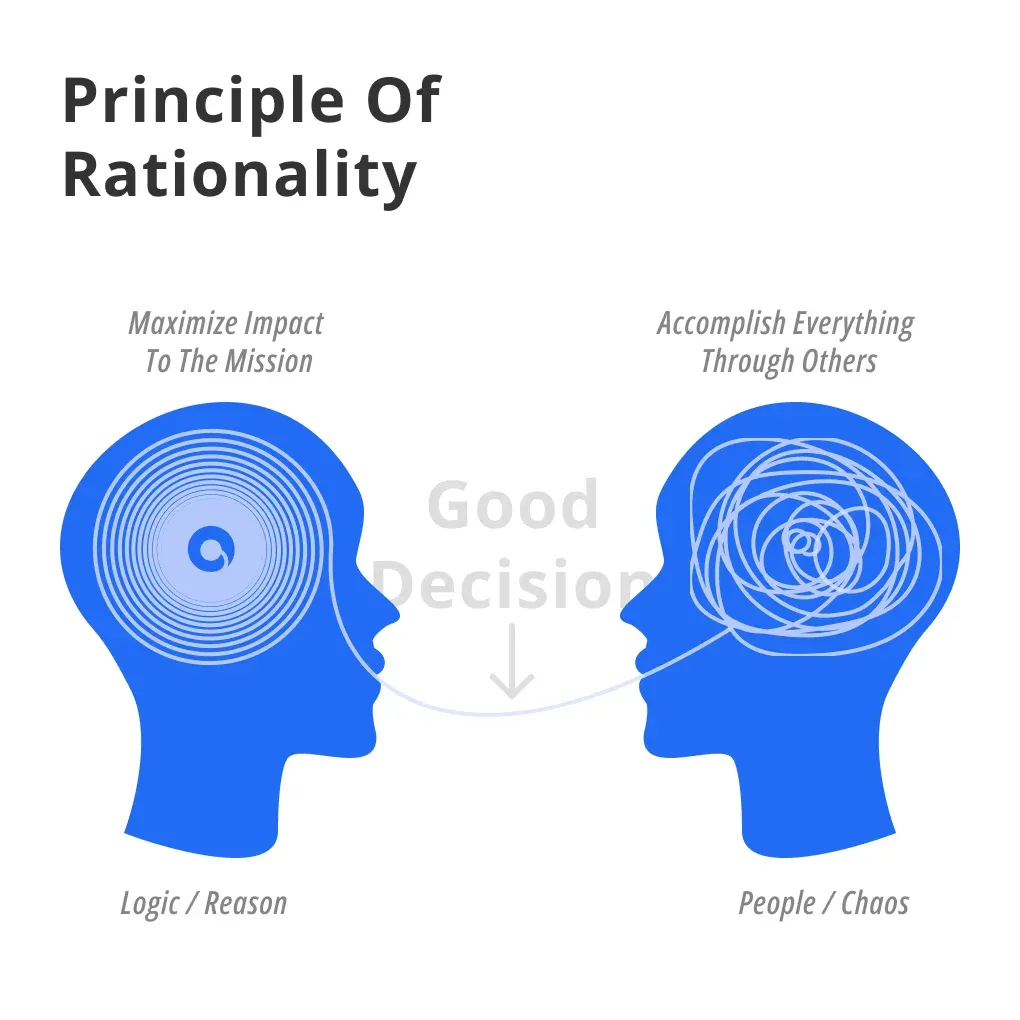
What is the Principle of Rationality?
The Principle of Rationality definition is a philosophical idea stipulating that reasonable actions and beliefs are those which are logically coherent and conformable to the dictates of reason.
The principle meaning of rationality considers logical reasoning as the primary determinant of rational actions and decisions.
History and origin
The Principle of Rationality definition has its roots deep in philosophy, dating back to ancient Greek philosophers like Socrates and Aristotle.
It was developed and expanded upon by subsequent philosophers such as Immanuel Kant and Descartes, who emphasized the role of reason in human behaviors.
Meaning of Rationality
The meaning of rationality extends beyond mere logic; it encompasses the ability to think critically, analyze situations, and make informed choices.
Understanding this concept is essential in various fields, including economics, philosophy, and psychology, where the meaning of rationality plays a pivotal role in human behavior.
Define Rationality in terms of Rationality Theory
To define rationality as per Rationality theory is to explain how individuals make decisions under conditions of uncertainty.
It highlights that rational agents weigh options based on potential outcomes and their probabilities. The rationality theory is fundamental in economics, as it helps predict market behaviors and the actions of consumers and firms.
Why is the Principle of Rationality Important?
Understanding the value and significance of the Principle of Rationality is crucial for any individual or organization. Let's explore the importance of meaning of rationality.
Promoting Coherent Decisions
The Principle of Rationality ensures the decisions are consistent and harmonious with one another. It encourages to identify and eliminate contradictions in thinking, beliefs, and actions.
Achieving Desired Goals
By applying the Principle of Rationality, individuals can structure their decisions to achieve specific goals effectively.
This logical framework ensures that actions are aligned with desired outcomes, enhancing personal and organizational success.
Understanding Human Behavior
Rationality theory underpins many social science models, helping to predict and interpret human behavior.
Grasping this principle enables a deeper meaning of rationality of how people act in various contexts, facilitating better communication and interaction.
Enhancing Problem-solving Skills
Rational thought processes foster effective problem-solving by encouraging the evaluation of evidence and alternative solutions.
The Principle of Rationality guides individuals toward practical and effective methods for addressing challenges.
Encouraging Critical Reflection
Embracing rationality encourages ongoing critical reflection on beliefs and actions. This process of evaluation and adjustment aligns our decisions with reason, promoting personal growth and informed decision-making.
Who can Use the Principle of Rationality?
The principle of rationality can be applied across various domains of life. Its effectiveness is not limited to a specific group but can benefit anyone willing to engage in analytical thinking, like
Students and Academics
Students can leverage rationality theory to enhance their learning processes and problem-solving skills.
By applying logical frameworks, they can make informed decisions regarding their studies, projects, and future career paths.
Professionals and Businesses
In the professional realm, rationality theory is crucial for effective decision-making and strategic planning.
Business leaders and employees can use rational approaches to assess risks, optimize resources, and enhance productivity, leading to improved outcomes.
Policy Makers
Governments and organizations can adopt meaning of rationality in formulating policies and regulations.
By utilizing data-driven analyses, policymakers can create effective solutions to societal issues, ensuring that resources are allocated efficiently.
Everyday Individuals
On a personal level, individuals can benefit from the principle of rationality in daily decision-making.
Whether it’s budgeting, health choices, or relationship dynamics, applying rational thought can lead to more beneficial outcomes.
Where can the Principle of Rationality be Applied?
The principle of rationality serves as a cornerstone across various domains and ensuring that their choices are informed and logical.
Here's a broad look at various situations and fields where the Principle of Rationality can be applied.
- Decision-Making: The principle of rationality is fundamental in decision-making processes across various fields, including economics, business, and public policy.
It helps individuals and organizations evaluate options logically, weigh the pros and cons, and choose the most beneficial course of action.
- Scientific Research: In scientific research, meaning of rationality underpins the formulation of hypotheses, experimentation, and analysis of results.
Researchers apply rational thought to ensure that conclusions are based on evidence, minimizing biases and errors, which enhances the reliability of findings.
- Ethics and Morality: Rationality theory plays a crucial role in ethical reasoning. Philosophers use rational principles to evaluate moral dilemmas, helping individuals and societies to arrive at justifiable conclusions regarding right and wrong actions.
- Education: In educational settings, meaning of rationality encourages critical thinking and problem-solving skills.
By promoting rational discourse, educators foster an environment where students can analyze information, question assumptions, and develop well-reasoned arguments.
- Policy Formulation: Governments and organizations utilize rationality definition in policy formulation to address societal issues effectively.
By employing data-driven approaches, they can create policies that are logical, fair, and beneficial for the public.
- Problem Solving: In problem-solving scenarios, applying rationality theory helps identify the root causes of issues and develop structured solutions.
This approach promotes critical thinking and systematic analysis, which can enhance the quality of solutions.
- Behavioral Economics: The rise of behavioral economics challenges the concept of 'economic man' who always acts rationally.
This rationality theory acknowledging that human decisions are not always based on rational calculations.
- The Role of AI: The advent of artificial intelligence brings new dimensions to the application of the principle of rationality.
It creates machines that mimic, and supposedly surpass, human capacity for rational decision-making.
- Rational Ignorance: Growing recognition of 'rational ignorance', where individuals intentionally choose not to gain knowledge about particular issues.
The reason behind this is that the cost of the learning process supposedly outweighs its benefits.
How Can One Develop Rational Thinking?
A crucial part of understanding the Principle of Rationality is knowing how to develop the capacity for rational thinking. Let's unwrap it a bit.
Understanding Rational Thinking
Rational thinking is the ability to think logically, make sound judgments, and evaluate information critically.
Developing this skill can enhance decision-making and problem-solving abilities in various aspects of life.
Practice Critical Analysis
Engage in activities that require analysis, such as reading complex texts, debating, or solving puzzles. This helps you to evaluate different viewpoints and identify biases.
Question Assumptions
Challenge your beliefs and assumptions by asking questions. Consider alternative perspectives and evaluate the evidence supporting your views.
Embrace Logic and Reasoning
Familiarize yourself with logical reasoning principles, such as deductive and inductive reasoning. Apply these principles when making decisions to ensure your conclusions are based on sound arguments.
Reflect on Decisions
After making decisions, reflect on the outcomes. Analyze what worked, what didn’t, and why. This reflection fosters continuous improvement in your rational thinking skills.
Seek Diverse Perspectives
Engage with individuals who hold different opinions. Exposure to diverse viewpoints broadens your understanding and sharpens your analytical skills.
Embracing Rationality Theory
Exploring rationality theory can provide a framework for understanding how decisions can be optimized.
The rationality theory examines the principles that guide rational behavior and decision-making, helping individuals evaluate their choices more effectively.
Practicing Critical Thinking
To foster rational thinking, individuals should practice critical thinking skills. This involves analyzing arguments, questioning assumptions, and evaluating evidence.
Asking oneself, “What does rationality mean in this context?” can help in assessing the validity of one’s thoughts and beliefs.
Challenges in Applying the Principle of Rationality
The principle of rationality emphasizes making decisions based on logical reasoning and objective analysis. However, applying this principle presents several challenges, like:
Cognitive Biases
Human cognition is often influenced by biases, such as confirmation bias or anchoring, which can distort judgment.
These biases lead individuals to make irrational decisions, undermining the rationality theory principle.
Emotional Influence
Emotions can heavily impact decision-making. Fear, joy, or anxiety may cloud judgment, causing individuals to prioritize feelings over facts, further complicating rational decision-making.
Information Overload
In an era of abundant information, distinguishing between relevant and irrelevant data can be overwhelming. This overload can hinder effective analysis, leading to paralysis by analysis rather than rational decision-making.
Social Pressures
Social dynamics, such as peer pressure or groupthink, can compel individuals to conform rather than think critically.
These pressures often lead to decisions that may not align with rational principles.
Best Practices for Applying the Principle of Rationality
The principle of rationality serves as a cornerstone for effective decision-making and objective analysis rather than on emotions or biases.
To effectively apply the Principle of Rationality, it helps to be aware of some best practices.
- Understand the Concept: The principle of rationality theory involves making decisions based on reason and logic rather than emotions or assumptions.
Start by clearly defining the problem or decision at hand.
- Gather Relevant Information: Collect all necessary data and information. Evaluate the credibility of your sources and consider multiple perspectives to form a well-rounded understanding.
- Analyze Options: List all possible options and analyze their potential outcomes. Use logical reasoning to weigh the pros and cons of each choice, considering both short-term and long-term implications.
- Make Informed Decisions: Choose the option that offers the most rational benefits based on your analysis. Ensure that your decision aligns with your values and objectives.
- Reflect and Adjust: After implementing your decision, reflect on the outcomes. Analyze what worked and what didn’t, allowing for adjustments and improvements in future decision-making processes.
- Accountability and Responsibility: Owning accountability for decisions and actions and being ready to adjust when rational evidence changes promotes the application of the Principle of Rationality in a responsible and effective way.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is the Core Idea Behind the Principle of Rationality?
The core idea is that individuals act in a way that they believe will best achieve their goals, given the information available to them.
What Does Rationality Mean?
Ultimately, what does rationality means can vary significantly among individuals. Personal beliefs, cultural backgrounds, and situational contexts can all affect how rationality is perceived and applied, posing challenges in its consistent implementation in real-world scenarios.
How Does the Principle of Rationality Impact Economic Theory?
It underpins many economic models by assuming that agents will maximize utility or profits through rational decision-making.
In What Ways Can the Principle of Rationality Be Criticized?
Critics argue real-life decisions are often influenced by emotion, misinformation, or cognitive biases, deviating from purely rational behavior.
Does the Principle of Rationality Apply to Artificial Intelligence?
Yes, AI systems are often designed to make decisions based on rationality principles, aiming to optimize outcomes based on their programming.
How Do Game Theory and the Principle of Rationality Intersect?
Game theory often relies on the principle of rationality to predict how players will strategize and react in competitive situations.