own product's positioning.
Creating Positioning Statement
A clear, concise statement that communicates the unique value proposition of the product to its target audience.
Aligning Marketing Efforts
Reinforcing the product position through consistent messaging in marketing efforts.
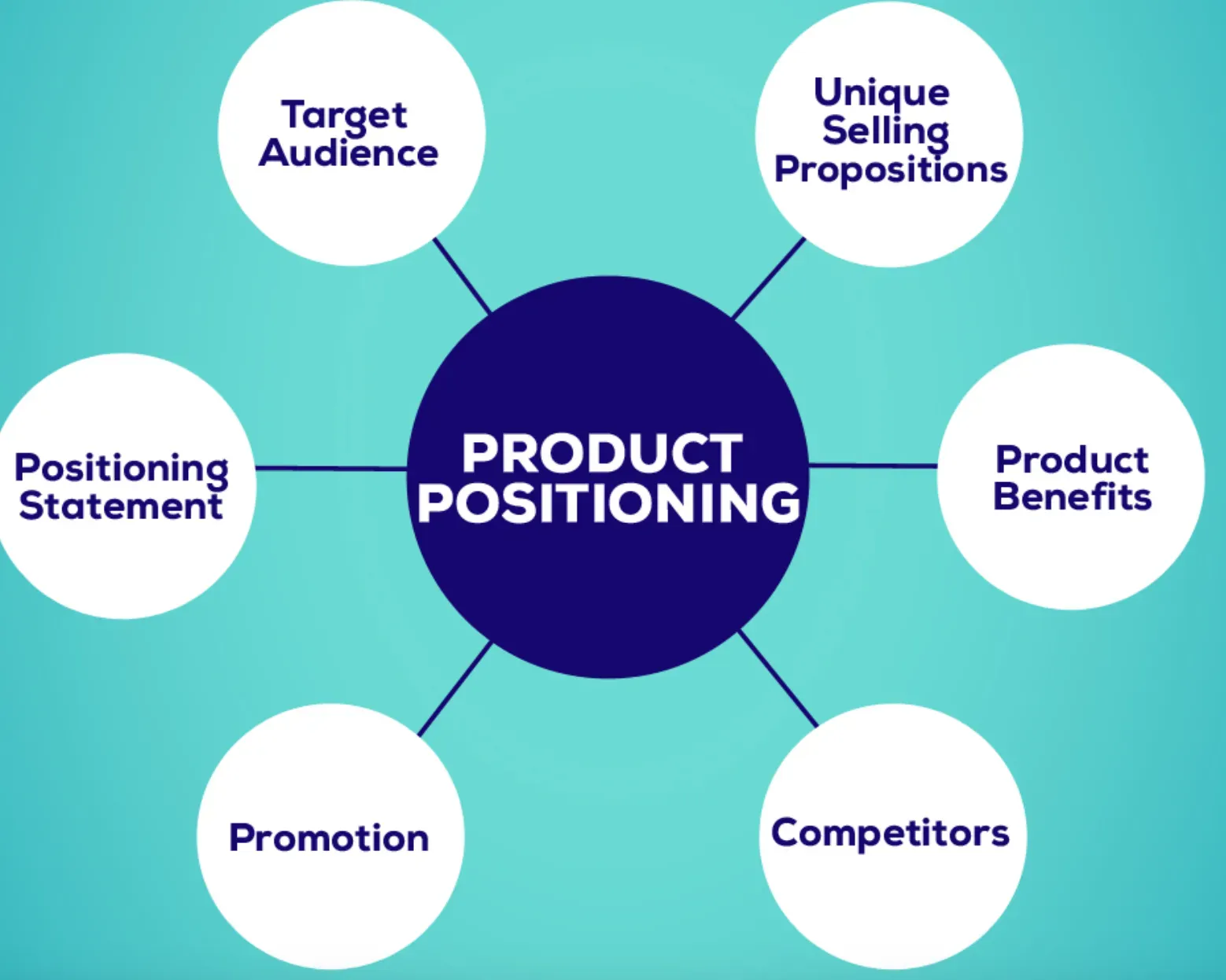
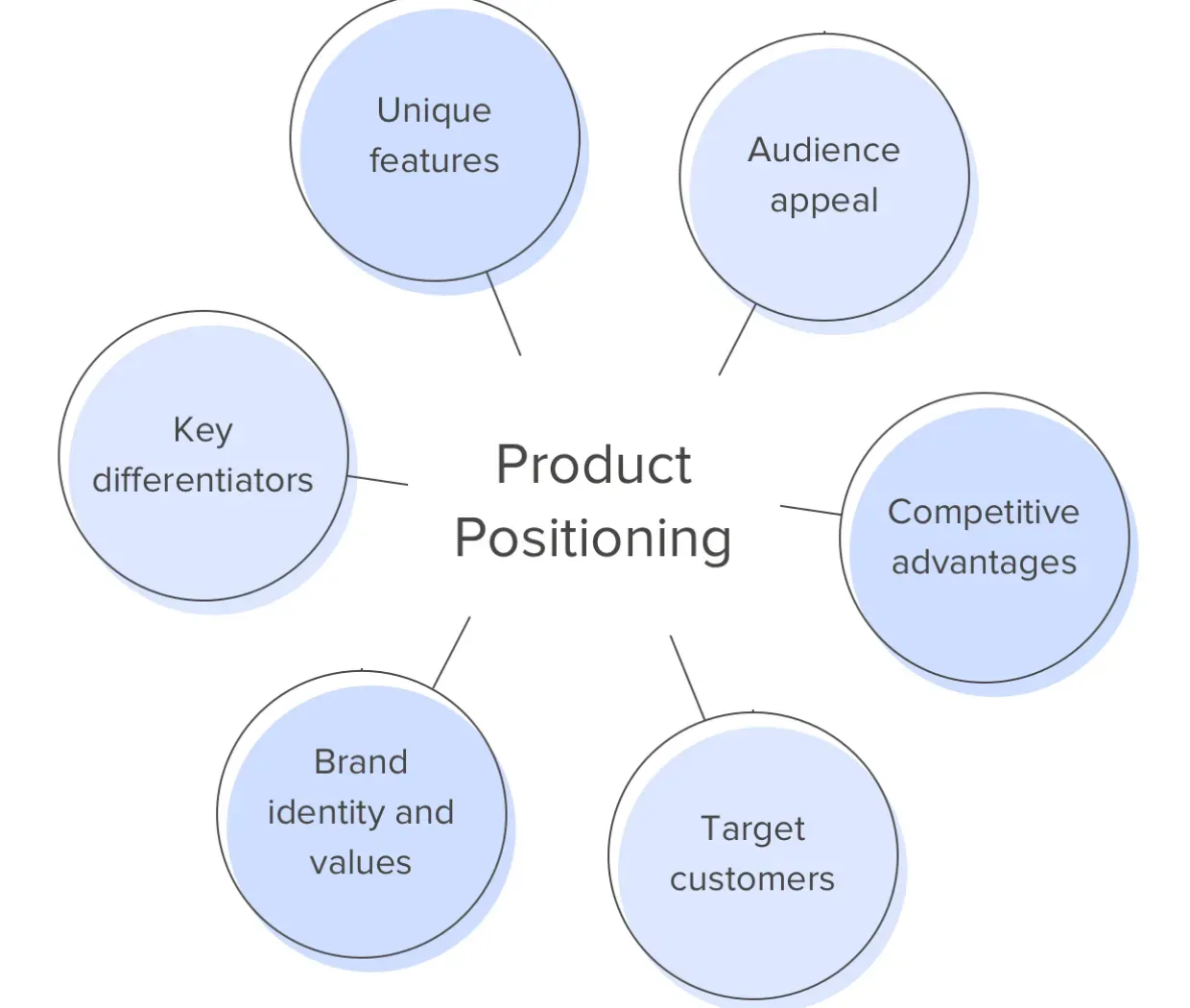
Key Components in Product Positioning
Getting familiar with the essential elements will simplify the concept of product positioning.
Value Proposition
The unique value that a product offers to consumers, is often its most distinctive characteristic.
Target Audience
The specific group of consumers that the product is designed and marketed for.
Competitive Landscape
Understanding the market landscape and where each competitor is positioned related to the product.
Product Features and Benefits
The key features of the product and the benefits they offer to the consumers form a crucial part of positioning.
Pricing Strategy
The product's price point plays a significant role in its positioning, signaling its value and quality to customers.
Types of Product Positioning
Let's shed some light on the different types of product positioning we come across in the real world.
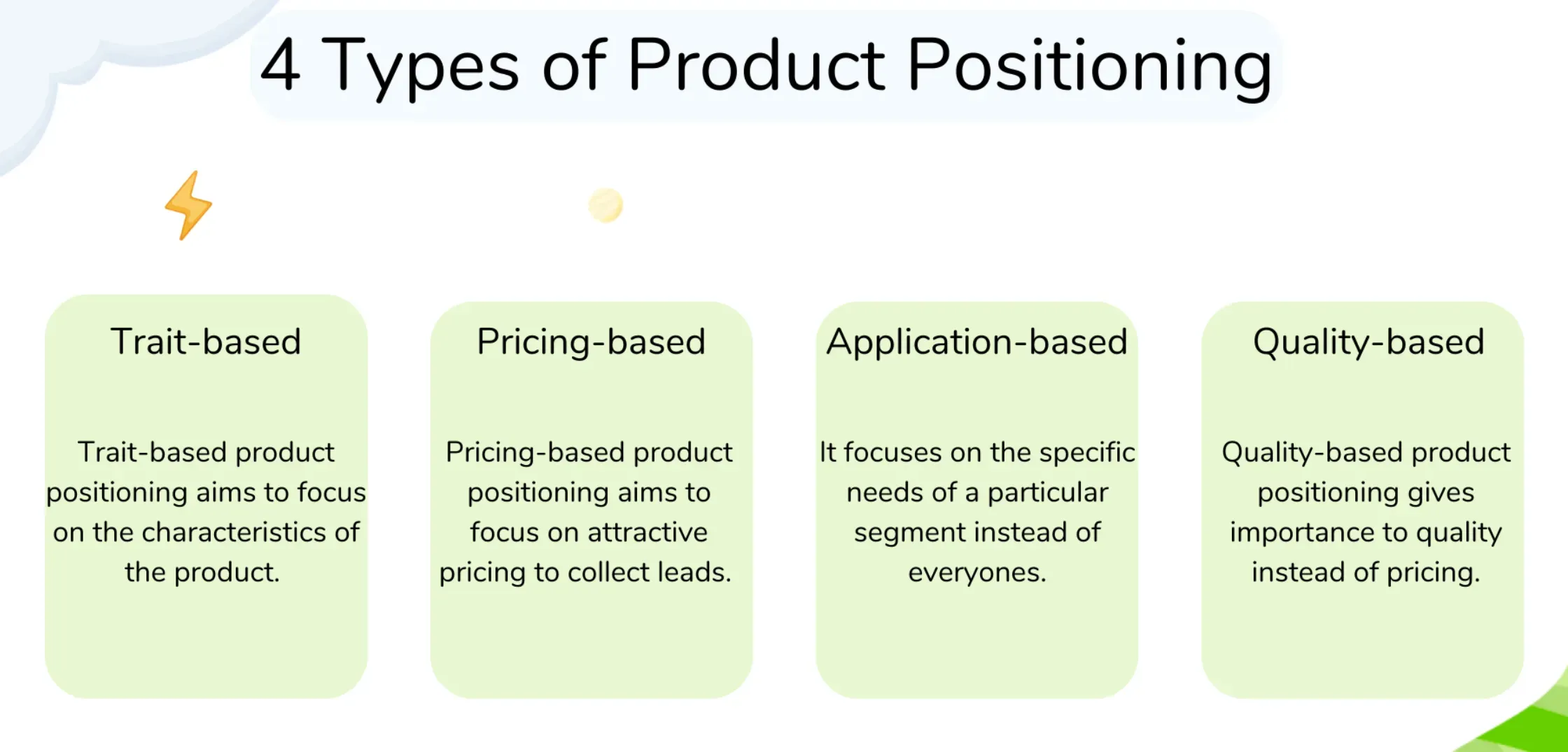
Quality-Based Positioning
A strategy focused on emphasizing the high quality or superior craftsmanship of a product.
Value-Based Positioning
Centered on showcasing the product as offering excellent value for the price.
Benefit-Based Positioning
Focuses on the unique benefits that a product offers its consumers.
Problem/Solution Positioning
Presents the product as a solution to a specific problem that the target audience faces.
Competition-Based Positioning
This strategy explicitly positions a product relative to a competitor, often highlighting the product's superior features.
Challenges in Product Positioning
Despite its many benefits, implementing a positioning strategy can come with its own set of challenges.
Defining the Unique Selling Proposition
Identifying the unique aspects of a product that truly set it apart can be tricky.
Understanding the Market Landscape
Thoroughly understanding the competitive landscape to position appropriately requires significant research and effort.
Aligning Perception with Reality
While positioning shapes perception, it’s a challenge to ensure that the product delivers according to its positioning.
Maintaining Positioning Over Time
Sustaining the product’s positioning over the long term in the face of market changes can be a challenge.
Adjusting Positioning
If the product or market changes significantly, adjusting the positioning can be challenging and requires careful strategy.
Best Practices in Product Positioning
Follow these best practices to put your product positioning strategy on the right track.
Know Your Audience
Thoroughly understanding the target market is key to effective product positioning.
Focus on Benefits
Highlighting clear, compelling benefits can make a product's position more resonant.
Be Consistent
Consistency in messaging across all marketing channels reinforces product positioning.
Keep it Simple
A clear and simple position is easier for the audience to understand and remember.
Regularly Review
Review and adjust positioning regularly to maintain its effectiveness in a changing market.
Trends in Product Positioning
As the marketing landscape evolves, so do the trends in product positioning.
Digital Positioning
In the age of digital marketing, positioning must consider online channels and how products appear in digital spaces.
Social Consciousness Positioning
Many brands are positioning their products around social issues, showcasing values besides just the product and price.
Personalized Positioning
Thanks to data, brands can position their products uniquely for different customer segments, stepping away from one-size-fits-all positioning.
Collaborations and Partnerships
Brands are collaborating and partnering more than ever, crafting mutual product positioning that expands their appeal.
Eco-Friendly Positioning
With growing awareness of environmental issues, positioning products as eco-friendly is increasingly popular and appealing to consumers.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
How does product positioning differ from brand positioning?
Product positioning focuses on a product's unique value and its place in the market, whereas brand positioning emphasizes the overall brand's identity and promise to consumers.
Can a product be repositioned without changing its features?
Yes, repositioning often involves changing the marketing message or target audience perception without altering the product's features.
What role does competitor analysis play in product positioning?
Competitor analysis helps identify gaps in the market and opportunities to position a product uniquely, ensuring it stands out from competitors.
How is product positioning reflected in marketing strategies?
Product positioning influences marketing strategies through targeted messaging that highlights the product's unique benefits and value proposition to its intended audience.
Why is consistent messaging important in product positioning?
Consistent messaging reinforces the product's position in the market, builds brand recognition, and ensures the product's value proposition is clear to the target audience.